Market Overview
The Australia Turret Systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady defense modernization momentum. Demand is supported by rising platform upgrades, localized manufacturing programs, and technology refresh cycles across armored and naval fleets. In 2024 and 2025, procurement activities focused on stabilization systems, remote weapon stations, and modular turret architectures. Capability enhancement initiatives emphasized survivability, precision targeting, and digital integration. Ongoing lifecycle upgrades and sustainment contracts continued to support stable market activity levels nationwide.
Demand concentration remains strongest in regions hosting major defense bases, testing ranges, and manufacturing hubs. Eastern and western coastal zones dominate due to naval installations and armored vehicle deployment centers. Infrastructure maturity, skilled labor availability, and defense-oriented industrial clusters support adoption. Government-backed modernization programs and long-term procurement planning strengthen ecosystem continuity. Close coordination between defense agencies, integrators, and subsystem suppliers further reinforces regional dominance patterns.
Market Segmentation
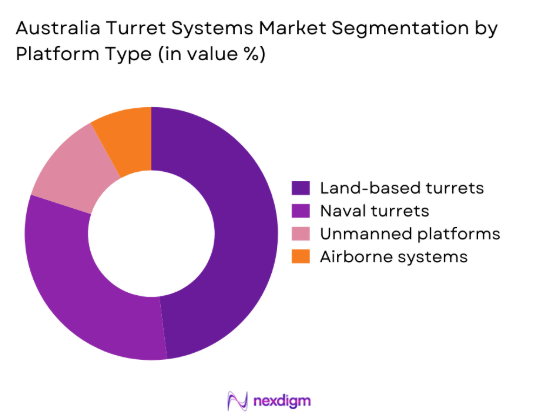
By Platform Type
The land-based turret segment dominates due to ongoing upgrades of armored vehicles and infantry fighting platforms across multiple defense programs. Demand is driven by enhanced mobility requirements, remote weapon integration, and survivability improvements. Naval turret systems follow closely, supported by patrol vessel modernization and coastal security initiatives. Airborne turret deployment remains limited but growing for surveillance platforms. Unmanned ground vehicle integration is expanding as autonomous warfare concepts mature. Platform standardization and modular designs increasingly influence procurement decisions.
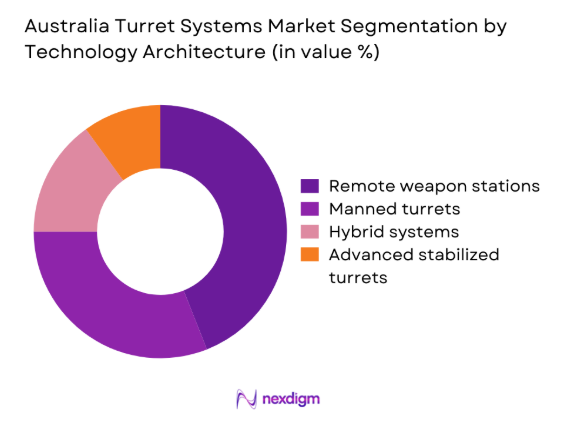
By Technology Architecture
Remote weapon stations dominate due to operational safety advantages and improved targeting accuracy. Manned turret systems continue in legacy platforms but face gradual replacement. Advanced stabilization and sensor-fusion technologies are increasingly integrated into new deployments. Digitally networked turrets gain traction for battlefield awareness and interoperability. Modular open-architecture systems attract higher adoption due to upgrade flexibility. Integration with command systems further enhances operational effectiveness.
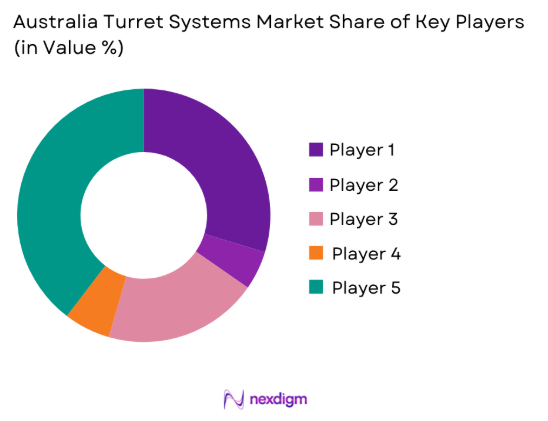
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by established defense manufacturers and specialized subsystem integrators. Market positioning is influenced by technology depth, compliance capabilities, and long-term defense relationships. Companies compete on integration expertise, system reliability, and lifecycle support capacity. Domestic production capabilities increasingly influence procurement decisions.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | UK | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rheinmetall | 1889 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kongsberg Defence | 1814 | Norway | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia Turret Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of armored fleets
Modernization programs emphasize replacing aging platforms with digitally enabled turret systems across land and naval forces. Increased focus on survivability drives adoption of stabilized and remotely operated turret solutions. Defense agencies prioritize modular architectures to support evolving mission requirements and rapid technology insertion. Procurement cycles increasingly favor scalable systems adaptable to future weapon upgrades. Domestic manufacturing partnerships strengthen supply resilience and technology transfer objectives. Integration of advanced optics and targeting enhances operational effectiveness across terrains. Capability gaps identified during exercises continue accelerating replacement initiatives. Fleet modernization aligns with broader defense readiness and interoperability goals. Operational feedback supports continued investment in next-generation turret technologies. Strategic planning frameworks reinforce sustained demand momentum.
