Market Overview
The GCC Aircraft MRO market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a mature maintenance ecosystem anchored by long-haul hub operations, diversified fleets, and expanding in-region heavy maintenance capabilities. Demand concentration across commercial, cargo, and government aviation sustains steady utilization of line, base, and component services, supported by growing engine shop capacity and parts pooling. Capital commitments remain oriented toward hangar expansion, digital maintenance workflows, and certification-driven capability upgrades.
The dominant activity clusters around Riyadh, Jeddah, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha, and Sharjah, where hub airports concentrate wide-body operations, cargo throughput, and business aviation. These cities benefit from integrated aviation ecosystems, skilled labor pools, and co-located component logistics. Policy alignment with localization agendas, aviation cluster development, and regulatory harmonization under civil aviation authorities has improved service depth. Strong connectivity to global parts networks and MRO training pipelines further reinforces regional service resilience.
Market Segmentation
By MRO Type
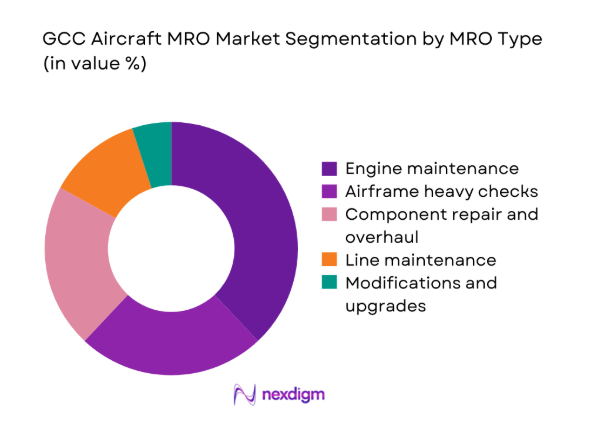
Engine maintenance dominates service demand due to higher technical intensity, shop visit frequency driven by utilization cycles, and the complexity of new-generation powerplants. Airframe heavy checks remain concentrated around wide-body fleets operating long-haul routes, while component repair benefits from rotable pooling and reliability programs. Line maintenance volume is anchored by hub-and-spoke operations with tight turnaround requirements. Modifications and upgrades are driven by cabin refresh cycles, connectivity retrofits, and compliance-driven updates. The service mix reflects a shift toward higher-value technical work retained in-region as hangar capacity and certifications expand.
By Aircraft Type
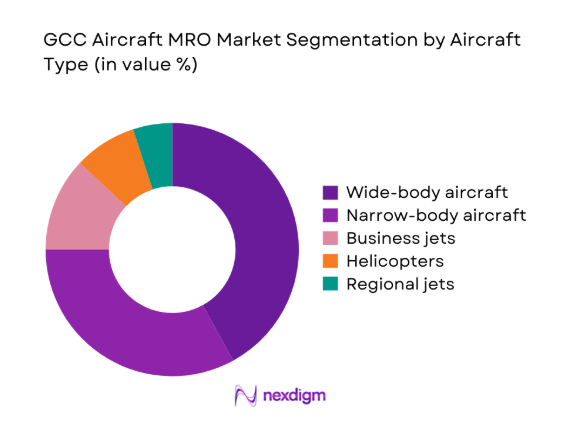
Wide-body aircraft account for a disproportionate share of MRO demand due to intensive utilization on long-haul networks and higher check complexity. Narrow-body fleets contribute consistent line and component activity linked to high-frequency operations. Business aviation demand is concentrated around VIP fleets requiring premium turnaround and customization, while helicopters support offshore, security, and emergency missions with specialized maintenance needs. Regional jets contribute limited volumes but require high dispatch reliability. Fleet mix evolution toward newer platforms is shifting demand toward engine programs, digital diagnostics, and condition-based maintenance capabilities.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by vertically integrated airline-affiliated providers, independent service specialists, and OEM-authorized centers co-located within major hubs. Competition emphasizes turnaround reliability, certification breadth, and access to rotable pools, with differentiation driven by engine shop capability, digital maintenance systems, and cross-border approvals enabling regional coverage.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| SR Technics | 1996 | Zurich | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lufthansa Technik | 1953 | Hamburg | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AFI KLM E&M | 1919 | Paris | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Etihad Engineering | 2014 | Abu Dhabi | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Turkish Technic | 1933 | Istanbul | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
GCC Aircraft MRO Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Fleet expansion and wide-body induction in GCC carriers
Wide-body induction continued as long-haul connectivity deepened across hubs, with 2024 adding 41 wide-body aircraft to active operations and 2025 scheduling 36 further inductions across multiple carriers. Airport slot utilization at major hubs exceeded 82 daily long-haul rotations during peak months in 2024, increasing engine cycles and shop visit frequency. Civil aviation authorities issued 19 new maintenance approvals during 2023–2025, enabling additional in-region checks. Training throughput rose with 2,140 licensed technicians certified between 2022 and 2025, supporting base maintenance capacity. Expanded hangar footprints added 14 wide-body bays since 2022, lifting throughput reliability.
