Market Overview
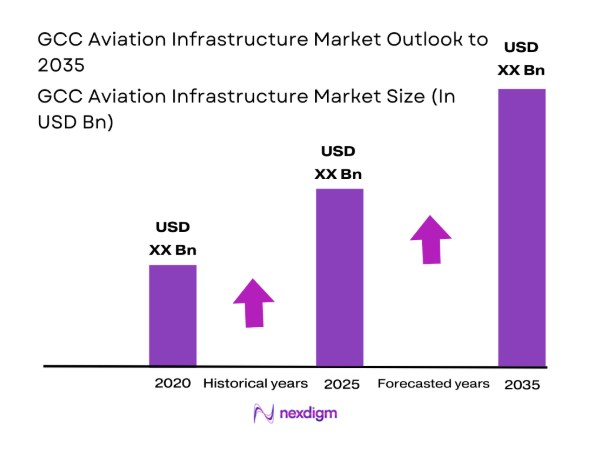
The GCC Aviation Infrastructure market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained capital deployment across airport development, airside systems, and digital aviation platforms. Investment flows concentrate on terminal modernization, runway rehabilitation, and air navigation upgrades to support expanding network connectivity and operational resilience. Programmatic funding frameworks prioritize safety compliance, passenger processing efficiency, and multimodal integration, reinforcing infrastructure-led competitiveness while anchoring long-term capacity creation across the regional aviation ecosystem.
Development momentum is led by Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, supported by advanced hub airports, integrated logistics zones, and strong EPC ecosystems. Qatar maintains high-specification terminal and airside assets aligned with premium transit demand. Oman, Kuwait, and Bahrain advance targeted upgrades anchored in fleet growth, cargo specialization, and tourism-linked demand clusters. Policy environments emphasize liberalization, private participation, and sustainability standards, accelerating adoption of smart airport systems and performance-based operations.
Market Segmentation
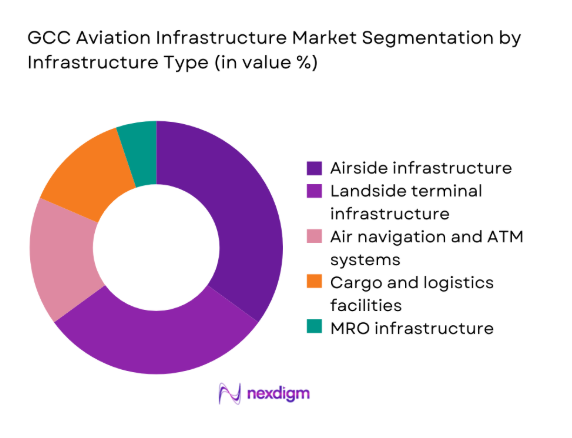
By Infrastructure Type
Airside assets dominate due to continuous runway, taxiway, apron rehabilitation, and airfield lighting upgrades required to sustain safety certifications and accommodate widebody operations. Landside terminal capacity expands to relieve congestion at hub airports, while baggage handling and passenger processing automation improves throughput. Air navigation and ATM systems attract steady upgrades aligned with airspace modernization programs. Cargo and logistics zones gain traction from regional transshipment growth. MRO infrastructure expands selectively around fleet concentration corridors, reinforcing uptime, compliance, and turnaround efficiency across high-traffic airports.
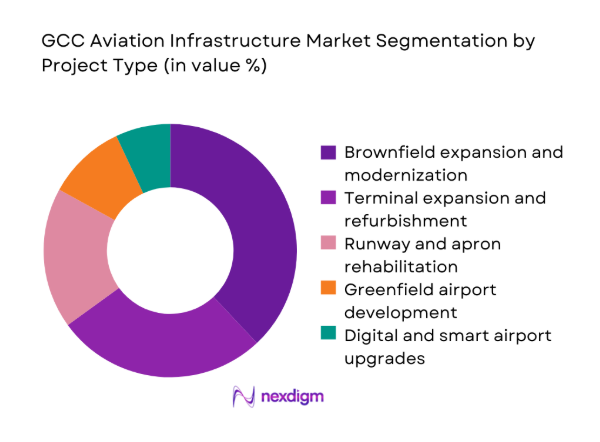
By Project Type
Brownfield expansion and modernization dominate as operators prioritize capacity uplift within constrained footprints, minimizing land acquisition risk and accelerating commissioning cycles. Terminal refurbishment programs emphasize digital passenger processing and energy efficiency retrofits. Greenfield development remains selective, focused on strategic hubs and cargo-oriented airports. Runway and apron rehabilitation sustain compliance and resilience amid high utilization cycles. Digital and smart airport upgrades scale rapidly as authorities embed biometric processing, predictive maintenance, and operational analytics into phased capital programs to optimize throughput and service quality.
