Market Overview
The global Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) market is valued at USD ~ billion, supported by sustained transformer manufacturing activity and grid expansion programs. India contributes a market value of USD ~ million, driven by large-scale power transmission upgrades and renewable energy evacuation requirements. Grid-connected transformer capacity additions exceeding 45,000 MVA annually and copper conductor consumption of over 1.4 million metric tons globally underpin demand. Rising focus on reducing eddy current losses and improving thermal efficiency in power and distribution transformers continues to structurally increase CTC penetration in transformer windings.
The market is dominated by China, India, Germany, Japan, and the United States due to their concentration of transformer manufacturing, grid modernization investments, and advanced conductor processing capabilities. In India, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana dominate CTC demand owing to dense transformer OEM clusters, port-based copper sourcing advantages, and strong export orientation. These regions also benefit from skilled metallurgical labor, proximity to copper rod suppliers, and established qualification approvals from utilities and EPC contractors.
Market Segmentation
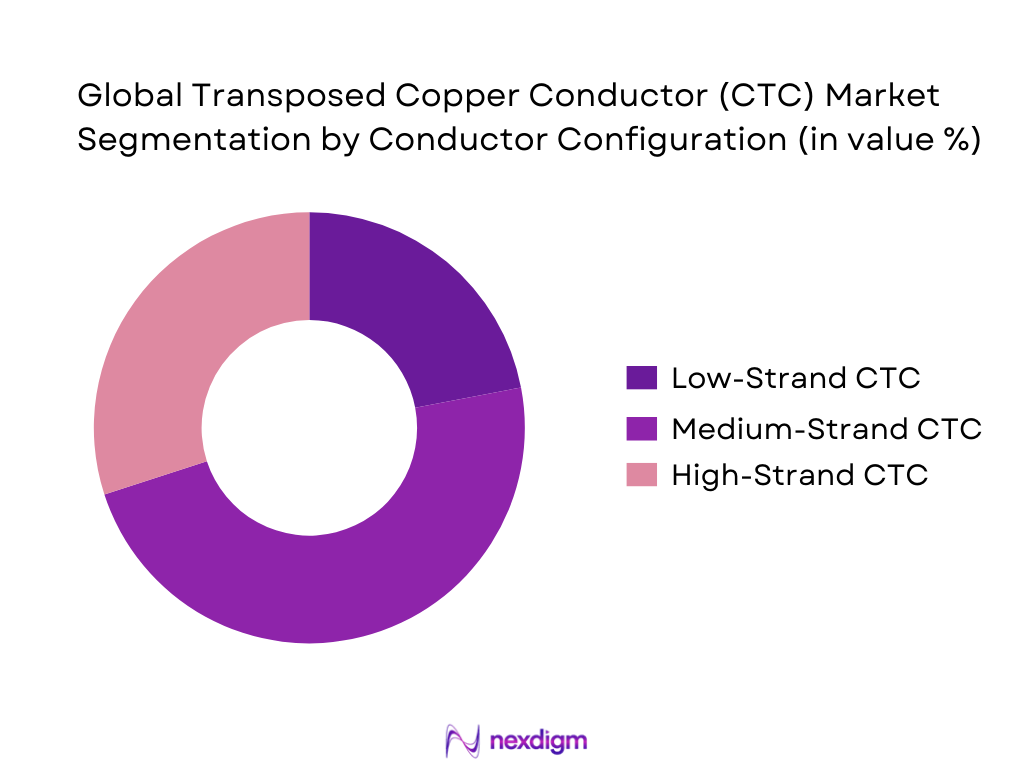
By Conductor Configuration
The India Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) market is segmented into low-strand, medium-strand, and high-strand CTC. Medium-strand CTC dominates this segment due to its optimal balance between loss reduction and manufacturability. Indian transformer OEMs increasingly specify medium-strand configurations for both distribution and power transformers as they offer superior electromagnetic performance without significantly increasing winding complexity. These conductors align well with standard utility tender specifications and are compatible with existing transposition and enameling infrastructure, making them cost-efficient for large-scale transformer production.
