Market Overview
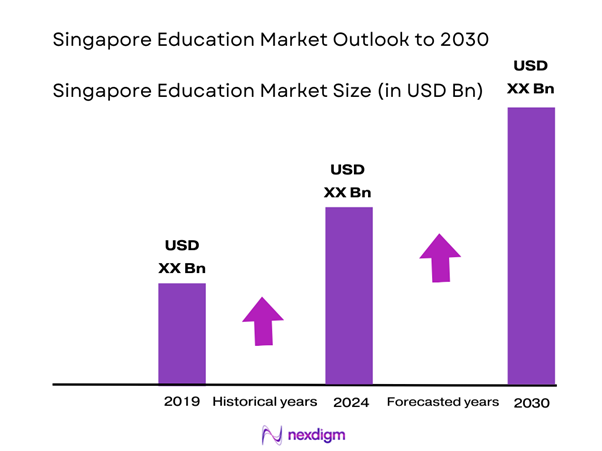
The Singapore education market is valued at USD 3.5 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. The market is driven by factors such as an increasing emphasis on high-quality education coupled with government support for educational institutions. The government’s investments in initiatives aimed at innovation and technology integration in schools further fuel this growth. As a global education hub, Singapore attracts international students, contributing substantially to the overall market size.
Dominant cities such as Singapore City illustrate the city-state’s strategic position in the education market. The educational landscape in Singapore is characterized by a mix of public and private institutions that offer various programs, attracting a diverse set of learners. Coupled with its robust international presence and reputation for excellence in education, Singapore City’s commitment to providing world-class educational resources solidifies its status as a dominant force in the market.
Technological innovations have played a crucial role in enhancing the Singapore education market. With a strong government initiative to incorporate technology in teaching, over 97% of schools have adopted e-learning tools and platforms, significantly improving accessibility and engagement. In 2023, approximately USD 700 million was invested by the Ministry of Education to facilitate the integration of digital resources and training for teachers. Such investments have paved the way for innovative learning models, making education more interactive and student centered.
Market Segmentation
By Education Level
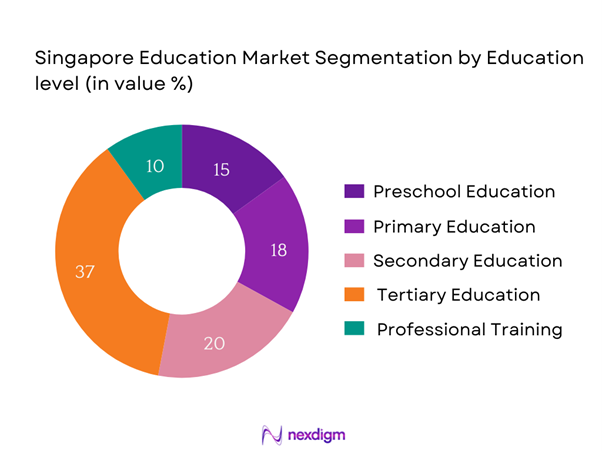
The Singapore education market is segmented by education level into preschool education, primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, and professional training. Tertiary education recently emerged as a dominant segment within the market. This segment encompasses universities, polytechnics, and specialized institutions, which collectively cater to a vast array of academic and vocational needs. High-quality universities like the National University of Singapore and Nanyang Technological University bolster this segment by attracting both local and international students. Factors such as global recognition, research opportunities, and robust graduate employment prospects solidify the dominance of tertiary education in the Singapore education landscape.
By Delivery Mode
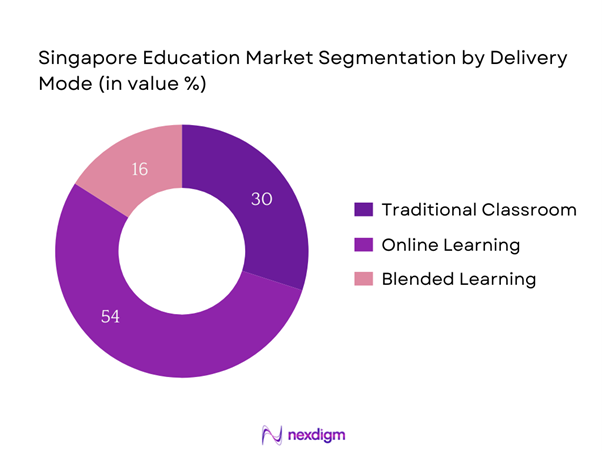
The Singapore education market is also segmented by delivery mode into traditional classroom education, online learning, and blended learning. Online learning has recently gained a dominant market share, primarily driven by advances in technology and changes in consumer preferences toward flexible learning options. The pandemic catalyzed this shift, with more institutions adapting online platforms to sustain educational delivery. Furthermore, renowned local and international universities expanded their online offerings, which not only facilitated a seamless learning experience but also increased accessibility for diverse demographics. The convenience, diverse course offerings, and increased time efficiency have made online learning the preferred choice for a growing number of students.
