Market Overview
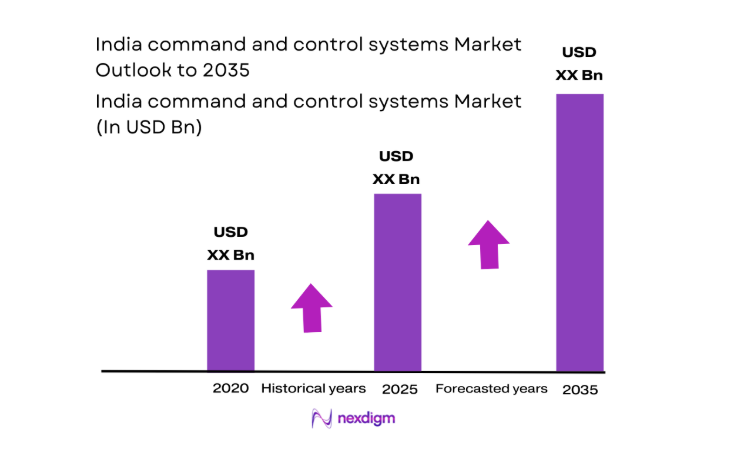
The India command and control systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained institutional demand across defense and security operations. The market is shaped by ongoing digital modernization priorities and the need for integrated, real-time operational coordination. Platforms increasingly emphasize secure communications, situational awareness, and resilient data exchange capabilities. Deployment strategies focus on scalable architectures that support evolving mission requirements without extensive system replacement. Lifecycle management practices prioritize continuity of operations through incremental upgrades and long-term sustainment frameworks.
Demand concentrates around Delhi NCR, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, and Kochi, reflecting defense headquarters presence, integrator clusters, and testing infrastructure maturity. Bengaluru and Hyderabad anchor software engineering ecosystems, while Pune and Chennai support systems integration and manufacturing. Kochi aligns with naval command requirements, and Delhi NCR hosts program management and policy coordination. The regional pattern follows procurement access, skilled labor pools, certification facilities, and secure connectivity readiness, reinforcing multi-city collaboration across development, integration, and operational validation activities.
Market Segmentation
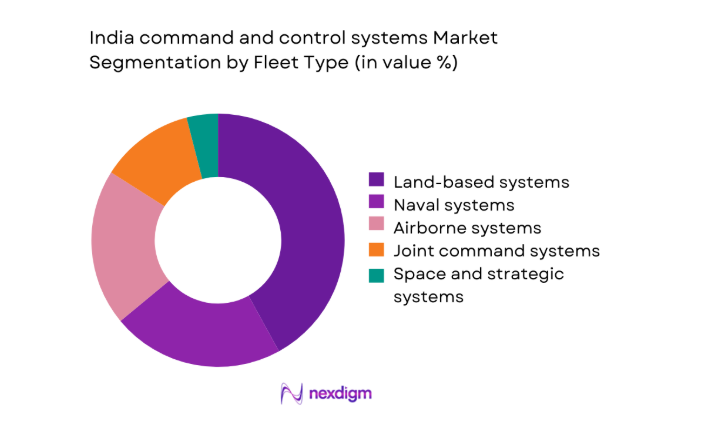
By Fleet Type
Land-based command networks dominate current deployments because army formations require continuous coordination across dispersed units and layered echelons. Air and naval environments follow closely, driven by integrated air defense and combat management modernization priorities. Joint command systems gain traction as interoperability becomes essential for multi-domain operations. The dominance of land-centric systems reflects higher installation counts, longer sustainment cycles, and broader training footprints. Programs increasingly emphasize modularity, enabling shared components across fleets while preserving mission-specific workflows. This structure encourages scalable upgrades, reduces qualification duplication, and supports synchronized exercises across formations without extensive retraining burdens.