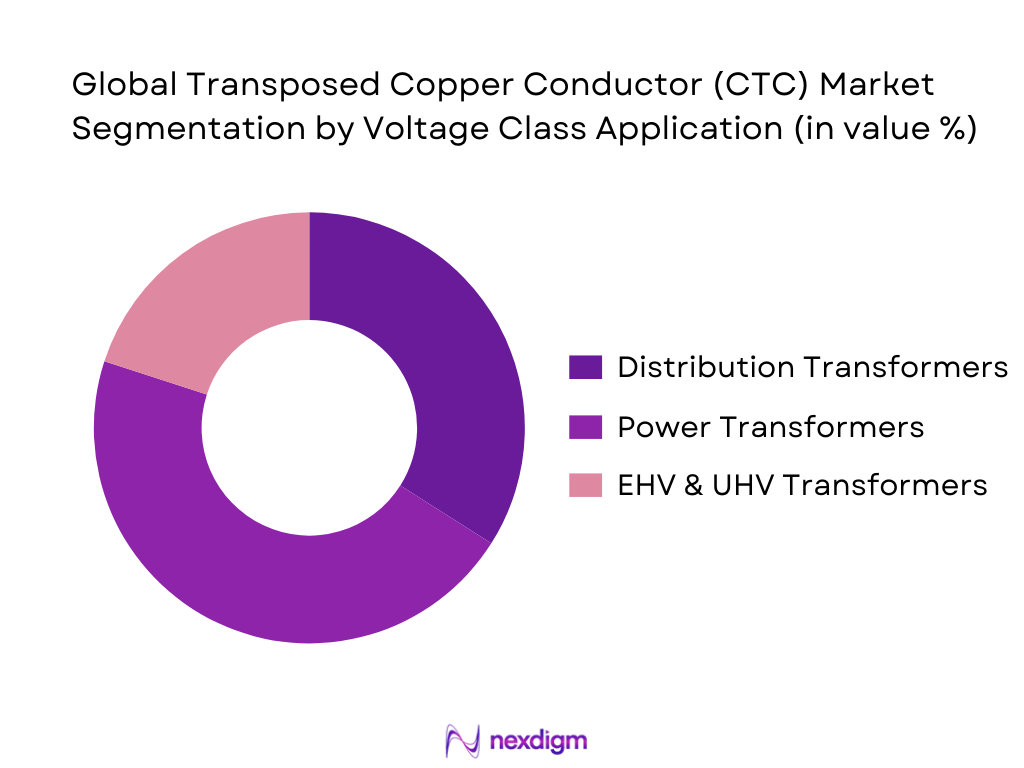
By Voltage Class Application
By voltage class, the market is segmented into distribution transformers, power transformers, and extra-high/ultra-high voltage transformers. Power transformers hold the dominant share as CTC is increasingly mandated for higher MVA ratings to control circulating currents and thermal hotspots. India’s growing inter-state transmission corridors, renewable evacuation substations, and urban load centers rely heavily on power transformers where CTC adoption directly improves operational efficiency and lifecycle performance, making this segment the largest consumer of transposed copper conductors.
Competitive Landscape
The Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) market is moderately consolidated, with a mix of global magnet wire specialists and India-based integrated conductor manufacturers. Entry barriers remain high due to stringent dimensional tolerances, transformer OEM qualification cycles, and capital-intensive transposition and enameling lines. Indian players benefit from cost competitiveness and proximity to transformer OEMs, while European and Japanese firms retain strength in ultra-high voltage and export-grade conductors.
