Market Overview
The Philippines Education Market is valued at USD 31.2 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. This significant size is primarily driven by the increasing enrollment rates in both public and private educational institutions, supported by government initiatives aimed at improving educational accessibility and quality. Furthermore, the rapid expansion of online education platforms and technologies has played a critical role in shifting traditional learning to more flexible modalities, thereby attracting a diverse range of learners.
Major cities such as Manila, Cebu, and Davao dominate the Philippines Education Market due to several factors, including dense populations, a high concentration of educational institutions, and the presence of international schools. Manila, being the capital, is a hub for higher education and professional training, attracting students from across the country and overseas.
In 2023, the Philippine government allocated approximately PHP 843 billion (about USD 15.1 billion) to the education sector, an increase from the previous year’s budget. This funding supports various educational programs and infrastructures, addressing issues like classroom shortages and teacher training. Notably, the government’s commitment to the “K to 12 Program” aims to enhance the quality of basic education in line with global standards. As GDP growth is targeted at around 6.5% for the year, this investment signifies an essential priority for socioeconomic development through education.
Market Segmentation
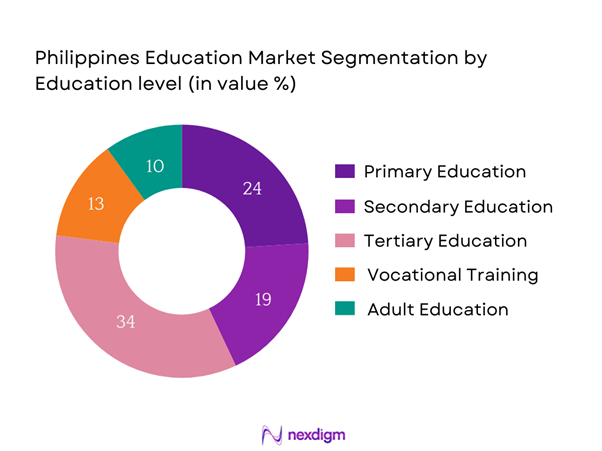
By Education Level
The Philippines Education Market is segmented by education level into primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, vocational training, and adult education. Tertiary education currently dominates the market share. This segment holds a significant position as universities and colleges offer a wide range of degree programs catering to both local and international students. The increasing demand for higher education, especially in professional fields like engineering, technology, and healthcare, drives the growth of this sub-segment, as graduates seek to enhance their employability in a competitive job market.
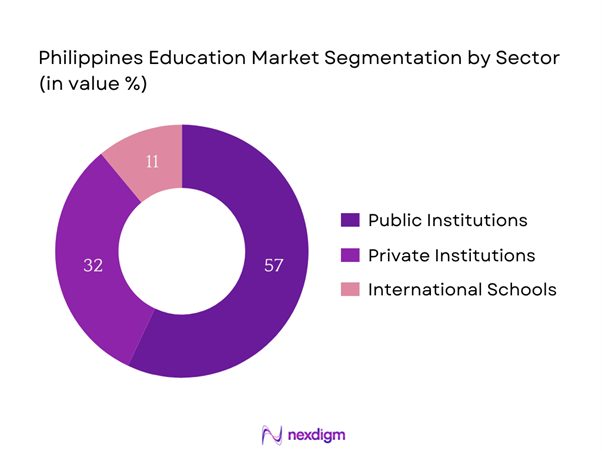
By Sector
The Philippines Education Market is also segmented by sector into public institutions, private institutions, and international schools. Among these, public institutions have the dominating market share due to their accessibility and affordability. The government’s commitment to providing free primary and secondary education has resulted in a substantial enrollment increase in public schools. Moreover, the continuing initiatives to improve public education infrastructure and quality significantly contribute to this segment’s growth, making it the favored choice for many families seeking education for their children.
Competitive Landscape
The Philippines Education Market is characterized by a few major players, including well-established universities and educational institutions that leverage their reputation and extensive networks. Key companies such as the University of the Philippines, De La Salle University, and Ateneo de Manila University lead the market due to their robust academic programs, diverse student bodies, and strong brand recognition. This consolidation highlights the impact these key institutions have on shaping educational standards and policies.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Focus | Number of Campuses | Student Enrollment Capacity | Online Learning Capability |
| University of the Philippines | 1908 | Diliman, Quezon City | – | – | – | – |
| De La Salle University | 1911 | Taft Avenue, Manila | – | – | – | – |
| Ateneo de Manila University | 1859 | Loyola Heights, Quezon City | – | – | – | – |
| Far Eastern University | 1928 | Sampaloc, Manila | – | – | – | – |
| Mapúa University | 1925 | Intramuros, Manila | – | – | – | – |
Philippines Education Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Enrollment Rates
The Philippines has experienced an increase in total enrollment in basic education, with over 28 million students enrolled in elementary and high schools as of the 2022-2023 school year. At the tertiary level, enrollment in higher education institutions reached approximately 3.8 million students, reflecting a growing emphasis on obtaining higher degrees. This surge in enrollment is driven by government initiatives aimed at achieving universal access to quality education, as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Such trends point to a continuing commitment to education improvement, bolstering future prospects in the sector.
Technological Advancements
The ongoing digital transformation in the Philippines is evident in education, with the government promoting digital literacy initiatives across schools. By 2023, around 70% of public schools had adopted some form of online learning platforms or hybrid models, largely accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Moreover, the Department of Information and Communications Technology reported that over 51 million Filipinos now have internet access, enabling wider use of educational technology. This convergence of technology and education demonstrates the potential for expanded learning opportunities and improved student engagement through innovative digital solutions.
