Market Overview
The Australia Military Marine Vessel Engines market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by sustained naval modernization programs and steady replacement of aging propulsion systems across frontline and auxiliary fleets. During the recent period, investment commitments reached nearly USD ~ million in advanced diesel and hybrid propulsion upgrades, while annual deployment volumes crossed ~ units across patrol and amphibious platforms. Engine retrofitting activity also increased, with more than ~ systems upgraded to meet operational endurance and emission efficiency requirements.
Market dominance is concentrated in Western Australia and South Australia, driven by the presence of major naval bases, shipyards, and sustainment hubs that anchor long-term fleet readiness programs. These regions benefit from dense maintenance ecosystems, skilled marine engineering workforces, and integrated defense supply chains. Policy-driven emphasis on sovereign naval capability has further strengthened localized engine servicing and overhaul networks, reinforcing their leadership position in procurement activity and lifecycle support.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
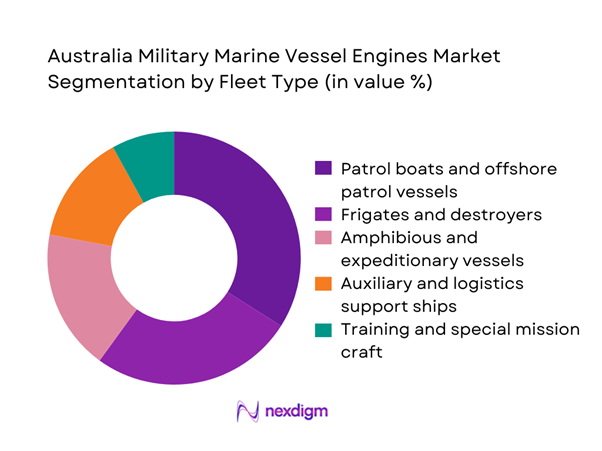
The fleet type segmentation is dominated by patrol boats and offshore patrol vessels, reflecting Australia’s strategic focus on maritime surveillance, border security, and rapid response operations. These platforms account for the highest engine replacement cycles due to high utilization intensity and extended operational hours. Frigates and destroyers follow closely, supported by long-term fleet recapitalization programs that prioritize propulsion efficiency and acoustic performance. Amphibious and expeditionary vessels represent a growing segment as regional security cooperation expands. Auxiliary and logistics ships also contribute steadily, driven by the need for reliable power generation and endurance across extended deployment missions.
By Technology Architecture
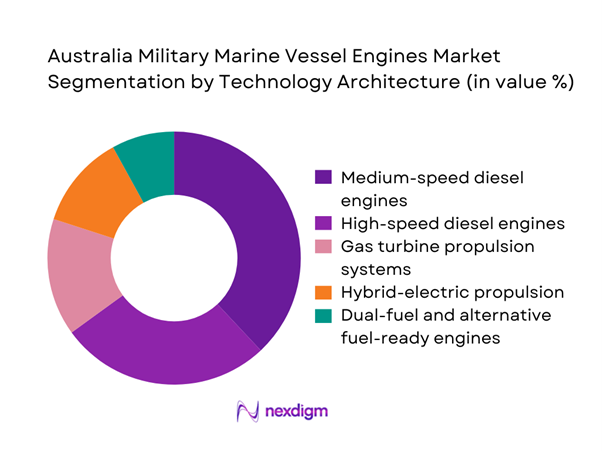
Technology architecture segmentation is led by medium-speed diesel engines due to their balance of power output, fuel efficiency, and proven reliability across multi-role naval vessels. High-speed diesel engines remain widely adopted in patrol and fast-response craft where acceleration and maneuverability are critical. Gas turbine propulsion maintains a niche role in high-performance surface combatants, while hybrid-electric systems are gaining traction in newbuild programs emphasizing acoustic stealth and fuel optimization. Dual-fuel and alternative fuel-ready engines are emerging as strategic investments aligned with future decarbonization pathways and operational flexibility.
