Market Overview
The Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship Market is a rapidly growing sector with an increasing focus on enhancing naval capabilities. In 2026, the market size is expected to reach USD ~ billion, with substantial contributions from both domestic and international defense procurement programs. This growth is driven by rising geopolitical tensions in the Indo-Pacific region, increasing defense budgets, and the adoption of advanced naval technologies, such as Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch Systems (EMALS) and unmanned aerial systems. Government defense programs like the Australian Defence White Paper and its emphasis on expanding naval capabilities further underpin this growth.
Australia is the primary player in the market, driven by its defense strategies and regional security concerns. The country’s increasing focus on enhancing its naval power projection and modernizing its fleet drives the demand for aircraft carriers. Additionally, key global defense players, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, influence the market through defense cooperation agreements and technology transfer. Australia’s prominent shipyards, including ASC Shipbuilding and Austal, contribute significantly to the development and maintenance of these carriers, making it a dominant market participant in the region.
Market Segmentation
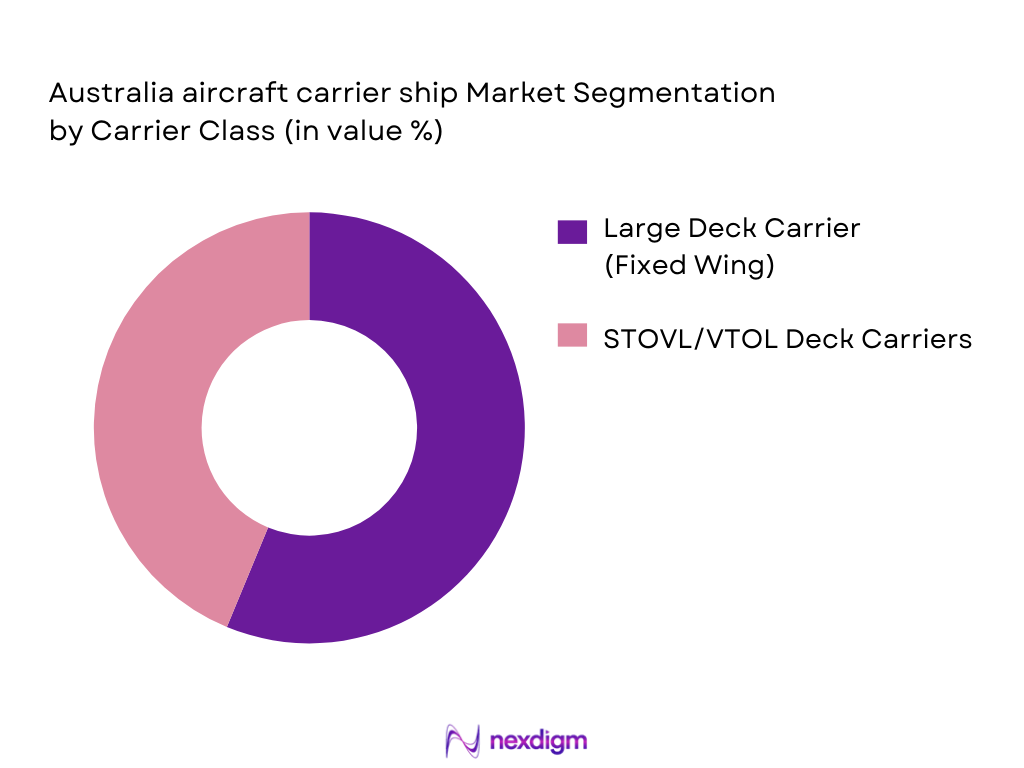
By Carrier Class
The Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship market is segmented by carrier class, which includes large deck carriers, STOVL/VTOL deck carriers, and amphibious carrier variants. Among these, large deck carriers are the most dominant due to their ability to carry and deploy a greater number of aircraft, including fixed-wing aircraft like the F-35B and rotary-wing aviation. These carriers play a crucial role in power projection, offering enhanced strategic flexibility in the Indo-Pacific region. The STOVL/VTOL deck carriers are also gaining traction due to their ability to operate in more diverse environments, making them highly suited for Australia’s defense needs. Lastly, amphibious carrier variants are also increasingly important as they provide support for amphibious assault operations and humanitarian missions.