| Company | Established | Headquarters | Key Parameters |
| Apar Industries | 1958 | India | Installed CTC capacity, export orientation, OEM approvals, strand range, in-house enameling, transformer grade focus |
| Precision Wires India | 1989 | India | Copper purity control, medium-strand specialization, utility qualification, domestic dominance |
| De Angeli Prodotti | 1948 | Italy | EHV conductor expertise, European grid compliance, premium insulation systems |
| Sumitomo Electric | 1897 | Japan | Advanced transposition tech, ultra-high voltage focus, global OEM relationships |
| Elektrisola | 1948 | Germany | Precision conductors, specialty transformers, high-spec export markets |
India Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) Market Analysis
Market Drivers
Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Reinforcement
Rapid renewable energy deployment intensifies demand for transformers and substations because variable generation sources require stronger evacuation networks, pooling substations, and reinforced transmission corridors. India’s renewable installed base has expanded significantly, with annual solar capacity additions of 15,033.24 MW followed by 23,832.87 MW in successive recent cycles, alongside wind capacity additions of 3,253.38 MW and 4,151.31 MW in the same periods. These additions translate directly into requirements for new grid interconnections, transformer bays, and reactive power support equipment. Transmission reinforcement projects linked to renewable evacuation, including strengthening schemes for 8.1 GW solar zones in Rajasthan, illustrate how renewable growth creates concentrated and predictable transformer demand. This environment favors modern transformer designs that adopt CTC to manage thermal stress and loss profiles under fluctuating load conditions. India’s macroeconomic capacity, underpinned by a current-price GDP of USD 4.51 trillion, enables sustained investment in such grid reinforcement. For CTC manufacturers, renewable integration acts as a demand multiplier, expanding both new-build transformer requirements and system-strengthening retrofits where advanced winding solutions are specified.
Make-in-India and Domestic Value Addition Requirements
India’s domestic value addition agenda supports sustained CTC demand by encouraging transformer OEMs and grid projects to localize sourcing, expand vendor development, and deepen manufacturing capabilities within the country. The scale of the national power sector highlights this opportunity: installed capacity stands at 446,190 MW, while cumulative additions of 730,794 MVA of transformation capacity and 195,181 circuit-km of transmission lines reflect the magnitude of domestically supplied equipment required. As localization deepens, transformer OEMs increasingly internalize technical specifications, qualification regimes, and supply continuity requirements. CTC suppliers capable of meeting IEC- and IS-aligned dimensional tolerances and consistent insulation quality become preferred partners because they reduce execution and warranty risks in large utility tenders. India’s large nominal GDP of USD 4.51 trillion provides the macroeconomic foundation for sustaining domestic manufacturing ecosystems at scale. For the CTC market, localization stabilizes demand: once domestic suppliers are qualified and integrated into repeat procurement cycles, reorder frequency increases and dependence on imported conductors declines.
Market Challenges
Copper Price Volatility and Working Capital Exposure
CTC manufacturing is highly copper-intensive, making producers directly exposed to fluctuations in copper prices through inventory valuation and working capital requirements. Recent global copper price movements highlight this volatility, with annual price levels recorded at USD 8,828.91681 per metric ton, USD 8,490.76173 per metric ton, and USD 9,142.10156 per metric ton across consecutive recent observations. Such variation materially affects the rupee value of copper rod and rectangular wire inventories held prior to transposition and enameling. In parallel, India’s large grid capex cycle increases production throughput, raising the absolute value of copper tied up in work-in-process across CTC lines. From a market perspective, producers face dual exposure: price movement between procurement and delivery, and potential rejection or rework if dimensional or insulation standards are not met. Additionally, milestone-based payment structures in utility and EPC contracts can lengthen receivable cycles, increasing financing pressure during periods of copper price volatility.
Tight Dimensional Tolerances and Yield Loss Risk
CTC is a precision-engineered conductor where strand geometry, edge radius, surface finish, and insulation build must conform tightly to transformer OEM and utility specifications. As grid expansion accelerates, the cost of non-conformance rises because transformer delivery schedules are tender-locked and delays can have system-wide implications. India’s transmission system, with approximately 177,699 circuit-km of lines and 527,446 MVA of transformation capacity, reflects a standardized, reliability-driven operating environment. High operational availability levels of 99.85 and low tripping rates of 0.28 per line demonstrate the reliability culture embedded in equipment acceptance standards. For CTC manufacturers, yield losses can arise from strand damage, insulation pinholes, transposition defects, or thickness variation—issues that become more expensive when copper prices are elevated. As a result, only suppliers with strong process control, in-line inspection, and consistent copper input quality can scale profitably, posing challenges for smaller or newly ramping players.
