Market Overview
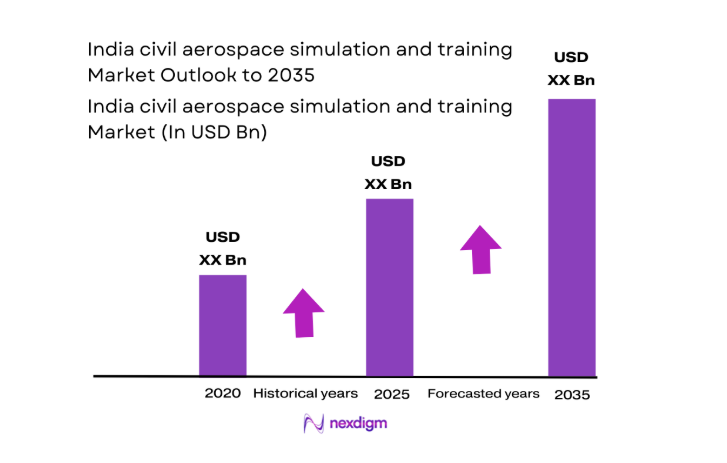
The India civil aerospace simulation and training market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported across multiple training categories and platforms. Demand intensity reflects recurrent qualification cycles, fleet transitions, and instructor availability across certified facilities. Utilization remains uneven, yet scheduling density stays high because compliance windows compress capacity. Technology mix includes full flight, fixed base, and procedural systems, with software refresh cycles driving upgrades. Service revenues remain masked, while contract structures emphasize availability, uptime, and regulatory readiness.
Operational concentration remains strongest around Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, where airline bases, engineering clusters, and regulatory access converge. These hubs benefit from dense instructor pools, spares logistics, and proximity to operators, accelerating turnaround times. Secondary cities show emerging demand anchored by regional connectivity initiatives and helicopter operations. Policy oversight, certification pathways, and ecosystem maturity reinforce clustering, while infrastructure reliability and power quality continue shaping site selection decisions across the country.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
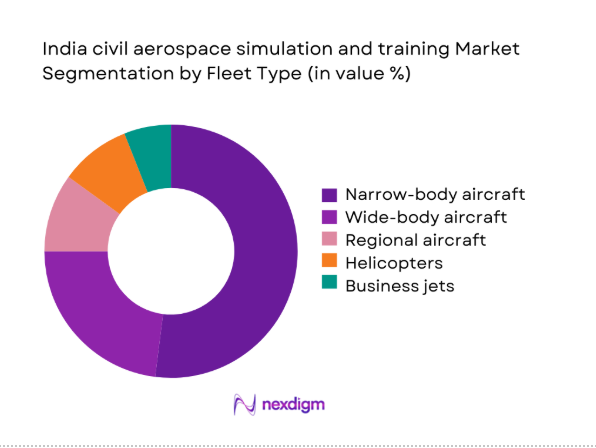
Narrow-body aircraft dominate training demand because domestic route density and rapid induction schedules compress qualification windows and prioritize standardized recurrent cycles. Wide-body exposure remains material for international operations, yet simulator hours concentrate around narrow-body types supporting frequent crew rotations. Regional aircraft and helicopters contribute stable utilization driven by connectivity missions and offshore requirements, while business aviation and general aviation remain episodic. In 2024 and 2025, operator scheduling favored platforms enabling quick transitions between variants, reinforcing modular device strategies. Training centers optimized bay allocations, instructor rosters, and night operations to maximize throughput. This structure sustains predictable demand patterns across certification checks, upgrade courses, and remedial sessions without relying on ad hoc aircraft availability.
By Technology Architecture
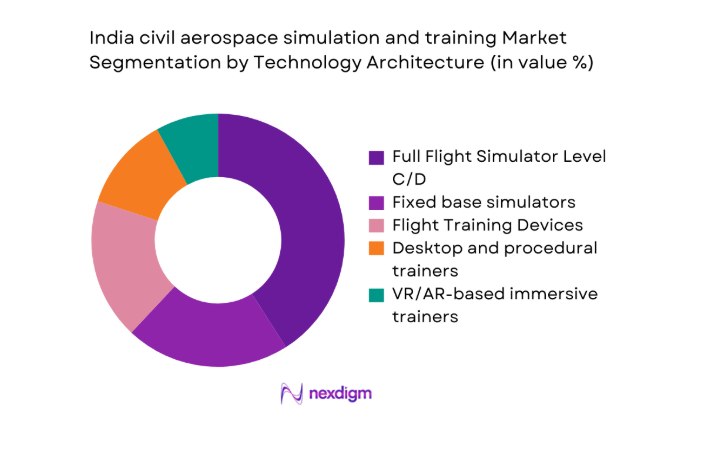
Full flight simulators anchor compliance-driven programs because regulatory acceptance and motion fidelity streamline check rides and recurrent assessments. Fixed base and flight training devices expand throughput for procedures, abnormal handling, and systems refreshers, improving scheduling flexibility. Desktop and immersive trainers gained traction during 2024 and 2025 as pre-simulator preparation tools that reduce time on premium assets. Networked classrooms support instructor standardization and multi-crew coordination exercises, while software updates shorten requalification cycles. Operators increasingly design blended pathways, sequencing lower-cost devices before high-fidelity sessions. This architecture mix balances availability, pedagogical effectiveness, and certification requirements across busy training calendars.
