Market Overview
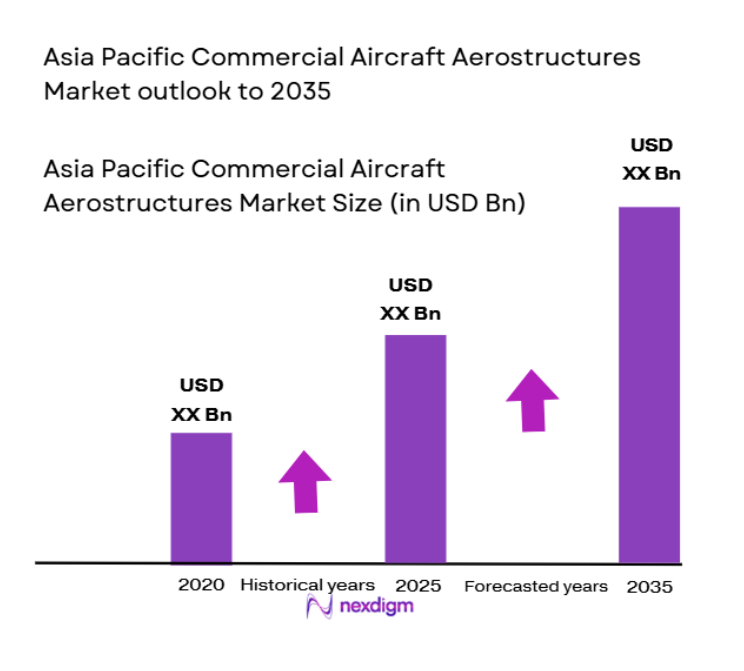
The Asia Pacific commercial aircraft aerostructures market is valued at approximately USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, supported by rising aircraft production, expanding airline fleets, and increasing adoption of lightweight structural materials. Demand is further driven by advancements in aircraft technology and the need for fuel-efficient designs that reduce operational costs. Growing passenger traffic across emerging aviation economies continues to accelerate manufacturing activity and long-term supplier contracts within the regional aerospace ecosystem.
China, India, and Japan remain dominant due to large-scale aircraft manufacturing capabilities, strong domestic aviation demand, and government-backed aerospace development programs. Lower labor costs and localization strategies have encouraged global manufacturers to diversify supply chains toward the region, while advanced materials expertise in Japan and expanding fleet programs in India strengthen production capacity. Rapid industrialization and ongoing aerospace projects across major economies further reinforce the region’s structural manufacturing leadership.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
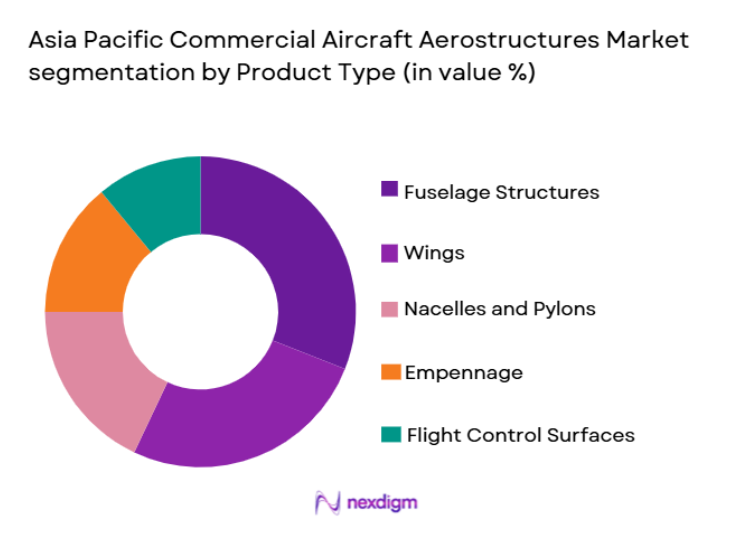
Asia Pacific Commercial Aircraft Aerostructures market is segmented by product type into fuselage structures, wings, empennage, nacelles and pylons, and flight control surfaces. Recently, fuselage structures have a dominant market share due to their high structural cost, engineering complexity, and essential role in aircraft integrity. Airlines increasingly prioritize modern aircraft with durable fuselage systems to support long operational lifecycles, while OEM production backlogs intensify demand. Growing preference for composite fuselages that enhance fuel efficiency further strengthens adoption, alongside rising aircraft assembly across regional manufacturing hubs.
