Market Overview
The Europe Turboprop Aircraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a mature but actively renewing fleet environment shaped by regional connectivity needs, sustainability objectives, and airline network optimization. Demand is supported by steady replacement of aging aircraft, increasing utilization on short-haul routes, and modernization of special mission fleets. Procurement cycles are influenced by regulatory compliance requirements, lifecycle management priorities, and long-term fleet planning strategies across commercial, cargo, and government operators within Europe’s diverse operating environments.
Operational activity is concentrated across Western and Northern Europe, with strong utilization around major regional hubs and secondary cities supported by dense airport networks and intermodal connectivity. Countries with extensive regional airline ecosystems, established MRO infrastructure, and advanced certification bodies demonstrate higher deployment intensity. Government-supported regional connectivity programs and public service obligation routes reinforce turboprop relevance in peripheral regions. Mature leasing markets, financing availability, and a skilled maintenance workforce further strengthen adoption across developed aviation clusters.
Market Segmentation
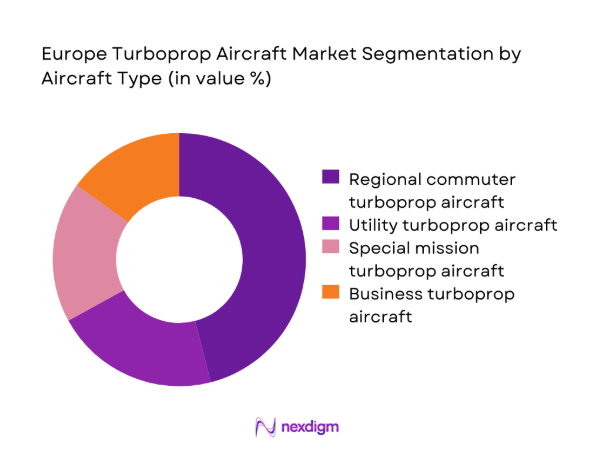
By Aircraft Type
Regional commuter turboprop aircraft dominate deployment due to route economics, fuel efficiency on short sectors, and suitability for high-frequency services linking secondary cities. Utility and special mission turboprops maintain consistent demand from border surveillance, maritime patrol, medical evacuation, and training fleets operated by government agencies. Business turboprops retain niche relevance for executive travel and charter operations serving low-density routes and remote locations. Fleet commonality preferences, mission flexibility, and lifecycle serviceability influence operator choices across types. Replacement of legacy commuter aircraft is the primary contributor to volume stability, while special mission conversions support sustained aftermarket activity.
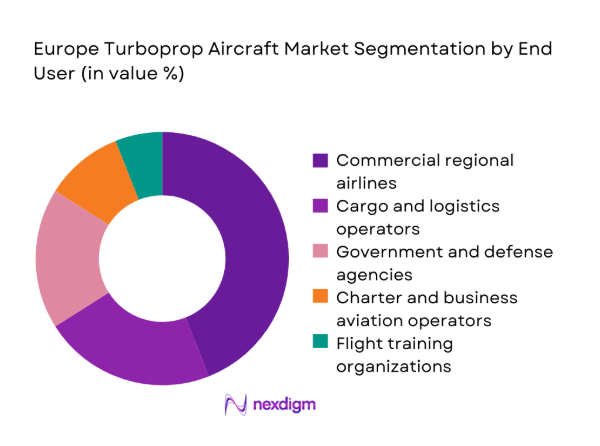
By End User
Commercial regional airlines account for the largest share of turboprop utilization due to route optimization on thin, short-haul corridors and constrained airport infrastructure. Cargo and express logistics operators leverage turboprops for feeder services connecting regional nodes to primary hubs, supporting e-commerce growth and time-definite deliveries. Government and defense agencies maintain steady procurement for surveillance, patrol, and transport missions, while charter operators support seasonal tourism demand. Flight training organizations sustain baseline demand for multi-engine turboprop platforms. Procurement decisions are shaped by mission profiles, fleet harmonization goals, and long-term maintenance support availability.