Competitive Landscape
The market exhibits a moderately concentrated structure, with a small group of global propulsion specialists dominating naval engine supply, supported by localized service partners and defense integrators. Long-term framework contracts, platform standardization, and sustainment agreements shape competitive positioning more strongly than short-term pricing dynamics.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rolls-Royce Power Systems | 1909 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| MAN Energy Solutions | 1758 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Wärtsilä | 1834 | Finland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Caterpillar Marine | 1925 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Cummins Marine | 1919 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia Military Marine Vessel Engines Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of Royal Australian Navy surface fleet
Fleet modernization programs have accelerated engine replacement cycles across surface combatants and patrol vessels, with more than ~ systems upgraded between 2022 and 2025. Capital allocation for propulsion modernization reached nearly USD ~ million during this period, reflecting strong institutional commitment to operational readiness. The introduction of new vessel classes has driven demand for higher-output engines, with annual deployment volumes exceeding ~ units in recent upgrade phases. Increased focus on endurance and reduced maintenance downtime has also led to wider adoption of digitally monitored engines, strengthening long-term demand visibility across naval sustainment contracts.
Rising focus on maritime border protection and patrol capability
Border protection initiatives have significantly increased operational tempo for patrol fleets, resulting in higher engine utilization and faster refurbishment cycles. Between 2022 and 2025, patrol vessel engine overhaul volumes crossed ~ units, supported by dedicated funding of around USD ~ million for propulsion reliability upgrades. Expanded offshore surveillance missions have intensified demand for high-speed diesel engines optimized for fuel efficiency and rapid response. This operational shift has also increased investments in onboard diagnostic systems, with more than ~ platforms now equipped for condition-based monitoring to minimize mission downtime.
Challenges
High capital cost of advanced propulsion systems
Advanced propulsion technologies such as hybrid-electric and integrated electric systems require substantial upfront capital, with average project investments exceeding USD ~ million per vessel between 2022 and 2025. These costs extend beyond engine procurement to include power management systems, control software, and crew training. Budgetary constraints have limited adoption to priority platforms, resulting in fewer than ~ vessels transitioning to next-generation propulsion architectures. The financial burden is further amplified by specialized maintenance requirements, increasing total ownership commitments and slowing fleet-wide standardization efforts.
Lengthy defense procurement and approval cycles
Defense acquisition processes introduce extended lead times that delay engine deployment schedules by up to ~ months in major naval programs. Between 2022 and 2025, more than ~ procurement initiatives experienced timeline extensions due to multi-layered compliance and testing protocols. These delays often defer engine production runs and create gaps in sustainment planning, impacting supplier capacity utilization. The prolonged approval environment also raises program management costs, with administrative and integration expenses reaching nearly USD ~ million across multi-year propulsion upgrade contracts.
Opportunities
Adoption of hybrid-electric propulsion in new naval programs
Hybrid-electric propulsion presents a major opportunity as upcoming vessel programs emphasize fuel efficiency, acoustic stealth, and operational flexibility. From 2022 to 2025, feasibility investments of nearly USD ~ million supported pilot deployments across ~ platforms. These early implementations demonstrated measurable reductions in fuel consumption and maintenance intervals, strengthening the business case for broader rollout. As new classes of patrol and support vessels enter design phases, projected hybrid system installations could exceed ~ units, creating sustained demand for power electronics, energy storage, and advanced control architectures.
Localization of engine assembly and maintenance operations
Localization initiatives are reshaping the supply landscape, with domestic assembly and overhaul facilities expanding capacity to support sovereign defense objectives. Between 2022 and 2025, infrastructure investments reached approximately USD ~ million, enabling the establishment of more than ~ specialized service centers. This shift reduces reliance on overseas supply chains and shortens turnaround times for critical engine components. Localized operations also enhance workforce development, with ~ technicians trained in advanced marine propulsion systems, strengthening long-term sustainability of fleet readiness programs.
Future Outlook
The Australia Military Marine Vessel Engines market is positioned for steady evolution through the next decade, driven by sustained naval modernization and rising emphasis on sovereign sustainment capabilities. Hybrid-electric propulsion and digitally integrated engines will increasingly define newbuild programs. Policy alignment with regional security cooperation is expected to reinforce long-term procurement pipelines, while localized maintenance ecosystems will continue to reshape competitive dynamics.
