Market Overview
The Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market reached USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, driven by increasing satellite manufacturing programs across communication, navigation, and earth observation missions. Regional governments have accelerated indigenous spacecraft development initiatives while commercial operators deploy broadband constellations requiring standardized satellite buses. Rising defense space investments and expanding private satellite startups further stimulate procurement of modular, scalable bus platforms. Strong demand for small and medium satellite buses supporting low earth orbit missions has sustained production growth across Asia Pacific supply chains.
China, Japan, and India dominate the Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market due to extensive domestic space programs, vertically integrated manufacturing ecosystems, and sustained public funding in satellite infrastructure. Major aerospace industrial clusters in Beijing, Shanghai, Tokyo, and Bengaluru concentrate satellite bus design, avionics development, and structural manufacturing capabilities. Government agencies and national defense organizations in these countries continue to prioritize sovereign satellite platforms for communication and surveillance resilience, while private space companies in emerging economies such as South Korea and Australia expand regional manufacturing capacity.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type:
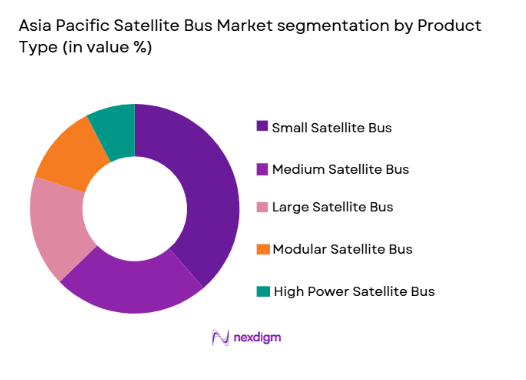
Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market is segmented by product type into small satellite bus, medium satellite bus, large satellite bus, modular satellite bus, and high power satellite bus. Recently, small satellite bus has a dominant market share due to factors such as rapid deployment of low earth orbit constellations, lower manufacturing cost, standardized architecture, and strong demand from commercial communication and earth observation missions across Asia Pacific space programs.
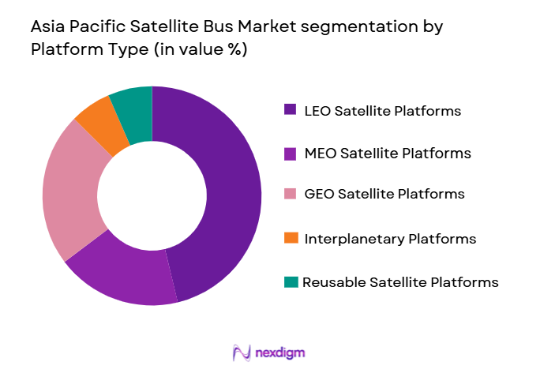
By Platform Type:
Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market is segmented by platform type into LEO satellite platforms, MEO satellite platforms, GEO satellite platforms, interplanetary platforms, and reusable satellite platforms. Recently, LEO satellite platforms has a dominant market share due to factors such as proliferation of broadband constellations, earth observation networks, and technology demonstration missions requiring lightweight, standardized satellite bus configurations suitable for rapid launch cycles and constellation deployment strategies.
Competitive Landscape
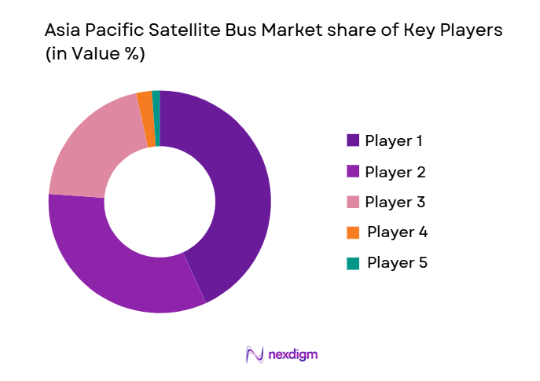
The Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market exhibits moderate consolidation with dominant participation from national aerospace manufacturers and state backed space organizations alongside emerging private satellite startups. Established companies leverage vertically integrated supply chains and heritage spacecraft platforms, while new entrants focus on modular small satellite buses and commercial constellation applications. Strategic collaborations between regional space agencies and private firms strengthen manufacturing capacity and technology localization, intensifying competition across standardized bus architectures and subsystem integration capabilities.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Bus Mass Class Focus |
| Mitsubishi Electric | 1921 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NEC Corporation | 1899 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| China Academy of Space Technology | 1968 | Beijing, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ISRO Satellite Centre | 1972 | Bengaluru, India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Satrec Initiative | 1999 | Daejeon, South Korea | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Asia Pacific Satellite Bus Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Low Earth Orbit Satellite Constellations for Broadband and Earth Observation:
The rapid deployment of low earth orbit satellite constellations across Asia Pacific has significantly accelerated demand for standardized satellite bus platforms supporting communication and earth observation missions. Governments and commercial operators in the region increasingly rely on constellation architectures to provide broadband connectivity to rural and maritime areas where terrestrial infrastructure remains limited. Satellite bus manufacturers have responded by developing modular small satellite platforms enabling mass production and reduced integration time. National space agencies and private firms are launching clusters of satellites requiring consistent bus architecture and interoperable subsystems. This shift toward constellation based deployment has increased procurement frequency compared with traditional single satellite missions. Regional launch vehicle advancements and declining launch costs further reinforce constellation expansion strategies. Demand for rapid manufacturing cycles and scalable bus production lines has stimulated investment in automated satellite assembly facilities. Asia Pacific nations view constellation capability as strategic digital infrastructure, driving long term satellite bus procurement programs.