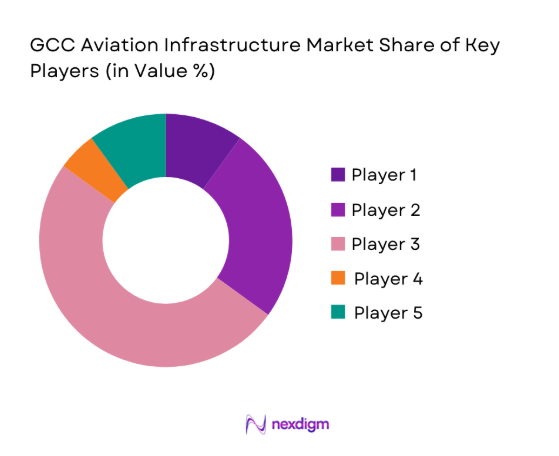
Competitive Landscape
Competition reflects a mix of global EPC integrators, airport operators, and aviation systems specialists with strong regional delivery capacity, compliance credentials, and lifecycle service models aligned to complex, multi-year programs.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Bechtel | 1898 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AECOM | 1990 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Jacobs | 1947 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Vinci Airports | 2000 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Group | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
GCC Aviation Infrastructure Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising passenger traffic driven by tourism diversification and mega-events
Air traffic movements across major GCC hubs increased from 2022 to 2024 as route networks expanded and slot utilization intensified at peak banks. In 2023, multiple terminals processed over 50 million passengers annually, while widebody fleet counts exceeded 900 aircraft regionwide by 2024, elevating gate and apron utilization. Visa facilitation expanded to more than 60 nationalities by 2025 in several markets, stimulating inbound flows. Hotel keys surpassed 450000 by 2024 in tourism corridors, raising seasonal surges. Airport dwell-time indicators improved following biometric processing pilots launched across 2023 and 2024, supporting sustained throughout growth.
Government aviation sector liberalization and hub development strategies
Civil aviation authorities implemented air service liberalization across bilateral agreements from 2022 to 2025, expanding fifth freedom access on more than 120 routes. National aviation strategies targeted hub capacity expansion with dedicated cargo corridors linking over 30 trade lanes by 2024. Slot coordination frameworks were digitized across three major hubs in 2023, reducing peak congestion incidents recorded in 2022. Public private partnership frameworks advanced with standardized concession tenures exceeding 20 years, enabling multi-phase delivery. Airport safety oversight aligned with ICAO audits completed across all GCC states by 2024, strengthening investor confidence and execution velocity.
Challenges
Capital-intensive projects with long payback periods
Mega terminal programs require multi-year construction cycles exceeding 48 months, extending capital lock-in and exposure to demand volatility observed in 2022 disruptions. Debt tenors for infrastructure projects commonly extend beyond 15 years, constraining balance sheet flexibility during phased commissioning. Annual maintenance windows expanded to 90 days at high-utilization airports in 2023, elevating operational complexity during upgrades. Financing syndicates tightened covenant thresholds following 2024 rate adjustments, delaying financial close for several airside packages. Long-lead equipment procurement cycles, often exceeding 14 months, compound schedule risk across integrated baggage and CNS deployments.
Execution risk in mega-project delivery and cost overruns
Phased construction within live airport environments elevated interface risk across 2022 to 2024, with more than 25 concurrent work packages coordinated per terminal in peak periods. Utility diversions exceeded 300 interface points at select hubs in 2023, complicating sequencing. Skilled workforce availability fluctuated as licensed airfield engineers declined by 12 percent between 2022 and 2024 due to regional project clustering. Weather-related productivity losses rose during extended summer periods exceeding 110 days annually. Systems integration testing cycles stretched beyond 180 days for large baggage systems, delaying operational readiness and handover timelines.
Opportunities
Smart airport and digital transformation initiatives
Biometric enrollment stations scaled from pilot deployments in 2022 to more than 1500 lanes across major hubs by 2024, reducing average queuing times recorded in operational logs. Digital twin adoption expanded to over 20 terminal programs in 2025, enabling scenario testing across capacity planning and asset lifecycle management. Predictive maintenance platforms integrated sensor feeds from 2023 installations covering thousands of baggage motors and airside lighting points, improving fault detection latency. Cybersecurity compliance frameworks aligned with national standards updated in 2024, unlocking broader cloud adoption for airport operations and passenger service platforms.
Expansion of dedicated air cargo and logistics zones
Dedicated cargo apron stands increased by over 140 positions between 2022 and 2025 across logistics-focused airports, supporting integrator fleet growth. Cold-chain certified warehouse capacity expanded with more than 60 new temperature-controlled chambers commissioned in 2024, enabling pharma and perishables handling. E-commerce fulfillment nodes within airport free zones rose to over 25 facilities by 2025, compressing last-mile transit times. Night curfew exemptions extended to additional corridors in 2023, lifting slot availability for freighters. Multimodal links connecting seaports to air cargo zones were upgraded across 2024, improving hinterland connectivity.
