Market Overview
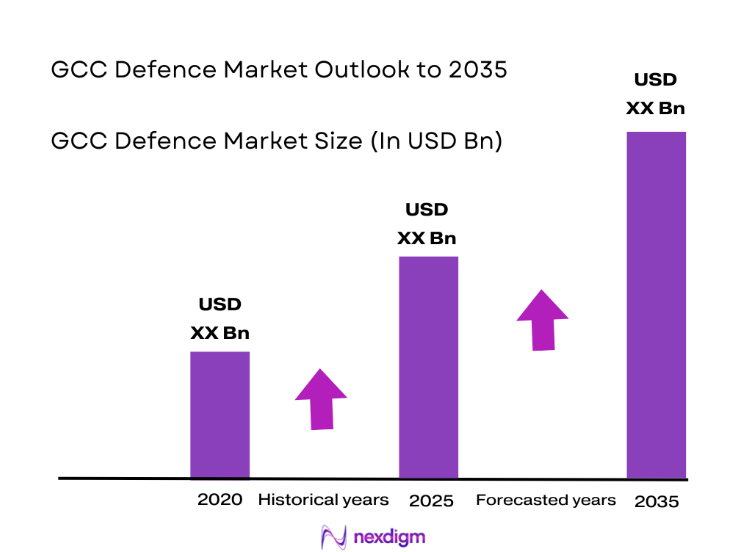
The GCC Defence market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained modernization programs, active procurement pipelines, and ongoing force readiness initiatives across air, land, naval, space, and cyber domains. Demand remains anchored in multi-domain capability integration, lifecycle sustainment, and operational readiness enhancement. Program continuity, long-term service contracts, and platform upgrades continue to underpin spending momentum, while localization policies are reshaping procurement structures, supplier selection criteria, and industrial participation frameworks.
The market is concentrated around major defence hubs in Riyadh, Abu Dhabi, Doha, Kuwait City, and Muscat, where command infrastructure, air bases, naval ports, and logistics depots anchor procurement and sustainment activity. Demand clusters near industrial free zones, military industrialization parks, and test ranges supporting qualification and certification. Ecosystem maturity is reinforced by local manufacturing clusters, MRO facilities, secure logistics corridors, and defense-focused digital infrastructure. Policy alignment around localization and offsets further deepens supplier ecosystems.
Market Segmentation
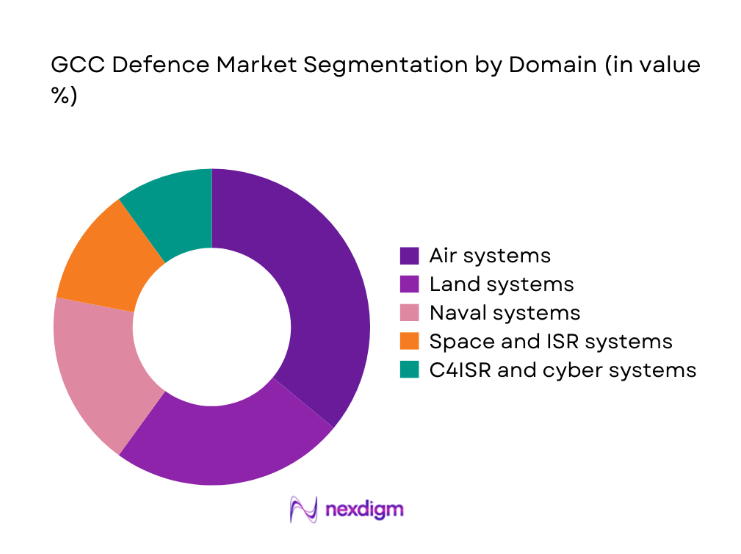
By Domain
Air systems dominate value contribution due to fleet modernization priorities, high operational tempo, and integration requirements across surveillance, strike, and air defense missions. Land systems maintain stable demand driven by border security, armored mobility, and rapid response units, while naval systems benefit from maritime security needs along energy shipping lanes. Space and ISR systems are expanding as secure communications and persistent surveillance become operational necessities. C4ISR and cyber systems show accelerating uptake as interoperability and network resilience become mission critical across joint-force operations and coalition frameworks.