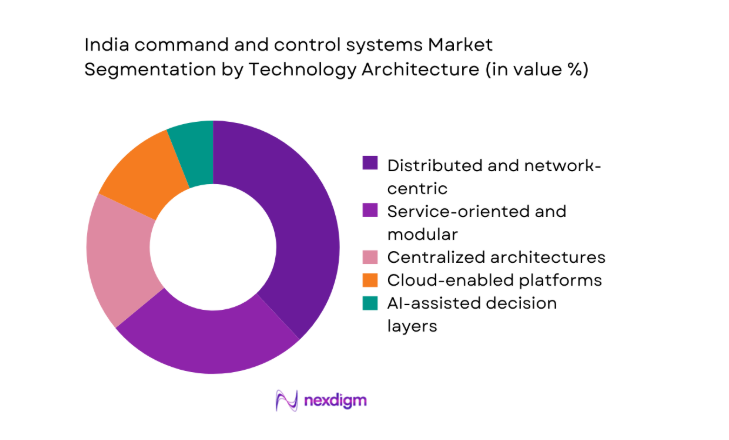
By Technology Architecture
Distributed and network-centric architectures lead adoption because they support resilient operations, rapid reconfiguration, and multi-site collaboration. Service-oriented platforms follow, driven by integration needs and incremental modernization strategies. Centralized systems persist within legacy environments, while cloud-enabled and AI-assisted layers expand decision support use cases. The dominance of distributed designs reflects operational requirements for redundancy, latency management, and scalable data fusion. Programs prioritize open interfaces and software-defined components to reduce lifecycle friction. This approach accelerates upgrades, improves testability, and aligns with joint operations that require consistent information flows across heterogeneous environments.
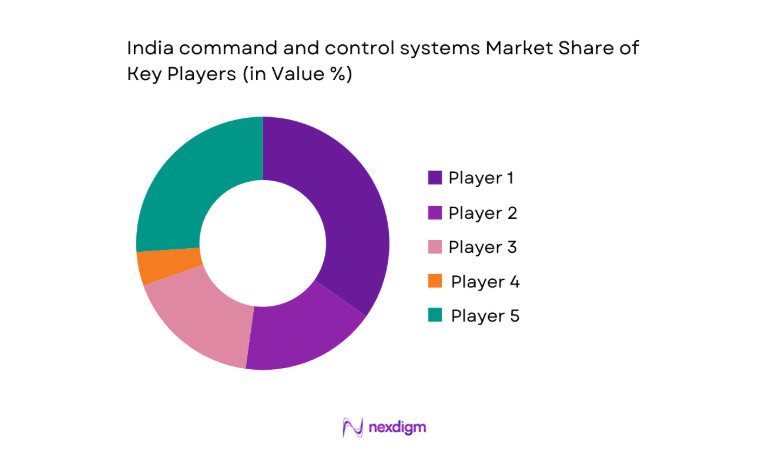
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment features a mix of domestic integrators and international technology partners focused on secure, interoperable, and scalable command platforms. Competition emphasizes delivery reliability, compliance readiness, and lifecycle support depth, while differentiation increasingly centers on software modularity and integration track records.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Bharat Electronics Limited | 1954 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen & Toubro Defence | 2011 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2007 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales India | 1953 | Noida | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab India | 2012 | Gurugram | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India command and control systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of network-centric warfare capabilities
Operational planners increasingly prioritize network-centric doctrines, encouraging integrated sensors, shooters, and decision nodes across multiple domains simultaneously today nationwide programs. Programs integrate legacy platforms, requiring careful interfaces, while commanders expect faster cycles, higher reliability, and consistent information assurance standards compliance. Field units demand resilient links, and integration teams coordinate 2 service networks using shared protocols and tested interoperability frameworks routinely. Exercises demonstrate decision timelines shrinking, which motivates procurement authorities to prioritize modular architectures supporting rapid configuration and secure collaboration workflows. Development roadmaps align training, doctrine, and sustainment, enabling commanders to coordinate 3 domains with predictable performance baselines across operations environments. Integration milestones reported internally show fewer handoffs, which improves tempo, reduces duplication, and clarifies responsibilities across participating organizations consistently measured. Software-defined components simplify updates, and operators report quicker configuration cycles during complex exercises conducted with multiple stakeholders under constrained schedules. Test events validate message standards, allowing cross-unit coordination, while security teams verify controls using documented accreditation checklists and procedures consistently. Command posts increasingly rely on shared displays, helping staffs reconcile inputs, prioritize tasks, and maintain operational coherence during pressure periods. This modernization driver remains persistent, because leadership links outcomes to connectivity, integration maturity, and disciplined configuration management practices across services.
