Market Overview
The Australia ship leasing market was valued at approximately USD ~ billion based on a recent historical assessment, supported by sustained charter activity across commercial shipping, offshore energy logistics, and government maritime operations. Market scale is driven by Australia’s dependence on seaborne trade, high vessel acquisition costs, and the preference for asset-light operational models among shipping operators. Additional momentum is provided by offshore oil and gas logistics, port service requirements, and coastal shipping activities, with leasing enabling fleet deployment while maintaining compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
Australia’s ship leasing activity is concentrated in maritime hubs such as Perth, Brisbane, Sydney, and Melbourne due to proximity to major ports, offshore energy basins, and trade corridors. Perth dominates offshore support vessel leasing because of Western Australia’s energy projects, while Brisbane and Melbourne benefit from containerized and bulk cargo movements linked to Asia-Pacific trade. Sydney’s role is reinforced by port services and government maritime contracts, with these cities benefiting from advanced port infrastructure, skilled maritime labor availability, and strong regulatory oversight that supports large-scale leasing operations.
Market Segmentation
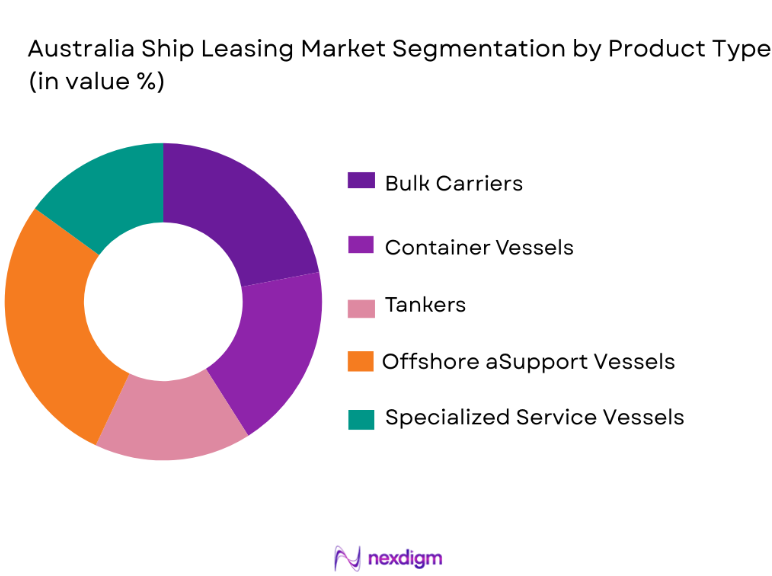
By Product Type
Australia ship leasing market is segmented by vessel type into bulk carriers, container vessels, tankers, offshore support vessels, and specialized service vessels. Recently, offshore support vessels had a dominant market share due to continuous offshore oil and gas operations, subsea construction activity, and maintenance logistics requirements along Australia’s western and northern coasts. These vessels are preferred under leasing models because project-based offshore operations demand short to medium-term deployment flexibility without long-term ownership commitments. Offshore support vessels also command higher daily charter rates due to advanced specifications, dynamic positioning systems, and compliance with stringent safety standards, which elevates their value contribution. The ability to redeploy these vessels across multiple offshore projects, including emerging renewable energy installations, further strengthens leasing demand. Additionally, international offshore contractors operating in Australian waters rely heavily on leased fleets to meet regulatory and operational requirements efficiently.
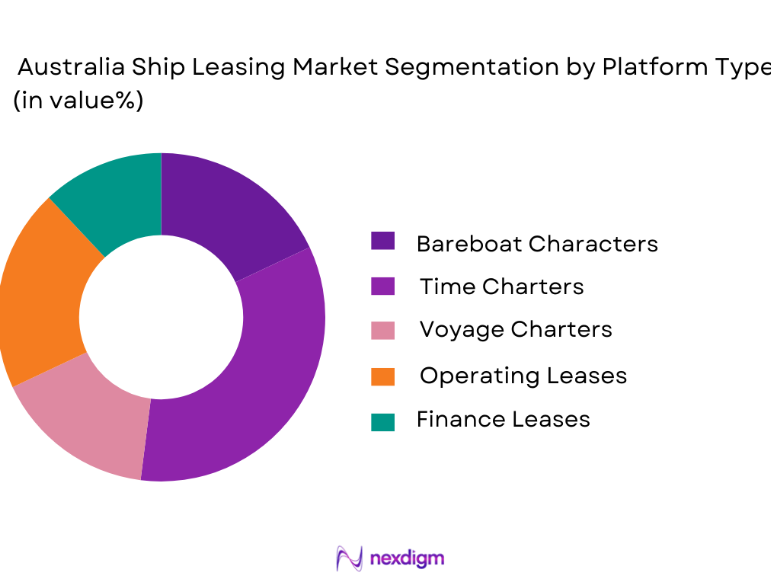
By Platform Type
Australia ship leasing market is segmented by lease type into bareboat charters, time charters, voyage charters, operating leases, and finance leases. Recently, time charters have held a dominant market share due to their balance between operational control and cost predictability for charterers. Time charters allow operators to manage routes, crew, and cargo while avoiding capital expenditure on vessel ownership, which is critical in volatile shipping cycles. Australian cargo operators and offshore contractors favor time charters for aligning vessel availability with contract durations and seasonal trade flows. This structure also supports compliance with local regulations while enabling rapid fleet scaling. The widespread acceptance of time charters among ports, logistics providers, and offshore firms reinforces their dominance within the leasing structure landscape.