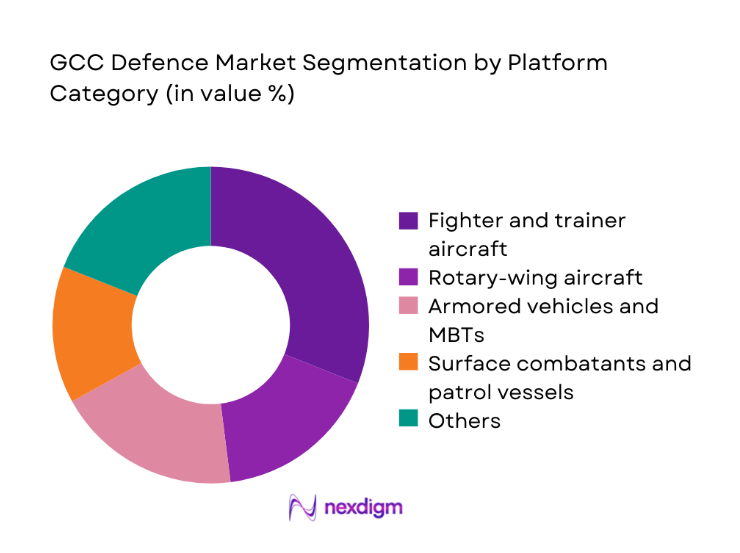
By Platform Category
Fighter and trainer aircraft account for the largest value share given fleet renewal cycles, mission readiness demands, and avionics upgrades. Rotary-wing aircraft retain strong relevance for ISR, transport, and special operations. Armored vehicles and MBTs sustain demand linked to mechanized brigades and border security. Surface combatants and patrol vessels gain traction from maritime domain awareness programs. Air defence systems and unmanned systems are rising in importance as layered defense architectures and persistent ISR become operational priorities across the region.
Competitive Landscape
The GCC defence ecosystem features a mix of global primes and fast-scaling regional integrators aligned with localization mandates, offsets, and sovereign capability goals. Competitive differentiation centers on delivery reliability, integration depth, sustainment capacity, and regulatory readiness to operate within national industrial participation frameworks and security clearance regimes.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| RTX | 2020 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| BAE Systems | 1999 | United Kingdom | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus Defence and Space | 2014 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
GCC Defence Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising geopolitical tensions and border security imperatives
Persistent security pressures across maritime chokepoints and border corridors continue to elevate readiness postures. Regional patrol coverage expanded across 14 forward operating bases during 2024, supported by 6 new coastal surveillance nodes activated in 2025. Annual joint exercises exceeded 28 engagements in 2024, compared with 19 in 2022, reinforcing interoperability needs across air, land, and naval commands. Cross-border incident reporting increased by 41 cases during 2023–2024, prompting wider deployment of layered surveillance. Command centers integrated 11 new secure data gateways in 2025, strengthening real-time coordination. These indicators reinforce sustained operational demand for platforms, ISR integration, and command resilience across contested environments.
Modernization of legacy platforms and force structure upgrades
Fleet renewal remains central to operational readiness as legacy platforms approach service limits. During 2024, maintenance cycles extended across 3 legacy aircraft squadrons and 2 armored brigades, while 9 avionics upgrade programs entered qualification phases in 2025. Depot-level overhaul throughput increased from 18 to 27 platforms annually between 2022 and 2024, reflecting capacity expansion. Training syllabi added 420 simulator hours in 2025 to support transition pipelines. Force structure realignment consolidated 4 command brigades into 2 integrated formations during 2024, improving interoperability. These institutional adjustments sustain demand for upgrades, sustainment, integration, and training ecosystems without revealing total market scale.
Challenges
Budget volatility linked to hydrocarbon revenue cycles
Fiscal planning remains exposed to commodity-linked volatility affecting multi-year defense programming. During 2023–2024, capital allocation revisions occurred across 5 major programs, resulting in schedule deferrals averaging 11 months. Treasury disbursement cadence shifted from quarterly to biannual tranches in 2024, compressing procurement windows. Contract amendments rose to 23 instances in 2025 compared with 14 in 2022, increasing execution risk. Foreign exchange settlement cycles lengthened by 37 days across 2024, complicating milestone payments. These constraints pressure delivery timelines, disrupt supply commitments, and elevate working-capital stress across integrators and MRO providers operating within fixed readiness mandates.
Export control restrictions and technology transfer limitations
Regulatory controls constrain access to advanced subsystems and source codes critical for localization. In 2024, 7 platform subsystems required additional licensing reviews, extending approval timelines by 6 months on average. Technology release waivers declined across 3 avionics categories in 2023, delaying domestic integration programs. Offset compliance audits increased to 12 reviews in 2025, raising documentation burdens. Secure data enclave accreditation expanded to 9 facilities by 2024, yet interoperability approvals lagged. These constraints slow indigenization roadmaps, limit local integration depth, and complicate lifecycle sustainment planning under sovereign capability objectives.
Opportunities
Localization and joint ventures under national industrial strategies
National strategies continue to expand industrial participation pathways. During 2024, 4 new joint ventures achieved production-readiness milestones, and 2 composite manufacturing lines reached qualification status in 2025. Local content thresholds increased across 3 program categories in 2024, incentivizing supplier localization. Workforce certification programs accredited 1,200 technicians in 2023–2024, improving sustainment capacity. Secure industrial zones added 5 accredited suppliers in 2025, broadening tier-two ecosystems. These institutional enablers, combined with policy continuity and procurement localization clauses, create scalable pathways for domestic manufacturing, systems integration, and lifecycle services.