Future Outlook
The outlook to 2035 reflects sustained capacity expansion anchored in hub competitiveness, airspace modernization, and cargo corridor specialization. Phased terminal programs and brownfield upgrades will dominate near-term delivery, while digital twins, biometrics, and predictive maintenance scale across operations. Policy emphasis on private participation and sustainability standards will shape procurement, with modular construction accelerating commissioning across constrained sites. Regional competition will intensify service quality benchmarks and lifecycle performance expectations.
Major Players
- Bechtel
- AECOM
- Jacobs
- Vinci Airports
- ADP Group
- TAV Airports
- Fraport
- GMR Airports
- Larsen & Toubro
- China Harbour Engineering Company
- Thales Group
- Indra Sistemas
- Siemens Mobility
- Honeywell Aerospace
- Smiths Detection
Key Target Audience
- Airport authorities and airport operating companies
- Civil aviation authorities and national aviation agencies
- Ministries of transport and infrastructure development agencies
- Public private partnership units within finance ministries
- Airlines and cargo operators
- Airport EPC contractors and systems integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Variables covered airside capacity constraints, terminal throughput, ATM modernization scope, cargo corridor connectivity, EPC delivery readiness, and regulatory compliance maturity across GCC airports. Data points emphasized asset condition, utilization bottlenecks, and phased commissioning dependencies influencing program sequencing.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The framework structured infrastructure classes by airside, landside, CNS, cargo, and MRO assets, mapping demand centers to hub typologies and project types. Comparative baselines aligned capacity expansion pathways with policy priorities, safety audits, and lifecycle performance benchmarks.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were stress-tested through structured consultations with airport operations leaders, airspace planners, and project controls specialists. Validation focused on delivery risks, integration timelines, and operational readiness indicators observed across live airport environments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into demand drivers, constraints, and opportunity themes, translating operational indicators into actionable implications for procurement strategies, phasing logic, and technology adoption roadmaps across GCC aviation infrastructure programs.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and airport-side vs airside infrastructure scope alignment, Primary interviews with GCAA/DGCA officials airport operators and EPC contractors, Tender database analysis of airside landside and ATC projects across GCC, Project pipeline tracking of greenfield airports and terminal expansions, OEM and integrator shipment tracking for CNS ATM and baggage systems, Capex benchmarking from airport authority financials and sovereign project disclosures)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and capacity pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and channel structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising passenger traffic driven by tourism diversification and mega-events
Government aviation sector liberalization and hub development strategies
Large-scale airport expansion programs under national vision agendas
Growth of air cargo driven by e-commerce and pharma logistics
Fleet expansion and new airline entrants increasing capacity requirements
Regional competition to establish global transit hubs - Challenges
Capital-intensive projects with long payback periods
Execution risk in mega-project delivery and cost overruns
Supply chain constraints for specialized aviation systems and equipment
Skilled labor shortages in airport engineering and systems integration
Geopolitical risks affecting traffic flows and investment continuity
Environmental compliance and carbon reduction pressures - Opportunities
Smart airport and digital transformation initiatives
Expansion of dedicated air cargo and logistics zones
Private sector participation via PPP and concession models
Retrofit and modernization of legacy terminals and runways
Deployment of advanced CNS and ATM modernization programs
Development of airport cities and non-aeronautical revenue zones - Trends
Adoption of biometric passenger processing and seamless travel
Integration of sustainability and net-zero airport design
Automation in baggage handling and airside operations
Use of digital twins and predictive maintenance platforms
Modular terminal construction for phased capacity expansion
Increased localization of EPC and system integration capabilities - Government Regulations
SWOT Analysis
Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Infrastructure Type (in Value %)
Airside infrastructure
Landside terminal infrastructure
Air navigation and ATM systems
Cargo and logistics facilities
Maintenance, repair and overhaul infrastructure - By Airport Type (in Value %)
International hub airports
Secondary commercial airports
Regional and domestic airports
Dedicated cargo airports
Military and dual-use airbases - By Project Type (in Value %)
Greenfield airport development
Brownfield expansion and modernization
Terminal expansion and refurbishment
Runway and apron rehabilitation
Digital and smart airport upgrades - By Ownership and Operating Model (in Value %)
Government-owned and operated
Public-private partnership concessions
Build-operate-transfer projects
Airport management contracts
Privatized airport operators - By Country (in Value %)
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Qatar
Kuwait
Oman
Bahrain
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
Cross Comparison Parameters (project delivery capability, regional footprint, EPC integration strength, technology portfolio breadth, compliance with ICAO standards, aftersales and O&M support, financial strength, track record in mega airport projects) - SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Bechtel
AECOM
Jacobs
Vinci Airports
ADP Group
TAV Airports
Fraport
GMR Airports
Larsen & Toubro
China Harbour Engineering Company
Thales Group
Indra Sistemas
Siemens Mobility
Honeywell Aerospace
Smiths Detection
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