Indigenous Space Industrialization and Sovereign Satellite Capability Programs:
Asia Pacific governments are intensifying domestic satellite manufacturing capabilities to achieve strategic autonomy in space infrastructure and defense communication networks. National space policies emphasize localized production of satellite buses, avionics, propulsion, and structural components to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers. China, India, and Japan have expanded public funding for indigenous satellite development programs supporting navigation, earth observation, and communication missions. Sovereign satellite capability ensures secure data transmission and surveillance resilience for defense and national security applications. Regional space agencies increasingly collaborate with domestic aerospace firms to transfer satellite bus technologies and build national supply chains. Industrialization initiatives also support commercial space startups that develop small satellite buses for regional markets. Government procurement frameworks prioritize domestic manufacturers, sustaining consistent demand for locally produced satellite buses. This policy driven industrial expansion has created stable long term growth in Asia Pacific satellite bus manufacturing ecosystems.
Market Challenges
Dependence on Space Grade Components and Export Control Restrictions:
Satellite bus manufacturing in Asia Pacific remains constrained by reliance on specialized space qualified electronic components, radiation hardened semiconductors, and propulsion subsystems often sourced internationally. Export control regulations governing advanced space technologies limit access to critical avionics, sensors, and onboard processing units required for high reliability satellite buses. These restrictions increase procurement complexity and lengthen development timelines for regional manufacturers seeking technology transfer approvals. Domestic substitution of space grade components requires extensive qualification and testing processes that demand high investment. Smaller satellite bus startups face particular barriers in establishing certified supply chains for mission critical components. Regulatory compliance and licensing procedures add uncertainty to international collaboration projects involving satellite bus subsystems. The combination of supply chain vulnerability and technology restrictions constrains scalability of indigenous satellite bus production. Asia Pacific manufacturers continue investing in domestic component ecosystems to mitigate these structural dependencies.
High Capital Intensity and Long Development Cycles for Satellite Bus Platforms:
Satellite bus design and manufacturing require substantial upfront capital for engineering development, structural testing, thermal vacuum validation, and mission qualification processes. Asia Pacific manufacturers must invest in specialized cleanroom facilities, vibration testing systems, and space simulation infrastructure before achieving production readiness. Development cycles for new bus platforms often span several years due to stringent reliability and mission assurance requirements. Limited production volumes compared with terrestrial aerospace systems restrict economies of scale in satellite bus manufacturing. Commercial satellite startups encounter financing challenges while sustaining long development phases prior to revenue generation. Government funded programs partially offset these costs but also impose compliance and performance obligations that extend development timelines. Rapid technology evolution in propulsion, power, and avionics subsystems further necessitates redesign cycles. These capital and time barriers slow entry of new manufacturers and constrain expansion speed of the Asia Pacific satellite bus market.
Opportunities
Commercialization of Small Satellite Manufacturing and Constellation Services:
The Asia Pacific space sector is transitioning toward commercial satellite manufacturing models driven by demand for communication, earth observation, and Internet of Things services. Private companies are emerging across India, Japan, South Korea, and Australia to design modular small satellite buses tailored for constellation deployment. Commercial satellite operators prefer standardized bus platforms that reduce mission integration cost and enable scalable production. Venture capital investment and public private partnerships are supporting manufacturing facilities dedicated to small satellite buses. Regional governments encourage commercialization through space startup incentives and procurement programs favoring domestic suppliers. The growth of commercial launch services in Asia Pacific further strengthens constellation business models reliant on frequent satellite deployment. Demand for turnkey satellite bus solutions bundled with payload integration and mission services is expanding. This commercialization trend offers sustained growth opportunities for Asia Pacific satellite bus manufacturers.
