Market Overview
The Europe Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained institutional procurement, multi-mission platform development, and expanding launch service pipelines across civil, defense, and commercial programs. Capital intensity remains high due to qualification cycles, systems engineering depth, and compliance frameworks, while program lifecycles emphasize reliability, mission assurance, and sovereign access to space. Industrial clustering, vertically integrated production, and long-term framework contracts continue to shape procurement stability and capacity planning across manufacturing and launch segments.
France, Germany, and the United Kingdom anchor demand concentration due to dense aerospace clusters, launch infrastructure access, and mission integration ecosystems. Southern Europe contributes propulsion, structures, and launch site operations, while Nordic hubs support small launch systems and spaceport development. Policy-driven mission pipelines, resilient supply networks, and mature integrator ecosystems reinforce regional specialization. Coordinated institutional programs, dual-use demand, and standardized platform adoption accelerate cross-border collaboration, while certification regimes and security clearances shape vendor participation and deployment readiness.
Market Segmentation
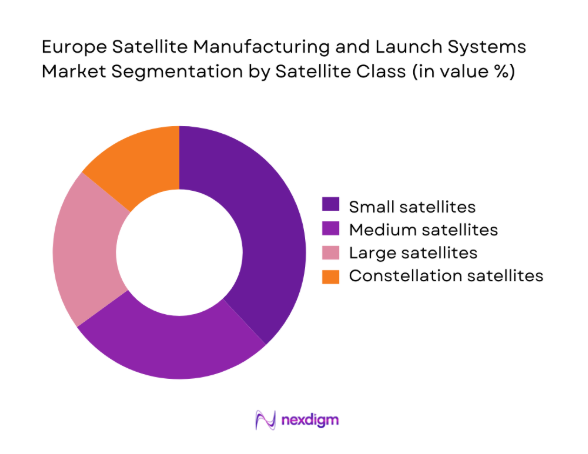
By Satellite Class
Demand concentration is strongest in small and medium satellites due to rapid constellation deployment, shorter production cycles, and standardized bus architectures. Constellation satellites benefit from batch manufacturing efficiencies and payload modularity, enabling accelerated cadence and mission diversification across connectivity, observation, and security applications. Large satellites remain central for high-throughput communications and strategic missions, requiring longer qualification timelines and bespoke payload integration. Platform commonality, electric propulsion adoption, and software-defined payloads favor scalable classes, while supply chain resilience and component qualification favor classes with repeatable production. Institutional procurement sustains large platforms, whereas commercial programs prioritize cadence, reliability, and flexible launch pairing across orbit profiles.
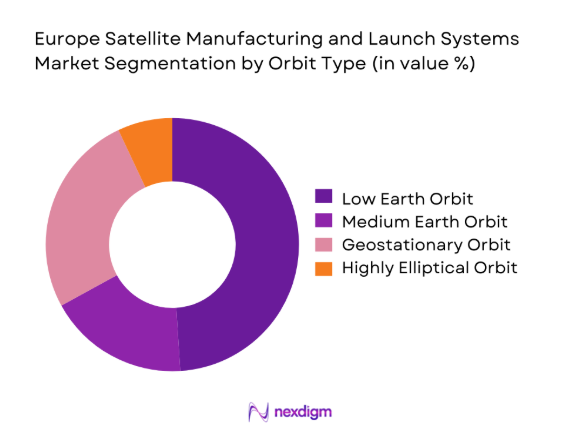
By Orbit Type
Low Earth Orbit dominates due to constellation economics, lower launch energy requirements, and rapid refresh cycles supporting connectivity and observation. Medium Earth Orbit supports navigation and timing missions with stable replenishment needs, while Geostationary Orbit sustains high-capacity communications and strategic payloads with extended lifecycles. Highly Elliptical Orbit serves niche coverage requirements, driving specialized mission design and launch planning. Manufacturing strategies increasingly optimize for LEO cadence through standardized buses and payload interfaces, while launch pairing strategies prioritize rideshare efficiency and dedicated small launch access. Policy emphasis on resilient architectures reinforces multi-orbit diversification, aligning manufacturing throughput with launch manifest stability and mission assurance requirements.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features vertically integrated manufacturers, launch service providers, and subsystem specialists aligned with institutional mission pipelines and commercial constellation programs. Competitive positioning reflects manufacturing throughput, launch reliability, certification depth, and program backlog visibility, with ecosystem partnerships supporting payload integration and mission assurance.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 2000 | Toulouse, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Alenia Space | 2007 | Cannes, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Arianespace | 1980 | Évry-Courcouronnes, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| OHB SE | 1981 | Bremen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Avio | 1912 | Colleferro, Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Europe Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of European sovereign space capabilities
Institutional programs increased mission authorizations across 2022 to 2025, with 12 new multi-year capability roadmaps approved and 46 mission definitions advanced into preliminary design review. National agencies expanded launch cadence planning from 6 to 10 annual institutional missions, while 18 sovereign payloads entered qualification pipelines. Export control frameworks were updated across 2023 and 2024, reducing license processing timelines by 30 days on average. Workforce pipelines added 4200 certified technicians and systems engineers across manufacturing hubs. Spaceport readiness milestones advanced across 4 coastal sites, enabling 28 additional integration windows annually and strengthening autonomous access.
