Market Overview
The Asia Pacific cruise missile market reached approximately USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, driven by rising defense modernization budgets, growing emphasis on long-range precision strike capabilities, and increased procurement of advanced missile systems. Governments across the region are investing heavily in deterrence technologies to strengthen national security frameworks. Rapid advancements in propulsion, stealth, and guidance technologies are further supporting deployment, while indigenous missile development programs are reinforcing domestic manufacturing capacity.
China, India, Japan, and South Korea dominate the regional landscape due to sustained defense investments, expanding military capabilities, and strategic emphasis on maritime security. China benefits from extensive missile production infrastructure, while India continues strengthening indigenous development initiatives. Japan’s technological expertise supports advanced missile research, and South Korea maintains robust manufacturing capabilities. These countries collectively shape regional defense dynamics through modernization programs and collaborative military strategies.
Market Segmentation
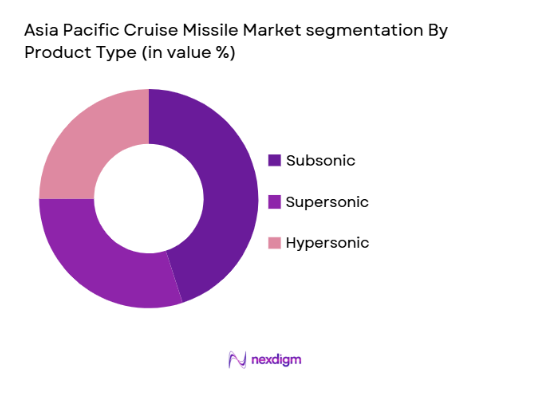
By Product Type
The Asia Pacific cruise missile market is segmented by product type into subsonic, supersonic, and hypersonic cruise missiles. Recently, subsonic cruise missiles have dominated the market share due to their cost-effectiveness, longer range, and precision in targeting. These missiles are ideal for strike operations and have seen significant use by major regional military powers. Subsonic missiles’ ability to cover vast distances while maintaining low radar visibility has made them a preferred option for strategic long-range attacks. Their application in naval and land-based defense systems has been instrumental in the growing military capabilities of Asia Pacific nations.
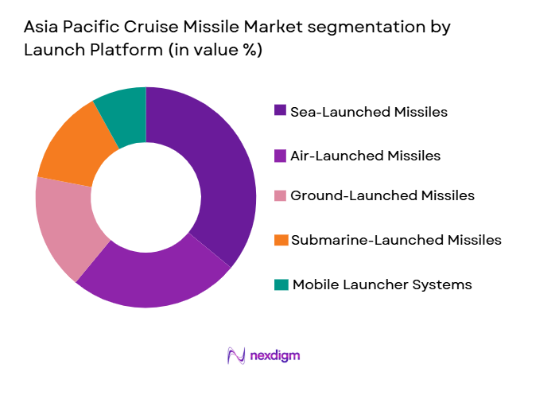
By Launch Platform
Asia Pacific Cruise Missile market is segmented by launch platform into air-launched missiles, sea-launched missiles, submarine-launched missiles, ground-launched missiles, and mobile launcher systems. Recently, sea-launched missiles have a dominant market share due to increasing naval modernization and the strategic importance of maritime security across contested waters. Nations are strengthening naval fleets to protect trade routes and territorial boundaries, driving demand for ship-based strike capabilities. Sea-launched platforms offer operational flexibility and extended reach, making them critical for deterrence strategies. Investments in advanced destroyers and frigates equipped with vertical launch systems further support adoption. Additionally, the ability to deploy missiles from naval assets enhances rapid response capabilities without reliance on fixed infrastructure. As maritime competition intensifies, defense planners continue prioritizing sea-based strike readiness, reinforcing the segment’s leadership within the regional missile ecosystem.