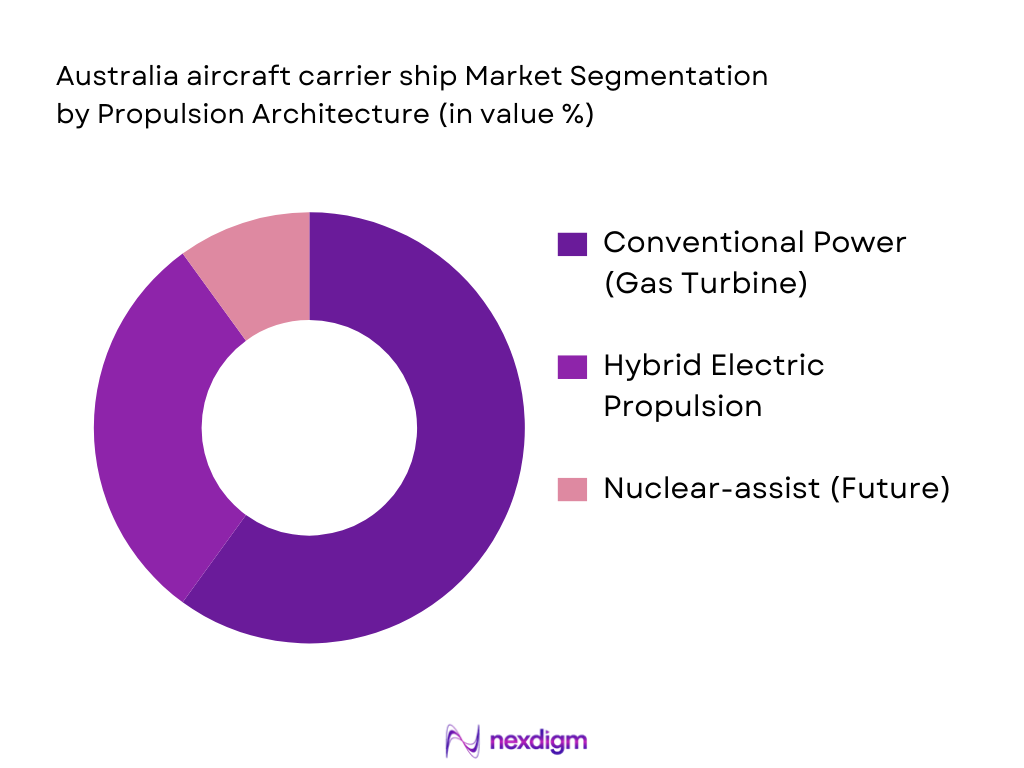
By Propulsion Architecture
The propulsion architecture segment of the Australian aircraft carrier ship market includes conventional power systems (gas turbine/diesel), hybrid electric propulsion, and nuclear-assist systems. Conventional power systems are currently the dominant segment due to their well-established technology, fuel efficiency, and reliability. These systems are widely used in current Australian naval carriers like HMAS Canberra and HMAS Adelaide. Hybrid electric propulsion systems are gaining attention due to their energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint, aligning with sustainability goals in naval operations. The nuclear-assist systems remain a future consideration, with strategic discussions about their adoption, especially for long-term operational sustainability and increased strategic autonomy.