Rising demand for LEO broadband constellations
Between 2022 and 2025, mission filings for LEO networks increased by 210 orbital plane submissions, with 184 payloads completing environmental testing and 96 entering final integration. Spectrum coordination cases processed annually reached 64, accelerating constellation deployment readiness. Manufacturing lines expanded takt time from 14 to 9 days per unit across standardized buses, while avionics qualification cycles shortened by 22 days through digital verification. Launch manifests incorporated 31 dedicated small-launch windows annually, complemented by 54 rideshare opportunities. Ground segment readiness added 120 gateway sites, enabling service activation alignment with deployment cadence.
Challenges
High development and qualification costs for launch systems
From 2022 to 2025, propulsion qualification campaigns required 26 hot-fire sequences per engine family, with 9 design iterations to meet reliability thresholds. Materials certification extended component lead times by 18 weeks due to non-destructive testing requirements across 7 standards. Test infrastructure availability constrained schedules, with 3 national test centers operating at 92 utilization, creating queue delays of 41 days. Safety case approvals required 14 distinct dossiers per vehicle configuration, while flight readiness reviews averaged 11 review boards. Workforce certification cycles added 180 training hours per technician, limiting rapid scale-up across parallel vehicle programs.
Limited launch cadence and schedule reliability constraints
Launch site throughput between 2022 and 2025 supported 22 windows annually, while weather and range conflicts caused 8 reschedules per year on average. Vehicle integration flow required 17 critical path handoffs, increasing sensitivity to supplier delays of 12 days per occurrence. Range safety modernization introduced 5 new compliance gates, extending pre-launch readiness by 21 days. Payload readiness mismatches led to 14 manifest reshuffles, disrupting constellation phasing. Propellant logistics required 6 coordinated supply approvals per campaign, while ground segment coordination across 9 entities added synchronization risk and compressed operational buffers.
Opportunities
Growth of European smallsat constellations for IoT and EO
Between 2022 and 2025, 73 institutional and commercial mission concepts progressed to system requirements review, with 58 payloads completing thermal vacuum campaigns. Regulatory filings approved 41 frequency assignments, enabling phased constellation activation. Manufacturing automation expanded line capacity by 3 parallel streams, supporting 180 units per year without yield loss. Launch pairing optimized 24 dedicated missions with 36 rideshare allocations, improving orbital plane coverage density. Ground segment interoperability added 14 standardized interfaces, reducing commissioning time by 19 days per mission and enabling faster service activation for logistics, agriculture, and maritime monitoring use cases.
Development of reusable and partially reusable launch vehicles
Reusable stage demonstrations completed 27 recovery trials across 2023 to 2025, achieving 19 successful recoveries with refurbishment cycles reduced to 32 days. Guidance and control software iterations improved landing dispersion by 45 meters across 11 test flights. Structural fatigue life testing validated 8 reflight cycles per stage, while thermal protection inspections reduced turnaround checks by 14 steps. Range coordination frameworks approved 6 recovery corridors, expanding mission planning flexibility. Ground operations digitization cut integration labor hours by 120 per campaign, enabling higher cadence readiness and improved schedule resilience for responsive access missions.