Competitive Landscape
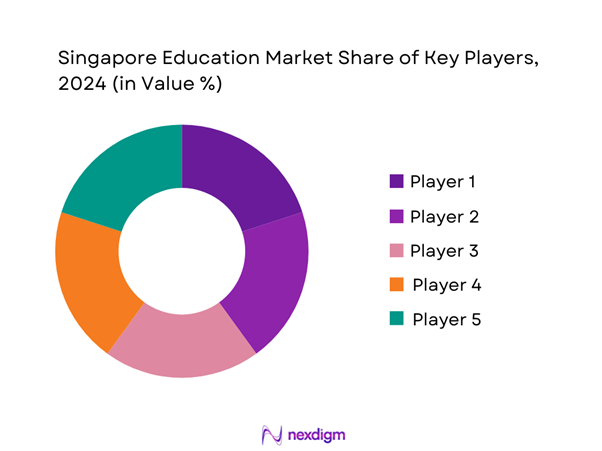
The Singapore education market is dominated by several major players, including local institutions and international universities that have established a strong presence within the region. Institutions like the National University of Singapore, Nanyang Technological University, and various international schools compete for students, showcasing unique programs and quality teaching staff.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Position | Program Offerings | International Reach | Online Learning Availability |
| National University of Singapore | 1905 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Nanyang Technological University | 1991 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Singapore Management University | 2000 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| Singapore Institute of Technology | 2009 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
| James Cook University Singapore | 2003 | Singapore | – | – | – | – |
Singapore Education Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Demand for Quality Education
The demand for quality education in Singapore has been steadily rising due to a significant focus on educational excellence. In 2023, Singapore’s youth literacy rate stood at 99.9%, reflecting the country’s commitment to high educational standards. Moreover, based on government data, Singapore has one of the highest educational expenditures in the world, with approximately USD 11.5 billion allocated for education in the fiscal budget of 2024. This funding supports curriculum development, teacher training, and infrastructure enhancements, ultimately promoting a high standard of education in the region.
Rising Number of International Students
Singapore has become an attractive destination for international students due to its robust educational framework and multicultural environment. In 2023, the number of international students in Singapore reached around 50,000, primarily hailing from countries like China, India, and Malaysia. The government aims to increase the international student population by providing scholarships and financial assistance. The country’s world-class universities consistently rank among the top global institutions, making Singapore an appealing choice for those seeking quality higher education.
Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance and Accreditation
Regulatory compliance and accreditation pose challenges for educational institutions in Singapore. The Ministry of Education closely monitors educational standards, ensuring institutions meet specific guidelines for operation. In 2023, more than 400 private educational organizations faced rigorous assessments, with only around 60% receiving accreditation under the Enhanced Registration Framework. Institutions lacking accreditation face challenges in attracting students, funding, and maintaining quality educational standards. The stringent regulatory environment necessitates ongoing compliance efforts to remain operational within the market.
Competition Among Institutions
The competition in the Singapore education market is intense, with over 200 established education providers vying for student enrollment. In 2023, the average student-to-teacher ratio in primary schools was approximately 15:1, while the secondary education sector faced a more competitive environment with a 17:1 ratio. With many institutions offering similar programs and quality of education, attracting and retaining students has become increasingly challenging. This competition pushes institutions to continuously innovate and improve their offerings, leading to potential strain on resources and profitability.
Opportunities
Expansion of EdTech Solutions
The expansion of EdTech solutions presents a significant opportunity for growth in Singapore’s education market. In 2023, investments in EdTech reached over USD 300 million, as schools and institutions embraced digital learning platforms and tools. The growing focus on remote and hybrid learning models has driven demand for innovative educational technologies. Reports indicate that the Singapore government aims to enhance technological integration in education, thereby creating a favorable environment for EdTech startups and solutions. Current trends indicate strong engagement among millennials and Gen Z in digital learning platforms, paving the way for future growth in this segment.
