Market Overview
The Australia submarine propulsion systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by ongoing fleet modernization and technology upgrades. Demand levels reflect sustained procurement cycles, rising defense readiness priorities, and increasing integration of advanced propulsion architectures. Recent procurement activity indicates steady system replacement volumes and component upgrades across operational submarines. Industrial participation has expanded alongside domestic assembly capabilities and technology transfer initiatives. System retrofitting and propulsion efficiency improvements continue to shape procurement volumes. Market activity remains concentrated around long-cycle defense programs and multiyear platform development timelines.
Australia’s submarine propulsion ecosystem is primarily concentrated around coastal defense hubs and naval shipbuilding centers. Strong institutional presence across South Australia and Western Australia supports platform integration and lifecycle maintenance activities. The ecosystem benefits from coordinated naval procurement frameworks, local industrial participation mandates, and structured capability development programs. Infrastructure readiness, skilled workforce availability, and access to allied technology partnerships reinforce regional dominance. Policy-driven investments and security commitments further strengthen long-term market stability.
Market Segmentation
By Propulsion Technology
Diesel-electric propulsion systems currently dominate due to widespread deployment across conventional submarine fleets and proven operational reliability. Air-independent propulsion adoption is expanding as endurance enhancement becomes a priority for regional missions. Nuclear propulsion remains limited but strategically significant due to long-term defense partnerships and future fleet transition plans. Technology selection is influenced by mission endurance requirements, operational stealth needs, and maintenance infrastructure availability. Integration complexity and lifecycle sustainment considerations continue to shape technology preference across procurement programs.
By Platform Type
Attack submarines account for the majority of propulsion system demand due to their central role in maritime security operations. Training and test platforms represent a smaller but consistent share driven by capability development requirements. Special mission submarines contribute selectively, driven by intelligence and surveillance mandates. Platform segmentation is influenced by fleet renewal cycles, operational doctrine, and interoperability requirements with allied naval forces. Procurement planning aligns propulsion investments closely with long-term fleet composition strategies.
Competitive Landscape
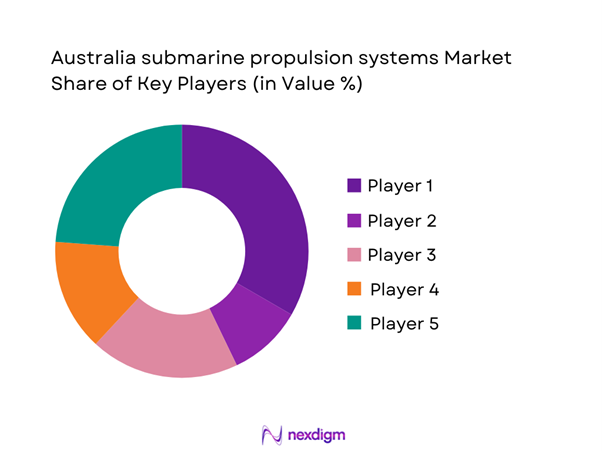
The competitive landscape is characterized by a limited number of specialized defense manufacturers with deep engineering capabilities and long-term naval program experience. Market participants compete on system reliability, integration capability, lifecycle support strength, and compliance with defense procurement standards. Strategic partnerships and local industrial participation remain central to securing long-term contracts.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Naval Group | 1626 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems | 1999 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rolls-Royce | 1906 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia submarine propulsion systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising Australian naval modernization programs
Rising Australian naval modernization programs are accelerating propulsion system upgrades across existing and planned submarine platforms nationwide. Defense modernization initiatives emphasize improved endurance, acoustic stealth, and propulsion efficiency across operational fleets. Increased allocation toward undersea warfare capabilities continues to elevate propulsion system integration requirements. Modernization programs prioritize compatibility with next-generation combat management systems and energy architectures. Domestic industrial participation requirements are expanding system assembly and integration opportunities. Long-term fleet recapitalization strategies are reinforcing sustained propulsion procurement cycles. Naval readiness objectives are driving replacement of legacy propulsion components. Program continuity ensures stable demand visibility for propulsion subsystem suppliers. Government-backed funding certainty supports multi-year development and qualification activities. These modernization efforts collectively strengthen market stability and technology adoption.
AUKUS-driven transition toward nuclear propulsion
AUKUS-driven transition toward nuclear propulsion significantly reshapes Australia’s long-term submarine propulsion requirements. Strategic alignment with allied naval forces accelerates adoption of advanced propulsion architectures. Nuclear propulsion introduces extended endurance and operational range advantages. Program timelines stimulate early-stage infrastructure and workforce development investments. Technology transfer frameworks enhance domestic technical competencies and integration capabilities. Nuclear propulsion planning increases demand for specialized engineering and safety systems. Supply chain restructuring supports long-duration component reliability requirements. Training programs are expanding to support nuclear-certified operational standards. Policy alignment ensures sustained government commitment toward propulsion modernization. These dynamics collectively elevate market complexity and long-term growth potential.
Challenges
High capital and lifecycle costs of propulsion systems
High capital and lifecycle costs of propulsion systems constrain procurement flexibility across naval budgets. Long development cycles increase financial exposure for program stakeholders. Specialized materials and engineering requirements elevate system integration expenses significantly. Maintenance-intensive components contribute to elevated lifecycle support burdens. Budget prioritization challenges can delay procurement schedules and modernization timelines. Cost escalation risks impact supplier pricing strategies and contract negotiations. Long-term sustainment obligations require continuous funding commitments. Limited supplier competition further restricts cost optimization opportunities. Fiscal planning complexity increases due to multi-decade platform service lives. These cost pressures remain a persistent barrier to rapid market expansion.
