Market Overview
The Asia Pacific aviation infrastructure market was valued at approximately USD ~billion based on a recent historical assessment, supported by rising passenger traffic, expanding cargo volumes, and aggressive airport development programs across emerging economies. Governments are allocating substantial capital toward terminal construction, runway modernization, and smart airport technologies to enhance operational efficiency. Strong economic growth, urbanization, and increasing airline penetration continue to stimulate large-scale infrastructure investments throughout the regional aviation ecosystem.
China, India, Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia remain dominant aviation hubs due to extensive airport expansion pipelines, mature airline networks, and strategic connectivity initiatives. These countries benefit from strong institutional funding, advanced construction capabilities, and policy frameworks encouraging private participation in infrastructure projects. Rapid growth in tourism and business travel further reinforces their leadership, while modernization of legacy airports and development of greenfield facilities continue to elevate regional capacity.
Market Segmentation
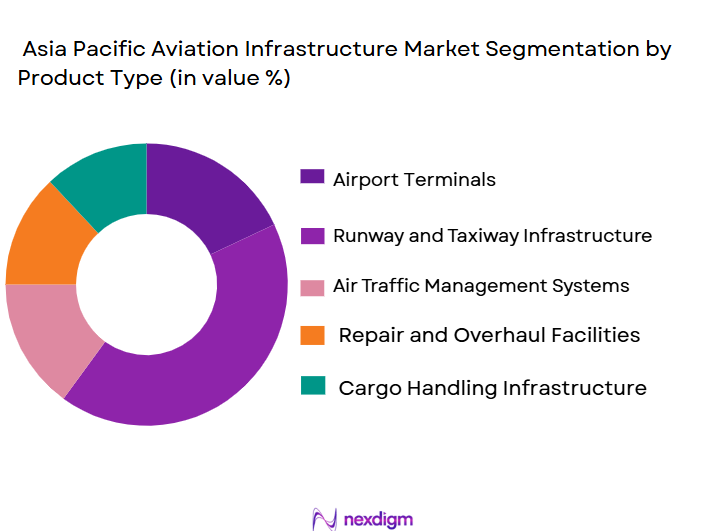
By Product Type:
The Asia Pacific aviation infrastructure market is segmented by product type into airports, air navigation systems, and ground handling equipment. Recently, airports have dominated the market share due to the surge in both international and domestic travel, necessitating substantial upgrades and expansions. This demand is particularly prominent in countries such as China and India, where rising air passenger numbers drive airport construction projects and technological upgrades to ensure safety, efficiency, and passenger convenience.
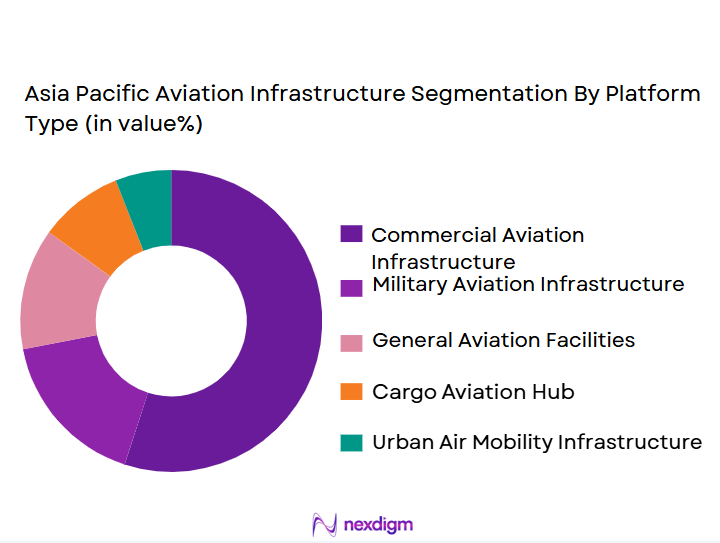
By Platform Type:
The market is also segmented by technology type into automation systems, surveillance systems, and passenger management systems. Automation systems have the largest market share owing to the increasing adoption of robotics, AI, and IoT in modernizing airport operations. Automation reduces operational costs, improves efficiency, and enhances the overall passenger experience, which is crucial as the region’s airports handle growing numbers of passengers. Countries like Singapore and Japan are leading in the adoption of automation, with state-of-the-art technologies implemented in terminal management and air traffic control.
