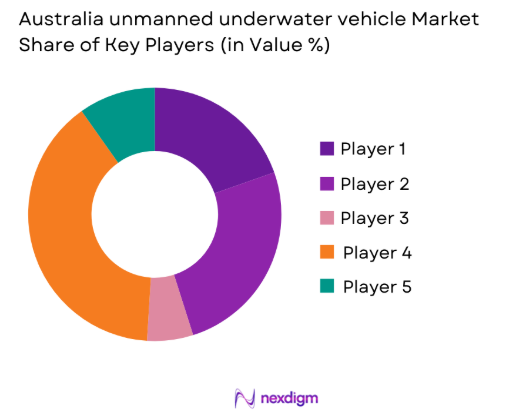
Market Overview
The Australia unmanned underwater vehicle market current size stands at around USD ~ million with active deployments exceeding ~ units across defense and commercial operations. Fleet utilization intensity increased by over 15 percent driven by maritime surveillance, seabed mapping, and inspection activities. Platform replacement cycles average 6 to 8 years, supporting stable procurement momentum. Autonomous mission hours expanded beyond ~ operational hours annually due to endurance improvements. Sensor integration density increased by nearly 20 percent as payload modularity improved. Operational readiness remains high across coastal and offshore zones supported by domestic integration capabilities.
Australia’s market concentration is strongest along Western Australia and Queensland due to offshore energy assets, naval infrastructure, and subsea research clusters. Defense installations and port cities dominate demand owing to surveillance, training, and inspection needs. Mature shipbuilding ecosystems and subsea engineering capabilities support localized integration. Regulatory clarity surrounding autonomous maritime operations enables controlled deployment. Academic and industrial collaboration further strengthens ecosystem maturity. Remote coastline monitoring requirements sustain long-term demand consistency.
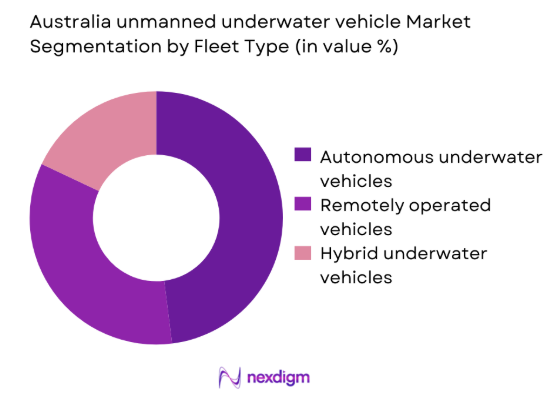
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
Autonomous underwater vehicles dominate deployments due to extended endurance, lower operational risk, and increasing autonomy levels. Remotely operated vehicles remain relevant for intervention-heavy missions requiring real-time control and visual feedback. Hybrid platforms are gaining adoption for dual-use missions combining survey and intervention capabilities. Fleet modernization programs favor modular architectures enabling rapid payload swaps. Defense agencies increasingly prioritize autonomous fleets for persistent surveillance. Commercial operators favor hybrid fleets for offshore inspection flexibility. Technological advancements in navigation and obstacle avoidance continue reshaping fleet composition preferences.
