Market Overview
The Asia Pacific aviation market reached approximately USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, supported by expanding commercial aircraft demand, fleet modernization programs, and sustained passenger traffic growth across emerging economies. Strong capital deployment into airport infrastructure, aircraft procurement, and aviation services has reinforced industry expansion, while digitally enabled aircraft and maintenance ecosystems continue to stimulate operational efficiency and long-term revenue generation across airlines and aviation stakeholders.
China, India, Japan, Singapore, and Australia represent the dominant aviation hubs due to extensive airport networks, high passenger volumes, and large aircraft order pipelines. China leads regional traffic with substantial airline activity, while India’s rapidly expanding passenger base and infrastructure investments reinforce its strategic position. Singapore functions as a major transit gateway supported by advanced airport capabilities, whereas Japan and Australia benefit from mature regulatory frameworks and strong international connectivity facilitating consistent aviation activity.
Market Segmentation
By Aircraft Type:
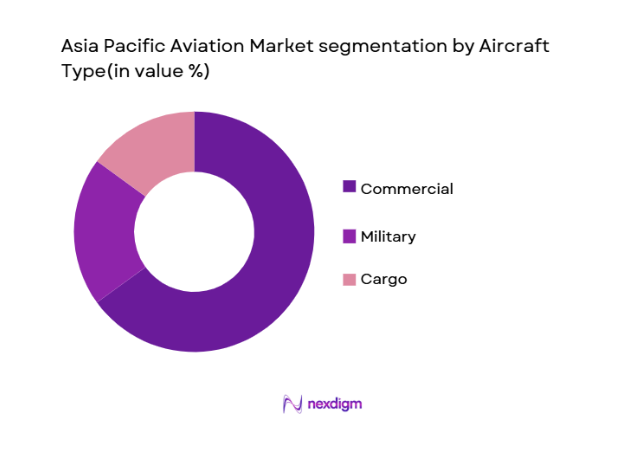
The Asia Pacific aviation market is segmented by aircraft type into commercial, military, and cargo aircraft. Recently, commercial aircraft have dominated the market share due to the rise in air travel demand, particularly in emerging economies such as China and India. The rapid expansion of middle-class populations in these countries, coupled with the growth of both domestic and international flight networks, has resulted in an increase in commercial aircraft acquisitions. The demand for low-cost carriers, along with improvements in airport infrastructure, has further contributed to the dominance of commercial aircraft in the market.
By End-User:
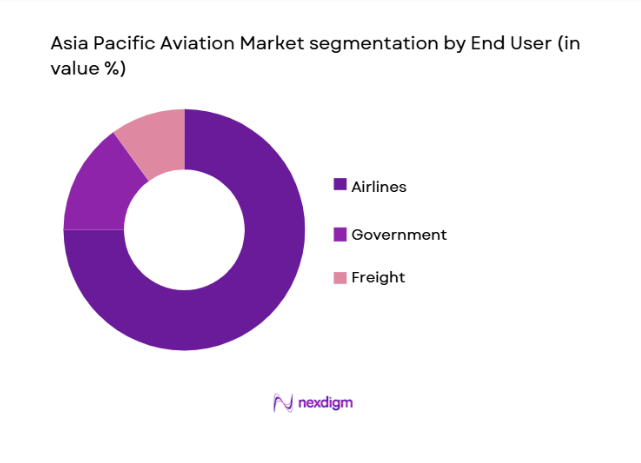
The market is also segmented by end-user into government, airlines, and freight companies. Airlines hold a dominant position in the market, primarily driven by the increasing demand for air travel, both domestic and international. The growth of low-cost carriers and the expansion of route networks across the region contribute significantly to the dominance of airlines in the aviation market. Additionally, the increasing number of air passengers, coupled with competitive pricing models, supports the rapid growth of airlines in the region.
Competitive Landscape
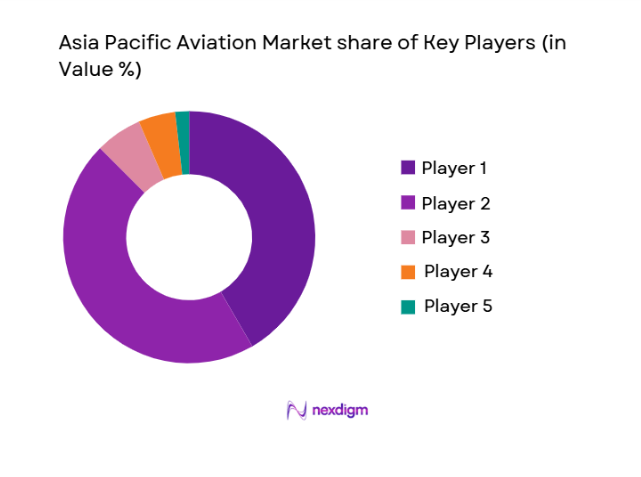
The Asia Pacific aviation market demonstrates moderate consolidation, with large aircraft manufacturers, airline groups, and integrated service providers exerting substantial influence over procurement cycles and technological adoption. Strategic alliances, joint ventures, and long-term service agreements reinforce competitive positioning, while regional carriers increasingly collaborate with global OEMs to support fleet expansion and maintenance capabilities.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Fleet Support Capability |
| Airbus | 1970 | Netherlands | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing | 1916 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| COMAC | 2008 | China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Singapore Technologies Engineering | 1967 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hindustan Aeronautics Limited | 1940 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia Pacific Aviation Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Regional Passenger Traffic:
Sustained increases in passenger demand continue to reshape airline capacity strategies across the Asia Pacific aviation ecosystem. The region accounts for a substantial portion of global traffic activity, supported by rising urbanization and improved air connectivity between economic centers. Liberalized visa policies and cross-border tourism corridors further encourage frequent travel, strengthening airline load factors. Growing middle-income populations increasingly prioritize air travel for both leisure and business purposes, accelerating route development. Governments are investing heavily in airport expansions to accommodate higher passenger throughput while improving operational resilience. Airlines respond by accelerating aircraft deliveries and optimizing network planning to prevent congestion. Technological enhancements in booking platforms simplify travel access, further stimulating demand. Cargo-passenger hybrid utilization models also support profitability on high-density routes. These combined forces ensure that passenger growth remains a foundational catalyst sustaining long-term aviation industry expansion across the region.