Rising aircraft utilization and hub-and-spoke connectivity growth
Passenger and cargo connectivity intensified hub rotations, with average daily departures at primary hubs reaching 1,280 in 2024 and 1,340 in 2025, elevating line maintenance events. Turnaround windows compressed to 55 minutes for narrow-body operations during peak periods, increasing reliance on predictive maintenance tooling. Air traffic movements recovered to 97 of pre-disruption levels by 2024, while night curfews remained limited across key airports, extending maintenance windows. Slot coordination committees approved 23 incremental night-time maintenance windows across 2023–2025. Ground handling incident rates declined from 3.2 to 2.4 per 10,000 movements, improving dispatch reliability.
Challenges
High capital intensity of engine shops and hangar infrastructure
Engine shop buildouts require multi-year certification pathways and heavy fixed assets. Between 2022 and 2025, 7 greenfield engine lines faced commissioning delays exceeding 11 months due to equipment lead times of 46 weeks and calibration bottlenecks. Utility load requirements rose by 28 megawatts across major MRO clusters, stressing grid connections. Tooling procurement cycles averaged 38 weeks in 2024, constraining ramp-up. Hangar occupancy rates surpassed 91 during peak seasons, creating queuing risks. Certification audits averaged 4 rounds per facility over 24 months, slowing operational readiness and constraining capacity elasticity.
Skilled labor shortages and dependence on expatriate technicians
Licensed technician availability remained constrained, with vacancy ratios near 1.8 positions per filled role in 2024. Training pipelines produced 620 new licenses in 2023 and 740 in 2024, insufficient against attrition of 9 per 100 staff annually. Visa processing cycles averaged 47 days in 2025, delaying crew onboarding. Language and type-rating gaps required 120 hours of recurrent training per technician annually. Overtime hours increased to 14 per technician per month during peak checks in 2024, elevating fatigue risk indicators recorded in 63 safety reports across major bases between 2022 and 2025.
Opportunities
Greenfield MRO hubs aligned with national aviation strategies
National aviation strategies designated 6 logistics zones between 2022 and 2025 for aerospace clusters, enabling co-location of hangars, parts depots, and training centers. Land parcels totaling 4,800 hectares were earmarked near hub airports, reducing tow times by 18 minutes per event in pilot implementations. Civil aviation authorities issued 12 fast-track certifications for facilities embedded within these zones during 2024–2025. Apprenticeship intakes reached 1,120 trainees across cluster programs by 2025, improving local talent supply. Integrated customs clearance reduced parts dwell times from 72 to 28 hours across participating free zones.
Engine MRO capability for new-generation platforms
Next-generation engines entering service since 2022 increased diagnostic data volumes to 9 terabytes per aircraft annually, enabling condition-based maintenance. Engine health monitoring alerts rose to 2.7 events per 1,000 cycles in 2024, improving early intervention. Shop visit intervals extended to 7,200 cycles, creating scheduling predictability for capacity planning. Regulatory approvals expanded with 8 additional type certificates granted across 2023–2025. Test cell utilization rates averaged 76 in 2024, indicating headroom for incremental lines. Local parts repair approvals increased to 214 part numbers by 2025, reducing offshoring dependency.
Future Outlook
The market is set to deepen in-region heavy maintenance as localization policies mature and capacity additions come online through 2035. OEM-authorized capabilities, digital MRO adoption, and engine shop expansion will shape competitive positioning. Regulatory harmonization and workforce localization programs are expected to improve throughput reliability, while hub connectivity growth sustains utilization across commercial, cargo, and government fleets.
Major Players
- SR Technics
- Lufthansa Technik
- AFI KLM E&M
- Etihad Engineering
- Turkish Technic
- Saudia Aerospace Engineering Industries
- Ameco Beijing
- HAECO
- GMF AeroAsia
- StandardAero
- GA Telesis
- SIA Engineering Company
- AAR Corp.