Rising defense procurement and border security focus
Heightened border surveillance requirements elevate demand for advanced weapon integration platforms nationwide. Maritime security operations increase adoption of naval turret systems for patrol vessels. Defense spending prioritizes situational awareness and force protection enhancements. Border security initiatives encourage deployment of remotely operated systems reducing personnel exposure. Regional security dynamics support continuous capability upgrades. Investment in surveillance infrastructure drives complementary turret system procurement. Inter-agency coordination improves technology standardization across deployments. Strategic doctrine increasingly emphasizes rapid response capabilities. Enhanced border monitoring accelerates technology refresh cycles. Long-term security planning sustains procurement consistency.
Challenges
High system integration complexity
Complex integration with legacy platforms increases deployment timelines and technical risks. Compatibility issues arise between new turrets and older vehicle architectures. Software interoperability challenges complicate command and control integration. Testing and certification requirements extend implementation schedules. Customization demands elevate engineering workload for suppliers. Limited standardization increases lifecycle maintenance complexity. Training requirements grow with technological sophistication. Integration delays may impact operational readiness. Dependence on specialized components increases supply vulnerability. System validation processes remain resource intensive.
Lengthy procurement and approval cycles
Defense acquisition processes involve extended evaluation and approval timelines. Multi-layered compliance requirements delay contract finalization. Budgetary reviews often postpone procurement decisions. Program approvals require alignment across multiple agencies. Testing and trials extend delivery schedules significantly. Political and strategic reviews affect funding continuity. Vendor qualification processes remain rigorous and time-consuming. Contract renegotiations may delay implementation phases. Administrative complexity affects supplier planning accuracy. Extended cycles limit rapid technology adoption.
Opportunities
Expansion of unmanned and remote systems
Growing adoption of unmanned platforms creates demand for lightweight turret solutions. Remote operation reduces personnel risk in high-threat environments. Autonomous vehicle programs require compact and modular weapon stations. Technological advancements improve remote targeting precision and reliability. Defense innovation programs encourage autonomous system integration. Increased testing activity supports accelerated development cycles. Export potential rises for advanced unmanned-compatible turrets. Collaboration with robotics developers expands application scope. Operational efficiency improvements attract sustained investment. Future warfare concepts strengthen long-term growth prospects.
Local manufacturing and technology partnerships
Government incentives encourage domestic production and technology transfer initiatives. Local assembly reduces dependency on imported systems. Partnerships improve compliance with national defense policies. Domestic manufacturing enhances supply chain resilience. Collaboration with research institutions accelerates innovation cycles. Skilled workforce development supports long-term industry growth. Localized production improves lifecycle support capabilities. Export competitiveness improves through indigenous development. Public-private partnerships strengthen industrial base maturity. Regional collaboration expands market access opportunities.
Future Outlook
The Australia Turret Systems market is expected to maintain steady expansion through continued modernization programs and defense capability enhancements. Increased adoption of remote and autonomous systems will shape procurement strategies. Policy support for domestic manufacturing will strengthen industry sustainability. Integration of advanced electronics and networking will define future product evolution.
Major Players
- BAE Systems
- Rheinmetall
- Elbit Systems
- Kongsberg Defence
- Saab AB
- Thales Group
- Leonardo
- General Dynamics
- EOS Defence Systems
- Moog
- Hanwha Defense
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Aselsan
- Northrop Grumman
- Denel Land Systems
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defence Australia
- Australian Defence Force procurement units
- Defense system integrators
- Armored vehicle manufacturers
- Naval shipbuilders
- Homeland security agencies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Defense acquisition and sustainment agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key market parameters were defined based on platform types, technology integration levels, and defense procurement structures. Data points were structured around operational deployment and capability enhancement trends.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation logic was developed using platform usage, technology maturity, and deployment patterns. Qualitative assessments supported quantitative structuring of market dynamics.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry specialists and defense professionals were consulted to validate assumptions. Feedback loops ensured alignment with operational realities and procurement behavior.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation methods. Insights were structured to reflect strategic, operational, and technological perspectives.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and turret system classification scope, segmentation framework by platform and weapon integration, bottom-up market sizing using defense procurement data, revenue attribution by contract value and delivery schedules, primary validation through defense OEMs and military procurement experts)
- Growth Drivers
- Challenges
- Opportunities
- Trends
- Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land combat vehicles
Naval combat platforms
Unmanned ground vehicles
Remote weapon stations - By Application (in Value %)
Main battle combat
Reconnaissance and surveillance
Border and perimeter defense
Naval close-in defense
Training and simulation - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Manned turrets
Unmanned turrets
Remote weapon stations
Hybrid stabilized systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Army
Navy
Homeland security
Defense research and testing agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
Network-enabled systems
C4ISR integrated systems - By Region (in Value %)
New South Wales
Victoria
Queensland
Western Australia
Rest of Australia
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (product range, weapon caliber compatibility, stabilization technology, integration capability, contract value, local manufacturing presence, aftersales support, lifecycle cost)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elbit Systems
Rheinmetall Defence
Leonardo
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
Saab AB
Thales Group
General Dynamics Land Systems
EOS Defence Systems
Moog Inc.
Denel Land Systems
Aselsan
Northrop Grumman
Hanwha Defense
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035