By Aircraft Type
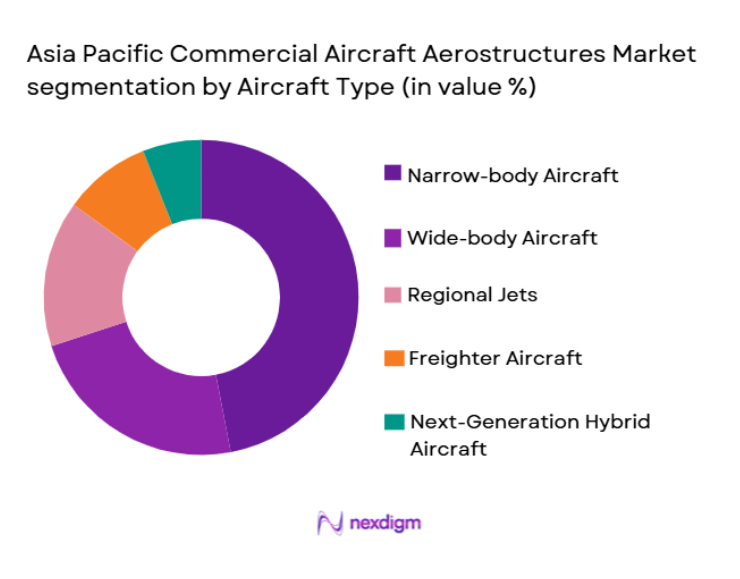
Asia Pacific Commercial Aircraft Aerostructures market is segmented by aircraft type into narrow-body aircraft, wide-body aircraft, regional jets, freighter aircraft, and next-generation hybrid aircraft. Recently, narrow-body aircraft have a dominant market share due to strong demand from low-cost carriers operating high-frequency routes across densely populated corridors. Their operational efficiency and suitability for short- to medium-haul travel align with regional passenger growth patterns. Increasing airline fleet modernization and cost-sensitive route economics further amplify production volumes, ensuring continued structural component demand across manufacturing networks.
Competitive Landscape
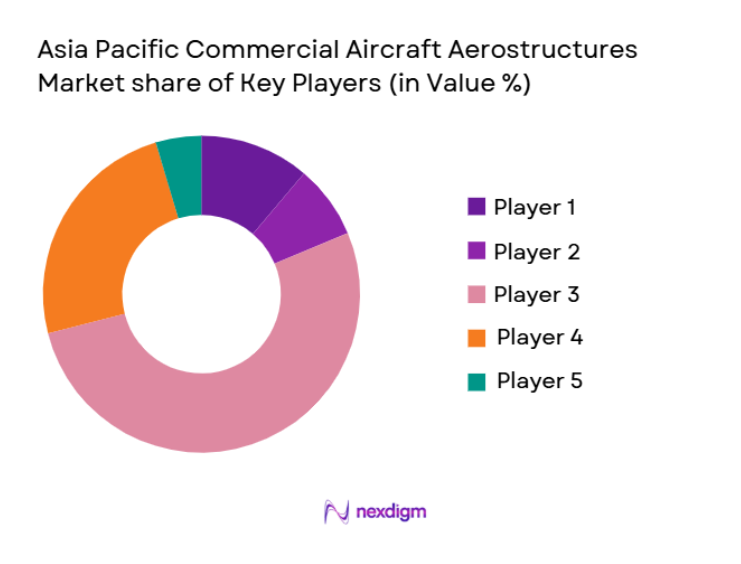
The Asia Pacific commercial aircraft aerostructures market demonstrates moderate consolidation, with major global suppliers collaborating closely with regional manufacturers to secure long-term contracts. Large aerospace firms maintain technological advantages in composite structures and automated fabrication, while partnerships and joint ventures enable localized production. Competitive intensity is shaped by OEM alignment, material innovation, and scale efficiencies that strengthen supplier positioning across commercial aircraft programs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Primary Aerostructure Specialization |
| Spirit AeroSystems | 2005 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GKN Aerospace | 1759 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1884 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | 1896 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Korea Aerospace Industries | 1999 | South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia Pacific Commercial Aircraft Aerostructures Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rapid Expansion of Commercial Aircraft Fleets Across Emerging Aviation Economies
The sustained increase in passenger traffic across Asia Pacific has compelled airlines to expand fleet capacity, directly accelerating demand for aerostructures. Strong economic growth and rising middle-class travel propensity have created structural pressure on carriers to procure fuel-efficient aircraft capable of operating high-density routes. Aircraft manufacturers are responding with higher production rates, which translates into larger procurement volumes for fuselage sections, wings, and structural assemblies. Regional governments are simultaneously investing in airport infrastructure, enabling airlines to scale operations without capacity bottlenecks. OEM backlogs remain elevated, reinforcing multi-year manufacturing schedules that stabilize supplier revenues. Furthermore, the emergence of domestic aircraft programs in countries such as China and India is strengthening internal supply chains and reducing reliance on imports. These developments encourage tier suppliers to expand facilities within the region, improving production resilience. Strategic localization policies also attract foreign investment into aerostructure manufacturing clusters. As production ecosystems mature, cost efficiencies improve and stimulate additional aircraft orders. Collectively, these forces establish fleet expansion as a fundamental catalyst for sustained aerostructure demand.
