Market Overview
The Europe Small Satellite market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a maturing ecosystem anchored by commercial constellations, institutional programs, and defense-driven missions. Investment flows, contract pipelines, and procurement frameworks continue to shape deployment cadence across observation, communications, and technology demonstration missions. Platform standardization, modular payload architectures, and rideshare access underpin manufacturing scalability. The market structure is influenced by constellation replenishment cycles, mission reliability requirements, and long-term service commitments.
Northern and Western European hubs dominate activity due to dense aerospace clusters, advanced manufacturing infrastructure, and proximity to launch access partnerships. Key cities benefit from established prime contractors, specialized subsystem suppliers, and deep venture ecosystems supporting payload analytics, propulsion, and ground segment software. Policy environments emphasize sovereign capability, spectrum coordination, debris mitigation, and export controls, reinforcing ecosystem maturity. Regional demand concentrates around Earth observation analytics, secure communications, maritime surveillance, and climate monitoring, supported by multi-year public programs and commercial service integrators.
Market Segmentation
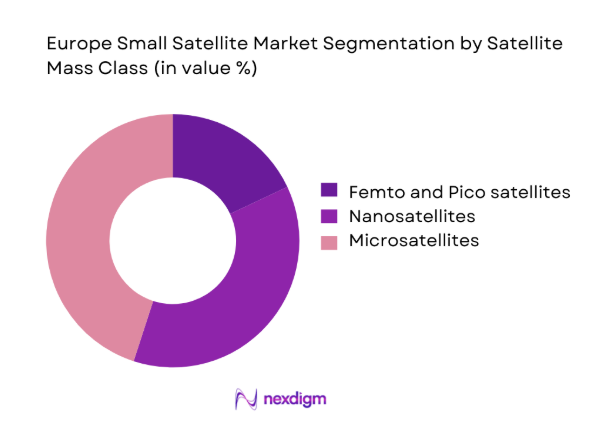
By Satellite Mass Class
Microsatellites dominate deployment preferences due to higher payload capacity, longer mission lifetimes, and improved power budgets for advanced sensors and software-defined radios. Nanosatellites retain strong relevance for constellation densification, rapid technology validation, and responsive missions, benefiting from standardized form factors and lower integration complexity. Pico and femto platforms primarily serve education-aligned technology demonstration and niche sensing use cases, with limited endurance and constrained payload envelopes. Procurement increasingly favors modular microsatellite buses for sovereign observation and secure communications, while nanosatellite clusters support latency-sensitive connectivity and revisit frequency requirements across maritime and environmental monitoring missions.
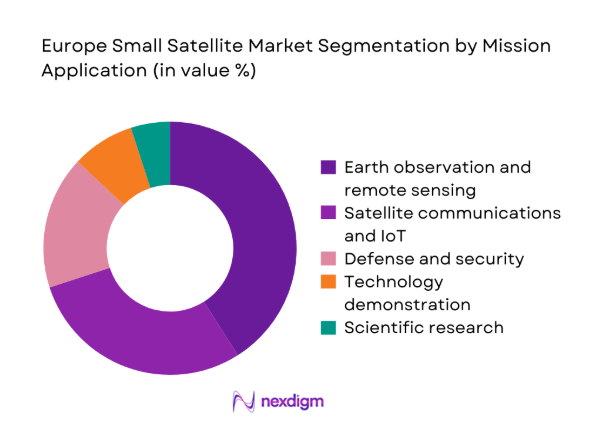
By Mission Application
Earth observation leads demand as governments and commercial operators prioritize climate monitoring, maritime domain awareness, and infrastructure analytics. Communications and IoT missions follow, driven by latency-sensitive connectivity for logistics, energy assets, and remote operations. Defense and security applications remain a consistent driver for sovereign surveillance and resilient communications, reinforcing demand for higher-performance payloads. Technology demonstration continues to anchor early adoption of reconfigurable radios, green propulsion, and onboard processing. Scientific missions support space weather and atmospheric studies, often catalyzing subsystem innovation that transitions into commercial platforms over successive deployment cycles.