Government-Led Airport Infrastructure Investments:
sector capital allocation toward aviation infrastructure is transforming operational capacity across major regional hubs. Authorities are developing new terminals, upgrading runway systems, and integrating automated traffic management technologies to improve efficiency. These projects support both domestic mobility and international transit flows, reinforcing aviation as a strategic economic enabler. Infrastructure modernization also attracts private investment through public-private partnership frameworks that reduce fiscal pressure while accelerating project timelines. Enhanced airport ecosystems stimulate adjacent industries such as logistics, hospitality, and aircraft maintenance. Improved cargo handling facilities strengthen supply chains for high-value goods, further boosting aviation utilization. Regulatory bodies simultaneously implement safety upgrades to align with global standards, increasing airline confidence. Regional governments view aviation as critical for trade competitiveness, prompting sustained financial commitments. This coordinated infrastructure expansion directly supports fleet growth, airline entry, and service diversification across the Asia Pacific aviation landscape.
Market Challenges
Persistent Supply Chain Disruptions in Aircraft Manufacturing:
Production ecosystems across the aviation industry continue to experience delays caused by constrained component availability and labor shortages. Engine manufacturing bottlenecks and semiconductor dependencies have extended aircraft delivery timelines, forcing airlines to adjust capacity planning. These disruptions elevate leasing costs as carriers seek interim fleet solutions to maintain operational schedules. Maintenance cycles are also affected when replacement parts face procurement delays, increasing aircraft downtime. Manufacturers must rebalance supplier networks while navigating geopolitical trade complexities that influence sourcing strategies. Rising logistics costs further compound procurement challenges for specialized aviation materials. Airlines consequently face unpredictable capital deployment schedules, complicating long-term financial planning. Smaller carriers remain particularly vulnerable due to limited bargaining power with suppliers. Although industry stakeholders are investing in localized manufacturing capabilities, structural supply chain fragility continues to constrain the pace of aviation expansion across the region.
High Capital Intensity and Financing Constraints:
Aviation remains one of the most capital-intensive transportation sectors, requiring substantial upfront investment for aircraft acquisition, infrastructure, and regulatory compliance. Interest rate fluctuations influence borrowing costs, affecting airline balance sheets and limiting aggressive fleet expansion. Leasing structures provide flexibility but introduce recurring financial obligations that can strain profitability during demand volatility. Currency fluctuations across emerging economies further complicate repayment structures for dollar-denominated aircraft contracts. Insurance expenses and compliance costs also add to financial burdens, particularly for new entrants. Investors often demand stable yield visibility before committing capital, creating funding hurdles for rapidly scaling operators. Economic uncertainty may delay discretionary travel spending, indirectly impacting revenue projections. Governments sometimes intervene with financial support, yet such measures vary widely across jurisdictions. This combination of high financing thresholds and macroeconomic sensitivity remains a structural constraint shaping aviation investment strategies.
Opportunities
Adoption of Sustainable Aviation Technologies:
Environmental accountability is reshaping procurement priorities as airlines pursue lower-emission operations. Sustainable aviation fuel compatibility, lightweight composite materials, and next-generation propulsion systems are gaining strategic importance within fleet modernization programs. Governments are introducing regulatory incentives to accelerate adoption, encouraging research partnerships between manufacturers and energy providers. Carbon reporting frameworks also motivate airlines to integrate efficiency-focused technologies that reduce lifecycle emissions. Investors increasingly favor environmentally responsible operators, improving access to green financing instruments. Airports are simultaneously implementing electrified ground handling infrastructure to complement airline sustainability initiatives. These developments support brand differentiation as travelers become more environmentally conscious. Technological innovation also unlocks long-term cost reductions through improved fuel efficiency. As regulatory momentum strengthens, sustainability transitions present a significant opportunity for stakeholders to enhance competitiveness while aligning with evolving environmental standards.
