Market Overview
The Global Transformer Copper Cable (Transformer Winding Copper Conductors) market is valued at USD ~ billion, rising from USD ~ billion in the 2025, supported by a steady increase in transformer manufacturing, grid refurbishment, and electrification-led equipment upgrades across utilities and industrial users. The demand base is anchored in enamelled copper winding wire, rectangular/flat conductors, paper-covered copper conductors, and continuously transposed conductor (CTC) used in distribution and power transformers, reactors, and large rotating equipment.
Market activity is concentrated in China, India, Japan, South Korea, Germany, and the United States, with East Asia leading due to dense electrical manufacturing ecosystems, copper processing depth, and high transformer export orientation, while India stands out for utility capex-driven transformer procurement and rising domestic winding-wire capability. In India specifically, the magnet winding wire market is valued at USD 4.38 billion, up from USD 4.22 billion in the prior year, reflecting broad-based electrification and equipment replacement demand that directly lifts transformer-grade copper conductor offtake.
Market Segmentation
By Product / Conductor Form
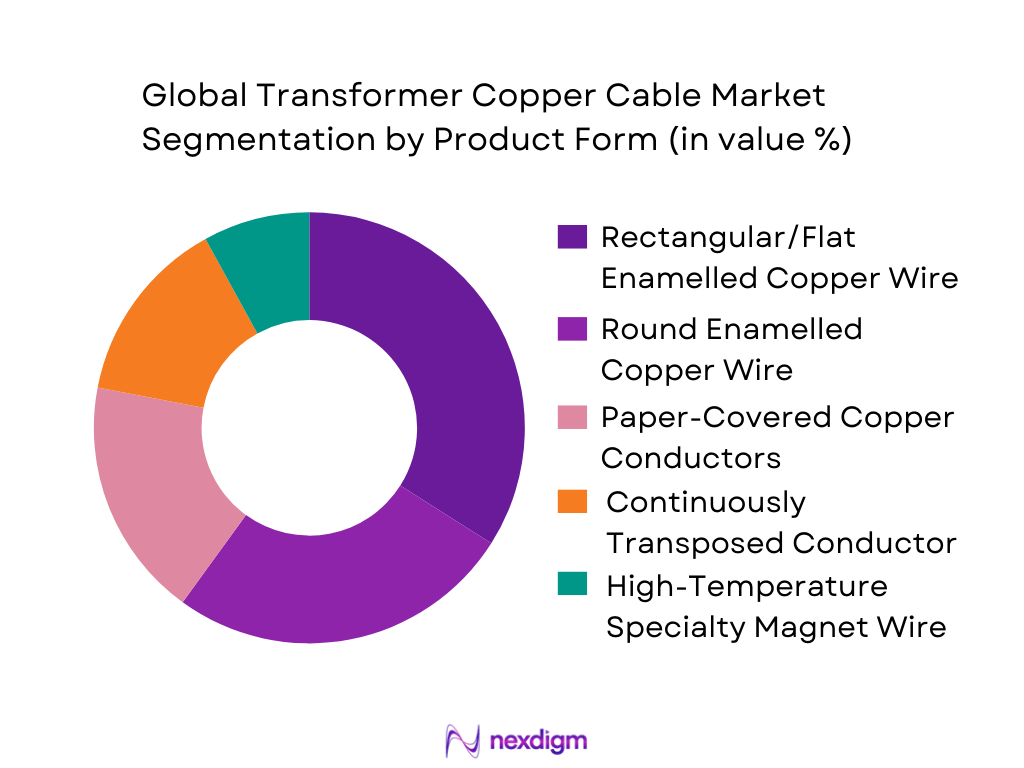
The Global Transformer Copper Cable market is segmented by product/form into round enamelled copper wire, rectangular/flat enamelled copper wire, paper-covered copper conductors (PICC/PTC), continuously transposed conductor (CTC), and high-temperature specialty magnet wire (polyimide/aramid systems). Recently, rectangular/flat enamelled copper wire holds the dominant share because it is the workhorse conductor for transformer windings where slot fill factor, thermal class stability, and mechanical stacking matter most. It also supports high-throughput winding lines and consistent dielectric build, making it the preferred format across both distribution and power transformer production. In India, this dominance is reinforced by OEM standardization for utility tenders and the scaling of domestic conductor processing capacity.