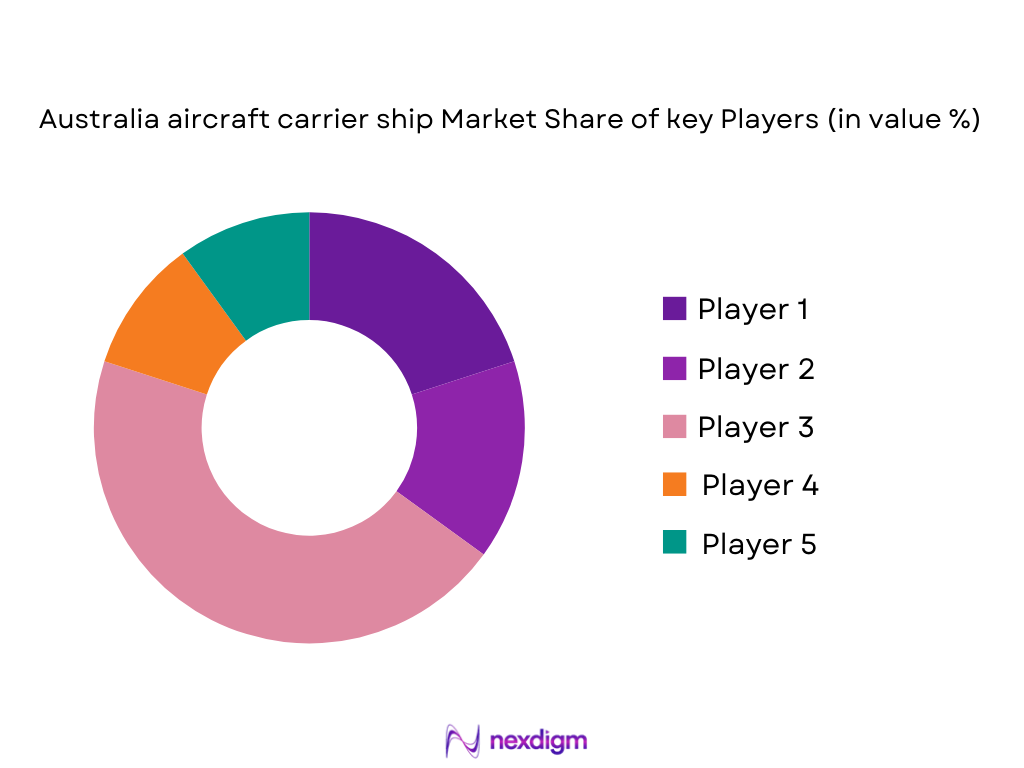
Competitive Landscape
The Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship Market is dominated by a few major global players, including established defense contractors like BAE Systems, Huntington Ingalls Industries, and Navantia, alongside domestic firms like Austal and ASC Shipbuilding. These companies have a significant role in both the design and construction of aircraft carriers for the Australian Navy, contributing heavily to the national defense sector through their advanced technological capabilities and defense contracting experience. The market is characterized by a limited number of participants, given the high barriers to entry, such as capital-intensive shipbuilding processes and the complexity of naval aircraft carrier systems.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Production Facilities | Fleet Integration Expertise | Defense Contracts (Current) | Naval Technology Development | Strategic Partnerships |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Huntington Ingalls Industries | 1886 | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Navantia | 2005 | Spain | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Austal Limited | 1988 | Australia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ASC Shipbuilding | 1985 | Australia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanization
Urbanization is a significant driver for the Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship market. The country’s rapid urban growth, especially in coastal cities like Sydney and Melbourne, plays a key role in the increasing demand for advanced naval capabilities, including aircraft carriers. By 2024, Australia’s urban population is projected to exceed ~ million people, with over ~ % of the population living in urban areas, according to the United Nations (UN) Department of Economic and Social Affairs. This urbanization trend increases the demand for efficient, technologically advanced defense systems, which directly influences the modernization of Australia’s naval fleet to secure its maritime borders and assert regional dominance.