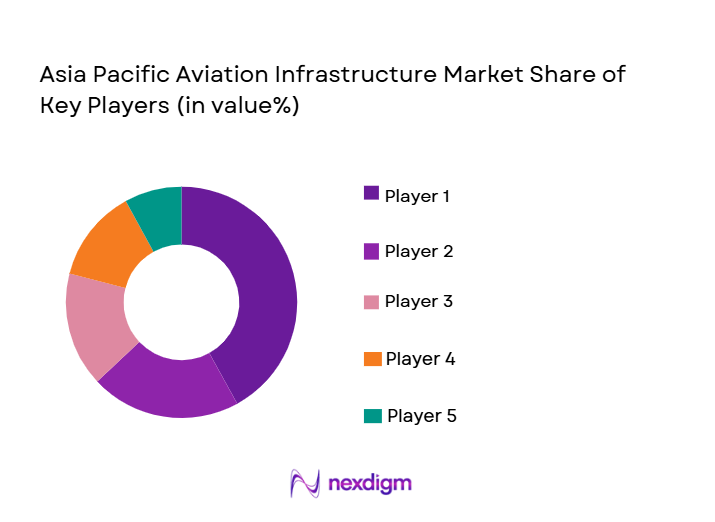
Competitive Landscape
The Asia Pacific aviation infrastructure market exhibits moderate consolidation, with large engineering firms and airport operators controlling high-value projects while regional construction companies compete through localized expertise. Strategic partnerships, concession models, and public-private collaborations are shaping project execution. Major players leverage technological capabilities, financing strength, and global experience to secure long-term contracts, creating high entry barriers for smaller participants.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Major Airport Projects |
| AECOM | 1990 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GMR Airports Infrastructure | 1978 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Adani Airports Holdings | 2019 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Turner Construction | 1902 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Fraport AG | 1924 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia Pacific Aviation Infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Accelerating Passenger Traffic and Airline Network Expansion:
Rapid growth in passenger volumes across Asia Pacific is compelling governments and airport authorities to significantly expand aviation infrastructure capacity. Rising middle-class income levels are making air travel more accessible, while low-cost carriers continue to stimulate demand through competitive pricing and broader route networks. Airports must therefore accommodate higher aircraft movements, larger passenger flows, and increasing baggage volumes without compromising operational efficiency. This pressure has led to widespread terminal expansions, runway upgrades, and adoption of automated technologies to streamline airport processes. Cargo transportation is also expanding as e-commerce accelerates cross-border trade, further increasing infrastructure requirements. Governments recognize aviation as a catalyst for economic development and tourism, prompting long-term capital commitments to airport projects. Regional connectivity initiatives are encouraging the development of secondary airports to reduce congestion at primary hubs. Airlines are simultaneously deploying larger fleets, necessitating enhanced ground handling capabilities and maintenance facilities. Technological integration such as biometric identification and digital traffic control is improving throughput while supporting safety compliance. Collectively, these dynamics position passenger growth as a foundational force driving sustained infrastructure investment across the region.
Government Investment and Policy Support for Airport Development:
Strong institutional backing from national governments is playing a decisive role in shaping aviation infrastructure expansion throughout Asia Pacific. Policymakers are introducing funding mechanisms, concession frameworks, and regulatory reforms designed to attract private capital into large-scale airport projects. Public-private partnership models are becoming increasingly prevalent because they distribute financial risk while accelerating project delivery timelines. Infrastructure development is often embedded within broader economic strategies aimed at improving trade corridors and regional mobility. Governments are also prioritizing smart and sustainable airport designs to align with environmental commitments and long-term operational resilience. Defense requirements and dual-use airfields further justify investment, ensuring strategic preparedness alongside commercial benefits. Incentives for domestic manufacturing and construction are helping build local expertise, strengthening supply chains and reducing dependency on foreign contractors. Additionally, aviation authorities are modernizing air traffic management systems to enhance safety and optimize airspace utilization. These coordinated policy efforts create a stable investment environment that encourages continuous infrastructure upgrades. As a result, government support remains a critical enabler of long-term market growth.
