Market Overview
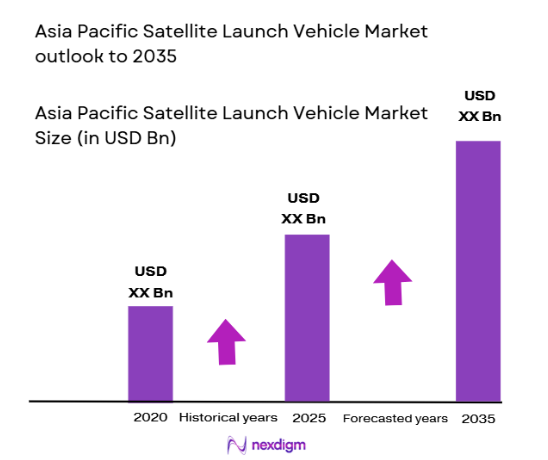
The Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market reached approximately USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, driven by sustained government space budgets, commercial satellite deployment contracts, and increasing defense-related launch missions across regional economies. National launch programs in China, India, and Japan supported vehicle development funding exceeding USD 6 billion collectively, while commercial launch revenues rose due to growing small-satellite constellations. Expansion of reusable vehicle technology programs and domestic manufacturing capabilities further strengthened regional launch supply chains and reduced dependency on foreign launch services.
China, India, and Japan dominate the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market due to mature launch infrastructure, sustained public funding, and integrated aerospace manufacturing ecosystems. China operates multiple operational launch sites and completed more than sixty orbital launch attempts, while India’s national launch program demonstrated consistent cost-efficient deployment capacity through polar and geosynchronous missions. Japan maintains advanced cryogenic propulsion and heavy-lift capabilities through established aerospace corporations. These countries also host dense satellite manufacturing clusters and government-backed commercial launch providers, enabling regional leadership in launch vehicle production and deployment.
Market Segmentation
By System Type:
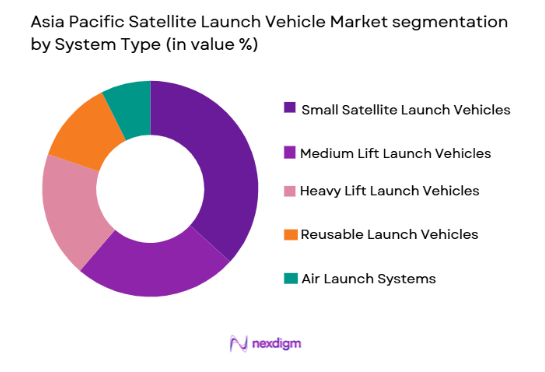
Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market is segmented by system type into small satellite launch vehicles, medium lift launch vehicles, heavy lift launch vehicles, reusable launch vehicles, and air launch systems. Recently, small satellite launch vehicles has a dominant market share due to factors such as demand patterns, brand presence, infrastructure availability, or consumer preference. Rapid expansion of low Earth orbit satellite constellations across communications, earth observation, and defense applications has significantly increased launch frequency requirements. Regional governments and private companies prioritized dedicated small-satellite launch systems to reduce wait times associated with heavy-lift missions. Lower development cost, faster production cycles, and responsive launch capability strengthened adoption. Commercial satellite operators increasingly selected dedicated small-satellite vehicles for precise orbital deployment and schedule certainty. Growth of private launch startups in China, India, and Japan further expanded availability of small-satellite launch services across the region.