By End-Use Electrical Equipment
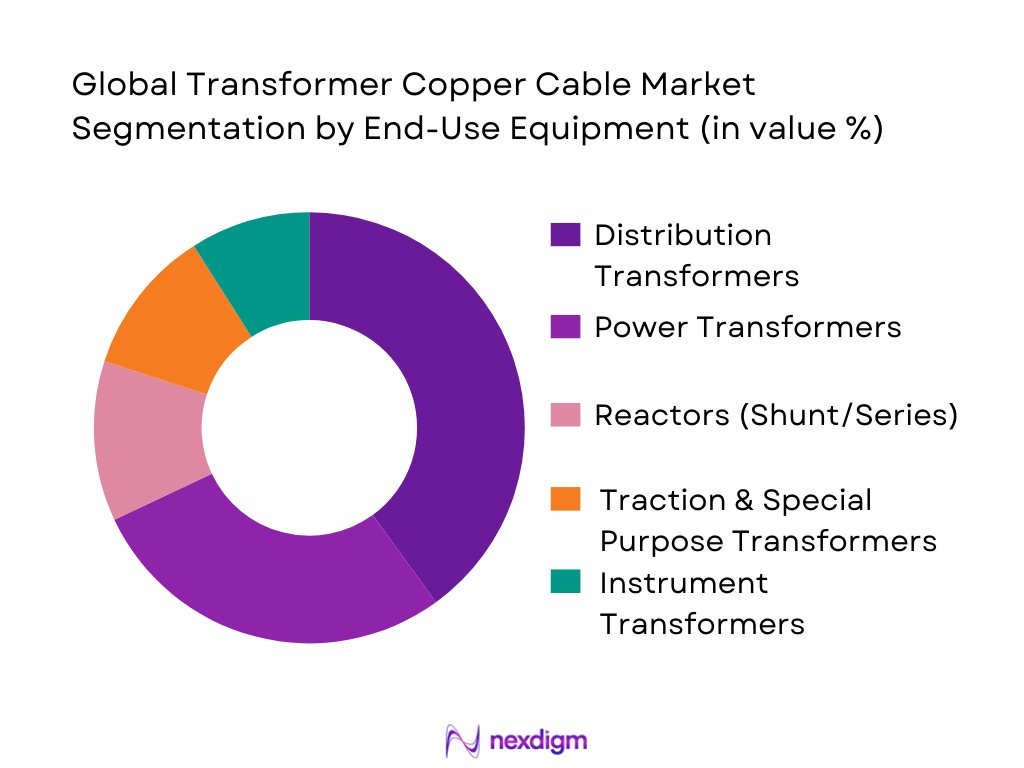
The market is segmented by end-use into distribution transformers, power transformers, reactors/shunt reactors, traction & special purpose transformers, and instrument transformers. Distribution transformers account for the largest share due to their high unit volumes, continuous replacement cycles, and fast procurement cadence across utilities and industrial parks. Even when individual unit copper content is lower than large power transformers, the cumulative copper conductor demand remains highest because distribution transformer production is continuous and geographically broad. India’s volume-heavy programs for feeder strengthening, substation augmentation, and rapid load growth in urban clusters further lift the dominance of this sub-segment, with OEMs optimizing designs for loss reduction and thermal reliability.
