Market Overview
The Asia Pacific aerospace composites market was valued at USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, supported by expanding aircraft manufacturing programs, increasing adoption of lightweight materials, and rising defense aviation procurement across the region. Growth is reinforced by the integration of carbon fiber structures into next-generation aircraft and the modernization of airline fleets. Verified Market Research reports that composite materials combining resin with fibers are increasingly preferred for durable, high-performance aircraft components, strengthening long-term industrial demand.
China, Japan, and India remain dominant contributors due to strong aerospace manufacturing ecosystems, government-supported aviation programs, and expanding domestic fleets. Mordor Intelligence notes that regional growth is closely linked to rising passenger traffic, airline fleet expansion, and procurement of newer aircraft with higher composite content. Japan and South Korea lead in high-grade carbon fiber production, while China anchors large-scale aerospace projects, collectively positioning the region as a major production hub for advanced materials.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
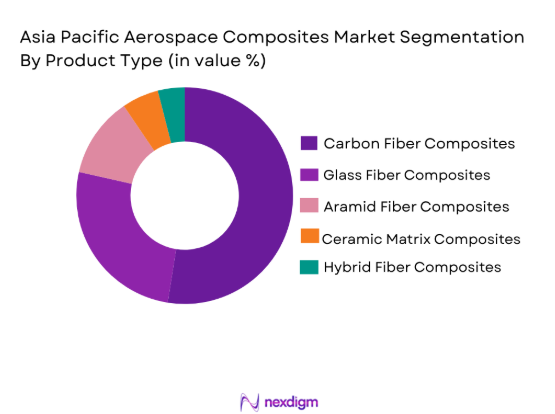
Asia Pacific aerospace composites market is segmented by product type into carbon fiber composites, glass fiber composites, aramid fiber composites, ceramic matrix composites, and hybrid fiber composites. Recently, carbon fiber composites has a dominant market share due to factors such as demand patterns, brand presence, infrastructure availability, and consumer preference. Carbon fiber composites are highly valued for their superior strength-to-weight ratio, which contributes to the fuel efficiency and enhanced performance of aircraft. Their growing adoption in commercial, military, and business jets, as well as increasing production capacity of carbon fiber manufacturers across the region, is helping solidify their dominance in the market.
By Platform Type
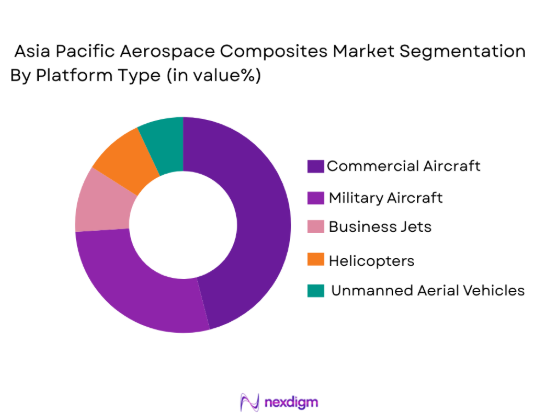
Asia Pacific aerospace composites market is segmented by platform type into commercial aircraft, military aircraft, business jets, helicopters, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Commercial aircraft has a dominant market share due to increased air travel demand, fleet expansion, and continuous upgrades to next-generation fuel-efficient aircraft. Composite materials in commercial aircraft are primarily used in fuselage and wings to reduce weight and improve operational efficiency. This segment’s dominance is further driven by the rising number of new aircraft orders in the region, especially in fast-growing economies such as China and India.
Competitive Landscape
The Asia Pacific aerospace composites market demonstrates moderate consolidation, with major global suppliers controlling advanced material technologies while regional manufacturers strengthen localized production capabilities. Leading companies benefit from long-term contracts with aircraft OEMs and defense agencies, enabling stable revenue streams and continuous innovation. Industry analysis identifies firms such as Toray Industries and Hexcel as influential players due to their strong carbon fiber portfolios and deep integration into aircraft supply chains, shaping competitive intensity across the region.