Competitive Landscape
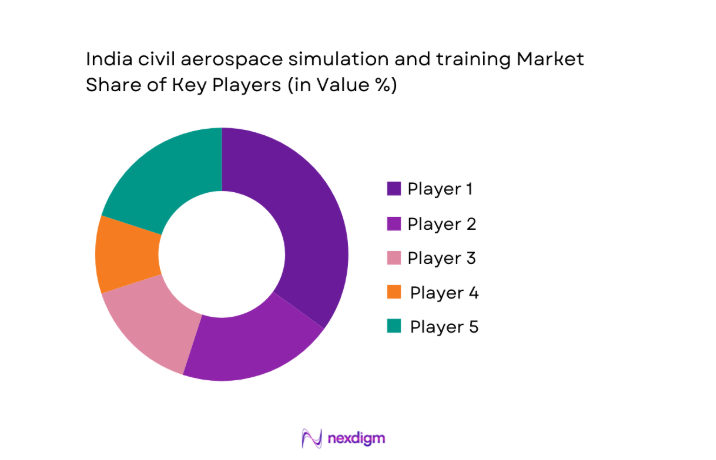
The competitive environment features global platform providers and regional service operators, with differentiation centered on certification coverage, availability guarantees, and instructor integration. Contract structures emphasize uptime, scheduling priority, and upgrade pathways, while partnerships expand local service depth.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| CAE | 1947 | Canada | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L3Harris Commercial Training Solutions | 1895 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Collins Aerospace | 2018 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| FlightSafety International | 1951 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India civil aerospace simulation and training Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising commercial aircraft fleet induction in India
Fleet induction momentum during 2024 accelerated training demand, because every new aircraft requires standardized simulators, instructors, and recurrent qualification cycles. Airlines scheduled parallel courses to reduce line disruptions, and training centers extended operating windows using data-driven roster planning systems. In 2025, additional variant introductions increased cross-qualification requirements, reinforcing modular curricula and standardized lesson plans across multiple device classes. Crew pairing rules and duty limitations intensified simulator utilization, because operators prioritized compliance without sacrificing network reliability during peak seasons. Maintenance coordination improved, enabling higher availability ratios and predictable slot allocation across fleets with differing cockpit architectures. Instructor pipelines expanded through structured mentoring, reducing bottlenecks that previously constrained throughput during seasonal induction waves. Digital briefing tools shortened classroom segments, reallocating minutes toward device sessions that demonstrate measurable proficiency improvements. Recurrent cycles tightened, increasing annual touchpoints per pilot while maintaining consistent assessment criteria across bases. Operational planners favored night sessions, balancing crew fatigue considerations with capacity optimization objectives during sustained induction phases. These combined effects sustained demand pressure across 2024 and 2025 without referencing aggregate market scale or financial magnitudes.
DGCA-mandated recurrent training and proficiency checks
Regulatory frameworks require periodic checks, and compliance cadence during 2024 reinforced predictable simulator booking patterns across airlines and training organizations. Standardization guidance emphasized scenario-based evaluation, prompting curriculum redesigns and additional sessions focused on abnormal and emergency procedures. In 2025, oversight audits increased documentation rigor, encouraging centers to invest in quality systems and instructor standardization programs. Operators adopted centralized scheduling to minimize missed slots, improving utilization consistency across geographically distributed facilities. Digital recordkeeping reduced administrative delays, allowing faster rebooking when operational disruptions affected planned sessions. Crew representatives collaborated on roster stability, aligning duty constraints with assessment windows to preserve safety margins. Recency rules encouraged continuous engagement rather than clustered check rides, smoothing demand across months and seasons. Quality assurance teams monitored pass rates and retraining triggers, refining lesson sequencing without expanding device time unnecessarily. Interoperability between training management systems simplified compliance reporting, reducing friction during inspections and renewals. This regulatory pull maintained steady demand drivers through 2024 and 2025 independent of broader economic cycles.