Competitive Landscape
The Global Transformer Copper Cable market is moderately consolidated at the high-performance end (CTC, paper-covered, high thermal class systems) and more fragmented in commoditized enamelled winding wire. Competition is shaped by copper input sourcing strength, tight dimensional control, insulation technology capability, OEM qualification depth, and delivery reliability under tender-driven cycles. India’s landscape features strong domestic winding-wire players with growing export participation, while global leaders differentiate via multi-region manufacturing footprints, high-temperature insulation systems, and long-standing OEM/utility approvals.
| Company | Est. Year | HQ | Product Strength (Transformer-grade) | Conductor Portfolio | Insulation / Thermal Class Capability | CTC / Transposed Capability | OEM Qualification Depth | India Presence / Supply Role | Typical End-Market Fit |
| Apar Industries | 1958 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Precision Wires India | 1989 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Essex Solutions (Superior Essex group) | 1930s (legacy) | USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elektrisola Group | 1948 | Germany | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Sumitomo Electric | 1897 | Japan | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Transformer Copper Cable Market Analysis
Market Drivers
Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Reinforcement Requirements
The rapid addition of renewable energy capacity introduces variability and new power injection points, accelerating the need for grid reinforcement and transformer deployment, which directly increases demand for transformer copper cables. Installed renewable capacity has risen from 205.52 GW to 253.96 GW, with solar capacity expanding from 94.17 GW to 132.85 GW and wind from 47.96 GW to 53.99 GW within the same reference window. This expansion necessitates new pooling substations, step-up transformers, and downstream distribution upgrades, all of which require copper-intensive windings and internal cabling. Transmission reinforcement supports this integration, with 490,306 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines and 118,740 MW of inter-regional transfer capacity enabling power evacuation across regions. Renewable-heavy nodes experience higher short-circuit duties and fluctuating loads, increasing technical stress on transformers and driving demand for better-quality winding conductors and insulation systems. India’s nominal GDP of USD 3,909,891.53 million enhances the ability of central and state authorities to finance grid evacuation, substation expansion, and loss-reduction programs that translate into sustained copper cable demand through transformer manufacturing.
Make-in-India and Domestic Value Addition Mandates
Domestic value addition policies and large public schemes are shifting procurement toward localized transformer and component supply chains, expanding the addressable market for India-manufactured transformer copper cables. RDSS is explicitly domestic in execution, covering 19.79 crore consumers and sanctioning 52.53 lakh distribution transformers, 1.27 crore poles, and 4.47 lakh circuit-km of LT lines. This creates a multi-buyer environment in which state discoms and utilities prefer suppliers offering shorter lead times, localized service support, and compliance with standardized technical specifications. Transmission expansion further supports domestic demand visibility, with 14,203 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines added in one fiscal cycle and a total network length of 490,306 circuit-km, implying continuous commissioning and maintenance of transformer assets. Export-oriented manufacturing is emerging as a parallel driver, with insulated wire and cable exports amounting to USD 2,024.10 million, encouraging investment in globally compliant production lines. These industrial outcomes are supported by India’s macroeconomic scale, with nominal GDP at USD 3,909,891.53 million, enabling sustained public procurement and private sector capex across electrical equipment value chains.
Market Challenges
Tight Dimensional and Conductivity Tolerances Impacting Yield
Transformer copper cables are governed by stringent geometric, insulation, and electrical performance requirements, where minor deviations can lead to scrap, rework, or failed routine tests at transformer OEM facilities. India’s compliance environment reinforces these demands through distribution transformer specifications aligned with IS 1180 (Part 1) and repeated regulatory updates issued during 2022, 2023, and 2024, encouraging utilities to tighten acceptance criteria. The challenge is magnified by scale: RDSS-sanctioned volumes of 52.53 lakh distribution transformers require OEMs to standardize winding designs and accelerate throughput, increasing the cost of any conductor variability that disrupts winding, impregnation, or final testing. Grid reinforcement further raises performance expectations, with 118,740 MW of inter-regional transfer capacity and 490,306 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines elevating transformer loading and fault-duty exposure. As a result, cable manufacturers must maintain precise process control across rod breakdown, annealing, enamelling or paper covering, and handling, as any inconsistency can materially impact acceptance rates and yields during rapid, multi-state dispatch cycles.