|
Company Name |
Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Primary Fiber Expertise |
| Toray Industries | 1926 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hexcel Corporation | 1948 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Teijin Limited | 1918 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Chemical Group | 1933 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Solvay SA | 1863 | Belgium | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia pacific aerospace composites Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Aircraft Fleet Expansion and Next‑Generation Manufacturing Demand
The rapid expansion of airline fleets across Asia Pacific is reshaping material demand patterns as aircraft manufacturers prioritize lightweight structural components that reduce fuel consumption while improving payload efficiency and operational range for commercial operators. Rising passenger traffic across major aviation corridors has compelled airlines to procure fuel‑efficient aircraft, and composite materials have become essential to achieving lower lifecycle costs through weight reduction and corrosion resistance. Governments throughout the region are simultaneously investing in aviation infrastructure, which indirectly accelerates aircraft deliveries and creates predictable procurement cycles for composite suppliers serving both commercial and defense programs. Composite adoption is further supported by the engineering flexibility these materials provide, allowing manufacturers to design aerodynamically optimized wings and fuselage sections that enhance performance under high stress conditions. Advanced manufacturing technologies such as automated fiber placement have improved production consistency, enabling large aerostructures to be fabricated with minimal defects and supporting scalable industrial output. Aircraft OEMs increasingly depend on carbon fiber reinforced polymers because they outperform traditional aluminum in fatigue tolerance, thereby extending service intervals and lowering maintenance requirements for airlines operating high‑utilization fleets. Defense modernization programs across Asia emphasize stealth characteristics and structural resilience, both of which rely heavily on composite architectures capable of supporting mission‑critical performance. Supply chain maturation within the region has reduced dependency on imported intermediate materials, encouraging domestic production and fostering cost competitiveness for local aerospace clusters. Sustainability pressures are also influencing procurement decisions, as lighter aircraft contribute to reduced emissions and help carriers align with tightening environmental standards imposed by aviation regulators. These converging factors establish fleet expansion and next‑generation manufacturing as a foundational catalyst sustaining long‑term growth for aerospace composites throughout Asia Pacific.
Defense Aviation Modernization and Indigenous Aircraft Programs
Regional governments are accelerating indigenous aircraft development to strengthen strategic autonomy, which has significantly increased demand for aerospace‑grade composites capable of meeting stringent defense specifications. Modern fighter aircraft, surveillance platforms, and transport fleets incorporate higher composite ratios to achieve radar signature reduction, improved maneuverability, and enhanced structural durability during demanding operational cycles. Public investment into domestic aerospace manufacturing has created vertically integrated ecosystems where research institutions, fiber producers, and aerostructure manufacturers collaborate to advance material science capabilities. Composite materials provide defense planners with opportunities to extend aircraft lifespan while reducing structural fatigue, an essential consideration for air forces seeking cost‑effective lifecycle management. Military procurement frameworks often prioritize technologically advanced materials, incentivizing suppliers to innovate in resin chemistry, fiber architecture, and thermal resistance to satisfy evolving mission requirements. Partnerships between global material specialists and regional manufacturers further accelerate knowledge transfer, enabling Asia Pacific producers to compete in high‑performance segments historically dominated by Western suppliers. The emergence of unmanned combat and surveillance aircraft also amplifies composite usage because weight savings translate directly into greater endurance and payload flexibility. Strategic stockpiling of critical fibers and precursor materials is reinforcing supply resilience, reducing vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions that could otherwise constrain production timelines. Certification frameworks across defense aviation increasingly recognize composites as mature structural materials, which supports broader integration across future aircraft platforms. Collectively, modernization priorities and indigenous aerospace ambitions are generating sustained, high‑value demand streams that reinforce the long‑term expansion trajectory of the Asia Pacific aerospace composites industry.