Competitive Landscape
The Asia Pacific cruise missile market is relatively consolidated, with major defense contractors dominating development and production through long-term government contracts. Competitive dynamics are shaped by technological expertise, indigenous manufacturing capabilities, and strategic partnerships. Companies are focusing on advanced propulsion, stealth features, and precision guidance to secure procurement programs while expanding collaborative defense initiatives across allied nations.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Missile Range Capability |
| Lockheed Martin Corporation | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon Technologies | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BrahMos Aerospace | 1998 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1884 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hanwha Aerospace | 1977 | South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia Pacific Cruise Missile Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Escalating Defense Modernization Programs Across Asia Pacific
Governments throughout the region are significantly increasing defense budgets to upgrade aging military inventories and strengthen combat readiness. Cruise missiles are becoming central to modernization strategies because they provide precision strike capability with minimal collateral damage. Military planners are prioritizing systems that enhance deterrence without requiring large-scale troop deployment. Investments in next-generation platforms are enabling integration of missiles across air, land, and naval forces, improving operational flexibility. Indigenous production initiatives are also gaining momentum, reducing reliance on foreign suppliers while fostering technological independence. Advanced research programs focused on propulsion and stealth are accelerating deployment timelines. Procurement frameworks increasingly emphasize interoperability with network-centric warfare architectures. Strategic alliances are facilitating technology transfer that supports domestic manufacturing growth. Rising security concerns across maritime and border regions continue to justify sustained expenditure. Collectively, modernization efforts are creating long-term demand stability for cruise missile systems.
Growing Geopolitical Tensions Driving Demand for Precision Strike Weapons
Heightened territorial disputes and shifting power balances are prompting nations to enhance deterrence capabilities through advanced missile arsenals. Precision strike weapons enable rapid response while minimizing escalation risks, making them attractive within contemporary defense doctrines. Military strategies are evolving toward stand-off engagement models that prioritize safety of personnel. Cruise missiles offer the flexibility to target high-value assets from extended distances, reinforcing strategic leverage. Defense agencies are therefore accelerating acquisition cycles to maintain readiness. Continuous testing and demonstration programs further validate operational effectiveness. Technological improvements in navigation accuracy are enhancing mission success rates. Regional collaborations are also emerging to co-develop sophisticated missile technologies. Budget allocations increasingly favor systems capable of countering advanced threats. As geopolitical uncertainties persist, precision strike investments remain a primary catalyst for market growth.
Market Challenges
High Development Costs and Technological Complexity
Designing cruise missiles involves sophisticated engineering across propulsion, navigation, stealth, and materials science, resulting in substantial research expenditures. Testing requirements add further financial burden due to the need for controlled environments and specialized infrastructure. Governments must balance defense priorities against fiscal constraints, occasionally delaying procurement timelines. Smaller defense contractors often lack resources to sustain long development cycles, limiting competitive diversity. Integration with evolving military platforms introduces additional engineering challenges. Rapid technological change also increases the risk of obsolescence before full deployment. Supply chains for advanced components can be both expensive and difficult to secure. Maintenance and lifecycle support further elevate total ownership costs. Budget overruns may trigger program reassessments. Consequently, financial and technical barriers remain persistent constraints within the market.
Export Controls and Regulatory Restrictions Limiting International Collaboration
Missile technologies are subject to stringent international controls intended to prevent proliferation, restricting cross-border trade and knowledge transfer. Compliance with multilateral agreements often complicates partnership opportunities between defense firms. Approval processes for exports can extend over several years, affecting revenue predictability. Governments may impose additional domestic restrictions to safeguard strategic technologies. These regulatory frameworks can discourage foreign investment in joint ventures. Suppliers must navigate complex documentation requirements to maintain compliance. Limitations on technology sharing can slow innovation cycles. Procurement diversification becomes challenging when access to external expertise is constrained. Diplomatic considerations frequently influence contract approvals. Overall, regulatory barriers continue shaping competitive dynamics and collaboration potential.
Opportunities
Advancement of Hypersonic Missile Technologies
Defense organizations are intensifying research into hypersonic systems capable of traveling at speeds exceeding traditional missile thresholds, dramatically reducing response times. These technologies promise enhanced survivability against interception while offering unprecedented strike precision. Governments are allocating substantial funding toward experimental programs aimed at achieving operational readiness. Collaboration between research institutions and defense contractors is accelerating breakthroughs in propulsion and thermal protection. Hypersonic capabilities are increasingly viewed as critical for maintaining strategic parity. Successful deployment could redefine deterrence frameworks across the region. Suppliers positioned within this innovation cycle stand to benefit from long-term contracts. Technological leadership in this domain also strengthens geopolitical influence. As testing milestones are achieved, procurement pathways are expected to expand. Hypersonic development therefore represents a transformative opportunity.
