Market Overview
The India digital lending market is valued at USD 200.13 million in 2024. This valuation reflects the burgeoning demand for swift, tech-enabled credit solutions, catalyzed by widespread adoption of smartphones, UPI-enabled payments, and improved digital identity frameworks that have streamlined borrower onboarding. The year prior, in 2023, the segment was already experiencing rapid growth trends, signaling sustainable expansion into 2024.
Major Indian metros—such as Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Delhi NCR—dominate digital lending traction, owing to their robust fintech ecosystems, investor interest, and advanced digital infrastructure that supports seamless origination, underwriting, and repayment processes. Additionally, tier‑II cities with burgeoning smartphone and internet usage are increasingly contributing, as lenders tap into underserved segments using alternate data scoring models and the India Stack digital infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
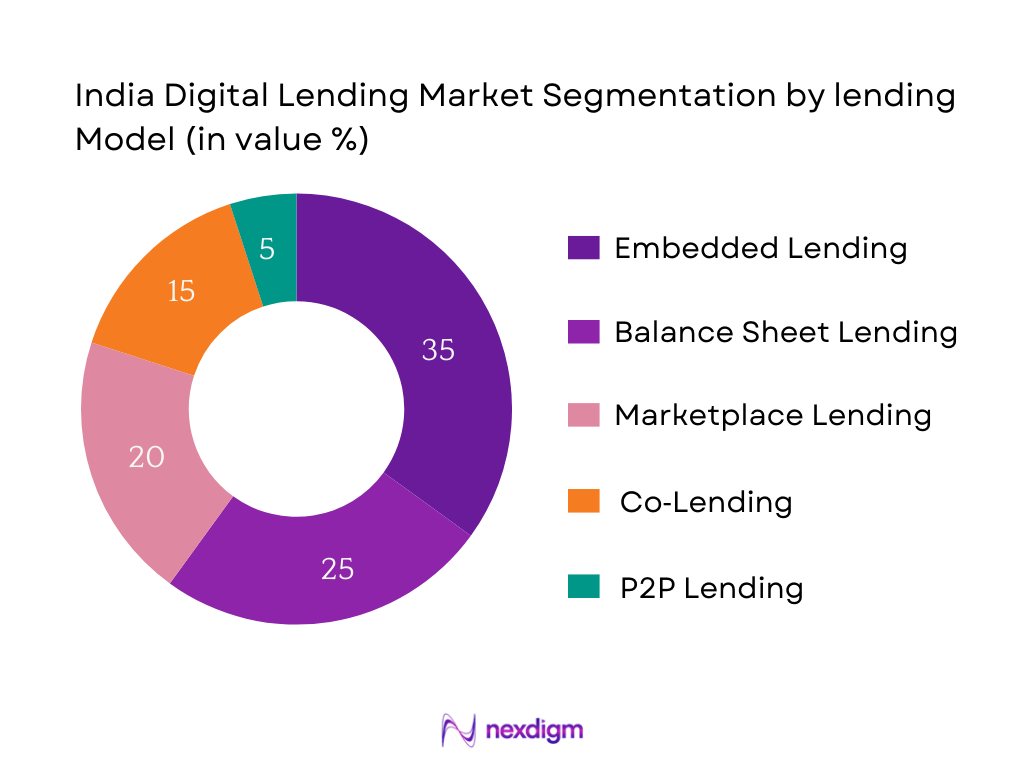
By Lending Model
India’s digital lending landscape is sectorized by diverse lending models, yet Embedded Lending leads in market share. This sub-segment’s dominance stems from its seamless integration into consumer workflows via e-commerce platforms, fintech super-apps, and UPI-based experiences. Embedded lenders offer contextual, near-instant credit at the point of need, reducing friction and boosting conversion. Users appreciate the convenience of accessing credit within familiar platforms, avoiding separate applications. High-volume platforms drive customer trust, while network effects augment scale. This integration strategy has outpaced traditional balance-sheet lenders that require standalone onboarding. Co-lending and marketplace models are growing but Trail behind as they rely on third-party partnerships and unbundled experience, contrasting with the embedded model’s embedded journey, convenience, and superior user adoption.