Market Challenges
High Production Costs and Capital‑Intensive Manufacturing Infrastructure
Aerospace composite production requires specialized equipment, controlled processing environments, and rigorous quality assurance protocols, all of which contribute to elevated manufacturing costs compared with traditional metallic materials. Establishing automated fiber placement lines, autoclave curing systems, and advanced inspection technologies demands substantial upfront investment, creating financial barriers for emerging suppliers attempting to enter the aerospace value chain. Raw material expenses remain another critical pressure point, as high‑grade carbon fibers and aerospace‑certified resins command premium pricing due to complex precursor chemistry and energy‑intensive production processes. Manufacturers must also maintain strict traceability across the supply chain to satisfy regulatory authorities, adding administrative overhead and operational complexity that can slow scaling efforts. Long qualification cycles further increase costs because new composite formulations must undergo extensive testing before approval for flight applications, delaying revenue realization for producers. Smaller aerospace firms frequently struggle to achieve economies of scale, making it difficult to compete with established players that benefit from higher production volumes and established OEM relationships. Currency fluctuations and logistics expenses can compound cost volatility, particularly when intermediate materials are sourced internationally. Recycling limitations associated with thermoset composites introduce additional lifecycle expenses, as disposal and environmental compliance requirements continue to tighten across industrial economies. Workforce specialization also raises operational costs since technicians require advanced training in composite layup, curing, and inspection methodologies. These cumulative financial demands reinforce high production costs as a structural constraint that shapes investment strategies and competitive positioning within the Asia Pacific aerospace composites sector.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Raw Material Constraints
Aerospace composites depend heavily on consistent access to precursor materials such as polyacrylonitrile fibers, specialty resins, and high‑temperature additives, making supply chain reliability a critical operational priority for manufacturers. Industry Research highlights that production constraints affecting roughly 30% of output are linked to limitations in precursor availability and resin systems, underscoring the fragility of upstream supply networks. Geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, and export controls can disrupt material flows, forcing aerospace suppliers to maintain higher inventory levels and increasing working capital requirements. Transportation bottlenecks and port congestion may also extend lead times, complicating production planning for aerostructure manufacturers operating on tight aircraft delivery schedules. The concentration of advanced fiber production among a limited number of global suppliers heightens exposure to operational disruptions, including plant shutdowns or regulatory interventions. Manufacturers often face challenges qualifying alternative materials because aerospace certification demands consistency in mechanical properties, limiting flexibility when shortages occur. Demand volatility across defense and commercial aviation cycles can further strain procurement strategies, as sudden surges in aircraft orders place pressure on already constrained supply pipelines. Efforts to localize production are underway but require time, capital, and technological expertise to achieve meaningful scale. Environmental regulations governing chemical processing may also restrict expansion of fiber manufacturing facilities, particularly in densely industrialized regions. Together, these vulnerabilities illustrate how raw material constraints continue to shape risk management strategies across the Asia Pacific aerospace composites ecosystem.
Opportunities
Thermoplastic Composite Adoption for High‑Rate Aircraft Production
Thermoplastic composites are gaining attention because they enable faster processing cycles, weldability, and improved damage tolerance compared with traditional thermoset materials, making them highly suitable for high‑rate aircraft manufacturing environments. As airlines seek quicker fleet renewal to accommodate rising travel demand, aircraft producers are exploring manufacturing methods that shorten assembly timelines without compromising structural integrity. Thermoplastics support automated production techniques that reduce manual labor dependency while improving repeatability, which is particularly valuable for large aerostructure components. Their recyclability potential also aligns with sustainability objectives, positioning them as a strategic material choice for manufacturers responding to environmental scrutiny. Advances in polymer chemistry are enhancing thermal stability, allowing thermoplastics to be deployed in increasingly demanding aerospace applications once reserved for thermosets. Collaboration between material scientists and OEM engineers is accelerating certification pathways, gradually removing barriers that historically limited adoption. Reduced need for refrigerated storage simplifies logistics and lowers handling costs across distributed manufacturing networks. Defense aviation programs are also evaluating thermoplastics for modular aircraft structures that facilitate rapid repair in operational settings. Investment momentum indicates growing confidence among suppliers seeking differentiated product portfolios that address emerging performance requirements. These dynamics collectively establish thermoplastic composite adoption as a transformative opportunity capable of reshaping manufacturing economics within the Asia Pacific aerospace composites market.
Regional Supply Chain Localization and Strategic Industrial Partnerships
Governments across Asia Pacific are encouraging domestic production of aerospace materials to enhance industrial resilience and reduce dependence on external suppliers, creating favorable conditions for localized composite manufacturing ecosystems. Incentive programs, tax benefits, and research funding are attracting private investment into fiber production, resin development, and aerostructure fabrication facilities. Strategic partnerships between global technology leaders and regional manufacturers are accelerating knowledge transfer, enabling local firms to adopt advanced production techniques while strengthening competitive positioning. Localization reduces transportation costs and mitigates exposure to cross‑border trade disruptions, allowing suppliers to respond more efficiently to OEM demand fluctuations. Industrial clusters that integrate research institutions with manufacturing hubs are fostering innovation pipelines capable of supporting next‑generation aircraft programs. Workforce development initiatives further enhance capability by expanding the pool of engineers skilled in composite design and processing. Defense procurement policies frequently prioritize domestic sourcing, reinforcing stable demand for locally produced materials. The growth of advanced air mobility platforms presents an additional avenue for regional suppliers to establish early leadership in emerging aerospace categories. Investors increasingly view localized composite production as a strategic asset with long‑term revenue potential tied to aviation expansion. Consequently, supply chain localization is evolving into a pivotal opportunity that strengthens regional self‑sufficiency while supporting sustained market growth.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific aerospace composites market is expected to experience sustained expansion driven by fleet modernization, defense procurement, and rapid material innovation. Technological advancements in automated manufacturing and recyclable composites are likely to reshape production efficiency while supporting environmental objectives. Regulatory frameworks encouraging domestic aerospace capabilities may further accelerate investments in advanced materials. Demand from commercial aviation and unmanned platforms is projected to remain strong, reinforcing long-term industrial momentum.