Dependence on Imported Insulation and Enameling Inputs
While copper drawing capacity is well established domestically, transformer copper cable manufacturing—especially for higher voltage classes—depends on specialty insulation papers, enamels, and varnishes that often require import and lengthy qualification cycles. The risk of dependence is amplified by the pace of deployment under RDSS, which includes 52.53 lakh distribution transformers and 4.47 lakh circuit-km of LT lines, meaning any disruption in insulation input availability can cascade into conductor delivery delays and transformer backlogs. Grid strengthening continues concurrently, with 4,762 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines added early in the fiscal cycle and a total network length of 490,306 circuit-km, maintaining constant pressure on transformer supply chains. Regulatory continuity through updates issued in 2022, 2023, and 2024 narrows flexibility in switching materials without re-testing. Export ambitions add further constraints, as insulated wire and cable exports of USD 2,024.10 million require consistent insulation systems and full traceability. In this context, import dependence becomes an operational risk driven by qualification rigidity and time-bound demand rather than weak market fundamentals.
Opportunities
Replacement of Aging Transformer Fleets
A major growth opportunity for transformer copper cables lies in the replacement and augmentation of aging distribution transformer fleets as utilities modernize feeders, uprate capacity, and reduce technical losses. RDSS provides a clear indicator of this replacement intensity, covering 19.79 crore consumers and sanctioning 52.53 lakh distribution transformers, along with 1.27 crore poles and 4.47 lakh circuit-km of LT lines. These sanctioned works translate directly into recurring demand for transformer manufacturing and rewinding, where copper cables are a critical input. At higher voltage levels, ongoing grid expansion creates refurbishment triggers, with 14,203 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines added in one fiscal cycle and 4,762 circuit-km added early in the current cycle. Inter-regional power flows of 118,740 MW increase transformer utilization at key nodes, encouraging condition-based replacement and uprating. For copper cable suppliers, this environment provides multi-year volume visibility and opportunities to supply higher-grade conductors aligned with standardized utility procurement frameworks.
Export-Oriented Copper Cable Manufacturing for Global Transformer OEMs
India’s rising exports of insulated wires and cables indicate a scalable opportunity for transformer copper cable manufacturers to integrate into global transformer OEM supply chains. Export shipments under insulated wire and cable categories have reached USD 2,024.10 million, demonstrating established international acceptance of Indian manufacturing. This export base can be leveraged into transformer-grade segments as domestic scale forces process industrialization; RDSS volumes of 52.53 lakh distribution transformers compel OEMs and suppliers to enhance consistency, testing discipline, and documentation—capabilities directly relevant to global qualification requirements. Grid expansion reinforces this credibility, with 490,306 circuit-km of 220 kV and above lines and 118,740 MW of inter-regional capacity reflecting a technically demanding operating environment that rewards reliable conductor performance. Global OEMs increasingly prefer suppliers capable of delivering both standard and customized winding conductors at scale, with robust quality systems. India’s nominal GDP of USD 3,909,891.53 million underpins continued investment in testing infrastructure, enamelling and paper covering lines, and compliance systems necessary to secure long-term international supply relationships.
Future Outlook
Over the next 5 years, the Global Transformer Copper Cable market is expected to grow steadily, driven by grid expansion, replacement of ageing transformer fleets, renewable-energy-led grid reinforcement, and rising efficiency requirements that push upgrades in conductor designs and insulation systems. India remains a structural growth engine due to sustained transformer procurement and expanding domestic winding-wire processing capability. Technology directionally shifts toward higher thermal class insulation, tighter dimensional tolerances, and higher strand-count optimized solutions (where applicable), with procurement increasingly rewarding suppliers that can ensure traceability, consistency, and faster lead times.