MRO, upgrades and life-extension of existing fleets
Lifecycle sustainment offers resilient demand anchored in readiness imperatives. In 2024, depot throughput rose to 31 platforms annually across 2 regional hubs, while condition-based maintenance expanded to 8 fleet types in 2025. Spare parts localization reduced lead times by 19 days during 2023–2024 through accredited supplier onboarding. Engine overhaul capacity increased by 3 lines in 2024, easing bottlenecks. Training pipelines added 260 certified maintainers in 2025, stabilizing workforce depth. These indicators support sustained opportunities in upgrades, retrofits, digital diagnostics, and performance-based sustainment frameworks across air, land, and naval fleets.
Future Outlook
The outlook emphasizes sustained multi-domain modernization supported by localization mandates and expanding sustainment ecosystems. Over the coming years, demand will remain anchored in readiness, ISR integration, air and missile defense layering, and digital command resilience. Policy continuity around industrial participation and workforce development is expected to deepen domestic integration while reinforcing partnerships and lifecycle service capacity across platforms.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- RTX
- Boeing Defense
- Northrop Grumman
- General Dynamics
- BAE Systems
- Thales
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Leonardo
- Dassault Aviation
- Naval Group
- Saab
- EDGE Group
- Hanwha Aerospace
- Rheinmetall
Key Target Audience
- Defence ministries and armed forces procurement agencies
- National offset and localization authorities
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
- State-owned defence industrial holding companies
- Prime contractors and systems integrators
- MRO and lifecycle sustainment providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Secure logistics and defence-grade infrastructure operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational readiness indicators, platform lifecycle stages, and sustainment capacity metrics were defined to reflect multi-domain defence requirements. Policy levers around localization, offsets, and export controls were mapped alongside force structure priorities. Data parameters focused on procurement cadence, training throughput, and depot utilization.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program pipelines were structured by domain and platform category to assess modernization and sustainment flows. Institutional indicators such as exercise tempo, base activation, and maintenance throughput were synthesized. Ecosystem mapping aligned industrial capacity with regulatory readiness and workforce accreditation.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through structured consultations with defense procurement officials, program managers, and sustainment leads. Operational data points were triangulated against institutional planning cycles and accreditation outcomes. Scenario checks tested robustness under budget cadence shifts and licensing constraints.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated into domain-specific narratives aligned to growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities. Cross-domain interdependencies were synthesized to reflect ecosystem dynamics. Outputs were structured to support strategic planning, localization roadmaps, and lifecycle sustainment prioritization.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and threat capability taxonomies, Primary interviews with defence ministries and procurement authorities across GCC, OEM and prime contractor shipment and contract tracking, Open-source intelligence and SIPRI/UNROCA cross-verification, Program-level platform delivery and MRO spend modeling, Scenario-based budget allocation and force structure modeling, Competitive benchmarking using contract awards and offsets data)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and force deployment pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and offset framework
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising geopolitical tensions and border security imperatives
Modernization of legacy platforms and force structure upgrades
Expansion of integrated air and missile defence networks
Maritime security requirements for energy shipping lanes
Localization mandates and offsets driving domestic production
Multi-domain ISR and C4ISR integration for joint operations - Challenges
Budget volatility linked to hydrocarbon revenue cycles
Export control restrictions and technology transfer limitations
Complex procurement cycles and long program lead times
Interoperability challenges across heterogeneous legacy fleets
Dependence on foreign OEMs for critical subsystems
Supply chain disruptions and skilled workforce shortages - Opportunities
Localization and joint ventures under national industrial strategies
MRO, upgrades and life-extension of existing fleets
Adoption of unmanned and autonomous systems
Cyber defence and electronic warfare modernization
Space-based ISR and secure communications programs
Regional training, simulation and readiness services - Trends
Shift toward integrated multi-layer air defence architectures
Growing role of unmanned systems in ISR and strike missions
Increased focus on sovereign capabilities and local content
Digitalization of command, control and battlefield management
Performance-based logistics and outcome-based contracts
Rapid acquisition pathways for emerging threats - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems and Platforms, 2020–2025
- By Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Domain (in Value %)
Land systems
Air systems
Naval systems
Space and ISR systems
C4ISR and cyber systems - By Capability Type (in Value %)
Combat platforms
Air and missile defence
Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
Electronic warfare
Cyber defence and network security
Logistics, MRO and sustainment - By Platform Category (in Value %)
Fighter and trainer aircraft
Rotary-wing aircraft
Armored vehicles and MBTs
Surface combatants and patrol vessels
Air defence systems
Unmanned aerial and surface systems - By Country (in Value %)
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Qatar
Kuwait
Oman
Bahrain
- Market structure and competitive positioning
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (platform portfolio breadth, localization and offset commitments, technology transfer depth, delivery timelines and program execution, lifecycle cost competitiveness, regional MRO footprint, cybersecurity and digital integration capability, government-to-government contracting strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarketing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Lockheed Martin
RTX
Boeing Defense
Northrop Grumman
General Dynamics
BAE Systems
Thales
Airbus Defence and Space
Leonardo
Dassault Aviation
Naval Group
Saab
EDGE Group
Hanwha Aerospace
Rheinmetall
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems and Platforms, 2026–2035
- By Unit Economics, 2026–2035