Competitive Landscape
Competition centers on vertically integrated platform providers, constellation operators, and subsystem specialists that enable rapid manufacturing, responsive launch integration, and mission assurance. Differentiation is shaped by platform standardization, payload integration depth, regulatory readiness, and post-launch service capabilities across operations and analytics.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 1970 | Toulouse, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Alenia Space | 2005 | Cannes, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| OHB SE | 1981 | Bremen, Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd | 1985 | Guildford, UK | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AAC Clyde Space | 2005 | Uppsala, Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Europe Small Satellite Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Earth observation and climate monitoring programs
Public agencies expanded observation tasking following 2023 floods and wildfires, increasing orbital asset utilization across coastal surveillance, hydrology, and agriculture monitoring. National meteorological services integrated 2024 satellite-derived datasets into operational forecasting, supported by 48 processing nodes and 12 cross-border data corridors. Environmental directives enacted in 2025 mandated persistent coverage of 6 critical basins, accelerating constellation densification. Institutional procurement cycles shortened from 24 months to 14 months, enabling faster replenishment. Ground segment upgrades added 320 edge-compute units across ports and inland hubs, improving revisit latency for emergency response coordination and compliance monitoring workflows.
Rising demand for low-latency connectivity and IoT backhaul
Maritime logistics digitization accelerated in 2024 with 2100 vessel terminals onboarded to satellite IoT links across North Sea routes. Energy operators deployed 680 remote sensors on offshore assets to enable predictive maintenance and incident reporting. Transport authorities connected 95 intermodal nodes to low-latency backhaul for real-time telemetry. Cross-border roaming frameworks finalized in 2025 harmonized spectrum usage across 14 administrations, reducing integration delays. Ground gateway expansion added 27 sites to improve coverage continuity, while onboard processing upgrades enabled adaptive routing for latency-sensitive telemetry and emergency communications across sparse coverage corridors.
Challenges
Spectrum congestion and regulatory approval delays
Coordination backlogs intensified in 2024 as 19 national regulators processed filings across shared bands, extending average authorization cycles to 11 months. Interference incidents recorded by monitoring agencies increased to 146 events, prompting additional coordination requirements across neighboring administrations. Licensing harmonization progressed unevenly, with only 9 authorities aligning procedures by 2025. Ground station siting approvals faced zoning constraints in 23 municipalities, delaying gateway activation. Compliance audits expanded documentation requirements by 38 fields per application, increasing operator burden and slowing constellation expansion timelines amid crowded orbital environments and coordination complexity.
Launch schedule uncertainty and capacity bottlenecks
Rideshare manifest changes in 2023 affected 31 missions, causing cascading delays across integration calendars. Weather-related scrubs reached 17 events in 2024 across northern launch corridors, disrupting deployment windows for time-sensitive payloads. Dedicated small launch capacity remained constrained, with 6 vehicles grounded for extended inspections following range safety reviews. Insurance underwriting tightened after 4 partial mission failures, increasing compliance checks before payload integration. Ground readiness windows narrowed to 72 hours, increasing logistical strain for payload transport and pre-launch testing, elevating risk for tightly sequenced constellation deployments.
Opportunities
Growth of sovereign European constellations for EO and comms
Policy frameworks enacted in 2024 prioritized sovereign coverage for border surveillance and critical infrastructure monitoring across 21 administrations. Budget appropriations authorized multi-year procurement cycles supporting 8 thematic mission portfolios, enabling stable replenishment planning. Interoperability standards published in 2025 unified data formats across 5 civil agencies and 3 defense commands, improving cross-mission tasking. Shared ground segment upgrades added 14 federated processing centers, reducing latency for multi-constellation fusion. Cooperative procurement consortia formed among 7 member states to pool launch access and integration resources, improving deployment cadence and resilience.
Commercialization of in-orbit servicing and hosted payloads
Demonstration missions in 2023 validated proximity operations across 4 servicing maneuvers, enabling refueling and inspection concepts for small platforms. Regulatory guidance issued in 2024 clarified licensing for hosted payload operations across 6 jurisdictions, reducing approval cycles. Hosted sensors onboarded 22 experimental payloads supporting climate analytics and maritime safety. Docking interface standards published in 2025 improved cross-platform compatibility for life-extension services. Ground operations centers added 9 dedicated service control rooms to manage rendezvous procedures, expanding serviceable mission classes and reducing replacement frequency for modular payload architectures.
Future Outlook
The market outlook through 2035 reflects sustained deployment of multi-mission constellations, growing emphasis on sovereign capability, and deeper integration of software-defined payloads. Regulatory convergence, improved launch access, and standardized platforms will support faster replenishment cycles. Collaboration across civil, defense, and commercial programs is expected to stabilize demand and strengthen ecosystem resilience.