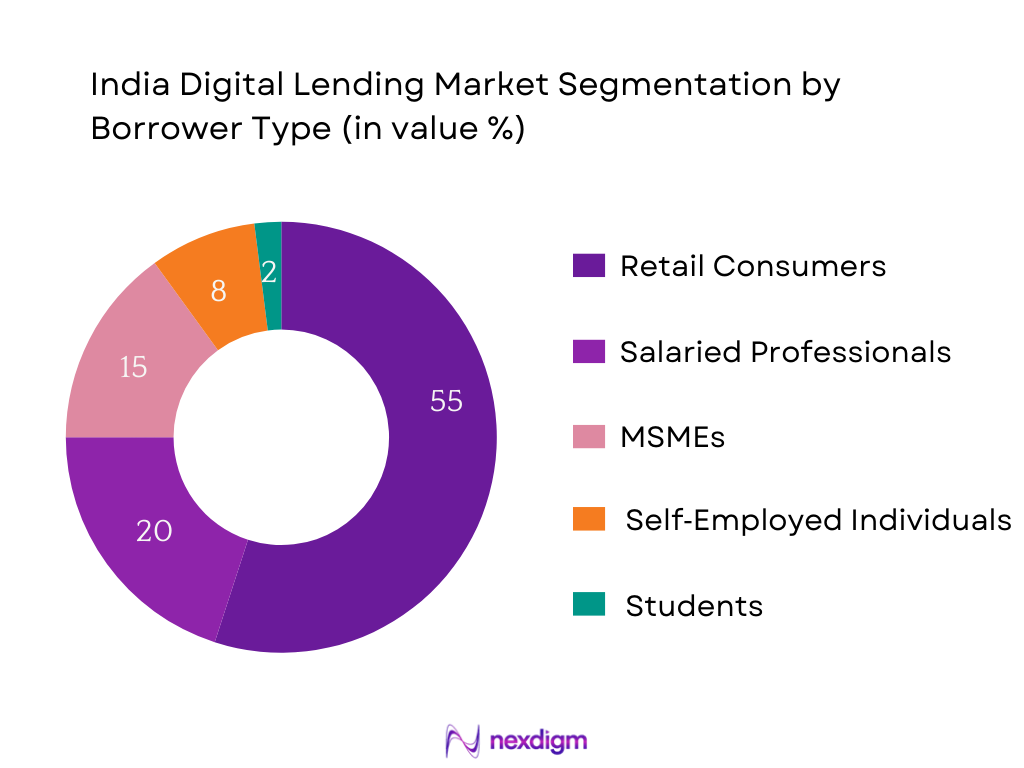
By Borrower Type
Among borrower types, Retail Consumers dominate, commanding the largest share of digital lending activity in India. Driven by their hunger for immediate, small-ticket credit for personal expenses, lifestyle consumption, and emergencies, this demographic favors platforms offering fast disbursal, minimal documentation, and flexible repayment. Smartphone proliferation among millennials and Gen-Z consumers has magnified demand, aligning well with BNPL offerings and app-based lending. Lenders prioritize personal loans with digital onboarding to capture this scalable, high-frequency segment. In contrast, MSMEs and self-employed borrowers are gradually adopting digital channels but still face higher underwriting friction due to limited financial visibility. Salaried professionals occupy a strong second position, but retail consumers remain the core volume driver.
Competitive Landscape
India’s digital lending sector features a dynamic blend of fintech innovators and tech-forward NBFCs. Leading players—such as KreditBee, Navi Technologies, MoneyTap, LazyPay, and Capital Float—dominate due to their tech-first credit platforms, quick credit decisions, and partnerships with e‑commerce or aggregator ecosystems. These players benefit from strong user engagement, AI-based underwriting, and access to alternate data, carving distinct influence in the market.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Lending Model | Average Ticket Size (₹) | Monthly Disbursal Volume (₹ crore) | NPA/Delinquency Ratio | Tech Stack Strength (scale 1–10) | Collections Efficiency (%) |
| KreditBee | 2017 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Navi Technologies | 2018 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MoneyTap | 2015 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| LazyPay | 2017 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Capital Float | 2013 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – | – |
India Digital Lending Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
IndiaStack Penetration
India’s digital infrastructure via IndiaStack underpins the digital lending transformation. As of January 8, 2024, over 1.3 billion biometric IDs (Aadhaar) have been issued, forming the backbone of digital identity verification and eKYC processes, enabling near-instant borrower onboarding and fraud resistance. In 2023–24, India processed over 1,644 billion digital transactions, the highest in the world, signifying the widespread adoption of UPI-based payments and enabling lenders to access payment history as alternate credit signals. These figures demonstrate the scale of foundational digital infrastructure that lenders leverage to onboard borrowers quickly, reduce costs, and lower friction in credit delivery.