Accelerated Adoption of Lightweight Composite Materials in Aircraft Manufacturing
Airlines increasingly prioritize operational efficiency, pushing manufacturers toward advanced materials that reduce aircraft weight while maintaining structural strength. Composite aerostructures deliver measurable fuel savings and lower lifecycle maintenance costs, making them integral to next-generation aircraft designs. Material innovation has also enabled improved corrosion resistance and fatigue performance, extending service intervals and supporting airline profitability objectives. Aerospace firms continue investing heavily in automated fiber placement and thermoplastic processing to scale composite output economically. As production technologies mature, suppliers can deliver complex geometries with reduced manufacturing waste. This technological progress encourages OEMs to redesign structural architectures around composite-intensive frameworks. Environmental considerations further amplify adoption, as lighter aircraft contribute to lower emissions. Collaborative research programs between manufacturers and material science companies accelerate certification pathways for new composites. Regional suppliers are upgrading capabilities to remain competitive in this evolving environment. Consequently, lightweight material integration is reshaping aerostructure engineering priorities across the market.
Market Challenges
High Capital Intensity and Certification Complexity in Aerostructure Manufacturing
Establishing aerostructure production facilities requires substantial financial investment in tooling, robotics, and precision machining infrastructure. Certification processes impose additional burdens, as structural components must meet rigorous safety and airworthiness standards before entering service. These requirements lengthen development timelines and delay revenue realization for suppliers. Smaller manufacturers often struggle to secure financing for large-scale programs, limiting competitive diversity within the market. Regulatory scrutiny also necessitates extensive testing and documentation, increasing operational overhead. Any design modification can trigger renewed validation cycles, further escalating costs. Workforce specialization adds another layer of expense because highly trained engineers and technicians remain scarce. Suppliers must simultaneously maintain quality assurance systems capable of meeting OEM expectations. Economic volatility can disrupt investment planning, particularly when aircraft production rates fluctuate. Collectively, these constraints elevate barriers to entry and concentrate production among established players.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Raw Material Price Volatility
Aerostructure manufacturing depends heavily on specialized metals and composite fibers that are sourced through globally distributed supply networks. Disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions, logistics bottlenecks, or trade restrictions can delay component deliveries and interrupt assembly schedules. Manufacturers often operate under just-in-time frameworks, leaving minimal buffer against shortages. Price volatility in raw materials further complicates contract negotiations, as long-term agreements may become financially unfavorable when input costs surge. Suppliers must therefore adopt hedging strategies or renegotiate pricing structures with OEM partners. Limited availability of aerospace-grade materials intensifies competition among manufacturers seeking production continuity. Transportation constraints also elevate procurement expenses and extend lead times. These uncertainties encourage firms to diversify sourcing but doing so requires rigorous qualification processes. Persistent instability ultimately pressures profit margins and operational planning across the aerostructure value chain.
Opportunities
Localization of Aerospace Manufacturing Ecosystems Within Asia Pacific
Governments across the region are actively promoting domestic aerospace capabilities through policy incentives, infrastructure development, and industrial partnerships. These initiatives encourage multinational firms to establish regional production bases, creating integrated supply chains that reduce transportation costs and delivery risks. Localization also supports faster response times for OEM production requirements. Domestic manufacturing expansion strengthens employment and technological expertise, further reinforcing policy momentum. Joint ventures between global suppliers and local companies facilitate knowledge transfer in advanced fabrication methods. As clusters mature, economies of scale improve cost competitiveness relative to traditional manufacturing hubs. Airlines increasingly favor locally produced components to minimize downtime associated with long logistics cycles. The rise of indigenous aircraft programs further accelerates structural demand within national borders. Such developments create durable growth avenues for both established suppliers and emerging entrants. Over time, localization could transform the region into a primary global aerostructure production center.
Integration of Automation and Digital Manufacturing Technologies
Aerospace manufacturers are rapidly adopting robotics, artificial intelligence, and digital twin platforms to enhance precision and throughput in structural fabrication. Automated assembly lines reduce human error while improving consistency across high-volume production runs. Digital simulation tools allow engineers to validate structural performance before physical prototyping, shortening development cycles. Predictive analytics also help identify maintenance needs for manufacturing equipment, minimizing downtime. These capabilities collectively enhance operational efficiency and reduce per-unit costs. Suppliers leveraging automation can meet aggressive OEM schedules without compromising quality standards. Advanced manufacturing additionally enables complex designs that were previously impractical using conventional methods. Investment in smart factories positions companies to handle future aircraft programs with greater agility. As technology costs gradually decline, adoption barriers diminish for mid-sized suppliers. This transition toward digital production represents a significant opportunity to modernize the aerostructure industry.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific commercial aircraft aerostructures market is expected to experience steady expansion over the next five years, supported by rising aircraft orders and sustained passenger demand. Technological advancements in composites and automated production will improve manufacturing efficiency while lowering lifecycle costs. Regulatory encouragement for domestic aerospace capabilities is likely to attract further investment into regional supply chains. Growing airline modernization strategies and infrastructure development should reinforce structural component demand.