Competitive Landscape
The Australia ship leasing market exhibits moderate consolidation, with a mix of global maritime lessors and regional operators serving commercial, offshore, and government clients. Large players benefit from diversified fleets, strong balance sheets, and long-term charter relationships, while smaller operators compete through niche vessel specialization and regional expertise.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Fleet Size |
| MMA Offshore | 1983 | Australia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Teekay Shipping | 1973 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Swire Pacific Offshore | 1974 | Singapore | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| CSL Australia | 1913 | Australia | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Svitzer Australia | 1833 | Denmark | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia Ship Leasing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Offshore Energy and Marine Infrastructure Projects
Expansion of offshore energy and marine infrastructure projects is a critical growth driver for the Australia ship leasing market: it is directly linked to sustained offshore oil and gas production, subsea maintenance contracts, and the gradual rollout of offshore renewable energy installations along Australia’s coastline. These activities require a wide range of specialized vessels including platform supply vessels, anchor handling tug supply vessels, and construction support ships that are capital intensive to own. Leasing enables operators to match vessel deployment precisely with project timelines, reducing idle capacity risks while maintaining compliance with strict maritime safety standards. Offshore contractors increasingly prefer leasing because project awards are competitive and time bound, requiring rapid mobilization without long procurement cycles. Government-supported energy security initiatives further stabilize demand. As offshore projects expand geographically, leased vessels can be redeployed efficiently, enhancing utilization rates. The complexity of offshore operations increases reliance on technically advanced vessels that are more economically accessed through leasing. This driver is reinforced by continued investments in offshore infrastructure maintenance and expansion programs. Overall, offshore energy growth sustains long-term leasing demand across vessel classes.
Preference for Asset-Light Fleet Management Models
Preference for asset-light fleet management models is another significant growth driver for the Australia ship leasing market: shipping companies and marine service providers increasingly seek to minimize balance sheet exposure while maintaining operational flexibility. Vessel ownership involves high capital expenditure, depreciation risk, and long asset lifecycles that are difficult to align with volatile freight markets. Leasing allows operators to adjust fleet size in response to demand fluctuations, regulatory changes, and trade cycle shifts. Australian operators face strict environmental and safety regulations, making ownership of aging vessels less viable, while leasing provides access to compliant modern fleets. Financial institutions often favor leasing due to predictable cash flow. Asset-light strategies also support faster market entry for new operators. This approach is increasingly adopted across bulk, container, and offshore segments. The trend is further strengthened by uncertainty in global shipping rates. Collectively, asset-light strategies reinforce leasing as a core operational model.
Market Challenges
Exposure to Shipping Cycle Volatility and Rate Fluctuations
Exposure to shipping cycle volatility and rate fluctuations represents a major challenge for the Australia ship leasing market: leasing revenues are closely tied to freight rates, offshore project activity, and global trade conditions. Periods of oversupply or reduced trade volumes can lead to lower charter rates and shorter contract durations. Lessors face utilization risks when vessels remain idle between contracts. Volatility complicates long-term revenue forecasting and investment planning. Australian operators are not insulated from global market swings, particularly in bulk and container segments. Currency movements further affect lease economics. Smaller lessors face higher financial stress during downturns. This challenge requires careful contract structuring and fleet diversification. Persistent volatility remains a structural constraint on stable market growth.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Cost Burden
Regulatory compliance and environmental cost burden is another critical challenge affecting the Australia ship leasing market: stringent maritime safety, emissions, and crewing regulations increase operating costs for leased vessels. Compliance requires continuous investment in vessel upgrades, monitoring systems, and certification processes. Older leased vessels may become non-compliant, reducing their market attractiveness. Environmental regulations targeting emissions and fuel efficiency raise lease rates for compliant vessels. Lessons must balance upgrade costs with competitive pricing pressures. Operators face penalties for non-compliance, increasing risk exposure. Regulatory alignment with international conventions adds complexity for foreign-flagged vessels. This challenge influences leasing contract terms and fleet renewal decisions. Regulatory pressure remains a persistent operational hurdle.