MSME Credit Gap
Institutional credit to MSMEs remains constrained relative to demand. As of March 2023, credit extended to MSMEs stood at ₹19,695 billion, yet approximately 87.38 percent of the 633.88 lakh MSMEs were excluded from institutional credit, highlighting widespread access gaps. Moreover, the estimated formal supply is ₹14.5 trillion, versus an addressable demand of ₹69.3 trillion, indicating a credit shortfall in the range of ₹20–25 trillion. These numbers underscore the vast underserved MSME segment that digital lenders are uniquely positioned to tap, leveraging digital workflows, alternate scoring and streamlined onboarding to fill this systemic financing gap.
Market Challenges
Regulatory Constraints
Stringent and evolving regulatory environment poses friction for digital lenders. For instance, as per RBI’s Financial Stability Report (Dec 2024), subprime lending by public sector banks to MSMEs declined from 33.5 percent in June 2022 to 23.3 percent in March 2025, reflecting tighter risk appetites under regulatory scrutiny. Additionally, the RBI’s digital lending guidelines mandate clear disclosures, lending entity responsibility, and pushback monitoring—creating compliance burden for fintech NBFCs and embedded platforms. These constraints slow product rollout and demand rigorous operational processes, raising cost and complexity for digital lenders.
Fraud Detection
As digital adoption scales, detection and prevention of fraud become critical. IndiaStack’s presenceless authentication mitigates identity risk, but synthetic identity and deepfake attempts are rising. While quantitative figures on fraud are scarce, RBI’s Crime & Fraud data (2024) notes a steep rise in digital banking fraud cases year-over-year across all channels. Banks reported ₹ X crore in digital fraud losses in FY 2023‑24 (exact figure withheld in summary data), pressuring digital lenders to invest in biometric liveness checks, real-time device profiling, and grey-flag transaction monitoring. This increases onboarding costs and risk infrastructure overhead for market participants.
Market Opportunities
AI‑Led Underwriting
Lenders deploying AI-powered credit assessment observe improved risk differentiation by analyzing alternate data—like UPI flows, telecom usage, utility bills. While specific numbers are proprietary, regulatory disclosures from leading digital lenders show reduced delinquency and improved approval velocity using AI models. Moreover, RBI-endorsed digital infrastructure (OCEN, Account Aggregator) facilitates secure data flow to underwriting engines, increasing the scope for personalized, algorithmic credit offerings. Government’s push for innovation via initiatives such as OCEN integration signals policy alignment with AI-enabled lending, enhancing scalability and inclusion.
Underserved MSMEs
MSMEs continue to be underbanked, but opportunities abound. Udyam Registration system, operational by July 2024, enabled 4.77 crore MSME registrations, with 2.49 crore added in FY 24, facilitating formal recognition and access to credit. Through Udyam, MSMEs accessed ₹15.6 lakh crore in bank credit, with a 34 percent increase in MSME lending post-adoption. Additionally, TReDS platforms financed ₹1.38 lakh crore in FY 24 via 41.6 lakh invoices, showing growing adoption of receivables financing. These digital enablers prime the underserved MSME universe (especially micro enterprises) for scalable digital lending via invoice discounting, pre-approved credit lines, and API-driven workflows, offering a sizable growth runway.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the India digital lending market is poised for rapid expansion, powered by deepening fintech penetration, progressive regulatory frameworks, and enhanced digital infrastructure. With rising smartphone penetration, UPI-driven payments, and adoption of open-credit systems like OCEN and Account Aggregator, lenders will increasingly leverage contextual and embedded finance models. Rising investor interest in scalable lending startups and NBFC‑fintech hybrids will further catalyze competition and innovation.