Major Players
- Spirit AeroSystems
- GKN Aerospace
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Korea Aerospace Industries
- Triumph Group
- Aernnova Aerospace
- FACC AG
- ST Engineering Aerospace
- AVIC Xi’an Aircraft Industry Group
- Chengdu Aircraft Industrial Group
- Shenyang Aircraft Corporation
- Mahindra Aerospace
- PT Dirgantara Indonesia
- Safran
Key Target Audience
- Commercial aircraft manufacturers
- Tier-1 aerospace suppliers
- Airline fleet operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Maintenance repair and overhaul providers
- Aerospace component distributors
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Extensive secondary research was conducted to determine critical market variables including production rates, fleet expansion, material adoption, and supplier capabilities. Industry databases and corporate disclosures were evaluated to define structural demand patterns.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Collected data was synthesized using bottom-up and top-down modeling approaches to estimate regional revenue distribution and segment performance. Cross-validation ensured consistency across aircraft production metrics and supplier outputs.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts, aerospace engineers, and procurement specialists were consulted to validate assumptions regarding manufacturing trends and material transitions. Their insights refined demand projections and competitive positioning assessments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated into a structured framework emphasizing accuracy, data integrity, and analytical coherence. The final report integrates quantitative evaluation with qualitative interpretation to support strategic decision-making.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising commercial aircraft deliveries across emerging aviation hubs
Expansion of low-cost carrier fleets requiring lightweight structures
Increased adoption of fuel-efficient composite aerostructures
Growing air passenger traffic driving aircraft production
Localization of aerostructure manufacturing in Asia Pacific economies - Market Challenges
High capital requirements for advanced manufacturing facilities
Supply chain disruptions impacting raw material availability
Stringent certification requirements delaying program timelines
Skilled labor shortages in aerospace manufacturing
Volatility in aircraft production rates - Market Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous aircraft programs in Asia Pacific
Strategic joint ventures between global OEMs and regional suppliers
Integration of automation and robotics in aerostructure fabrication - Trends
Shift toward composite-intensive aircraft designs
Digital twin technology adoption in structural testing
Increased outsourcing to cost-competitive manufacturing bases
Modular aerostructure production techniques
Sustainability-driven material innovation - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Civil aviation authority airworthiness standards
Regional policies promoting domestic aerospace manufacturing
Environmental compliance mandates influencing material selection - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Fuselage Structures
Wing Assemblies
Empennage Structures
Nacelles and Pylons
Flight Control Surfaces - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Narrow-Body Aircraft
Wide-Body Aircraft
Regional Jets
Freighter Aircraft
Next-Generation Hybrid Aircraft - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Line Fit Installations
Retrofit Programs
Structural Upgrades
Lightweight Replacement Structures
Damage Repair Fitments - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Commercial Airlines
Aircraft Original Equipment Manufacturers
Maintenance Repair and Overhaul Providers
Aircraft Leasing Companies
Cargo Operators - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct OEM Contracts
Tier-1 Supplier Agreements
Long-Term Manufacturing Partnerships
Government-Backed Procurement Programs
Aftermarket Sourcing - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Advanced Carbon Fiber Composites
Aluminum Lithium Alloys
Titanium Structures
Thermoplastic Composites
Additive Manufactured Components
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- CrossComparison Parameters (Manufacturing Capability, Material Expertise, Production Scale, Geographic Presence, OEM Partnerships, R&D Investment, Cost Competitiveness, Delivery Timelines, Automation Integration, Aftermarket Support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Spirit AeroSystems
GKN Aerospace
Kawasaki Heavy Industries Aerospace Company
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Aerospace Systems
Korea Aerospace Industries
Aernnova Aerospace
Triumph Group
FACC AG
ST Engineering Aerospace
Astra Aerospace
Mahindra Aerospace
PT Dirgantara Indonesia
Shenyang Aircraft Corporation
Chengdu Aircraft Industrial Group
AVIC Xi’an Aircraft Industry Group
- Airlines prioritizing fuel efficiency through lightweight structural adoption
- OEMs focusing on scalable production to meet backlog demand
- MRO providers expanding structural repair capabilities
- Leasing firms demanding durable aerostructures to preserve asset value
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


