Market Overview
The South Korea education market is valued at USD 37 billion, based on a five-year historical analysis. The growth is driven by rising demand for quality education and increasing expenditure on educational services. South Korea is known globally for its rigorous and competitive education system, with a strong emphasis on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education and innovative teaching methodologies. Significant investment by the government to bolster educational infrastructure and the rising participation in online education platforms have also contributed to the market’s expansion, making it one of the most advanced education markets in Asia.
Major cities like Seoul, Busan, and Incheon dominate the South Korea education market due to their dense populations and concentration of educational institutions. Seoul, as the capital, houses some of the country’s most prestigious universities and research centers, drawing local and international students alike. The presence of numerous private educational institutions and international schools in these metropolitan areas further strengthens their dominance in the market. The set-up of vocational institutions also exemplifies a shift towards practical skills training, aligning with national development goals.
Market Segmentation
By Education Level
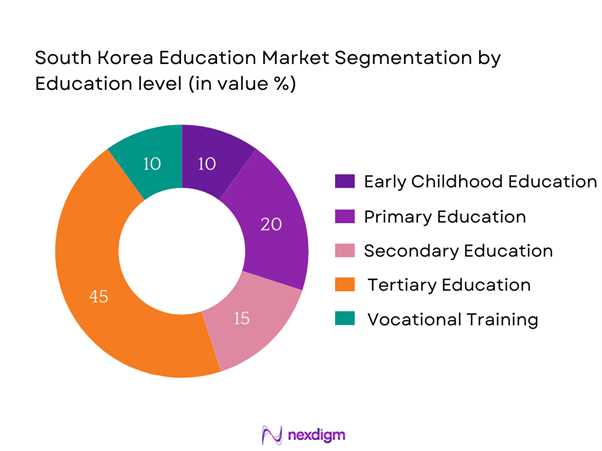
The South Korea education market is segmented by education level into early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, tertiary education, and vocational training. Tertiary education currently holds the dominant share in the market. The emphasis on higher education in South Korea is evidenced by a strong societal belief in university degrees as a pathway to prosperity and social mobility. In 2023, approximately 1.5 million students enrolled in universities, with many institutions providing high-quality programs that attract domestic and international students. The government’s backing of higher education through scholarship programs and subsidies has also played a crucial role in sustaining interest and enrollment in this segment.
By Type of Institution
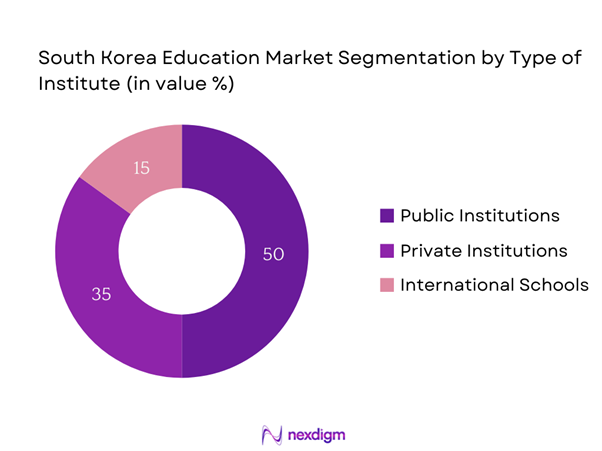
The South Korea education market is additionally segmented by type of institution into public institutions, private institutions, and international schools. Public institutions dominate the market due to their accessibility, high academic standards, and robust support from the government. Approximately 50% of K-12 students are enrolled in public schools, which are viewed as more affordable compared to private alternatives. The quality of education offered at these institutions, coupled with the rigorous national curriculum, enhances their attractiveness. Furthermore, government funding and emphasis on public education initiatives reinforce the essential role of public institutions in shaping the overall education landscape in South Korea.
Competitive Landscape
The South Korea education market is dominated by several key players, reflecting a blend of public and private institutions. The competitive landscape is characterized by significant institutional diversity, with public universities and private academies vying for student enrollment.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Student Enrollment (2024) | Academic Programs Offered | Specialization Areas | Government Affiliations |
| Seoul National University | 1946 | Seoul | – | – | – | – |
| Korea University | 1905 | Seoul | – | – | – | – |
| Yonsei University | 1885 | Seoul | – | – | – | – |
| POSTECH | 1986 | Pohang | – | – | – | – |
| KAIST | 1971 | Daejeon | – | – | – | – |
South Korea Education Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Skilled Workforce
The South Korean labor market increasingly favors a skilled workforce, especially in technology and engineering sectors. As of 2022, approximately 70% of jobs required post-secondary education, reflecting a strong correlation between education and employment opportunities. Additionally, data from the Ministry of Education indicates that graduates in STEM fields have a job placement rate of 85%, underscoring the demand for specialized skills. The South Korean government aims to grow its skilled workforce to support economic growth, projecting an increase in the number of graduates in vocational and technical education programs by 200,000 students annually.
Government Investment in Education Technology
The South Korean government has committed significant investments to enhance education technology, with planned expenditure reaching USD 1 billion annually. In 2022, the government launched the “Digital Education Innovation Strategy,” which aims to integrate advanced technologies like AI and big data into educational settings. This initiative includes funding for tech startups focusing on educational solutions. By 2025, the government projects the integration of technology in over 80% of K-12 institutions. These efforts align with the national agenda focused on technological advancement and future-proofing the workforce.
Market Challenges
High Tuition Costs
Tuition fees in South Korea’s higher education institutions have been notably high, averaging around USD 6,000 per year for universities as of 2022. This expense poses a barrier for many families, especially amidst rising living costs, with household debt hitting approximately USD 1.5 trillion. The situation has led to increased reliance on student loan programs, with education loans exceeding USD 10 billion in 2023. This financial burden on students and families often leads to discussions about access and equity in education, prompting calls for reform in funding models.