Industrialization
Industrialization continues to be a major factor influencing the demand for advanced military infrastructure like aircraft carriers. Australia’s industrial growth has seen a steady increase in the defense sector, contributing to the creation of a robust defense ecosystem. In 2024, Australia’s defense industry is projected to generate more than USD ~ billion, contributing to the rapid advancement of defense technologies. This growth in industrial capabilities, especially in shipbuilding, has led to the strengthening of Australia’s domestic defense manufacturing base. As the country’s industrial output rises, including increased shipyard productivity, the demand for naval platforms like aircraft carriers will also increase to match strategic objectives.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
One of the key challenges faced by the Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship market is the high initial cost associated with procuring, designing, and building an aircraft carrier. As of 2024, the cost to build a single large aircraft carrier in Australia is expected to surpass AUD ~ billion. The high initial costs for these vessels create significant budgetary pressures on Australia’s defense spending. According to the Australian Government’s Department of Defence, the nation’s defense budget in 2024 is forecasted to be around AUD ~ billion, with a large portion of these funds allocated to large-scale projects like aircraft carriers. This financial burden often necessitates careful prioritization within defense procurement programs.
Technical Challenges
The technical challenges involved in the construction and integration of aircraft carriers are considerable. With Australia’s focus on indigenous shipbuilding, the local industry faces complex challenges in acquiring the necessary technologies to build and maintain these advanced naval assets. For instance, the integration of advanced propulsion systems, such as nuclear propulsion or hybrid systems, presents a steep learning curve for local manufacturers. In 2024, Australia has yet to fully establish the capability to manufacture all the necessary components for its aircraft carriers domestically, forcing reliance on international suppliers for key systems and technologies. These technical hurdles continue to slow the development of Australia’s naval capabilities.
Opportunities
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements present a major opportunity for the Australian Aircraft Carrier Ship market, especially with developments in propulsion technology, automation, and defense systems integration. As of 2024, Australia is investing heavily in emerging technologies, such as Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch Systems (EMALS) and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for aircraft carriers. These technologies promise to increase the operational efficiency of aircraft carriers, allowing them to operate with fewer crew members and reduced maintenance needs. In 2024, the Australian Government has allocated AUD ~ billion to support the integration of these cutting-edge technologies into its naval fleet, reinforcing the country’s commitment to enhancing its defense capabilities.
International Collaborations
International collaborations present another key opportunity for Australia in enhancing its aircraft carrier capabilities. In 2024, Australia’s defense ties with the United States and the United Kingdom, particularly through the AUKUS agreement, are set to significantly influence the development of Australia’s aircraft carrier fleet. The AUKUS pact, signed, aims to foster advanced defense technology sharing, including the development of submarines and aircraft carriers. By 2024, Australia expects to enhance its collaboration with these nations, gaining access to next-generation naval technologies and expertise. This collaboration enables Australia to overcome domestic technological limitations while ensuring interoperability with allied forces in joint maritime operations.
Future Outlook
Over the next 5 years, the Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship Market is expected to see substantial growth driven by ongoing advancements in naval technology, rising defense budgets, and the increased focus on power projection capabilities in the Indo-Pacific region. The modernization of the Royal Australian Navy’s fleet, including the addition of more advanced aircraft carriers, will play a crucial role in meeting the growing demands for military dominance and international cooperation. As geopolitical tensions rise, particularly in the Indo-Pacific, Australia’s naval presence is set to expand, strengthening the demand for more aircraft carriers and supporting technologies.