Expansion of Indigenous Defense Manufacturing Ecosystems
Countries across Asia Pacific are prioritizing domestic production to enhance strategic autonomy and reduce dependence on imports. Policy incentives and defense offsets are encouraging local industry participation in missile programs. This shift is fostering technology transfer and workforce development, strengthening industrial resilience. Domestic manufacturing shortens supply chains and improves readiness during crises. Governments are also supporting startups specializing in advanced materials and electronics. Public-private partnerships are accelerating innovation across propulsion and guidance technologies. Localization enhances export potential for allied markets. National pride associated with self-reliant defense capabilities further reinforces political commitment. As ecosystems mature, production scalability is expected to improve. Indigenous manufacturing expansion thus presents a significant growth avenue for the regional cruise missile market.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific cruise missile market is expected to expand steadily over the next five years, supported by sustained defense spending and rapid technological innovation. Advancements in hypersonic propulsion and stealth capabilities will likely redefine operational effectiveness. Regulatory frameworks promoting domestic manufacturing are anticipated to accelerate production capacity. Rising geopolitical uncertainties and maritime security priorities are expected to reinforce procurement momentum, positioning cruise missiles as a cornerstone of regional defense strategies.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- BrahMos Aerospace
- MBDA Missile Systems
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Hanwha Aerospace
- Tactical Missiles Corporation
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Roketsan
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- Aerospace Long-March International Trade Co.
- DRDO
- LIG Nex1
Key Target Audience
- Nationaldefenseministries
- Armed forces procurement agencies
- Naval command authorities
- Air force modernization divisions
- Defense technology integrators
- Missile system manufacturers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Critical variables including defense budgets, procurement pipelines, technological adoption, and geopolitical developments were identified through structured secondary research. Military expenditure databases and defense publications supported baseline demand evaluation.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Top-down and bottom-up models were applied to estimate market size and segment distribution. Procurement data was cross-verified with contractor activity to ensure analytical consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights from defense analysts, aerospace engineers, and military strategists were used to validate assumptions regarding missile deployment trends and innovation priorities, strengthening analytical accuracy.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated datasets were consolidated into a cohesive analytical framework emphasizing reliability and strategic relevance. The final report integrates quantitative insights with qualitative interpretation to support informed defense planning.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Subsonic Cruise Missiles
Supersonic Cruise Missiles
Hypersonic Cruise Missiles
Land Attack Cruise Missiles
Anti-Ship Cruise Missiles - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Air-Launched Platforms
Sea-Launched Platforms
Submarine-Launched Platforms
Ground-Launched Platforms
Mobile Launcher Platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Integrated Launch Systems
Modular Launch Platforms
Canister-Based Deployment
Vertical Launch System Fitments
Retrofit Missile Integration - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
National Defense Forces
Naval Forces
Air Forces
Strategic Missile Commands
Joint Defense Task Forces - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct Government Procurement
Defense Contracts
Foreign Military Sales
Joint Development Programs
Technology Transfer Agreements - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Advanced Guidance Systems
Stealth Shaping Technologies
Solid Fuel Propulsion
Ramjet and Scramjet Engines
AI-Enabled Targeting Systems
- Growth Drivers
Increasing defense modernization programs across Asia Pacific
Rising geopolitical tensions driving strategic deterrence investments
Advancements in hypersonic propulsion technologies
Expansion of indigenous missile development initiatives
Growing focus on precision strike capabilities - Market Challenges
High development and testing costs
Complex regulatory and export control frameworks
Technological barriers in hypersonic systems
Supply chain constraints for advanced components
Integration challenges across multi-domain platforms - Market Opportunities
Collaborative defense programs between regional allies
Expansion of next-generation precision strike systems
Investment in AI-driven guidance technologies - Trends
Shift toward hypersonic missile development
Increasing deployment of stealth-enabled cruise missiles
Integration of network-centric warfare capabilities
Miniaturization of guidance electronics
Emphasis on long-range strike capabilities - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Missile technology control compliance requirements
National defense procurement policies
Strategic weapons development frameworks - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- Naval forces prioritizing long-range maritime strike capabilities
- Air forces investing in precision air-launched missiles
- Governments strengthening strategic deterrence frameworks
- Joint commands emphasizing multi-domain operational readiness
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