Competitive Environment
The South Korean education market is characterized by intense competition among both public and private institutions. As of 2023, over 400 universities and colleges are vying for student enrollment, leading to varying quality standards. The large influx of private educational academies, or “hagwons,” has created a fragmented landscape where educational quality can differ significantly. With approximately 60% of high school graduates enrolling in private universities to gain a competitive edge, the challenge remains for institutions to differentiate themselves through quality and unique value propositions in this saturated market.
Opportunities
Growth of EdTech Solutions
Current trends indicate a rapid expansion of EdTech solutions in South Korea, fueled by advances in mobile technology and increased demand for flexible learning options. The EdTech sector was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2022, supported by major investments from venture capital, totaling USD 200 million. Additionally, as of 2023, nearly 30% of students have engaged in online learning platforms, reflecting a significant shift toward digital education. The appetite for blended learning environments continues to rise, indicating a favorable outlook for EdTech companies to innovate and scale offerings to meet the growing demand.
Increase in Global Collaborations
There has been a marked increase in international collaborations among South Korean educational institutions, which presents significant growth opportunities. In 2023, over 300 partnerships were established between South Korean universities and institutions in countries such as the U.S., Canada, and Australia. This trend is driven by the quest for diverse learning experiences and the growing mobility of students seeking international education. The government’s “Study in Korea” initiative has attracted 160,000 international students annually, paving the way for collaborative research projects and cultural exchanges, enhancing the quality and reputation of South Korea’s education sector on a global scale.
Future Outlook
In the coming years, the South Korea education market is expected to witness robust growth driven by a confluence of factors. Government support for educational innovation, increased investments in educational technology, and a growing emphasis on lifelong learning will create new opportunities. As the demand for skill-based education continues to rise, educational institutions are likely to adapt their offerings to meet these evolving needs. Furthermore, the shift toward online and blended learning modalities will provide greater access to quality education, broadening the market appeal and enrollments across various demographics.
Major Players
- Seoul National University
- Korea University
- Yonsei University
- POSTECH
- KAIST
- Hanyang University
- Ewha Womans University
- Sookmyung Women
- Chung-Ang University
- Korea National Open University
- SMUC
- UOS (University of Seoul)
- Kyung Hee University
- Sejong University
- Dongguk University
Key Target Audience
- Educational Institutions
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Education, Korea)
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Non-governmental Organizations in Education
- Corporate Training Providers
- Education Technology Companies
- Policy Makers
- Curriculum Developers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase entails constructing a comprehensive ecosystem map that includes all major stakeholders within the South Korea education market. Extensive desk research is conducted, utilizing both secondary sources and proprietary databases to gather relevant industry-level information. The primary objective is to identify the critical variables influencing market dynamics including demographic trends, funding sources, and regulatory factors.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This step involves the compilation and analysis of historical data relevant to the South Korea education market. The analysis focuses on key metrics such as enrollment rates, institution types, student demographics, and expenditure levels. By evaluating this data, we can gain insights into revenue generation, service delivery dynamics, and overall market penetration.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses will be formulated and validated through in-depth consultations with industry experts and stakeholders. This includes structured interviews with institutional leaders, policymakers, and educators to gather qualitative data on operational challenges, financial performance, and market trends. Such insights will be essential to refining and corroborating the initial market data.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves synthesizing findings and insights from multiple sources, including direct engagement with educational institutions and stakeholders. This will facilitate a robust understanding of product offerings, enrollment performance, and policy impacts. This comprehensive interaction aims to verify statistics derived from the bottom-up approach, ensuring a validated and accurate analysis of the South Korea education market.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Historical Overview
- Timeline of Major Educational Policies and Reforms
- Business Cycle Analysis
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Skilled Workforce
Government Investment in Education Technology - Market Challenges
High Tuition Costs
Competitive Environment - Opportunities
Growth of EdTech Solutions
Increase in Global Collaborations - Trends
Digital Transformation in Education
Focus on Lifelong Learning - Government Regulation
New Education Policies
Accreditation and Standardization - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Sector Value, 2019-2024
- By Enrollment Rates, 2019-2024
- By Average Tuition Fees Trends, 2019-2024
- By Education Level (In Value %)
Early Childhood Education
Primary Education
Secondary Education
Tertiary Education
Vocational Training - By Type of Institution (In Value %)
Public Institutions
Private Institutions
International Schools - By Delivery Method (In Value %)
Traditional Classroom
Online Learning
Blended Learning - By Region (In Value %)
Seoul
Busan
Incheon
Gyeonggi Province - By Subject Focus (In Value %)
STEM Education
Arts and Humanities
Language Studies
- Market Share of Major Players by Value/Volume, 2024
Market Share by Educational Segment, 2024 - Cross Comparison Parameters (Institution Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strengths, Weaknesses, Revenue Streams, Partnerships, Number of Enrolled Students, Distribution Channels, Innovation Strategy)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Institutions
- Tuition Fee Analysis by Major Institutions
- Detailed Profiles of Major Educational Institutions
Seoul National University
Korea University
Yonsei University
POSTECH
SKKU
KAIST
Hanyang University
Ewha Womans University
Sookmyung Women’s University
Chung-Ang University
Korea National Open University
SMUC
UOS
Kyung Hee University
Sejong University
- Student Demographics and Enrollment Data
- Parental Investment in Education
- Educational Needs and Challenges Faced
- Decision-Making Process for Institutions
- By Sector Value, 2025-2030
- By Enrollment Rates, 2025-2030
- By Tuition Fees Trends, 2025-2030