Major Players
- Toray Industries
- Hexcel Corporation
- Teijin Limited
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group
- Solvay SA
- SGL Carbon
- Owens Corning
- Gurit Holding
- TATA Advanced Materials
- Park Aerospace
- Hyosung Advanced Materials
- Jiangsu Hengshen
- Zhongfu Shenying
- Formosa Plastics Corporation
- Materion Corporation
Target Audience
- Aircraft manufacturers
- Defense procurement agencies
- Airlines and fleet operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Aerospace component suppliers
- Advanced material distributors
- Unmanned aerial vehicle manufacturers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Primary variables including material demand, aircraft production trends, fiber adoption rates, and supplier capacity were identified through industry databases and regulatory publications. Macroeconomic indicators influencing aviation expansion were also evaluated to establish contextual market drivers.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market sizing relied on triangulation using manufacturer revenues, procurement data, and verified industry reports. Segment shares were derived by analyzing fiber utilization patterns and aircraft manufacturing statistics across Asia Pacific economies.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert commentary, corporate disclosures, and aerospace material studies to ensure alignment with real procurement behavior. Cross-verification minimized analytical bias and strengthened data reliability.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into a structured framework integrating quantitative metrics with qualitative insights. The final output emphasizes actionable intelligence for stakeholders evaluating investment, expansion, or strategic entry into the aerospace composites value chain.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising aircraft production across Asia Pacific manufacturing hubs
Increasing demand for lightweight fuel efficient airframes
Expansion of indigenous defense aircraft programs
Growth in unmanned and advanced mobility platforms
Adoption of automated composite manufacturing technologies - Market Challenges
High capital investment required for composite fabrication facilities
Complex certification processes for aerospace grade materials
Supply chain constraints for high performance fibers
Skilled workforce shortages in composite engineering
Recycling and sustainability limitations of advanced composites - Market Opportunities
Localization of aerospace supply chains within Asia Pacific
Emerging demand for thermoplastic composites in next generation aircraft
Partnerships between global OEMs and regional manufacturers - Trends
Shift toward automated fiber placement and digital manufacturing
Integration of multifunctional composite structures
Increasing use of ceramic matrix composites in propulsion systems
Rapid scaling of composite usage in urban air mobility vehicles
Growing focus on recyclable composite materials - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Strengthening airworthiness certification standards for composite structures
Defense offset policies encouraging domestic composite production
Government funding for advanced materials research - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Structural Composites
Interior Composites
Engineered Composite Components
Thermoplastic Composite Systems
Hybrid Composite Assemblies - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Commercial Aircraft
Military Aircraft
Business Jets
Helicopters
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Line Fit Installations
Retrofit Upgrades
Modular Composite Kits
Integrated Structural Fitments
Lightweight Replacement Structures - By End User Segment (In Value%)
Aircraft OEMs
MRO Service Providers
Defense Contractors
Space System Integrators
Advanced Air Mobility Manufacturers - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct OEM Contracts
Tier Supplier Agreements
Government Defense Procurement
Long-Term Strategic Partnerships
Distributor Led Sourcing - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers
Aramid Fiber Composites
Ceramic Matrix Composites
Automated Fiber Placement Technology
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Material Innovation Capability, Manufacturing Scale, Certification Expertise, Supply Chain Integration, Automation Adoption, Regional Presence, Strategic Partnerships, Product Portfolio Breadth, Cost Competitiveness
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Toray Industries
Teijin Limited
Mitsubishi Chemical Group
Hexcel Corporation
Solvay SA
SGL Carbon
Gurit Holding
Park Aerospace
Hyosung Advanced Materials
Kineco Limited
Tata Advanced Materials
SAMPE Korea
Jiangsu Hengshen
Zhongfu Shenying Carbon Fiber
Formosa Plastics Corporation
- Aircraft OEMs prioritizing lightweight structures to improve operational efficiency
- Defense agencies investing in composite intensive next generation platforms
- MRO providers expanding composite repair capabilities
- Advanced mobility manufacturers driving demand for scalable composite production
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035