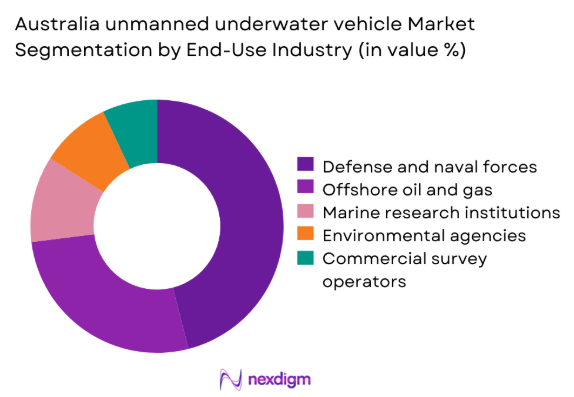
By End-Use Industry
Defense and naval applications dominate demand due to continuous maritime security requirements and surveillance operations. Offshore energy remains the second-largest user driven by subsea inspection and asset integrity monitoring. Marine research institutions contribute steady demand through oceanographic and environmental programs. Environmental agencies utilize systems for habitat assessment and pollution monitoring. Commercial survey operators support infrastructure planning and seabed mapping. Growing offshore renewable projects are increasing adoption across non-defense sectors.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by established global manufacturers supported by local integration partners. Market positioning depends on platform reliability, endurance performance, and mission adaptability. Companies focus on technology differentiation, service responsiveness, and regulatory compliance. Strategic partnerships with defense agencies and offshore operators strengthen market presence. Competition remains moderate with emphasis on innovation and lifecycle support.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Kongsberg Maritime | 1814 | Norway | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab AB | 1937 | Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Technologies | 1895 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Teledyne Marine | 1960 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Australia unmanned underwater vehicle Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization and maritime security programs
Naval modernization initiatives are expanding investment in autonomous underwater platforms supporting surveillance and maritime domain awareness. Increased patrol requirements across extended coastlines are driving sustained demand for persistent underwater monitoring solutions. Defense agencies prioritize autonomous capabilities to reduce operational risk and manpower dependency. Integration of unmanned systems enhances mine countermeasure effectiveness and reconnaissance precision. Strategic defense programs emphasize interoperability between surface and subsurface assets. Technological upgrades in navigation systems improve mission accuracy and endurance. Fleet expansion aligns with regional maritime security cooperation objectives. Training programs increasingly incorporate unmanned systems for operational readiness. Modernization budgets favor scalable and modular platform architectures. Long-term defense planning sustains continuous procurement momentum.
Expansion of offshore energy exploration activities
Offshore energy exploration continues expanding, requiring reliable underwater inspection and survey capabilities. Unmanned systems support pipeline inspection, seabed mapping, and structural integrity assessments. Increased offshore drilling depth necessitates advanced autonomous navigation and sensing capabilities. Operators favor unmanned platforms to reduce human exposure and operational risk. Survey frequency has increased with stricter environmental compliance requirements. Autonomous systems improve data collection efficiency across extended subsea assets. Integration with digital twins enhances predictive maintenance planning. Energy operators value rapid deployment and reduced downtime. Offshore developments in remote regions strengthen demand for autonomous operations. Sustained exploration activity supports long-term system adoption.
Challenges
High system acquisition and maintenance costs
Unmanned underwater vehicle systems involve significant upfront capital investment for platforms and sensors. Advanced navigation, propulsion, and communication technologies increase procurement complexity. Maintenance requires specialized technical expertise and certified service infrastructure. Spare parts availability can extend downtime for mission-critical operations. High lifecycle costs limit adoption among smaller commercial operators. Budget constraints affect fleet expansion decisions across non-defense sectors. Customization requirements further elevate integration expenses. Limited local manufacturing increases dependency on imported components. Training costs add to overall ownership expenditure. Cost sensitivity remains a barrier for wider commercialization.
Limited underwater communication bandwidth
Underwater communication remains constrained by acoustic signal limitations and environmental interference. Data transmission speeds are significantly lower than surface or aerial systems. Real-time control becomes challenging during deep-sea operations. Signal attenuation affects reliability across long mission ranges. Communication delays restrict high-resolution data streaming capabilities. Environmental noise impacts command accuracy and mission coordination. Hybrid communication systems increase system complexity and cost. Limited bandwidth restricts autonomous decision-making efficiency. Operators rely on post-mission data retrieval for analysis. These constraints hinder full autonomy deployment in complex environments.
Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous mine countermeasure programs
Rising maritime security concerns increase demand for autonomous mine detection and neutralization systems. Naval forces prioritize unmanned solutions to reduce personnel exposure during high-risk missions. Autonomous platforms enable persistent surveillance of strategic waterways. Technological advances improve detection accuracy and classification capabilities. Integration with command systems enhances operational responsiveness. Increased defense collaboration accelerates technology adoption across allied forces. Autonomous mine countermeasure programs receive sustained funding support. Interoperability standards facilitate multinational operations. Growing emphasis on rapid deployment strengthens demand for portable systems. Long-term security strategies favor autonomous underwater assets.