Opportunities
Export-Focused CTC Manufacturing for Global OEMs
India has a strong opportunity to scale export-grade CTC manufacturing by leveraging its expanding domestic transformer ecosystem and experience gained through large grid investments. Recent transmission expansion, including 4,036 circuit-km of extra-high-voltage lines, 6 new substations, and 19,720 MVA of added transformation capacity in a single execution cycle, reflects the sophistication of India’s high-voltage supply chain. This environment helps domestic CTC manufacturers develop process maturity, quality systems, and qualification depth aligned with international standards. As Indian suppliers demonstrate consistency with IEC- and IS-aligned requirements, they become viable partners for global transformer OEMs that demand tight tolerances, traceability, and delivery reliability. India’s macroeconomic scale, supported by a current-price GDP of USD 4.51 trillion, enables investments in manufacturing infrastructure and export logistics. The export opportunity for CTC is therefore specialized, centered on supplying engineered, OEM-qualified conductors rather than generic wire products.
Adoption in High-Efficiency and Green Transformers
The transition toward high-efficiency and “green” transformer designs presents a high-conviction opportunity for the CTC market, as these designs prioritize reduced losses, better thermal behavior, and compatibility with renewable-heavy grids. India’s renewable expansion highlights the technical demands placed on the grid, with solar additions of 15,033.24 MW and 23,832.87 MW, and wind additions of 3,253.38 MW and 4,151.31 MW across successive recent cycles. Such growth requires transformers capable of handling dynamic loading and frequent load variation. Transmission reinforcement linked to renewable evacuation, including projects associated with 8.1 GW solar zones, further increases demand for modern transformer fleets. In this context, CTC adoption rises because OEMs seek to control localized losses and temperature rise under variable operating conditions. Supported by India’s large economic scale, the shift toward efficiency increases the strategic value of engineered conductors that meet demanding thermal and electrical performance requirements without compromising manufacturability.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast period, the Global Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) market is expected to expand steadily, driven by sustained investments in grid reliability, renewable integration, and transformer efficiency standards. India is projected to remain one of the fastest-growing markets due to power transmission expansion, industrial electrification, and export-oriented transformer manufacturing. Increasing use of higher-strand configurations, automation in conductor processing, and foreign collaborations for advanced insulation technologies will further shape the market trajectory.
The India Transposed Copper Conductor (CTC) market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of ~ during the period 2025–2030, supported by continuous transformer capacity additions, replacement of aging infrastructure, and policy emphasis on loss reduction.
Major Players
- Apar Industries
- Precision Wires India
- Sterlite Power
- Hindalco Industries
- SPS CTC Wire
- De Angeli Prodotti
- LWW Group
- Elektrisola
- Sumitomo Electric
- Furukawa Electric
- Von Roll
- Essex Solutions
- Jiangsu Zhongchao
- Guangdong Huacheng
- Zhejiang Wanma
Key Target Audience
- Transformer manufacturing companies
- Power transmission utilities (Power Grid Corporation of India, State Electricity Boards)
- Renewable energy EPC contractors
- Industrial electrical equipment manufacturers
- Copper rod and wire producers
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies (Central Electricity Authority, Ministry of Power, Bureau of Indian Standards)
- Infrastructure and energy project developers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The research begins with mapping the complete CTC ecosystem, including copper suppliers, conductor processors, transformer OEMs, utilities, and EPCs. Extensive secondary research is conducted using industry databases, trade statistics, and regulatory publications to identify variables influencing demand.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on transformer production, grid investments, and copper consumption is analyzed to establish market baselines. Production-to-consumption correlations and OEM procurement data are used to construct reliable market values.