Market Challenges
High Capital Intensity and Financing Constraints:
Aviation infrastructure projects demand extremely high upfront investment, often requiring billions of dollars before revenue generation begins. Securing financing can therefore become a complex process involving government approvals, lender participation, and long-term concession agreements. Economic volatility may disrupt funding pipelines, particularly in emerging markets where fiscal priorities frequently shift. Construction delays caused by regulatory procedures or contractor challenges can further escalate costs, undermining project viability. Airports must also balance affordability for airlines with the need to recover capital expenditures through user charges. Smaller economies sometimes struggle to justify large airport investments without guaranteed traffic growth, increasing financial risk. Currency fluctuations can raise procurement expenses for imported materials and technology systems. Investors often require predictable regulatory environments before committing capital, making policy uncertainty a significant barrier. Additionally, infrastructure projects typically involve long payback periods, discouraging short-term investors. These financial pressures collectively constrain the pace at which new aviation facilities can be developed across the region.
Land Acquisition, Environmental Compliance, and Urban Constraints:
Developing aviation infrastructure frequently involves acquiring large land parcels, a process that can trigger legal disputes, community resistance, and prolonged negotiations. Urban density in major metropolitan areas limits expansion opportunities, forcing planners to consider costly relocation or reclamation strategies. Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, requiring comprehensive impact assessments before construction begins. Airports must address concerns related to noise pollution, carbon emissions, and ecological disruption, often necessitating expensive mitigation measures. Public opposition can delay approvals and increase political scrutiny, particularly for greenfield projects near residential zones. Climate resilience is another growing requirement, as infrastructure must withstand extreme weather events and rising sea levels. Compliance with sustainability standards can elevate construction costs but remains unavoidable for regulatory approval. Additionally, integrating new infrastructure with existing transport networks demands complex planning coordination. These constraints collectively slow project execution timelines and raise overall development risk.
Opportunities
Adoption of Smart Airport Technologies and Digital Ecosystems:
The transition toward digitally enabled airports presents a significant opportunity for infrastructure providers seeking long-term growth. Advanced technologies such as automated baggage handling, biometric verification, and artificial intelligence-driven traffic management are transforming operational efficiency. Airports investing in digital ecosystems can process passengers faster while reducing labor dependency and operational bottlenecks. Data analytics platforms are enabling predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime for critical assets such as runways and boarding systems. Governments increasingly support smart infrastructure because it enhances safety and aligns with broader digital transformation agendas. Technology integration also improves passenger satisfaction, strengthening airport competitiveness in attracting global airlines. Vendors specializing in cybersecurity, cloud platforms, and communication systems stand to benefit from these upgrades. Furthermore, digitalization supports scalable infrastructure capable of accommodating future travel demand without proportional cost increases. As airports evolve into technology-centric transport hubs, smart systems represent a powerful avenue for value creation across the aviation ecosystem.
Expansion of Green and Sustainable Airport Infrastructure:
Sustainability initiatives are reshaping infrastructure planning as airports strive to reduce carbon footprints and comply with global environmental targets. Renewable energy installations, energy-efficient terminals, and green construction materials are increasingly incorporated into new developments. Governments are encouraging environmentally responsible designs through regulatory incentives and funding programs. Sustainable airports not only reduce operational costs over time but also improve public acceptance of large infrastructure projects. Investors are demonstrating growing preference for assets aligned with environmental, social, and governance principles, improving financing prospects. Electric ground vehicles, optimized flight paths, and waste reduction systems further support eco-friendly operations. Climate-resilient infrastructure is becoming essential to protect long-term asset value against environmental risks. Airlines also favor airports that support sustainable aviation fuel logistics and emissions reduction strategies. As environmental accountability becomes central to aviation policy, sustainable infrastructure development offers substantial long-term growth potential for industry participants.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific aviation infrastructure market is positioned for strong expansion as passenger demand, cargo activity, and airline fleet growth continue to intensify capacity requirements. Technological modernization and smart airport adoption will reshape operational models while improving efficiency. Governments are expected to maintain supportive regulatory frameworks and funding mechanisms to accelerate infrastructure delivery. Sustainability initiatives will increasingly guide design priorities, encouraging green construction and energy optimization. Collectively, these factors indicate a resilient growth trajectory over the next five years.