By EndUser:
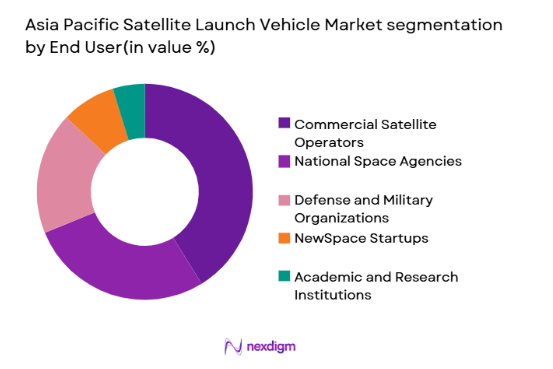
Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market is segmented by enduser into commercial satellite operators, national space agencies, defense and military organizations, NewSpace startups, and academic and research institutions. Recently, commercial satellite operators has a dominant market share due to factors such as demand patterns, brand presence, infrastructure availability, or consumer preference. Regional communications, earth observation, and navigation service providers expanded satellite fleets to meet broadband connectivity and geospatial data demand. Private satellite constellation operators contracted frequent launches for low Earth orbit deployments, creating sustained commercial launch demand. Government policies encouraging private space participation enabled commercial launch procurement channels. Increasing investment in satellite-based services such as remote sensing and maritime monitoring accelerated commercial launch requirements. Growing venture funding in space startups across Asia Pacific further increased private satellite launches and associated launch vehicle utilization.
Competitive Landscape
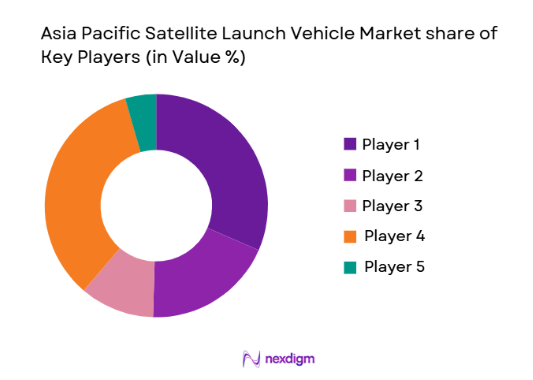
The Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market shows moderate consolidation led by state-backed aerospace corporations and emerging private launch providers. National agencies and large aerospace manufacturers maintain technological leadership in heavy and medium lift systems, while venture-funded startups compete in small-satellite launch services. Strategic government contracts and domestic launch mandates reinforce local supplier dominance. Vertical integration across propulsion, structures, and launch operations enables established players to maintain cost and reliability advantages while new entrants focus on agile and reusable launch technologies.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Launch Vehicle Class |
| China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | 1999 | Beijing, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation | 2001 | Beijing, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Indian Space Research Organisation | 1969 | Bengaluru, India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | 1884 | Tokyo, Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Galactic Energy | 2018 | Beijing, China | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
 Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Analysis
Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Low Earth Orbit Satellite Constellations:
Expansion of Low Earth Orbit satellite constellations across communications, navigation, and earth observation applications is significantly increasing launch frequency requirements in the Asia Pacific region. Governments and private operators are deploying multi-satellite constellations to improve broadband coverage, disaster monitoring, maritime tracking, and defense surveillance capabilities. This constellation architecture requires frequent launches of small satellites, creating sustained demand for responsive and cost-efficient launch vehicles. Regional countries are prioritizing indigenous launch capability to secure strategic autonomy in space access and reduce dependence on foreign providers. Commercial satellite companies are entering long-term launch service agreements with domestic providers to ensure deployment continuity. Increasing demand for real-time geospatial data and connectivity services is accelerating constellation expansion across Asia Pacific economies. As satellite numbers rise, launch cadence requirements expand proportionally, strengthening vehicle production and service demand. The shift from single large satellites to distributed constellations structurally increases launch vehicle utilization rates across the region. This transformation is reinforcing long-term growth in small and medium lift launch vehicle development programs.
Government Investment in Sovereign Launch Capability:
Government investment in sovereign launch capability is a primary structural growth driver in the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market due to strategic defense and technological independence priorities. Regional governments are allocating substantial aerospace budgets to develop indigenous launch vehicles, propulsion systems, and launch infrastructure. National space programs in China, India, Japan, and South Korea emphasize domestic launch autonomy to ensure secure satellite deployment for communications, navigation, and reconnaissance missions. Sovereign launch capability reduces reliance on foreign launch services, which can be constrained by export controls or geopolitical factors. Public funding supports research institutions, state aerospace corporations, and private launch startups through contracts and subsidies. Defense space programs are also driving demand for rapid launch readiness and responsive deployment systems. Infrastructure expansion including new launch sites and integration facilities further strengthens domestic launch ecosystems. Policy frameworks encouraging private sector participation amplify government investments. These sustained national programs ensure continuous development and procurement of launch vehicles across the region.