Future Outlook
Through 2035, policy-backed mission pipelines, constellation deployment cycles, and advances in reusable launch systems are expected to reinforce sovereign access and commercial cadence. Manufacturing will continue shifting toward standardized platforms and digital verification, while multi-orbit architectures and responsive launch planning will shape resilient deployment strategies across civil, defense, and commercial missions.
Major Players
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Thales Alenia Space
- Arianespace
- Avio
- OHB SE
- Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd
- RUAG Space
- GMV
- Exotrail
- Isar Aerospace
- Rocket Factory Augsburg
- PLD Space
- Skyrora
- Orbex
- D-Orbit
Key Target Audience
- Satellite operators and constellation owners
- Launch service procurement teams
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names such as European Space Agency and national space agencies
- Defense ministries and space commands
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Satellite subsystem suppliers
- Ground segment and mission operations providers
- Spaceport operators and range authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were defined across satellite classes, orbit profiles, mission types, launch vehicle configurations, integration workflows, and regulatory gates. Demand drivers, qualification cycles, and supply chain constraints were mapped to operational milestones. Institutional mission pipelines and commercial constellation phasing informed variable prioritization.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Manufacturing throughput, integration cadence, and launch manifest capacity were constructed using operational indicators from 2024 and 2025. Scenario frameworks aligned production takt times with launch window availability and regulatory readiness. Sensitivity testing assessed impacts of test infrastructure utilization and range coordination constraints.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on cadence scalability, reusability readiness, and platform standardization were validated through expert workshops with systems engineers, mission planners, and compliance leads. Iterative reviews refined assumptions on qualification bottlenecks, workforce readiness, and supply chain resilience across propulsion and avionics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into integrated manufacturing–launch system pathways aligned to multi-orbit deployment strategies. Cross-functional insights were consolidated to ensure coherence between regulatory readiness, operational cadence, and mission assurance. Final outputs emphasize actionable pathways for scalable production and reliable launch access.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and satellite manufacturing and launch system taxonomy, OEM and launch service provider primary interviews, ESA and national space agency procurement analysis, Launch cadence and manifest tracking, Satellite production capacity and backlog assessment, Regulatory and export control review, Competitive intelligence from financial filings and contracts)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Mission and application pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and industrial base structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of European sovereign space capabilities
Rising demand for LEO broadband constellations
Increased Earth observation programs for climate and security
Public funding through ESA and national space programs
Commercialization of small satellite missions
Growth of in-orbit services and responsive launch demand - Challenges
High development and qualification costs for launch systems
Limited launch cadence and schedule reliability constraints
Dependence on public funding cycles and political priorities
Supply chain bottlenecks in propulsion and avionics
Export control and ITAR-related compliance burdens
Competition from non-European launch providers - Opportunities
Growth of European smallsat constellations for IoT and EO
Development of reusable and partially reusable launch vehicles
Expansion of commercial rideshare and dedicated small launch services
Public-private partnerships for sovereign launch access
Emergence of in-orbit servicing and manufacturing missions
Increased defense-driven demand for resilient space architectures - Trends
Shift toward LEO constellations and mass satellite production
Investments in reusable launch technologies
Vertical integration by satellite OEMs and launch providers
Standardization of satellite platforms and buses
Increased use of electric propulsion and advanced materials
Digitalization of manufacturing and mission operations - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Satellite Class (in Value %)
Small satellites
Medium satellites
Large satellites
Constellation satellites - By Orbit Type (in Value %)
Low Earth Orbit
Medium Earth Orbit
Geostationary Orbit
Highly Elliptical Orbit - By Application (in Value %)
Earth observation
Telecommunications and broadband
Navigation and timing
Science and exploration
Defense and security - By Launch Vehicle Type (in Value %)
Small launch vehicles
Medium-lift launch vehicles
Heavy-lift launch vehicles
Rideshare launch services - By End User (in Value %)
Government and defense
Commercial operators
Scientific and research institutions - By Country (in Value %)
France
Germany
United Kingdom
Italy
Spain
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (launch success rate, manufacturing throughput, payload capacity range, cost per kilogram to orbit, reusability maturity, program backlog, geographic footprint, government contract exposure)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Airbus Defence and Space
Thales Alenia Space
Arianespace
Avio
OHB SE
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd
RUAG Space
GMV
Exotrail
Isar Aerospace
Rocket Factory Augsburg
PLD Space
Skyrora
Orbex
D-Orbit
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035