Regional Collaboration in Lunar, Deep Space, and Scientific Missions:
Asia Pacific space agencies are increasing collaboration on lunar exploration, planetary missions, and scientific satellite programs that require advanced satellite bus architectures. Joint missions between regional countries enable shared development of propulsion systems, thermal control technologies, and deep space communication subsystems. These cooperative initiatives stimulate innovation in high reliability satellite bus platforms beyond conventional earth orbit applications. Collaborative missions distribute development cost across participating nations while expanding technological capability of regional manufacturers. Satellite bus suppliers gain experience in complex mission environments such as lunar orbit and interplanetary trajectories. Scientific and exploration missions also demand specialized bus designs supporting long mission lifetimes and radiation resilience. Regional cooperation strengthens Asia Pacific presence in global deep space programs and elevates technological sophistication of local satellite bus platforms. This collaborative exploration trend opens new high value market segments for Asia Pacific satellite bus providers.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market is expected to expand steadily as regional governments and commercial operators intensify satellite constellation deployment and indigenous spacecraft manufacturing. Technological progress in modular bus architectures, electric propulsion, and miniaturized avionics will reduce production costs and enable scalable satellite manufacturing. Regulatory support for domestic space industries and defense space programs will sustain procurement demand. Increasing private investment in space startups and satellite services will further strengthen regional satellite bus ecosystems over the coming years.
Major Players
- Mitsubishi Electric
- NEC Corporation
- China Academy of Space Technology
- Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology
- ISRO Satellite Centre
- Satrec Initiative
- Dhruva Space
- Azista BST Aerospace
- Astroscale
- Japan Space Systems
- Korea Aerospace Research Institute
- Gilmour Space Technologies
- Thai Aerospace Industries
- Vietnam National Space Center
- SpaceTech Asia
Key Target Audience
- Satellite manufacturers
- Space agencies
- Defense space organizations
- Commercial satellite operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Aerospace component suppliers
- Satellite communication service providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key market variables including satellite bus mass class, platform type, orbit category, propulsion technology, and end user demand were identified through secondary aerospace industry databases and regional space program documentation analysis.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market size and segmentation were constructed using satellite launch statistics, spacecraft manufacturing data, and procurement records across Asia Pacific countries, aligning supply chain activity with satellite bus production volumes and pricing benchmarks.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through consultation with satellite system engineers, space policy specialists, and aerospace manufacturing experts across Asia Pacific to confirm technology trends, procurement dynamics, and industrial capability assumptions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All quantitative and qualitative insights were synthesized into a structured market model integrating segmentation, competitive analysis, and forecast drivers to produce a comprehensive Asia Pacific Satellite Bus market assessment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising regional demand for communication and broadband satellite constellations
Expansion of indigenous satellite manufacturing capabilities across Asia Pacific
Increasing defense space programs and secure satellite deployment - Market Challenges
High capital intensity and long development cycles for satellite bus platforms
Supply chain dependence on specialized space grade components
Technology transfer restrictions and export control limitations - Market Opportunities
Growth of small satellite constellations for IoT and connectivity services
Regional collaboration on lunar and deep space missions
Commercialization of satellite manufacturing and launch ecosystems - Trends
Shift toward modular and scalable satellite bus architectures
Adoption of electric propulsion and high efficiency power subsystems
Integration of software defined satellite platforms
Miniaturization of avionics and payload interfaces
Rise of private satellite manufacturing startups in Asia Pacific - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
National space industrialization policies across major Asia Pacific economies
Defense space command expansion and sovereign satellite requirements
Export control and technology security frameworks affecting collaboration - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Small Satellite Bus
Medium Satellite Bus
Large Satellite Bus
Modular Satellite Bus
High Power Satellite Bus - By Platform Type (In Value%)
LEO Satellite Platforms
MEO Satellite Platforms
GEO Satellite Platforms
Interplanetary Platforms
Reusable Satellite Platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Communication Payload Integration
Earth Observation Payload Integration
Navigation Payload Integration
Scientific Payload Integration
Technology Demonstration Integration - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Commercial Satellite Operators
Government Space Agencies
Defense and Intelligence Organizations
Academic and Research Institutions
NewSpace Startups - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct OEM Procurement
Government Contracts
Public Private Partnerships
International Collaboration Programs
Commercial Leasing Models - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Aluminum Honeycomb Structures
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Structures
Additive Manufactured Components
Radiation Hardened Electronics
High Efficiency Power Systems
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- CrossComparison Parameters (Bus Mass Class, Payload Capacity, Power Generation Capability, Mission Lifetime, Orbit Compatibility, Modularity Level, Propulsion Type, Thermal Control Technology, Avionics Architecture, Manufacturing Integration Level)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Mitsubishi Electric
NEC Corporation
China Academy of Space Technology
Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology
ISRO Satellite Centre
Korea Aerospace Research Institute
Astroscale
Gilmour Space Technologies
Azista BST Aerospace
Dhruva Space
Satrec Initiative
Thai Aerospace Industries
Vietnam National Space Center
SpaceTech Asia
Japan Space Systems
- Government agencies driving domestic satellite bus production programs
- Commercial operators demanding cost efficient modular bus platforms
- Defense organizations prioritizing secure and resilient satellite architectures
- Research institutions utilizing small satellite buses for scientific missions
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035