Growing Focus on Lifelong Learning
There is an increasing emphasis on lifelong learning and continuous skill development in Singapore, spurred by changes in the labor market. In 2022, over 60% of Singaporean adults reported participating in some form of continuing education or training. The SkillsFuture initiative encourages individuals to engage in continuous learning, with the government investing USD 1.5 billion in training programs. As industries evolve and new technologies emerge, the lifelong learning market is expected to grow substantially, creating opportunities for educational providers to offer specialized training and skills development courses.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Singapore education market is expected to experience significant growth driven by continuous government support, ongoing advancements in technology, and increasing consumer demand for flexible and quality learning options. The emphasis on online education and professional training will continue to shape the landscape, providing learners with accessible pathways toward achieving their educational goals. As Singapore reinforces its status as an international educational hub, the market will likely attract a diverse array of students, both locally and internationally.
Major Players
- National University of Singapore
- Nanyang Technological University
- Singapore Management University
- Singapore Institute of Technology
- James Cook University Singapore
- Temasek Polytechnic
- Singapore American School
- Canadian International School
- Raffles Girls’ School
- Anglo-Chinese School
- Raffles Institution
- Joseph’s Institution
- Ngee Ann Polytechnic
- Institute of Technical Education
- Singapore University of Technology and Design
Key Target Audience
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Education, SkillsFuture Singapore)
- Educational Policy Makers
- Private Education Providers
- Corporate Training Institutions
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- International Student Recruitment Agencies
- Educational Technology Companies
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) in Education
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing an ecosystem map that encompasses all major stakeholders within the Singapore education market. This step is underpinned by extensive desk research, utilizing a combination of secondary and proprietary databases to gather comprehensive industry-level information. The primary objective is to identify and define the critical variables that influence market dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this phase, historical data pertaining to the Singapore education market will be compiled and analyzed. This includes assessing enrollment numbers, tuition fee trends, and the relationship between schools and respective student demographics. Furthermore, an evaluation of service quality metrics will be conducted to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the revenue estimates.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be developed and subsequently validated through expert interviews with industry practitioners. The consultations will provide critical operational and financial insights which will be invaluable in refining and corroborating the market data gathered from secondary sources.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves direct engagement with multiple educational institutions to acquire insights into program offerings, student preferences, and other pertinent factors. This interaction will serve to verify and complement the statistics gathered through desk research and expert consultation, ensuring a comprehensive, accurate, and validated analysis of the Singapore education market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Market Trends and Genesis
- Timeline of Major Players
- Business Cycle Analysis
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Demand for Quality Education
Rising Number of International Students
Technological Innovations in Learning - Market Challenges
Regulatory Compliance and Accreditation
Competition Among Institutions - Opportunities
Expansion of EdTech Solutions
Growing Focus on Lifelong Learning - Trends
Globalization of Education
Innovative Pedagogies - Government Regulation
Education Policies and Frameworks
Funding and Grants for Educational Institutions - SWOT Analysis
- Stake Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Number of Students, 2019-2024
- By Average Tuition Fees, 2019-2024
- By Education Level (In Value %)
Preschool Education
Primary Education
Secondary Education
Tertiary Education
Professional Training - By Delivery Mode (In Value %)
Traditional Classroom
Online Learning
Blended Learning - By Sector (In Value %)
Public School System
Private and International Schools
Higher Education Institutions - By Region (In Value %)
Central Region
Eastern Region
Western Region
Northern Region - By Age Group (In Value %)
0-6 Years
7-12 Years
13-18 Years
19-24 Years
25+ Years
- Market Share of Major Players Based on Value, 2024
Market Share of Major Players by Education Level, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Market Focus, Number of Programs, Quality Ratings, Technological Adoption, Marketing Strategies)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis for Major Educational Programs
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
National University of Singapore
Nanyang Technological University
Singapore Management University
Singapore University of Technology and Design
Singapore Institute of Technology
Temasek Polytechnic
Singapore American School
Canadian International School
Raffles Girls’ School
Anglo-Chinese School
Raffles Institution
St. Joseph’s Institution
Ngee Ann Polytechnic
Institute of Technical Education
James Cook University Singapore
- Market Demand and Utilization
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Number of Students, 2025-2030
- By Average Tuition Fees, 2025-2030