Opportunities
Growth of Offshore Renewable Energy Support Leasing
Growth of offshore renewable energy support leasing presents a significant opportunity for the Australia ship leasing market: planned offshore wind and marine renewable projects require specialized installation, maintenance, and logistics vessels. These projects are long term yet phased, making leasing more suitable than ownership. Specialized vessels command premium lease rates due to technical complexity. Government support for renewable energy enhances project certainly. Leasing enables rapid mobilization of international expertise and vessels. Domestic operators can expand portfolios through renewable support vessels. This opportunity supports diversification beyond oil and gas. It also encourages investment in modern low-emission fleets. Renewable energy growth provides a new, stable demand stream.
Rising Demand for Environmentally Compliant Modern Fleets
Rising demand for environmentally compliant modern fleets creates another strong opportunity for the Australia ship leasing market: operators increasingly seek vessels meeting advanced emissions and fuel efficiency standards. Leasing provides access to compliant fleets without ownership risk. Lessors investing in modern vessels gain competitive advantage. Regulatory pressure increases replacement of older tonnage. Demand spans commercial shipping, offshore support, and government segments. Environmentally compliant vessels attract long-term charters. This opportunity aligns with sustainability goals. It supports premium lease pricing. Long-term, it strengthens market resilience.
Future Outlook
The Australia ship leasing market is expected to demonstrate steady growth over the next five years, supported by offshore energy activity, trade recovery, and fleet modernization initiatives. Technological adoption, including digital fleet management and low-emission propulsion, will shape leasing preferences. Regulatory support for maritime safety and environmental compliance will favor modern leased vessels. Demand from offshore renewables and government maritime programs is anticipated to strengthen overall market stability.
Major Players
- MMA Offshore
- Teekay Shipping
- Swire Pacific Offshore
- CSL Australia
- Svitzer Australia
- Serco Marine
- Maersk Supply Service
- Pacific Basin Shipping
- DOF Subsea
- Bourbon Offshore
- KOTUG Australia
- Transocean
- Siem Offshore
- Toll Marine Logistics
- ASP Ship Management
Key Target Audience
- Shipping and logistics companies
- Offshore energy operators
- Port authorities
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Defense and maritime security agencies
- Marine infrastructure developers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Fleet management companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables include vessel types, lease structures, end-user demand, regulatory impacts, and trade activity influencing ship leasing dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data, industry disclosures, and maritime databases are analyzed to construct market size and structural insights.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings are validated through consultations with maritime operators, lessors, and industry experts.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated insights are synthesized into structured market analysis and forecasts.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising preference for asset-light fleet management models
Growth in offshore energy and marine infrastructure projects
Increasing regional and international maritime trade volumes
Fleet renewal driven by environmental and safety regulations
Government outsourcing of maritime logistics capabilities - Market Challenges
Exposure to global shipping cycle volatility
High compliance costs related to environmental standards
Limited availability of specialized vessels during peak demand
Dependence on international lessors for advanced vessel types
Operational risks linked to short-term charter structures - Market Opportunities
Expansion of offshore wind and renewable marine support leasing
Growing demand for low-emission and fuel-efficient vessels
Increased long-term leasing for government and defense programs - Trends
Shift toward long-term operating leases
Rising adoption of digitally enabled vessel monitoring
Increased leasing of specialized offshore vessels
Focus on sustainability-compliant fleets
Integration of flexible contract and pricing structures - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Strengthening maritime safety and environmental compliance
Support for coastal shipping and port infrastructure development
Defense logistics modernization and capability enhancement - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Bulk carriers
Container vessels
Oil and chemical tankers
Offshore support vessels
Specialized service and utility vessels - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Commercial cargo shipping
Offshore oil and gas operations
Offshore renewable energy support
Government and defense logistics
Coastal and regional transport services - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Bareboat charter arrangements
Time charter contracts
Voyage charter agreements
Operating lease structures
Finance lease structures - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Shipping line operators
Offshore energy companies
Government and defense agencies
Port and terminal operators
Marine service and logistics providers - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct leasing from vessel owners
Specialized ship leasing companies
Broker-facilitated charter contracts
Government procurement frameworks
Long-term strategic lease agreements - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Conventional steel hull vessels
Fuel-efficient propulsion systems
Low-emission and LNG-fueled vessels
Digitally monitored fleet technologies
Ice-class and reinforced hull designs
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet size, vessel age profile, lease tenure flexibility, technology integration, regulatory compliance capability, geographic coverage, financial strength, service portfolio breadth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Teekay Shipping Australia
Swire Pacific Offshore Australia
Toll Marine Logistics
ASP Ship Management
CSL Australia
Serco Marine Australia
DOF Subsea Australia
Bourbon Offshore Asia-Pacific
Pacific Basin Shipping Australia
Maersk Supply Service Australia
Svitzer Australia
Transocean Australia
KOTUG Australia
MMA Offshore
Siem Offshore Australia
- Commercial operators prioritize flexibility and cost optimization
- Offshore energy firms rely on leased vessels for project scalability
- Government users focus on compliance and rapid deployment needs
- Logistics providers emphasize reliability and fleet availability
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