Market Challenges
High Capital Intensity and Long Development Cycles:
High capital intensity and long development cycles present a significant challenge in the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market because launch vehicle programs require substantial investment before commercialization. Development of propulsion systems, structural components, avionics, and ground infrastructure demands multi-year funding commitments and specialized engineering expertise. Many emerging private launch companies face financial strain due to extended testing and certification timelines before revenue generation begins. Launch vehicle failures during testing can cause costly delays and redesign requirements, further increasing program expenditure. Access to advanced materials and propulsion technologies is also capital intensive and often restricted by export regulations. Government funding can mitigate some costs but does not eliminate long commercialization horizons. Investors may perceive launch vehicle development as high risk compared to downstream space services. The requirement for repeated qualification flights increases costs prior to operational deployment. These factors collectively constrain entry and scalability for new launch vehicle developers across Asia Pacific.
Regulatory and Launch Approval Complexity:
Regulatory and launch approval complexity is a major operational challenge in the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market due to strict safety, environmental, and airspace management requirements. Launch providers must obtain multiple national clearances related to range safety, orbital debris mitigation, and environmental impact compliance. Coordination with aviation and maritime authorities is required to secure launch windows and exclusion zones, increasing scheduling complexity. Cross-border launch services face export control and technology transfer restrictions, especially for propulsion and guidance systems. Licensing processes differ significantly across Asia Pacific countries, complicating regional launch operations for commercial providers. Delays in regulatory approval can disrupt satellite deployment timelines and contractual commitments. Insurance and liability requirements also add administrative and financial burdens. As launch frequency increases, regulatory frameworks must scale accordingly, but institutional capacity constraints often create bottlenecks. These regulatory challenges can limit operational flexibility and raise launch service costs across the region.
Opportunities
Development of Reusable and Responsive Launch Vehicles:
Development of reusable and responsive launch vehicles represents a major opportunity in the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market as operators seek cost reduction and rapid deployment capability. Reusable first-stage technologies can significantly lower per-launch cost and improve vehicle utilization rates, enabling competitive commercial launch pricing. Responsive launch systems capable of rapid integration and short-notice deployment are increasingly valuable for defense and disaster response satellite missions. Asia Pacific governments are funding reusable launch demonstrators and recovery infrastructure to advance domestic capability. Private startups are innovating in vertical landing and modular propulsion architectures to support reuse. Reduced turnaround time between launches can expand launch cadence and revenue potential. Commercial satellite constellation operators prefer reusable launch providers for frequent deployment schedules. Adoption of reusable technologies also aligns with sustainability and debris reduction goals. These developments can position Asia Pacific providers competitively in the global launch services market.
Expansion of Regional Commercial Launch Service Markets:
Expansion of regional commercial launch service markets presents strong opportunity in the Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle sector due to growing satellite demand from emerging economies. Countries in Southeast Asia and Oceania are increasing satellite procurement for communications, earth observation, and navigation applications. Many of these nations lack domestic launch capability and rely on regional providers for satellite deployment. Asia Pacific launch companies can capture this demand through commercial launch service offerings and rideshare missions. Regional cooperation programs and public-private partnerships can facilitate shared launch infrastructure and cost-efficient access to space. Small satellite operators prefer geographically proximate launch providers to reduce logistics complexity and scheduling delays. Increasing venture funding in regional space startups further expands commercial launch demand. Establishing dedicated commercial launch corridors and spaceports can strengthen regional service networks. These dynamics create sustained growth potential for Asia Pacific launch vehicle providers beyond domestic missions.