Growing offshore wind and subsea inspection demand
Offshore wind farm development creates demand for regular seabed and foundation inspections. Unmanned underwater vehicles provide cost-effective monitoring of underwater infrastructure. Expansion of renewable energy projects increases inspection frequency requirements. Autonomous systems reduce reliance on crewed vessels and divers. High-resolution imaging supports structural integrity assessments. Environmental monitoring around installations drives additional deployment needs. Integration with digital monitoring platforms enhances operational efficiency. Renewable energy policies support sustained offshore infrastructure growth. Service providers adopt unmanned solutions to improve scalability. This trend strengthens long-term commercial market potential.
Future Outlook
The Australia unmanned underwater vehicle market is expected to experience sustained technological advancement driven by defense modernization and offshore energy expansion. Increasing autonomy, improved endurance, and enhanced sensor integration will shape future deployments. Regulatory clarity and growing acceptance of autonomous operations will further support market development. Collaborative programs between government and industry are likely to accelerate innovation. Overall market momentum remains positive through the forecast period.
Major Players
- Kongsberg Maritime
- Saab AB
- L3Harris Technologies
- Teledyne Marine
- Thales Group
- Atlas Elektronik
- Exail
- General Dynamics Mission Systems
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing Defense
- Fugro
- Ocean Infinity
- Anduril Industries
- Austal
- SeeByte
Key Target Audience
- Naval defense agencies
- Offshore oil and gas operators
- Offshore wind farm developers
- Marine research organizations
- Port and harbor authorities
- Environmental monitoring agencies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Australian Department of Defence and maritime regulators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market scope, platform classifications, application areas, and operational environments were defined to establish analytical boundaries. Data points were structured around deployment trends and technology adoption patterns.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation frameworks were developed using fleet type, end-use, and operational roles. Quantitative and qualitative indicators were aligned to reflect industry-specific dynamics.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts, operators, and technical specialists were consulted to validate assumptions and refine market behavior interpretations.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated through triangulation, ensuring consistency across data inputs, assumptions, and market behavior analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope for unmanned underwater vehicles in Australia, platform and mission-based segmentation framework, bottom-up fleet and deployment-based market sizing, revenue attribution across defense and commercial contracts, primary interviews with naval operators and offshore service providers, triangulation using procurement data and OEM disclosures, assumption modeling for mission endurance and replacement cycles)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and integration landscape
- Regulatory and maritime compliance environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising naval modernization and maritime security programs
Expansion of offshore energy exploration activities
Growing demand for autonomous seabed mapping
Technological advancements in navigation and endurance
Increasing defense spending on unmanned systems - Challenges
High system acquisition and maintenance costs
Limited underwater communication bandwidth
Operational complexity in deep-sea environments
Regulatory constraints on autonomous maritime systems
Dependence on skilled operators and technicians - Opportunities
Expansion of autonomous mine countermeasure programs
Growing offshore wind and subsea inspection demand
Integration of AI-based navigation and sensing
Public–private partnerships in marine research
Export potential for Australian-developed UUV platforms - Trends
Shift from remotely operated to fully autonomous systems
Increased use of swarm and collaborative UUVs
Integration of AI and machine learning for navigation
Growing use of modular payload architectures
Rising adoption of dual-use civilian–defense platforms - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base or Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
Remotely Operated Vehicles
Hybrid UUVs - By Application (in Value %)
Mine countermeasures
Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
Seabed mapping and hydrography
Offshore energy inspection
Environmental monitoring
Search and recovery - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Tethered systems
Untethered autonomous systems
Hybrid communication systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and naval forces
Offshore oil and gas
Marine research institutions
Commercial survey operators
Environmental agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Acoustic communication
Fiber-optic tethered communication
Hybrid acoustic-optical communication - By Region (in Value %)
Western Australia
Northern Territory
Queensland
New South Wales
Victoria
Other coastal regions
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (product portfolio breadth, depth rating capability, endurance and range, autonomy level, sensor integration, pricing strategy, after-sales support, local partnerships)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Kongsberg Maritime
Saab AB
L3Harris Technologies
Teledyne Marine
Atlas Elektronik
Exail (ECA Group)
Bluefin Robotics (General Dynamics)
Boeing Defense
Lockheed Martin
Thales Group
Fugro
Ocean Infinity
Anduril Australia
Austal
SeeByte
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base or Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035