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions are validated through structured interviews with transformer manufacturers, conductor producers, and industry experts. These discussions provide insights into pricing trends, qualification cycles, and technological shifts.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Data from bottom-up and top-down approaches is triangulated to ensure consistency and accuracy. The final output integrates quantitative validation with qualitative insights to deliver a robust market assessment.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definition and Boundary Mapping, CTC Technical Assumptions and IEC/IS Standards Alignment, Abbreviations and Nomenclature, Transformer-Grade Copper Purity Benchmarks, Bottom-Up Plant Capacity Assessment, Top-Down Grid Investment Correlation, Primary Interviews with Transformer OEMs and Utilities, Supplier and EPC Validation, Demand Normalization Logic, Limitations and Forward-Looking Assumptions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of CTC Adoption in Power and Distribution Transformers
- Technology Shift from Rectangular Conductors to CTC
- Voltage-Class-Driven Adoption Lifecycle
- Global Transformer Manufacturing and Procurement Ecosystem
- Global CTC Supply Chain and Processing Flow
- India’s Strategic Position in the Global CTC Value Chain
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of CTC Usage in Indian Transformer Manufacturing
- Role of CTC in Loss Reduction and Thermal Performance Improvement
- India Transformer Industry Structure and CTC Consumption Linkage
- Domestic vs Export-Oriented CTC Demand Dynamics
- India CTC Supply Chain Localization Status
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- By Conductor Configuration (In Value %)
Low-Strand CTC
Medium-Strand CTC
High-Strand CTC - By Voltage Class Application (In Value %)
Distribution Transformers
Power Transformers
Extra-High and Ultra-High Voltage Transformers - By End-Use Transformer Type (In Value %)
Oil-Immersed Transformers
Dry-Type Transformers
Traction and Special Purpose Transformers - By Manufacturing Process (In Value %)
- Continuous Transposition
Discrete Transposition
Hybrid Transposition - By End User (In Value %)
Transformer OEMs
Power Utilities and Grid Operators
EPC Contractors - By Geography within India (In Value %)
Western India
Southern India
Northern India
Eastern India
Central India
- Market Drivers
Grid Capacity Expansion and Transformer Capacity Additions
Rising Adoption of Loss-Optimized Transformer Designs
Renewable Energy Integration and Grid Reinforcement
Make-in-India and Domestic Value Addition Requirements - Market Challenges
Copper Price Volatility and Working Capital Exposure
Tight Dimensional Tolerances and Yield Loss Risk
Dependence on Imported Enameling Inputs - Opportunities
Replacement of Legacy Transformer Fleets
Export-Focused CTC Manufacturing for Global OEMs
Adoption in High-Efficiency and Green Transformers - Trends
Shift Toward Higher Strand Count CTC
Automation of Transposition and Enameling Lines
OEM-Specific Custom CTC Designs - Regulatory and Standards Landscape
BIS and IEC Compliance Requirements
Utility-Specific Technical Acceptance Norms - Cost Structure and Margin Analysis (Copper Input Share, Conversion Cost, Yield Loss)
- Porter’s Five Forces (Supplier Power, OEM Bargaining Strength, Entry Barriers, Substitutes, Competitive Rivalry)
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Mapping (Copper Rod Suppliers, CTC Processors, Transformer OEMs, Utilities, EPCs)
- By Value, 2019-2025
- By Volume, 2019-2025
- Demand Split by Domestic Consumption and Exports, 2019-2025
- Transformer OEM Demand Patterns (Tender-Driven vs Long-Term Sourcing)
- Utility Technical Acceptance and Qualification Criteria
- Procurement and Vendor Approval Cycles
- Unmet Needs and Technical Pain Points
- Decision-Making and Vendor Lock-In Dynamics
- Market Share Analysis of Major Players (Value/Volume Mix)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Installed CTC Capacity, Annual Output Tonnes, Strand Range Capability, Voltage Class Coverage, Enameling Technology, OEM Qualification Count, Export Intensity, In-House Copper Rod Dependency)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Benchmarking (By Strand Count, Voltage Class, OEM Grade)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Apar Industries
Precision Wires India
Sterlite Power
Hindalco Industries
SPS CTC Wire
De Angeli Prodotti
LWW Group
Elektrisola
Sumitomo Electric
Furukawa Electric
Von Roll
Essex Solutions
Jiangsu Zhongchao
Guangdong Huacheng
Zhejiang Wanma
- By Value, 2026-2030
- By Volume, 2026-2030
- Demand Split by Domestic Consumption and Exports, 2026-2030
- Existing India – Foreign Joint Venture
- Potential Foreign Collaboration and Joint Venture Opportunities