Major Players
- Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Wärtsilä
- Caterpillar Marine
- Cummins Marine
- GE Marine
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
- Yanmar Marine
- ABC Engines
- Bergen Engines
- Fairbanks Morse Defense
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Siemens Energy Marine
- MTU Australia
Key Target Audience
- Royal Australian Navy procurement divisions
- Australian Department of Defence acquisition agencies
- Border Force and maritime security authorities
- Naval shipbuilders and prime defense contractors
- Marine propulsion system integrators
- Fleet sustainment and MRO service providers
- Investments and venture capital firms focused on defense technology
- Government and regulatory bodies including the Australian Maritime Safety Authority
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core demand indicators, fleet modernization schedules, and propulsion technology adoption rates were mapped to establish the primary analytical framework. Operational usage patterns and maintenance cycles were reviewed to determine replacement drivers. Regulatory and defense policy parameters were incorporated to define market boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data models were developed to estimate engine deployment volumes and investment flows across major vessel categories. Supply-side capabilities were assessed through production capacity and service network mapping. Scenario modeling was applied to evaluate technology transition pathways.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Preliminary assumptions were tested through structured discussions with naval engineers and procurement specialists. Feedback loops refined demand forecasts and risk assessments. Technology adoption timelines were recalibrated based on operational feasibility insights.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Quantitative and qualitative findings were consolidated into a unified market narrative. Strategic implications were aligned with policy and industry trends. Final outputs were structured to support investment, procurement, and planning decisions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market definitions and scope boundaries, military marine vessel engine taxonomy across diesel gas turbine and hybrid propulsion systems, market sizing logic by fleet size overhaul cycles and new build programs, revenue attribution across engine sales spares and MRO services, primary interview program with naval operators shipyards and engine OEMs, data triangulation validation assumptions and limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and MRO channel structure
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of Royal Australian Navy surface fleet
Rising focus on maritime border protection and patrol capability
Lifecycle replacement of aging propulsion systems
Increasing demand for higher fuel efficiency and lower emissions
Growth in amphibious and expeditionary mission requirements
Expansion of sovereign naval shipbuilding programs - Challenges
High capital cost of advanced propulsion systems
Lengthy defense procurement and approval cycles
Integration complexity with legacy vessel platforms
Supply chain dependency on overseas OEMs
Stringent military certification and compliance requirements
Skilled workforce shortages in marine engineering and MRO - Opportunities
Adoption of hybrid-electric propulsion in new naval programs
Localization of engine assembly and maintenance operations
Growth in mid-life upgrade and retrofit projects
Rising demand for condition-based and predictive maintenance solutions
Collaboration with allied navies for common engine platforms
Development of alternative fuel-ready military engines - Trends
Shift toward integrated full-electric and hybrid propulsion architectures
Increasing use of digital twins for engine performance optimization
Expansion of long-term performance-based logistics contracts
Greater emphasis on acoustic signature reduction technologies
Adoption of modular engine designs for fleet standardization
Rising investment in cyber-secure shipboard control systems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Patrol boats and offshore patrol vessels
Frigates and destroyers
Amphibious and expeditionary vessels
Auxiliary and logistics support ships
Training and special mission craft - By Application (in Value %)
Main propulsion systems
Auxiliary power generation
Hybrid-electric drive support
Emergency and backup power systems
Onboard mission systems power supply - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
High-speed diesel engines
Medium-speed diesel engines
Gas turbine propulsion systems
Hybrid-electric and integrated electric propulsion
Dual-fuel and alternative fuel-ready engines - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval defense forces
Maritime border security agencies
Government research and surveillance fleets
Allied defense cooperation and joint task forces
State-based maritime security units - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone mechanical engine systems
Digitally monitored engines with onboard diagnostics
Integrated platform management systems
Condition-based monitoring with shore connectivity
SATCOM-enabled remote performance management - By Region (in Value %)
New South Wales
Western Australia
South Australia
Victoria
Queensland
Northern Territory
Tasmania
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (engine power range, fuel efficiency, lifecycle cost, digital integration level, emissions compliance, acoustic performance, local support capability, delivery lead time)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
MTU (Rolls-Royce Power Systems)
MAN Energy Solutions
Wärtsilä
Caterpillar Marine
Cummins Marine
Rolls-Royce Naval Propulsion
GE Marine
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
Yanmar Marine
ABC Engines
Bergen Engines
Fairbanks Morse Defense
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Siemens Energy Marine
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and lifecycle support expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