Future Outlook
The Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market is expected to expand steadily over the next five years driven by increasing satellite constellation deployment, government-backed launch infrastructure expansion, and commercialization of reusable launch technologies. Regional space policies supporting private participation and sovereign launch capability will accelerate domestic vehicle development programs. Rising demand for broadband connectivity, earth observation, and defense space assets will sustain launch frequency growth. Technological advances in propulsion efficiency, additive manufacturing, and responsive launch systems will further enhance regional competitiveness in global launch services.
Major Players
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
- China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
- Korea Aerospace Research Institute
- Galactic Energy
- iSpace China
- LandSpace Technology
- OneSpace Technology
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Interstellar Technologies
- Space Pioneer
- CAS Space
Key Target Audience
- Satellite manufacturing companies
- Commercial satellite operators
- Defense space agencies
- National space agencies
- Aerospace component suppliers
- Space launch service providers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables including launch frequency, satellite deployment demand, propulsion technology adoption, government funding levels, and commercial launch contracts were identified through secondary aerospace data sources and industry publications across Asia Pacific.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market sizing and segmentation were constructed using launch activity databases, national space budgets, company financial disclosures, and satellite deployment statistics to map system type and end-user demand structures across regional economies.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary findings were validated through consultations with aerospace engineers, launch service providers, satellite operators, and policy experts to confirm technological trends, procurement dynamics, and regulatory impacts affecting launch vehicle demand.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated data and insights were synthesized into structured market models, segmentation frameworks, and competitive analysis to produce the final Asia Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle market report with consistent assumptions and cross-checked metrics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising demand for small satellite constellation deployment across Asia Pacific
Government investments in sovereign launch capability development
Expansion of commercial space startups and private launch providers
Increasing defense space programs and surveillance satellite launches
Advancements in reusable and cost efficient launch technologies - Market Challenges
High capital intensity and long development cycles for launch vehicles
Stringent launch safety and regulatory approval requirements
Limited launch infrastructure in emerging Asia Pacific economies
Supply chain constraints for advanced propulsion components
Competition from established global launch service providers - Market Opportunities
Regional small satellite launch services tailored for LEO constellations
Development of reusable and responsive launch vehicle systems
International collaboration for shared launch infrastructure - Trends
Shift toward reusable and partially reusable launch vehicles
Growth of private launch startups in India, China, and Japan
Integration of additive manufacturing in rocket engine production
Emergence of mobile and sea based launch platforms
Adoption of methane and green propellant technologies - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
National space policy frameworks supporting domestic launch capability
Export control and technology transfer regulations in launch systems
Defense space command programs driving sovereign launch development - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Small Satellite Launch Vehicles
Medium Lift Launch Vehicles
Heavy Lift Launch Vehicles
Reusable Launch Vehicles
Air Launch Systems - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Ground Launched Orbital Vehicles
Sea Based Launch Platforms
Air Launched Rockets
Mobile Transporter Erector Launchers
Suborbital Test Launchers - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Dedicated Launch Services
Rideshare Launch Configurations
Responsive Launch Systems
Modular Launch Architectures
Custom Mission Integrated Vehicles - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Commercial Satellite Operators
National Space Agencies
Defense and Military Organizations
NewSpace Startups
Academic and Research Institutions - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Government Contracts
Commercial Launch Agreements
Public Private Partnerships
International Cooperative Programs
Defense Procurement Programs - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Composite Cryogenic Tanks
Additively Manufactured Engines
Solid Propellant Boosters
Methane Fueled Propulsion Systems
Autonomous Flight Control Systems
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- CrossComparison Parameters (Payload Capacity, Orbit Capability, Reusability Level, Launch Cost Efficiency, Propulsion Type, Launch Frequency, Integration Flexibility, Manufacturing Approach, Infrastructure Access, Mission Customization)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation
Indian Space Research Organisation
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
Korea Aerospace Research Institute
Galactic Energy
iSpace China
LandSpace Technology
OneSpace Technology
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Interstellar Technologies
Space Pioneer
CAS Space
- Commercial satellite operators prioritizing dedicated and rideshare launch options
- Defense agencies increasing investment in responsive launch readiness
- Space agencies supporting indigenous launch vehicle development programs
- Private startups driving innovation in small and reusable launch vehicles
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