Rising defense capital outlay and multi-year acquisition programs
Budget planning emphasizes continuity, enabling program offices to sequence deliveries, manage risk, and synchronize training across multiple formations effectively nationwide. Multi-year frameworks reduce uncertainty, and suppliers align capacity, schedules, and certification plans with predictable approval milestones across complex portfolios consistently. Program managers coordinate reviews, integrating feedback from 2 services, ensuring interoperability objectives remain visible throughout execution phases and audits cycles. Stable funding windows encourage tooling investments, yet teams still prioritize qualification evidence before expanding deployment across operational theaters carefully planned. Contract structures incentivize milestones, and oversight committees track progress using dashboards that aggregate schedule, quality, and readiness indicators consistently reported. Suppliers adjust staffing curves, coordinating test assets, documentation, and training material deliveries with phased acceptance activities across review gates cycles. The approach supports learning loops, because early increments reveal integration gaps before broader fielding commitments escalate under controlled governance frameworks. Stakeholders reference schedules, and commanders plan exercises, reducing last-minute changes that previously disrupted certification and readiness reporting cycles repeatedly observed. Documentation cadence improves, helping auditors verify traceability, while engineers address deviations without halting dependent workstreams during synchronized review intervals routinely. Consequently, acquisition predictability strengthens, and integrated roadmaps remain credible references for coordinating complex delivery sequences nationwide across organizations consistently aligned.
Challenges
Complex interoperability across legacy and new platforms
Diverse interfaces persist, and engineering teams reconcile message formats, timing constraints, and security policies across heterogeneous operational environments consistently evolving. Legacy equipment often lacks documentation, forcing reverse engineering efforts that delay integration milestones and complicate acceptance testing procedures significantly today. Gateways mitigate gaps, yet each translation layer introduces latency, maintenance overhead, and additional certification evidence requirements for operators teams regularly. Configuration management becomes complex, because updates must preserve backward compatibility while meeting new operational data exchange standards under audit scrutiny. Testing matrices expand quickly, requiring coordinated schedules, shared facilities, and disciplined defect triage across multiple participating stakeholders teams continuously engaged. Security accreditation timelines extend, because evidence must address composite architectures rather than isolated components previously evaluated under updated frameworks requirements. Field retrofits create logistics burdens, and spares planning becomes complicated when variants proliferate across different service inventories simultaneously nationwide deployments. Documentation repositories grow, yet discoverability suffers, increasing onboarding time for engineers assigned to cross-platform integration tasks during accelerated delivery cycles. Program risk registers reflect dependencies, and mitigation plans require coordination across procurement, operations, and sustainment organizations with shared accountability structures. Despite progress, interoperability complexity remains a persistent challenge, demanding governance discipline, standardized testing, and transparent configuration control across programs nationally.
Long procurement cycles and program approval delays
Approval gates involve multiple committees, and documentation queues lengthen, slowing contract actions and deferring planned integration activities significantly nationwide schedules. Iterative reviews aim to reduce risk, yet rework increases when requirements interpretations change during extended decision windows across programs repeatedly. Budget phasing constraints interact with approvals, causing delivery gaps that complicate training calendars and readiness verification events across commands frequently. Vendors maintain teams, but idle periods raise overhead pressure and distract attention from continuous improvement initiatives during prolonged waits cycles. Contract amendments accumulate, and traceability becomes difficult, increasing audit effort and management oversight burdens across organizations under compressed timelines pressures. Stakeholders attempt parallel processing, yet dependencies remain, and final signatures still govern transitions between critical program phases nationwide consistently observed. Communication plans mitigate uncertainty, but morale fluctuates when milestones shift, affecting retention of specialized engineering talent within integration teams repeatedly. Scheduling buffers grow, and leadership requests additional reporting, which consumes effort otherwise allocated to testing activities during extended review periods. Interdependent projects suffer cascading effects, because synchronized fielding plans rely on predictable approval cadence across portfolios under centralized governance structures. Reducing delays requires process reform, digital workflows, and delegated authorities, while maintaining compliance with oversight expectations across procurement ecosystems nationwide.