Major Players
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Thales Alenia Space
- OHB SE
- Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd
- AAC Clyde Space
- GomSpace
- Exotrail
- Spire Global
- ICEYE
- Planet Labs
- Isar Aerospace
- Rocket Factory Augsburg
- Skyrora
- PLD Space
- D-Orbit
Key Target Audience
- Satellite constellation operators and service integrators
- Earth observation analytics providers
- Defense and intelligence procurement agencies
- Telecommunications operators and IoT service providers
- Launch service aggregators and mission integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
- Insurance and risk underwriting entities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Program mandates, orbital regimes, payload classes, and regulatory constraints are mapped to define scope and comparability. Manufacturing readiness, ground segment maturity, and launch access dependencies are identified to frame system boundaries. Policy objectives and mission assurance requirements inform variable selection.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Mission pipelines, procurement calendars, and deployment cadences are synthesized into an integrated analytical model. Platform architectures and integration workflows are aligned with regulatory and spectrum conditions. Scenario structures reflect constellation replenishment cycles and operational dependencies across regions.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational assumptions are stress-tested through practitioner inputs from engineering, licensing, and operations functions. Regulatory interpretations and coordination pathways are validated with institutional stakeholders. Deployment constraints and ground segment readiness are triangulated to refine scenario robustness.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are consolidated into decision-ready narratives aligned to buyer use cases and policy priorities. Comparative frameworks translate operational realities into strategic implications. Outputs are structured to support procurement planning, partnership evaluation, and long-term program design.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and small satellite classes and mission typologies, European operator and constellation mapping, Payload and platform BOM cost modeling, Launch access and rideshare capacity assessment, Spectrum allocation and licensing analysis, Supply chain and manufacturing capacity benchmarking, Contract pipeline and procurement tracking)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Earth observation and climate monitoring programs
Rising demand for low-latency connectivity and IoT backhaul
Government funding for sovereign space capabilities
Cost reductions in smallsat manufacturing and integration
Growth of European launch access and rideshare opportunities
Increased defense and security surveillance requirements - Challenges
Spectrum congestion and regulatory approval delays
Launch schedule uncertainty and capacity bottlenecks
Radiation resilience and reliability constraints for COTS components
Debris mitigation and space traffic management compliance
Fragmented demand and limited long-term procurement visibility
Supply chain constraints for avionics and radiation-hardened parts - Opportunities
Growth of sovereign European constellations for EO and comms
Commercialization of in-orbit servicing and hosted payloads
Expansion of maritime, agriculture, and energy monitoring services
Dual-use programs bridging civil and defense demand
Emerging small launch vehicles improving mission flexibility
Public-private partnerships for constellation deployment - Trends
Shift toward larger microsatellites for higher payload capacity
Adoption of software-defined payloads and reconfigurable radios
Constellation architectures with rapid replenishment cycles
Use of additive manufacturing and digital twins in production
Increased standardization of satellite buses
Focus on green propulsion and deorbit compliance - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Satellite Mass Class (in Value %)
Femto and Pico satellites
Nanosatellites
Microsatellites - By Orbit Regime (in Value %)
Low Earth Orbit
Medium Earth Orbit
Highly Elliptical Orbit
Geostationary Transfer and Low GEO - By Mission/Application (in Value %)
Earth observation and remote sensing
Satellite communications and IoT
Navigation augmentation and timing
Technology demonstration and in-orbit validation
Scientific research and space weather
Defense and security - By End Use Sector (in Value %)
Commercial enterprises
Government and civil agencies
Defense and intelligence organizations
Academic and research institutions - By Platform Architecture (in Value %)
Standardized CubeSat platforms
Modular microsatellite buses
Custom mission-specific platforms - By Launch Mode (in Value %)
Rideshare launches
Dedicated small launch vehicles
In-orbit deployment from stations and carriers
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (manufacturing scale, platform standardization, payload integration capability, mission success rate, cost per kilogram to orbit, vertical integration depth, regulatory compliance readiness, constellation deployment experience)
SWOT Analysis of Key Players
Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Airbus Defence and Space
Thales Alenia Space
OHB SE
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd
AAC Clyde Space
GomSpace
Exotrail
Spire Global
ICEYE
Planet Labs
Isar Aerospace
Rocket Factory Augsburg
Skyrora
PLD Space
D-Orbit
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