Technology transfer and sovereign capability constraints
Technology transfer restrictions limit domestic access to critical propulsion design knowledge and components. Sovereign capability development requires extended learning curves and regulatory approvals. Export control compliance slows integration of advanced propulsion technologies. Intellectual property limitations restrict local manufacturing scalability. Workforce certification requirements constrain rapid capability development. Dependence on allied partners introduces schedule coordination challenges. Infrastructure readiness gaps affect installation and testing timelines. Regulatory alignment across international partners increases administrative complexity. Capability assurance requirements raise entry barriers for new participants. These constraints collectively moderate near-term market scalability.
Opportunities
AUKUS-related industrial collaboration
AUKUS-related industrial collaboration creates opportunities for shared propulsion development and localized production capabilities. Joint research initiatives support advanced propulsion innovation pathways. Industrial partnerships enhance knowledge transfer and technical skill development. Collaborative frameworks enable access to advanced testing and validation infrastructure. Long-term agreements provide visibility for sustained supplier engagement. Cross-border cooperation supports standardization of propulsion components. Enhanced interoperability drives common system architecture adoption. Local industry participation strengthens domestic manufacturing ecosystems. Workforce development programs expand specialized engineering capacity. These collaborations significantly expand long-term market potential.
Local manufacturing and sustainment programs
Local manufacturing and sustainment programs present significant opportunities for propulsion system suppliers. Domestic assembly reduces reliance on overseas production dependencies. Sustainment contracts provide stable long-term revenue streams. Localized support improves fleet availability and operational readiness. Industrial participation policies encourage investment in tooling and facilities. Skills development initiatives strengthen workforce capabilities. Supply chain localization reduces lead times and logistical risks. Maintenance hubs enhance lifecycle cost efficiencies. Government incentives support domestic production scalability. These factors collectively enhance market attractiveness for suppliers.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to remain strongly influenced by long-term naval modernization priorities and strategic defense partnerships. Continued focus on propulsion efficiency, endurance, and system integration will drive sustained demand. Technological collaboration and domestic capability expansion will shape competitive dynamics. Regulatory alignment and infrastructure investments are expected to support steady market progression through the forecast period.
Major Players
- BAE Systems
- Saab
- Naval Group
- ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
- Rolls-Royce
- General Dynamics Electric Boat
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Siemens
- Wärtsilä
- MAN Energy Solutions
- L3Harris Technologies
- Curtiss-Wright Corporation
- Kongsberg Gruppen
- Thales Group
Key Target Audience
- Australian Department of Defence
- Defence Science and Technology Group
- Royal Australian Navy procurement divisions
- Shipbuilding and naval engineering firms
- Submarine maintenance and overhaul providers
- Defense system integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government regulatory and certification bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key propulsion system parameters, platform categories, and operational requirements were identified through structured market scoping. Technical, regulatory, and operational variables were mapped to define market boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was analyzed across platform deployment, procurement activity, and technology adoption patterns. Segmentation logic was developed to reflect real-world procurement and operational use cases.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through consultations with defense industry specialists and naval engineering experts. Assumptions were refined based on system deployment realities and procurement timelines.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated data points were synthesized into a structured market framework. Insights were aligned with defense modernization trends and future propulsion development pathways.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for submarine propulsion systems, Fleet and propulsion taxonomy development based on Australian naval programs, Bottom-up market sizing using platform-level propulsion integration costs, Revenue attribution across OEMs and subsystem suppliers, Primary validation through naval architects and defense procurement experts, Data triangulation using defense budgets and shipbuilding timelines, Assumptions mapping linked to AUKUS and future fleet transition)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational and mission-based usage framework
- Defense ecosystem and supplier landscape
- Propulsion system value chain structure
- Regulatory and defense procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising Australian naval modernization programs
AUKUS-driven transition toward nuclear propulsion
Increased maritime security and Indo-Pacific tensions
Lifecycle replacement of Collins-class submarines
Growing defense budget allocation for undersea warfare
Advancements in propulsion efficiency and stealth - Challenges
High capital and lifecycle costs of propulsion systems
Technology transfer and sovereign capability constraints
Long development and certification timelines
Supply chain dependence on foreign OEMs
Skilled workforce shortages in nuclear propulsion - Opportunities
AUKUS-related industrial collaboration
Local manufacturing and sustainment programs
Development of hybrid propulsion technologies
Expansion of maintenance, repair, and overhaul services
Integration of digital propulsion management systems - Trends
Shift toward nuclear-powered submarine platforms
Adoption of air-independent propulsion upgrades
Increased focus on acoustic signature reduction
Localization of propulsion component manufacturing
Integration of digital twins and predictive maintenance - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Conventional attack submarines
Nuclear-powered submarines
Special mission and research submarines
Training and test platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Patrol and surveillance
Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
Deterrence and strategic operations
Training and fleet readiness - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Diesel-electric propulsion
Air-independent propulsion systems
Nuclear propulsion systems
Hybrid and integrated electric propulsion - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Naval defense forces
Government shipbuilding agencies
Defense research organizations
Naval maintenance and overhaul yards - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Integrated platform management systems
Wired propulsion control systems
Hybrid digital control networks
Autonomous and AI-assisted propulsion control - By Region (in Value %)
New South Wales
South Australia
Western Australia
Victoria
Rest of Australia
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (propulsion technology depth, system integration capability, defense certifications, local manufacturing presence, lifecycle support capability, R&D investment, contract backlog, strategic partnerships)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
BAE Systems
Saab Kockums
Naval Group
ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems
General Dynamics Electric Boat
Rolls-Royce
Wärtsilä
MAN Energy Solutions
Kawasaki Heavy Industries
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
Siemens
L3Harris Technologies
Curtiss-Wright Corporation
Kongsberg Gruppen
Thales Group
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035