Market Challenges
Limitations in Infrastructure
Despite progress, the Philippines faces significant infrastructural challenges within its educational system. The country has an approximate shortfall of 164,000 classrooms needed to accommodate the growing student population. Data from the Department of Education indicates that many schools remain overcrowded, with an average student-to-teacher ratio of about 29:1 in some regions. Additionally, rural areas often lack access to essential educational facilities, further exacerbating the issue. Addressing these infrastructural deficits will be crucial for enhancing educational quality and accessibility.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
The regulatory landscape of the Philippines education sector presents several compliance challenges for institutions. As of 2023, private schools and universities must adhere to stringent accreditation processes set by the Commission on Higher Education (CHED), with only about 40% of institutions currently accredited. Many schools face difficulties meeting the standards regarding curriculum, faculty qualifications, and facility requirements. This complexity often leads to barriers for new educational institutions attempting to enter the market, hindering sector growth and innovation.
Opportunities
Rise of EdTech Solutions
The investments in educational technology (EdTech) have surged significantly, with the Philippine EdTech market receiving over USD 70 million in funding as of 2023. This reflects a growing recognition of the need to transition to more innovative learning solutions. As the demand for remote and blended learning grows, EdTech companies are increasingly providing platforms that facilitate interactive learning, personalized education, and real-time assessments. The latest data reveals that around 60% of students express preference for online learning tools, presenting immense growth potential for EdTech solutions in the Philippines.
Demand for Upskilling and Reskilling
With increasing competition in the job market, there has been a notable demand for upskilling and reskilling initiatives. In 2023, approximately 68% of employers in the Philippines reported difficulty finding candidates with the right skills for job openings, highlighting the need for further training and education. The Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) is actively promoting technical vocational education programs to meet industry needs, with over 1.2 million beneficiaries projected annually. This expanding sector indicates a robust opportunity for training providers and educational institutions focused on workforce skills enhancement.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Philippines Education Market is expected to show significant growth driven by continuous government support for educational initiatives, technological advancements in online education, and increasing consumer demand for accessible and quality learning solutions. The focus on digital learning and the rising popularity of vocational training programs are set to reshape the educational landscape, catering to diverse student needs and preferences.
Major Players
- University of the Philippines
- De La Salle University
- Ateneo de Manila University
- Far Eastern University
- Mapúa University
- San Beda University
- University of Santo Tomas
- Polytechnic University of the Philippines
- Centro Escolar University
- Lyceum of the Philippines University
- Adamson University
- University of San Carlos
- International School Manila
- Philippine Science High School
- University of the Cordilleras
Key Target Audience
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Department of Education (Philippines)
- Commission on Higher Education (CHED)
- Local Government Units (LGUs)
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) focused on education
- Educational Technology Companies
- Training and Development Corporations
- Corporate Sector wanting employee training programs
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map that includes all major stakeholders within the Philippines Education Market. This step is supported by extensive desk research, utilizing secondary and proprietary databases to gather comprehensive industry-level information. The primary objective is to identify and define the critical variables influencing market dynamics, such as enrollment trends, funding sources, and technological integration.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This phase focuses on compiling and analyzing historical data related to the Philippines Education Market. It includes assessing enrollment statistics, the ratio of educational institutions, and the resultant revenue generation across various segments. A comprehensive evaluation of the quality of education metrics will also be conducted to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the estimated market values.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be developed and subsequently validated through computer-assisted telephone interviews (CATIs) with industry experts and representatives from leading educational institutions. These consultations provide valuable insights into market trends, operational challenges, and financial performance, which will refine and substantiate the collected market data.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves direct engagement with multiple educational institutions to gain detailed insights into enrollment patterns, program offerings, and technological adoption. This interaction aims to validate and complement the statistics derived from both top-down and bottom-up approaches, thereby ensuring a comprehensive, accurate, and validated analysis of the Philippines Education Market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Overview Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Enrollment Rates
Government Investment in Education
Technological Advancements - Market Challenges
Limitations in Infrastructure
Regulatory and Compliance Issues - Opportunities
Rise of EdTech Solutions
Demand for Upskilling and Reskilling - Trends
Personalized Learning Approaches
Integration of International Curriculums - Government Regulations
Education Policies
Accreditation Standards - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Enrollment Numbers, 2019-2024
- By Average Tuition Fees, 2019-2024
- By Education Level (In Value %)
Primary Education
Secondary Education
Tertiary Education
Vocational Training
Adult Education - By Sector (In Value %)
Public Institutions
Private Institutions
International Schools - By Geographic Region (In Value %)
Luzon
Visayas
Mindanao - By Mode of Learning (In Value %)
Traditional Classroom
Online Learning
Hybrid Learning - By Student Demographics (In Value %)
Age Groups
Gender
Socio-Economic Background
- Market Share of Major Players on the Basis of Value, 2024
Market Share Breakdown by Education Level, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Organizational Structure, Revenues, Revenues by Education Level, Number of Institutions, Distribution Channels, Student Enrollment Capacity, Innovative Offerings, and more)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis Basis SKUs for Major Players
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
University of the Philippines
Ateneo de Manila University
De La Salle University
Adamson University
Far Eastern University
University of Santo Tomas
Mapúa University
San Beda University
International School Manila
Philippine Science High School
Centro Escolar University
Polytechnic University of the Philippines
Lyceum of the Philippines University
University of San Carlos
University of the Cordilleras
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Enrollment Numbers, 2025-2030
- By Average Tuition Fees, 2025-2030