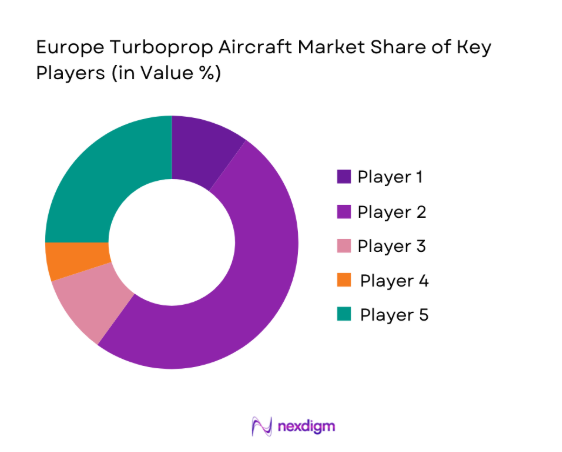
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a concentrated OEM structure supported by a broad ecosystem of engine suppliers, avionics providers, and certified MRO networks. Market positioning is shaped by fleet renewal programs, long-term service agreements, financing support, and regulatory compliance capabilities across Europe’s diverse operating environments.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ATR | 1981 | Toulouse, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| De Havilland Canada | 1928 | Toronto, Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Pilatus Aircraft | 1939 | Stans, Switzerland | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Textron Aviation | 2014 | Wichita, United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Daher | 1863 | Paris, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Europe Turboprop Aircraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising demand for short-haul regional connectivity
Short-haul regional connectivity remains structurally important across Europe due to fragmented geography and peripheral population centers. In 2024, Europe recorded 432 commercial airports with scheduled services, supporting dense intercity networks. Around 178 secondary airports handle fewer than 1,000,000 passengers annually, where turboprops maintain route viability. In 2025, regional airlines operated 6,400 weekly departures under public service obligation frameworks across remote regions. Rail alternatives remain limited in mountainous and island territories spanning 14 countries. Aviation authorities approved 92 new regional routes in 2024, sustaining aircraft utilization across short sectors while maintaining connectivity standards for healthcare, tourism, and essential mobility.
Airline network optimization on thin routes
Network optimization strategies increasingly prioritize right-sized capacity on thin routes to stabilize load factors. In 2024, 312 city pairs across Europe recorded average daily demand below 220 passengers, favoring turboprop deployment. Regional carriers reported average stage lengths of 420 kilometers on feeder routes during 2025 operations, aligning with turboprop performance envelopes. Slot-constrained hubs across 9 countries encouraged redistribution to secondary airports. Air navigation service providers recorded 18,600 daily regional movements in 2024, with turboprops supporting frequency over capacity. Regulatory authorities approved 64 seasonal network reconfigurations in 2025, enabling carriers to maintain connectivity without oversupplying low-density corridors.
Challenges
Competition from high-speed rail on short sectors
High-speed rail expansion directly competes with turboprop routes on dense corridors. By 2024, Europe operated 11,300 kilometers of high-speed rail, connecting 23 metropolitan regions. Passenger rail volumes exceeded 1,200,000,000 annual trips in 2025, diverting short-haul aviation demand. In 2024, 47 regional air routes under 500 kilometers experienced suspension following rail timetable enhancements. National transport agencies in 7 countries implemented intermodal substitution policies prioritizing rail under 3-hour travel times. Airport authorities reported 128 slot reassignments to longer-haul services during 2025, reducing turboprop frequency on trunk regional corridors while compressing feeder network density.
Volatility in airline profitability and fleet investment cycles
Airline profitability volatility constrains fleet planning cycles for regional operators. In 2024, 62 European regional carriers reported negative operating margins for at least two quarters, delaying fleet renewal commitments. Aircraft utilization fluctuated between 7 and 9 block hours daily across 2025, creating uncertainty in maintenance planning. Credit rating agencies downgraded 14 regional airlines during 2024, increasing financing constraints for fleet acquisitions. Civil aviation authorities processed 39 deferred aircraft registrations in 2025 due to postponed deliveries. Fuel price indices recorded 28 monthly adjustments across 2024–2025, compounding planning risk and reinforcing cautious capital deployment across turboprop fleets.
Opportunities
Fleet replacement cycle of aging regional turboprops
Aging regional turboprop fleets present structured replacement opportunities as compliance and reliability requirements tighten. In 2024, European registries listed 1,140 turboprops exceeding 20 years of service, with 312 surpassing 25 years. Airworthiness directives issued 76 recurring inspections for older airframes during 2025, elevating downtime risks. Maintenance authorities recorded 4,800 unscheduled maintenance events in 2024 across aging fleets. Emissions certification updates implemented in 2025 affected aircraft manufactured before 2005 in 11 jurisdictions. Fleet planners prioritize modernization to maintain dispatch reliability above 98 operational availability while aligning with evolving safety oversight expectations.
Growth of cargo feeder and express logistics networks
Express logistics networks continue expanding regional feeder operations to meet delivery time commitments. In 2024, European express operators managed 420 regional feeder routes connecting 68 primary hubs. Parcel volumes handled at regional airports increased by 31,000,000 consignments during 2025, intensifying demand for short-haul lift. Customs authorities processed 2,300,000 time-definite shipments through secondary gateways in 2024. Night-time operations approvals expanded across 9 countries in 2025, enabling turboprops to operate within noise compliance thresholds. Infrastructure agencies commissioned 24 new regional cargo ramps by 2025, strengthening operational feasibility for turboprop feeder fleets.