- Sabena technics
- FL Technics
Key Target Audience
- Commercial airlines and cargo operators
- Business aviation fleet owners and charter operators
- Military and government aviation maintenance commands
- Airport authorities and aviation cluster developers
- Aircraft lessors and asset management firms
- Parts distributors and component pooling providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational variables were defined across fleet mix, utilization cycles, check intervals, certification pathways, and hangar capacity. Service scope boundaries covered line, base, component, and engine activities. Regulatory variables captured approvals, audits, and compliance timelines across civil aviation authorities. Workforce variables included licensing throughput and type-rating availability.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Service workflows were mapped from induction to release-to-service, integrating turnaround constraints and capacity utilization. Demand drivers were constructed using traffic movements, hub rotations, and fleet induction schedules. Supply-side readiness was modeled through hangar bays, engine lines, and parts logistics nodes. Sensitivity testing addressed bottlenecks in tooling lead times and certification queues.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Operational hypotheses were validated through interviews with maintenance planners, quality managers, and airport operations leads. Facility audits triangulated throughput assumptions against bay occupancy and test cell utilization. Regulatory interpretations were cross-checked with compliance officers to ensure approval timelines and audit cycles reflected current practice. Workforce availability assumptions were stress-tested with training providers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into service-line narratives, capacity scenarios, and ecosystem implications. Contradictions were reconciled through iterative review of operational data points. Scenario narratives aligned regulatory, workforce, and infrastructure trajectories with service demand evolution. Final outputs emphasized actionable implications for operators, authorities, and investors.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and MRO Scope Mapping, Fleet and Aircraft Utilization Data Modeling, Airline and MRO Provider Primary Interviews, Hangar Capacity and Engine Shop Audits, Parts Supply Chain and Turnaround Time Tracking, Regulatory and GCAA/CAA Compliance Review, Contract and Pricing Benchmark Analysis)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and maintenance pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Fleet expansion and wide-body induction in GCC carriers
Rising aircraft utilization and hub-and-spoke connectivity growth
Aging of narrow-body fleets driving heavy checks and component overhauls
Localization policies encouraging domestic MRO capability build-up
OEM partnerships and engine shop investments in the region
Growth of cargo and ACMI operations post-pandemic - Challenges
High capital intensity of engine shops and hangar infrastructure
Skilled labor shortages and dependence on expatriate technicians
OEM exclusivity constraints and proprietary parts pricing
Volatility in airline profitability impacting maintenance spend cycles
Supply chain disruptions for rotable components and spares
Certification complexity across multiple civil aviation authorities - Opportunities
Greenfield MRO hubs aligned with national aviation strategies
Engine MRO capability for new-generation platforms
Digital MRO, predictive maintenance and data analytics adoption
Expansion of business aviation and VIP aircraft services
Component pooling and regional spares logistics hubs
Military and government fleet sustainment outsourcing - Trends
Shift toward long-term power-by-the-hour contracts
Increasing OEM footprint and authorized service centers
Consolidation among independent MRO providers
Adoption of paperless MRO and AI-driven maintenance planning
Growth of in-region heavy checks for wide-body aircraft
Sustainability-driven maintenance practices and materials - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Fleet, 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Aircraft Event, 2020–2025
- By MRO Type (in Value %)
Engine maintenance
Airframe heavy checks
Component repair and overhaul
Line maintenance
Modifications and upgrades - By Aircraft Type (in Value %)
Narrow-body aircraft
Wide-body aircraft
Regional jets
Business jets
Helicopters - By End Use (in Value %)
Commercial airlines
Low-cost carriers
Business aviation operators
Military and government aviation
Charter and ACMI operators - By Service Provider Type (in Value %)
Airline-affiliated MROs
Independent third-party MROs
OEM-authorized service centers
Joint venture MRO facilities - By Geography (in Value %)
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Qatar
Kuwait
Oman
Bahrain
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (service breadth, engine shop capability, OEM authorizations, turnaround time performance, pricing models, geographic coverage, certifications and approvals, digital MRO maturity) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
SR Technics
Lufthansa Technik
AFI KLM E&M
Etihad Engineering
Turkish Technic
Saudia Aerospace Engineering Industries
Ameco Beijing
HAECO
GMF AeroAsia
StandardAero
GA Telesis
SIA Engineering Company
AAR Corp.
Sabena technics
FL Technics
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Fleet, 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Aircraft Event, 2026–2035