Challenges
High capital cost of full flight simulators
Acquiring high-fidelity devices remains demanding, because procurement cycles involve customization, certification, and long lead times that constrain rapid capacity expansion. During 2024, operators prioritized utilization improvements rather than immediate acquisitions, emphasizing scheduling efficiency and maintenance planning discipline. Financing structures vary, yet risk committees remain cautious about long payback horizons associated with specialized assets. In 2025, currency movements and logistics complexity added uncertainty, further encouraging shared access models and time-based leasing arrangements. Spares provisioning and software upgrades introduce additional planning burdens, affecting total lifecycle commitments beyond initial purchase decisions. Smaller centers struggle to justify single-type investments, prompting partnerships that require governance and revenue-sharing negotiations. Regulatory acceptance processes extend timelines, delaying revenue realization and complicating project sequencing with fleet induction schedules. Energy reliability and floor loading constraints also shape site feasibility, increasing preparatory engineering requirements before installation approvals. Instructor training for new devices consumes scarce resources, temporarily reducing throughput during transition periods. These factors collectively moderate expansion pace despite persistent training demand across multiple operator categories.
Long certification timelines and regulatory approvals
Certification pathways require extensive documentation, witness testing, and iterative findings resolution, which lengthen commissioning schedules and defer operational readiness. In 2024, several projects adopted phased acceptance strategies, yet initial scope limitations constrained immediate revenue-generating utilization opportunities. Coordination among manufacturers, regulators, and operators demands calendar alignment, increasing project management complexity and stakeholder dependencies. During 2025, audit backlogs and travel constraints occasionally extended review cycles, affecting planned training capacity introductions. Change management for software updates triggers revalidation steps, adding incremental downtime that must be absorbed within already tight schedules. Documentation quality varies, requiring rework and additional demonstrations that consume engineering and instructor availability. Interfacing national guidance with international standards introduces interpretation challenges, prolonging clarification loops and decision gates. Temporary approvals help bridge gaps, yet conservative operational policies often restrict full commercial use until final sign-off. Training organizations therefore maintain contingency arrangements with partner centers, increasing coordination overhead and cost exposure. The cumulative effect slows capacity realization even when hardware readiness milestones appear technically complete.
Opportunities
Localization of simulator manufacturing and integration
Localized integration ecosystems can shorten lead times, improve service responsiveness, and tailor configurations for domestic fleet mixes across multiple operator categories. In 2024, pilot projects demonstrated faster installation cycles, reducing dependency on long-distance logistics and specialized import procedures. Component sourcing partnerships expanded during 2025, enabling incremental upgrades without complete device replacements or prolonged downtime windows. Workforce development programs strengthened engineering benches, improving first-time pass rates during acceptance testing and periodic revalidation events. Software localization supported language preferences and procedural alignment, enhancing instructor effectiveness and trainee comprehension outcomes. Co-development arrangements encouraged knowledge transfer, building domestic competencies in motion systems, visuals, and data packages. Shared facilities for integration testing reduced duplication, accelerating certification preparation and documentation harmonization efforts. Operators benefited from quicker configuration changes following fleet updates, minimizing training disruptions during transition periods. Maintenance turnaround times improved, raising availability metrics and scheduling confidence for high-demand recurrent programs. These dynamics position localization as a durable lever for capacity resilience and operational agility.
Growth of third-party training centers and academies
Independent centers expand geographic coverage, reduce travel burdens, and introduce competitive scheduling options for operators managing diverse fleet portfolios. In 2024, several academies adopted multi-type strategies, enabling cross-utilization and smoothing demand volatility across seasonal peaks. Collaborative agreements in 2025 standardized curricula, supporting consistent outcomes while preserving operational flexibility for partner airlines. Shared instructor pools mitigated scarcity risks, and joint rostering improved coverage during check ride surges. Digital marketplaces simplified slot discovery, increasing transparency and reducing idle time across distributed device networks. Specialized tracks for cabin crew and maintenance staff diversified utilization beyond pilot-only programs. Quality frameworks aligned assessment standards, easing regulatory oversight and strengthening stakeholder confidence in outsourced arrangements. Regional hubs reduced positioning flights, lowering fatigue and improving punctuality for line operations. Capacity buffers created by networks absorbed disruptions from weather, maintenance, or fleet changes. This expansion pathway complements operator-owned assets while accelerating overall training accessibility.