Future Outlook
The market outlook through 2035 reflects steady fleet renewal across regional aviation, supported by sustainability policies and connectivity mandates. Electrification pilots and sustainable fuel adoption will influence procurement strategies, while public service obligation routes preserve demand in peripheral regions. Competitive dynamics will emphasize lifecycle serviceability, regulatory compliance, and flexible financing models.
Major Players
- ATR
- De Havilland Canada
- Textron Aviation
- Pilatus Aircraft
- Viking Air
- Daher
- Tecnam
- RUAG
- Safran Aircraft Engines
- Pratt & Whitney Canada
- RTX
- GE Aerospace
- Liebherr-Aerospace
- Honeywell Aerospace
- MTU Aero Engines
Key Target Audience
- Regional airline operators
- Cargo and express logistics operators
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names including European Union Aviation Safety Agency and national civil aviation authorities
- Defense and homeland security agencies
- Airport authorities and regional airport operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Primary variables included fleet age distribution, route density by country, certification pathways, utilization intensity, and maintenance cycle requirements. Data points were defined around operational performance, regulatory compliance triggers, and replacement timelines. Variable selection reflected mission profiles across commercial, cargo, and special mission turboprop operations.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Analytical construction mapped fleet evolution across countries, route categories, and operator types. Operational indicators such as stage length, movement density, and airport infrastructure readiness were synthesized. Policy frameworks governing regional connectivity and emissions compliance were incorporated to frame structural demand drivers and constraints.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses on replacement cycles, feeder network expansion, and intermodal competition were validated through structured consultations with operators, maintenance organizations, and regulatory stakeholders. Scenario testing assessed sensitivity to infrastructure investment cycles, certification updates, and utilization volatility across operating environments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into a cohesive narrative linking operational realities with policy and infrastructure conditions. Cross-validation ensured internal consistency across segmentation, competitive positioning, and future outlook. The final output aligns strategic insights with actionable implications for fleet planning and ecosystem stakeholders.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and aircraft class certification scope, Fleet census and active turboprop tracking by country, OEM orderbook and backlog triangulation, Operator utilization and route network analysis, MRO spend and parts consumption modeling, Lease rate and residual value benchmarking, Regulatory airworthiness and emissions compliance review)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and route deployment patterns
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising demand for short-haul regional connectivity
Airline network optimization on thin routes
Lower operating costs versus regional jets
Airport slot and runway constraints favoring turboprops
Government support for regional air connectivity
Sustainability-driven fleet renewal toward fuel-efficient aircraft - Challenges
Competition from high-speed rail on short sectors
Volatility in airline profitability and fleet investment cycles
High capital cost and long delivery lead times
Pilot availability and training constraints
Regulatory pressure on noise and emissions compliance
Residual value risk for aging turboprop fleets - Opportunities
Fleet replacement cycle of aging regional turboprops
Growth of cargo feeder and express logistics networks
Special mission demand for surveillance and maritime patrol
Electrification and hybrid propulsion technology pilots
Public service obligation route expansion
Leasing and ACMI growth for regional operators - Trends
Shift toward higher-capacity turboprops for route economics
Increased focus on lifecycle cost and fuel efficiency
Rising adoption of power-by-the-hour MRO contracts
Digital fleet health monitoring and predictive maintenance
Cabin reconfiguration for premium regional travel
Sustainable aviation fuel compatibility adoption - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Aircraft Type (in Value %)
Utility turboprop aircraft
Regional commuter turboprop aircraft
Special mission turboprop aircraft
Business turboprop aircraft - By Seating Capacity (in Value %)
Up to 9 seats
10–19 seats
20–39 seats
40–60+ seats - By Application (in Value %)
Regional passenger transport
Cargo and logistics
Charter and business aviation
Special mission and ISR
Training and utility - By End User (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Charter and business aviation operators
Cargo and logistics operators
Government and defense agencies
Flight training organizations - By Country (in Value %)
United Kingdom
France
Germany
Italy
Spain
Nordic countries
Rest of Europe
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (fleet size, delivery backlog, operating cost per seat, fuel efficiency metrics, MRO network coverage, financing solutions, residual value performance, regional presence) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ATR
De Havilland Canada
Textron Aviation
Pilatus Aircraft
Viking Air
Daher
Tecnam
RUAG
Safran Aircraft Engines
Pratt & Whitney Canada
RTX
GE Aerospace
Liebherr-Aerospace
Honeywell Aerospace
MTU Aero Engines
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