India Focus: Demand–Supply Fundamentals
India’s transformer copper conductor demand is anchored in utility tender cycles, industrial electrification, and rapid distribution transformer deployment, with increasing emphasis on loss-optimized designs and stable thermal performance. On the supply side, India has strengthened its winding-wire ecosystem through scaled domestic players, improving quality systems, and export momentum in broader winding-wire categories. In transformer-grade products, differentiation increasingly depends on enamel performance consistency, paper covering quality, conductor geometry control, and OEM qualification depth, rather than only conversion cost.
Major Players
- Apar Industries
- Precision Wires India
- Ram Ratna Wires
- Vidya Wires
- KSH International
- SH Haryana Wires
- Essex Solutions (Superior Essex)
- Elektrisola Group
- Sumitomo Electric Industries
- Furukawa Electric
- Von Roll Group
- De Angeli Prodotti
- REA Magnet Wire
- Tongling Jingda (Jingda Special Magnet Wire)
- Jiangsu Zhongchao Holding
Key Target Audience
- Transformer OEMs and winding shops (Power & Distribution transformer manufacturers)
- Electric utilities and grid operators (Power Grid Corporation of India, State DISCOMs, transmission utilities)
- EPC contractors and substation integrators (grid expansion and refurbishment contractors)
- Copper rod producers and upstream copper processors (securing offtake and downstream integration)
- Insulation materials and enamels suppliers (paper, resins, varnishes, aramid systems)
- Renewable energy IPPs and grid-interconnection developers (evacuation infrastructure build-out)
- Investments and venture capitalist firms (infrastructure and industrial manufacturing investments)
- Government and regulatory bodies (Ministry of Power, Central Electricity Authority, Bureau of Indian Standards, Bureau of Energy Efficiency)
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We build an ecosystem map covering copper rod suppliers, conductor processors, insulation suppliers, transformer OEMs, utilities, and EPCs. Desk research is supported by standards mapping (IEC/IS), conductor form factors, and transformer application definitions. The outcome is a structured variable set around demand drivers, qualification constraints, and supply capacities.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
We construct demand using transformer output linkage, conductor intensity by transformer class, and procurement cadence across utilities and OEMs. Supply is assessed through installed processing lines, product mix (round/rectangular/PICC/CTC), and regional production hubs. The model is reconciled using import–export flows and consumption checks.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We validate assumptions through CATIs with transformer OEM sourcing heads, winding-wire QA teams, utility pre-qualification stakeholders, and distributor/stockist networks. Interviews capture real-world price pass-through logic, rejection/yield loss reasons, and lead-time variability across conductor types.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
We triangulate results using bottom-up and top-down reconciliations, cross-checking with trade flows, capacity utilization logic, and OEM qualification breadth. Final outputs include segmentation, competitive benchmarking, and a forward outlook anchored in grid build, replacement demand, and evolving efficiency norms.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definition and Boundary Mapping, Transformer-Grade Copper Cable Technical Assumptions and IEC/IS Standards Alignment, Abbreviations and Nomenclature, Copper Purity and Conductivity Benchmarks for Transformer Windings, Bottom-Up Capacity Assessment of Transformer Copper Cable Manufacturing, Top-Down Correlation with Global and Indian Transformer Installations, Primary Interviews with Transformer OEMs, Utilities, and EPC Contractors, Supplier and Distributor Validation, Demand Normalization Logic Across Transformer Types, Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Copper Cable Usage in Transformer Windings
- Technology Shift from Conventional Rectangular Wires to Engineered Copper
- Cable Solutions
- Voltage-Class-Driven Adoption Lifecycle Across Transformer Ratings
- Global Transformer Manufacturing and Procurement Ecosystem