Opportunities
Upgrades and life-cycle extensions of existing C2 networks
Installed bases present upgrade paths, allowing phased improvements without disrupting operations or retraining entire staffs simultaneously across commands nationwide deployments. Modular designs enable component swaps, and sustainment teams prioritize reliability enhancements validated through routine operational testing cycles consistently applied procedures. Software refreshes introduce analytics features, helping planners visualize dependencies, manage workflows, and reduce coordination friction during exercises across formations regularly. Hardware retrofits improve throughput, while compatibility layers preserve interfaces, shortening downtime and simplifying acceptance processes for operators teams significantly overall. Documentation updates accompany upgrades, and training packages focus on deltas, reducing classroom time and accelerating field adoption cycles across units. Sustainment contracts align incentives, encouraging proactive maintenance planning and inventory optimization across geographically dispersed support locations within service networks nationwide. Engineering teams reuse components, shortening qualification timelines and improving consistency across successive upgrade increments delivered to users during scheduled releases. Feedback loops mature, because operational data informs backlog priorities and sequencing decisions for future enhancement cycles across planning boards routinely. Budget predictability supports planning, and stakeholders communicate roadmaps, reducing surprises and strengthening confidence among operational leadership during execution phases consistently. Consequently, lifecycle extensions deliver value, improving availability, resilience, and usability without wholesale replacement of proven infrastructure across service portfolios nationally.
Export of indigenized C2 subsystems to friendly nations
Indigenous subsystems demonstrate maturity, and reference deployments help marketing teams articulate value propositions to prospective partner governments during evaluations cycles. Compliance documentation supports approvals, while modular packaging simplifies customization for different doctrines, languages, and operational constraints across regions consistently required. Training toolkits accompany exports, enabling faster adoption and reducing integration support burdens for receiving organizations during initial operating capability phases. Partnerships leverage local integrators, expanding reach and aligning delivery schedules with sovereign procurement processes and oversight requirements across markets internationally. Product roadmaps incorporate feedback, ensuring exported variants remain compatible with core architectures and shared update cycles across supported configurations globally. Certification reuse lowers friction, and test evidence packages accelerate acceptance reviews conducted by partner technical authorities during procurement stages abroad. Support ecosystems scale, because spares, documentation, and remote assistance become standardized across multiple customer environments with predictable service windows globally. Risk sharing models emerge, aligning incentives and smoothing cash flow variability for both suppliers and government stakeholders across programs internationally. Export success stories reinforce credibility, encouraging further co-development discussions and joint exercises with aligned security partners during regional engagements regularly. This opportunity complements domestic programs, diversifying demand sources and sustaining engineering pipelines across product families over extended planning horizons globally.
Future Outlook
The market will continue prioritizing joint operations, software-defined architectures, and secure data exchange. Policy emphasis on indigenization should deepen ecosystem capabilities and reduce qualification duplication. Multi-year programs will stabilize delivery planning, while modular upgrades will accelerate field improvements. Exports and partnerships can broaden demand, and governance reforms could shorten approval timelines. Overall, execution discipline and interoperability will shape outcomes.