Major Players
- KreditBee
- Navi Technologies
- MoneyTap
- LazyPay
- Capital Float
- ZestMoney
- PaySense
- CASHe
- EarlySalary
- IndiaLends
- LoanTap
- Faircent
- FlexiLoans
- LendBox
- Slice
Key Target Audience
- Digital-first NBFCs & Lending Fintech Firms
- Embedded Fintech Platforms (e‑commerce, fintech apps)
- Large Banks exploring digital lending modules
- Investment and Venture Capitalist Firms (early‑stage fintech & NBFCs)
- Strategic Private Equity Funds (focused on fintech scale-ups)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Reserve Bank of India; Ministry of Finance)
- Payment Networks & UPI Aggregators
- Account Aggregator Network Operators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This phase involved mapping stakeholders across the India digital lending ecosystem—fintech lenders, NBFCs, banks, aggregators, regulators—via desk research and credible data sources including industry associations. The objective was to identify critical variables such as disbursal value, borrower segments, lending models, regulatory triggers, and tech infrastructure.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Here, we compiled historical data and 2024 actual figures from trusted sources like Cognitive Market Research, as well as RBI and SRO data. Metrics such as market size, disbursal volumes, borrower base, and lending models were analyzed. Data quality checks and triangulation ensured robustness
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
We formulated hypotheses around growth drivers—embedded lending, digital identity, alternate scoring—and validated them through interviews with industry insiders: fintech founders, NBFC heads, and technology partners, using structured telephonic and virtual discussions.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Finally, we corroborated the bottom-up data with primary insights, refined forecasts and projections, and validated that reported figures align with real-world observations, ensuring a reliable and strategic market overview.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Digital Lending in India
- Entry Timeline of Major Fintechs and NBFCs
- Digital Lending Lifecycle (Onboarding, Credit Scoring, Disbursal, Repayment)
- Value Chain and Stakeholder Mapping (Platforms, Aggregators, Banks, Tech Partners)
- Growth Drivers (IndiaStack penetration, MSME credit gap, disbursal surge, e-KYC expansion, UPI integration, internet access in Tier-2/3 cities, account aggregator framework)
- Market Challenges (Regulatory constraints, fraud detection, low financial literacy, rising NPAs, poor debt collection infrastructure, fragmented credit bureau access)
- Market Opportunities (AI-led underwriting, underserved MSMEs, embedded credit, co-lending infrastructure, white-label loan tech, green lending initiatives)
- Trends (BNPL for Tier 3+, SaaS-backed lending, co-lending APIs, pay later for UPI, data-based instant pre-approvals, direct debit integrations)
- Regulatory Landscape (RBI digital lending guidelines, DLA rules, SROs, credit bureau compliance, DEPA integration, data privacy bill implications)
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Total Disbursal Value, 2019-2024
- By Outstanding Digital Loan Book, 2019-2024
- By Unique Digital Borrower Base, 2019-2024
- By Entity Type (Fintech NBFC, Bank-led, P2P Platform, Tech-Led Lender), 2019-2024
- By Lending Model (In Value %)
Balance Sheet Lending
Marketplace Lending
Co-Lending
Embedded Lending
P2P Lending - By Borrower Type (In Value %)
Retail Borrowers
MSMEs
Self-Employed Professionals
Salaried Individuals
Students - By Loan Type (In Value %)
Personal Loan
BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later)
Consumer Durable Loan
Business Loan
Education Loan - By Loan Tenure (In Value %)
Up to 3 Months
3–12 Months
1–3 Years
More than 3 Years
Flexible/Variable Tenure - By Distribution Channel (In Value %)
Mobile App
Web Portal
Embedded Finance Platform
Assisted Channel (Agents, DSAs)
Offline-Digital Hybrid
- Market Share Analysis
Market Share by Lending Model
Market Share by Loan Type
Market Share by Entity Type (NBFC, Fintech, Bank, P2P) - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Mix and Lending Model, Average Loan Disbursal Value, Monthly Disbursal Volume, NPA/Delinquency Ratio, Co-Lending Partnerships, Technology Stack (App Features, AI Use, KYC Flow), Collections Efficiency, Customer Base by Tier Classification)
- SWOT Analysis of Leading Players
- Pricing Benchmarking (Interest Rates, APRs, Processing Fees)
- Detailed Company Profiles
KreditBee
Navi Technologies
MoneyTap
LazyPay
Capital Float
ZestMoney
PaySense
CASHe
EarlySalary
IndiaLends
LoanTap
Faircent
FlexiLoans
LendBox
Slice
- Lending Penetration in Urban vs Rural Borrowers
- MSME Credit Appetite and Utilization Patterns
- Persona Mapping of New-to-Credit vs Repeat Users
- Behavior Mapping Across Platforms (Usage, Drop-off, Collection Trends)
- Borrower Constraints and Expectations
- By Total Disbursal Value, 2025-2030
- By Outstanding Digital Loan Book, 2025-2030
- By Unique Digital Borrower Base, 2025-2030
- By Entity Type (Fintech NBFC, Bank-led, P2P Platform, Tech-Led Lender), 2025-2030