- Global Transformer Copper Cable Supply Chain and Processing Flow
- India’s Strategic Position in the Global Transformer Copper Cable Value Chain
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Transformer Copper Cable Usage in Indian Transformer Manufacturing
- Role of Copper Cables in Loss Reduction and Thermal Performance Optimization
- India Transformer Industry Structure and Copper Cable Consumption Linkage
- Domestic vs Export-Oriented Transformer Copper Cable Demand Dynamics
- India Transformer Copper Cable Supply Chain Localization Status
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- By Product Type (In Value %)
Enamelled Rectangular Copper Cables
Enamelled Round Copper Cables
Paper Insulated Copper Conductors
Continuously Transposed Conductors (CTC)
Specialty Transformer Copper Cables - By Voltage Class Application (In Value %)
Distribution Transformers
Power Transformers
Extra-High and Ultra-High Voltage Transformers - By End-Use Transformer Type (In Value %)
Oil-Immersed Transformers
Dry-Type Transformers
Traction and Special Purpose Transformers - By Insulation System (In Value %)
Enamel-Based Insulation
Paper-Based Insulation
Hybrid Paper–Enamel Insulation
High-Temperature Insulation Systems - By Manufacturing Process (In Value %)
Continuous Drawing and Enameling
Paper Covering and Insulation Wrapping
Transposition and Strand Assembly
Hybrid and Customized Processing - By End User (In Value %)
Transformer OEMs
Power Utilities and Grid Operators
EPC Contractors - By Geography within India (In Value %)
Western India
Southern India
Northern India
Eastern India
Central India
- Market Drivers
Grid Capacity Expansion and Transformer Capacity Additions
Rising Adoption of Loss-Optimized and High-Efficiency Transformer Designs
Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Reinforcement Requirements
Make-in-India and Domestic Value Addition Mandates - Market Challenges
Copper Price Volatility and Working Capital Exposure
Tight Dimensional and Conductivity Tolerances Impacting Yield
Dependence on Imported Insulation and Enameling Inputs - Opportunities
Replacement of Aging Transformer Fleets
Export-Oriented Copper Cable Manufacturing for Global Transformer OEMs
Adoption in High-Efficiency, Green, and Smart Transformers - Trends
Shift Toward Higher Performance and Multi-Insulation Copper Cables
Automation of Drawing, Enameling, and Quality Inspection Lines
OEM-Specific Custom Copper Cable Designs - Regulatory and Standards Landscape
BIS and IEC Compliance Requirements
Utility-Specific Technical Acceptance and Qualification Norms - Cost Structure and Margin Analysis (Copper Input Share, Conversion Cost, Yield Loss, Compliance Cost)
- Porter’s Five Forces (Supplier Power, OEM Bargaining Strength, Entry Barriers, Substitutes, Competitive Rivalry)
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping (Copper Rod Suppliers, Copper Cable Processors, Transformer OEMs, Utilities, EPC Contractors)
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- Demand Split by Domestic Consumption and Exports, 2019-2025
- Transformer OEM Demand Patterns (Tender-Driven vs Long-Term Sourcing)
- Utility Technical Acceptance and Qualification Criteria
- Procurement and Vendor Approval Cycles
- Unmet Needs and Technical Pain Points
- Decision-Making and Vendor Lock-In Dynamics
- Market Share Analysis of Major Players(Value/Volume Mix)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Installed Copper Cable Capacity, Annual Output Tonnes, Product Portfolio Coverage, Voltage Class Compatibility, Insulation Technology Capability, Transformer OEM Qualification Count, Export Intensity, In-House Copper Rod Dependency)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Benchmarking (By Product Type, Voltage Class, Transformer Rating, OEM Specification Grade)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Apar Industries
Precision Wires India
Sterlite Power
Hindalco Industries
RR Shramik
Superior Essex
Elektrisola
Sumitomo Electric
Furukawa Electric
LS Cable & System
Nexans
Tongling Jingda
Ningbo Jintian
Zhejiang Wanma
Jiangsu Zhongchao
- By Value, 2026-2030
- By Volume, 2026-2030
- By Average Realized Price, 2026-2030
- Demand Split by Domestic Consumption and Exports, 2026-2030
- Existing India–Foreign Joint Ventures
- Future Foreign Collaboration and Joint Venture Opportunities