Major Players
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Larsen & Toubro Defence
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Mahindra Defence Systems
- Alpha Design Technologies
- Data Patterns
- Astra Microwave Products
- Paras Defence and Space Technologies
- Thales India
- Saab India
- Lockheed Martin India
- Boeing India
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Collins Aerospace
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defence procurement directorates
- Indian Army, Navy, and Air Force acquisition commands
- Defence Research and Development Organisation program offices
- Ministry of Home Affairs security modernization units
- Public sector shipyards and defense manufacturing agencies
- Private system integrators and platform primes
- Investments and venture capital firms
- State disaster management authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study identifies operational use cases, platform categories, and lifecycle stages shaping adoption. Variables include integration scope, certification pathways, sustainment models, and governance dependencies. Stakeholder workflows and interoperability constraints are mapped to define boundaries.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segment structures are constructed around fleet types and technology architectures. Deployment patterns, upgrade cycles, and program phasing inform scenario framing. Consistency checks ensure alignment between operational requirements and delivery models.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Working hypotheses are tested through structured discussions with practitioners across operations, integration, and sustainment. Feedback refines assumptions on interoperability, scheduling, and governance. Contradictions are reconciled through iterative reviews.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings are synthesized into coherent narratives linking drivers, challenges, and opportunities. Cross-checks ensure internal consistency and clarity. The final output emphasizes practical implications for planning, delivery, and lifecycle management.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope boundaries for Indian C2 programs, Platform and mission-based taxonomy across land air naval and joint domains, Bottom-up program-wise market sizing using contract awards and deliveries, Revenue attribution across hardware software integration and lifecycle support, Primary interviews with MoD users DPSUs integrators and system architects)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage across defense and homeland security missions
- Ecosystem structure and prime–subsystem integrator roles
- Supply chain and indigenization pathways
- Regulatory and procurement environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of network-centric warfare capabilities
Rising defense capital outlay and multi-year acquisition programs
Emphasis on jointness and theater commands
Indigenization and Make in India procurement mandates
Need for real-time ISR fusion and faster decision cycles
Cyber and electronic warfare resilience requirements - Challenges
Complex interoperability across legacy and new platforms
Long procurement cycles and program approval delays
High customization and integration risk
Cybersecurity and information assurance compliance costs
Dependence on imported subsystems and export controls
Skill gaps in systems engineering and secure software - Opportunities
Upgrades and life-cycle extensions of existing C2 networks
Export of indigenized C2 subsystems to friendly nations
Integration of AI analytics and edge computing
Private sector participation in defense digitization
Dual-use adoption in homeland security and disaster response
Open architecture and modularization programs - Trends
Shift toward joint and integrated command frameworks
Adoption of software-defined and service-oriented C2
Increased use of secure tactical data links and SATCOM
Growing focus on cyber-hardened architectures
Use of digital twins and simulation for mission planning
Migration toward cloud-native and edge-enabled systems - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land-based command and control systems
Naval combat management and C2 systems
Airborne and air defense C2 systems
Joint and integrated command systems
Space and strategic command systems - By Application (in Value %)
Battlefield management systems
Air defense command and control
Naval combat management
ISR data fusion and mission planning
Homeland security and disaster management command centers - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Centralized architectures
Distributed and network-centric architectures
Service-oriented and modular architectures
Cloud-enabled command platforms
AI-enabled decision support architectures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Indian Army
Indian Navy
Indian Air Force
Paramilitary and internal security forces
Civil disaster management agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Wired and fiber networks
Tactical radio networks
SATCOM links
Private LTE and 5G networks
Mobile ad hoc and mesh networks - By Region (in Value %)
North India
West India
South India
East India
Central India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product portfolio breadth, Interoperability standards compliance, Indigenous content percentage, Cybersecurity certifications, Program delivery track record, After-sales support footprint, Pricing competitiveness, Export control compliance)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Bharat Electronics Limited
Larsen & Toubro Defence
Tata Advanced Systems
Mahindra Defence Systems
Alpha Design Technologies
Data Patterns
Astra Microwave Products
Paras Defence and Space Technologies
Thales India
Saab India
Lockheed Martin India
Boeing India
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Collins Aerospace
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