Future Outlook
The market trajectory emphasizes blended architectures, stronger compliance tooling, and deeper partnerships between operators and specialized centers. Through 2035, ecosystem maturity should favor reliability, data-driven scheduling, and faster certification cycles. Technology refreshes will prioritize instructor effectiveness and scenario realism while preserving uptime. Policy continuity and fleet transitions will keep recurrent demand structurally resilient across planning horizons.
Major Players
- CAE
- L3Harris Commercial Training Solutions
- Thales
- Collins Aerospace
- FlightSafety International
- TRU Simulation + Training
- Indra Sistemas
- Simaero
- MPS
- Airbus Flight Training
- Boeing Global Services
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Air India Engineering Services Limited
- Bird Group
Key Target Audience
- Scheduled airlines operating commercial fleets
- Charter and business aviation operators
- Helicopter operators supporting offshore and utility missions
- Maintenance, repair, and overhaul organizations
- Directorate General of Civil Aviation
- Ministry of Civil Aviation
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Airport operators and infrastructure developers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study identifies fleet categories, device architectures, certification pathways, and utilization drivers shaping training demand. It maps regulatory requirements, operational constraints, and instructor availability considerations. Data points focus on activity indicators from 2024 and 2025 without disclosing market size or revenues.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
The framework organizes segmentation, ecosystem roles, and capacity workflows across operators and training centers. It evaluates scheduling practices, technology mixes, and compliance processes influencing throughput. Cross-validation ensures consistency across operational indicators and qualitative insights.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions are reviewed with practitioners overseeing training operations, quality systems, and fleet transitions. Feedback refines interpretations of utilization, certification timing, and device deployment strategies. Iterations reconcile operational realities with policy expectations.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into coherent narratives covering segmentation, competition, and outlook. The output emphasizes decision-relevant insights while respecting masking requirements for sensitive metrics. The presentation maintains consistency, clarity, and auditability.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and civil flight simulation and training scope mapping, Simulator taxonomy and platform architecture segmentation, Bottom-up build of device shipments and training hours with utilization normalization, Revenue attribution across OEM hardware software licenses and training services, Primary interviews with airline training heads DGCA-approved ATOs and simulator OEMs)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Training and certification pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and service delivery structure
- Regulatory environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising commercial aircraft fleet induction in India
DGCA-mandated recurrent training and proficiency checks
Capacity constraints at live aircraft training bases
Airline focus on safety performance and standardization
Expansion of domestic and regional air connectivity
Cost optimization versus in-aircraft training hours - Challenges
High capital cost of full flight simulators
Long certification timelines and regulatory approvals
Shortage of qualified instructors and examiners
Dependence on imported simulator hardware and spares
Volatility in airline profitability and training budgets
Infrastructure and power reliability constraints - Opportunities
Localization of simulator manufacturing and integration
Growth of third-party training centers and academies
Adoption of VR and mixed reality for procedural training
Regional training hubs for South Asia and Middle East carriers
Upskilling programs for maintenance and engineering staff
Airline fleet transitions driving new type rating demand - Trends
Shift toward competency-based training and assessment
Increased use of data-driven training analytics
Fleet-specific simulator capacity planning
Hybrid training models combining classroom and simulation
Partnerships between OEMs and Indian training providers
Lifecycle upgrades of legacy simulator platforms - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Narrow-body aircraft
Wide-body aircraft
Regional aircraft
Business jets
Helicopters
General aviation - By Application (in Value %)
Initial pilot training
Recurrent and type rating training
Cabin crew training
Maintenance technician training
Procedural and systems training - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Full Flight Simulator Level C/D
Fixed base simulators
Flight Training Devices
Desktop and procedural trainers
VR/AR-based immersive trainers - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Scheduled airlines
Charter and business aviation operators
Helicopter operators
Flight training organizations
MRO and engineering organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
Networked multi-simulator environments
Cloud-enabled training platforms
Live Virtual Constructive integrated systems - By Region (in Value %)
North India
West India
South India
East India
Central India
Northeast India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Simulator portfolio breadth, Certification levels and compliance, Installed base in India, After-sales support footprint, Training services integration, Pricing and commercial models, Localization and partnerships, Technology roadmap)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
CAE
L3Harris Commercial Training Solutions
Thales
Collins Aerospace
Boeing Global Services
Airbus Flight Training
FlightSafety International
TRU Simulation + Training
Indra Sistemas
Simaero
MPS
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Tata Advanced Systems
Air India Engineering Services Limited
Bird Group
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