Major Players
• GMR Airports Infrastructure
• Adani Airports Holdings
• Turner Construction
• Fraport AG
• VINCI Airports
• Changi Airport Group
• Beijing Capital International Airport Company
• Larsen & Toubro
• TAV Airports Holding
• Korea Airports Corporation
• Malaysia Airports Holdings
• Airports of Thailand
• Japan Airport Terminal Co.
• Fluor Corporation
Key Target Audience
• Airlines
• Infrastructure developers
• Construction contractors
• Aerospace system integrators
• Logistics and cargo operators
• Investments and venture capitalist firms
• Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Primary variables including passenger growth, airport construction activity, cargo expansion, and government spending were identified through verified industry databases and aviation authority publications to define the analytical framework.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data and financial disclosures were synthesized with infrastructure project pipelines to estimate market size and segmentation. Macroeconomic indicators and aviation demand patterns were incorporated for structural accuracy.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts, infrastructure planners, and aviation analysts were consulted to validate assumptions regarding investment trends, technology adoption, and regulatory developments influencing regional infrastructure growth.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated datasets were consolidated into a structured report integrating qualitative insights with quantitative metrics, ensuring methodological consistency and actionable intelligence for stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks.
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rapid Passenger Traffic Expansion Across Emerging Economies
Government Investment in Mega Airport Projects
Rising Air Cargo Demand Supporting Logistics Infrastructure
Integration of Smart Airport Technologies
Growth of Low Cost Carrier Networks - Market Challenges
High Capital Requirements for Infrastructure Development
Land Acquisition and Regulatory Approval Delays
Environmental Compliance Pressures
Capacity Constraints at Major Aviation Hubs
Supply Chain Disruptions in Construction Materials - Market Opportunities
Development of Green and Carbon Neutral Airports
Expansion of Secondary and Regional Airports
Adoption of Digital and Automated Airport Ecosystems - Trends
Shift Toward Smart Airport Ecosystems
Increasing Use of Sustainable Infrastructure Designs
Growth in Airport Privatization Initiatives
Integration of Biometric Passenger Systems
Expansion of Multimodal Transport Connectivity - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Strengthening Civil Aviation Safety Regulations
Government Funding Programs for Airport Expansion
Policies Encouraging Private Sector Participation - SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Airport Terminals
Runway and Taxiway Infrastructure
Air Traffic Management Systems
Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul Facilities
Cargo Handling Infrastructure - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Commercial Aviation Infrastructure
Military Aviation Infrastructure
General Aviation Facilities
Cargo Aviation Hubs
Urban Air Mobility Infrastructure - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Greenfield Developments
Brownfield Expansions
Modular Infrastructure
Smart Integrated Infrastructure
Retrofit Projects - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Airport Authorities
Airlines
Defense Organizations
Private Infrastructure Developers
Government Transport Agencies - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Public Private Partnerships
Government Direct Contracts
Engineering Procurement and Construction Contracts
Lease and Operate Agreements
Build Operate Transfer Models - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Smart Airport Technologies
Sustainable Construction Materials
Advanced Radar and Navigation Systems
Automated Passenger Processing Systems
Digital Air Traffic Platforms
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
CrossComparison Parameters (Infrastructure Type, Project Scale, Technology Integration, Procurement Model, EndUser Focus, Sustainability Standards, Construction Capability, Geographic Presence, Lifecycle Support, Digital Enablement) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Adani Airports Holdings
GMR Airports Infrastructure
Changi Airport Group
Beijing Capital International Airport Company
Japan Airport Terminal Co.
Sydney Airport Corporation
Aéroports de Paris Group
Fraport AG
VINCI Airports
TAV Airports Holding
Korea Airports Corporation
Malaysia Airports Holdings Berhad
Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited
China Communications Construction Company
Larsen & Toubro
- Airport authorities prioritizing capacity expansion to handle rising passenger volumes
- Airlines advocating for technologically advanced terminals to improve operational efficiency
- Defense organizations investing in dual use airbase infrastructure
- Private developers increasing participation through long term concession models
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