Expansion of Secondary City Air Connectivity:
Aviation growth is increasingly shifting toward underserved metropolitan clusters where rising economic activity drives new travel demand. Governments promote regional connectivity schemes that incentivize airlines to operate routes linking smaller cities with primary hubs. This strategy reduces congestion at major airports while distributing economic benefits more evenly across national geographies. Airlines gain access to previously untapped passenger pools, improving aircraft utilization rates. Infrastructure upgrades at regional airports support reliable operations and encourage tourism inflows. Cargo carriers also benefit from shorter logistics chains connecting manufacturing zones with export gateways. Digital demand forecasting tools enable carriers to identify viable routes with greater accuracy, minimizing operational risk. Leasing firms view these markets as stable long-term opportunities due to predictable mobility patterns. As regional incomes expand, secondary city connectivity is positioned to become a major contributor to aviation network diversification.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific aviation market is expected to maintain steady expansion driven by fleet modernization, rising passenger mobility, and continuous airport capacity upgrades. Technological integration across operations will improve efficiency while sustainability initiatives influence procurement decisions. Regulatory frameworks supporting infrastructure investment are likely to reinforce airline confidence. Growing tourism flows and cross-border trade activity should further elevate aircraft utilization, positioning the region as a central engine of global aviation growth.
Major Players
• Boeing
• COMAC
• Singapore Technologies Engineering
• Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
• Korean Aerospace Industries
• Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
• Embraer
• ANA Holdings
• Japan Airlines
• Qantas Airways
• Cathay Pacific Airways
• China Southern Airlines
• AirAsia Aviation Group
• IndiGo
Key Target Audience
•Aircraft leasing companies
• Airport operators
• Aerospace component manufacturers
• Cargo logistics providers
• Maintenance repair and overhaul providers
• Government and regulatory bodies
• Investments and venture capitalist firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Primary variables including fleet size, aircraft procurement activity, passenger demand indicators, infrastructure investments, and airline financial performance were identified. Macroeconomic indicators and aviation policy developments were also evaluated to establish foundational market parameters.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Collected data was structured using top-down and bottom-up approaches to estimate market size and segmentation. Industry databases, financial disclosures, and aviation authority publications were synthesized to construct a consistent analytical framework.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings were validated through consultations with aviation analysts, airline strategists, and aerospace specialists. Conflicting data points were reconciled through triangulation to ensure accuracy and analytical reliability.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated datasets were consolidated into actionable insights supported by structured forecasting models. The final output emphasizes clarity, methodological transparency, and alignment with current aviation industry dynamics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rapid expansion of regional air passenger traffic
Large scale airport infrastructure investments
Fleet expansion by low cost carriers
Government initiatives supporting aviation connectivity
Rising cross border tourism and trade activity - Market Challenges
Volatility in aviation fuel pricing
Airspace congestion across major hubs
High capital expenditure requirements
Supply chain disruptions for aircraft components
Regulatory variations across multiple jurisdictions - Market Opportunities
Adoption of sustainable aviation technologies
Growth of secondary city air routes
Expansion of aircraft leasing ecosystems - Trends
Acceleration of digitalization in airline operations
Increasing deployment of fuel efficient aircraft
Emergence of smart airports with automated systems
Growth in regional cargo aviation networks
Integration of artificial intelligence in flight operations - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Liberalization of bilateral air service agreements
Implementation of stricter aviation safety standards
National programs supporting airport privatization
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Commercial Aircraft Systems
Air Traffic Management Systems
Airport Infrastructure Systems
Maintenance Repair and Overhaul Systems
Avionics and Navigation Systems - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Narrow Body Aircraft
Wide Body Aircraft
Regional Aircraft
Cargo Aircraft
Business Jets - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Line Fit Installations
Retrofit Upgrades
Modular Integrations
Fleet Modernization Packages
Aftermarket Enhancements - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Commercial Airlines
Low Cost Carriers
Cargo Operators
Government Aviation Authorities
Private Charter Operators - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct OEM Contracts
Leasing Company Procurement
Government Aviation Tenders
Third Party Integrators
Long Term Service Agreements - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Composite Airframe Materials
Next Generation Fuel Efficient Engines
Digital Flight Deck Technologies
Predictive Maintenance Platforms
Sustainable Aviation Fuel Compatible Systems
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
CrossComparison Parameters (Fleet Portfolio, Regional Presence, Aircraft Order Backlog, MRO Capabilities, Technology Integration, Strategic Partnerships, Financial Strength, Sustainability Initiatives, Customer Base Diversity, Pricing Strategy) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Airbus
Boeing
COMAC
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Embraer
Singapore Technologies Engineering
Korean Aerospace Industries
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Qantas Airways
ANA Holdings
China Southern Airlines
AirAsia Group
Japan Airlines
IndiGo
Cathay Pacific Airways
- Airlines prioritizing fleet modernization to improve operational efficiency
- Cargo operators expanding capacity to support e commerce logistics
- Governments investing in regional connectivity programs
- Private operators increasing demand for business aviation services
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