Major Players in the Market
- BAE Systems
- Huntington Ingalls Industries
- Navantia
- Austal Limited
- ASC Shipbuilding
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- Raytheon Technologies
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Fincantieri
- Thales Group
- General Dynamics NASSCO
- Leonardo
- L3 Technologies
- Saab Group
Key Target Audience
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Australian Department of Defence, Royal Australian Navy)
- Shipbuilders (Austal Limited, ASC Shipbuilding)
- Naval Equipment Suppliers (Raytheon Technologies, Lockheed Martin)
- Defense Contractors (Huntington Ingalls Industries, BAE Systems)
- Shipyards and Manufacturing Facilities (Navantia, Fincantieri)
- Military Strategic Planners (Australian Defence Force)
- Naval Aviation Technology Providers (Northrop Grumman, Leonardo)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
In this initial phase, an in-depth analysis of the Australia Aircraft Carrier Ship Market is conducted by identifying the key players, market trends, technological developments, and defense budgets through secondary research. This includes reviewing reports from defense ministries and market experts.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
A historical analysis is performed to identify past trends in aircraft carrier procurements and technological advancements. Data sources like defense budgets, procurement policies, and industry news are compiled to assess growth patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are validated through consultations with industry experts from defense contractors, shipyards, and the Australian Navy. These experts provide valuable insights into the future of naval strategies, carrier programs, and procurement processes.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final phase involves synthesizing data from primary and secondary research to generate actionable insights. Detailed reports are created through expert validation, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the market forecasts and recommendations.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Scope (Carrier type categories: supercarrier, STOVL/CTOL, amphibious carrier variants), Sovereign Capability Framework (Sovereign industrial base index), Data Sources (Defense budgets, shipyard capacity metrics, alliance compacts), Primary Research Approaches (Defense stakeholder interviews, naval integrator consultations), Assumptions (Cost per vessel benchmarks, geopolitical risk multipliers), Limitations & Data Confidence Scores)
- Strategic rationale (maritime security, air‑sea control doctrine)
- Historical carrier capability & RAN legacy (HMAS Sydney/Melbourne lineage)
- Evolution of Australia’s naval aviation platforms
- Strategic Policy & Force Modernization Drivers
- National Defense Strategy & Integrated Investment Program impact
- AUKUS naval capability uplift & interoperability implications
- Indo‑Pacific security gradients & maritime threat vectors
- Industry Value Chain & Ecosystem
- Domestic shipbuilding capacity (Austal, BAE Systems Australia)
- Foreign naval integrators & technology suppliers
- Supply chain readiness indices & sovereign tech transfer levers
- Growth Drivers
Maritime deterrence acceleration metrics
Alliance force multiplication (AUKUS & interoperability)
Technology adoption drivers (EMALS, UAV deployment capability) - Market Challenges
High acquisition & sustainment unit cost curves
Industrial base capacity bottlenecks
Regulatory & security clearance constraints - Opportunity
Sovereign shipyard scaling
Allied supplier ecosystems
Export potential of indigenous naval components - Competitive Trends
Advanced propulsion systems
AI‑enabled carrier air traffic management
Survivability & radar signature mitigation
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By Carrier Class (In Value %)
Large Deck Carrier (Fixed Wing Capability)
STOVL/VTOL Deck Carriers
Amphibious Carrier Variants - By Propulsion Architecture (In Value %)
Conventional Power (Gas Turbine / Diesel)
Hybrid Electric Propulsion
Nuclear‑assist (Future Scenarios) - By Aircraft Complement (In Value %)
F‑35B/STOVL fighters
Rotary Wing Aviation
Unmanned Combat & ISR Platforms - By Procurement Source (In Value %)
Domestic Build (Sovereign Shipyard)
Foreign Built (Allied Transfer) - By Capability System Integration (In Value %)
Catapult & Arresting Gear Systems
Combat Management & Sensor Suites
Aviation Logistics Systems
- Market Share – Current & Directed Programs
- Carrier design opportunities relative to allied benchmarks
- Cross‑comparison parameters (Company Profile, Strategic Alliances with Australia, Local Content % & Technology Transfer, Defense Industrial Base Integration, Cost per Vessel (AU$), Capability Upgrade Pathways, Naval Aviation Integration Capability, Sustainment Footprint)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Huntington Ingalls Industries
BAE Systems plc
Naval Group
Fincantieri S.p.A.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Northrop Grumman
Lockheed Martin
Navantia
ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
General Dynamics NASSCO
Raytheon Technologies
Leonardo S.p.A.
Austal Limited
Babcock International
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Royal Australian Navy capability requirements
- Navy operational doctrines impacting procurement
- Force design imperatives & readiness indices
- Fleet deployment patterns (Indo‑Pacific emphasis)
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


