Market Overview
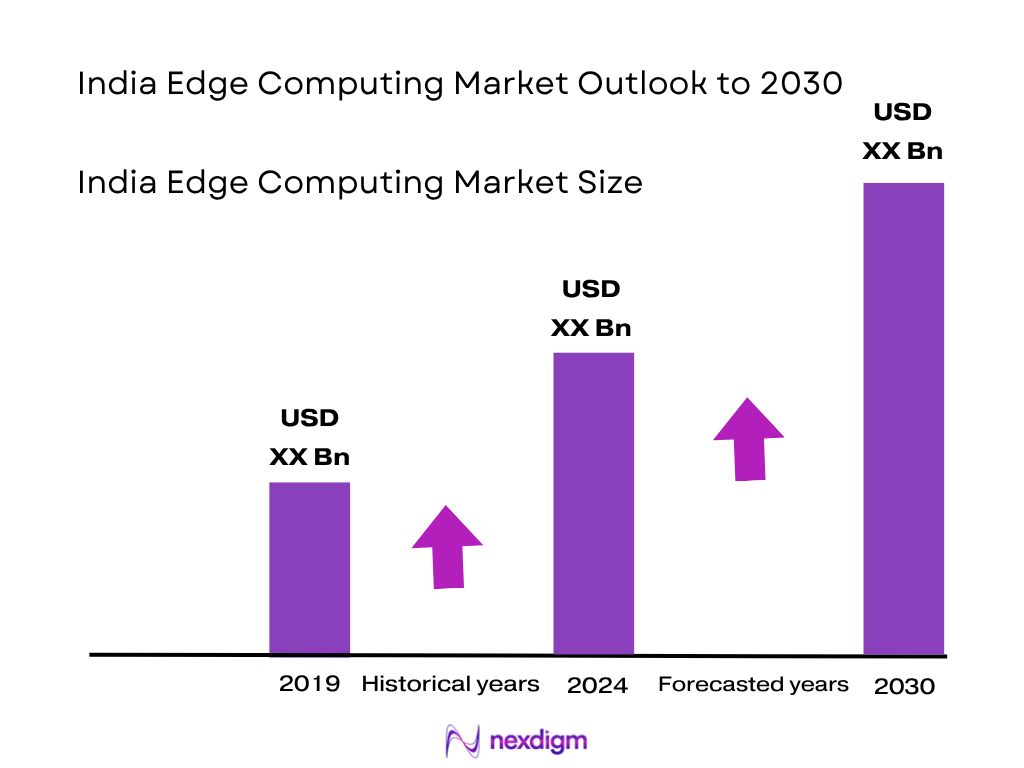
The India edge computing market is valued at USD 1,603.1 million, supported by historical data from 2023 and 2024, driven by rising demand for low‑latency data processing at the network periphery, fueled by expanding IoT deployments, industrial automation, and 5G edge rollouts. Indian metro hubs—especially Mumbai‑Navi Mumbai, Delhi NCR, Bangalore, and Hyderabad—dominate edge computing adoption. These cities boast major data‑centre capacity, robust digital infrastructure and enterprise concentrations, affordable real‑estate for edge nodes, and strong government and telecom investments. The India edge computing market stood at USD 1,603.1 million in 2024. Over 2024–2033, it is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 42.4 %, aiming to reach USD 41,374.9 million by 2033.
Market Segmentation
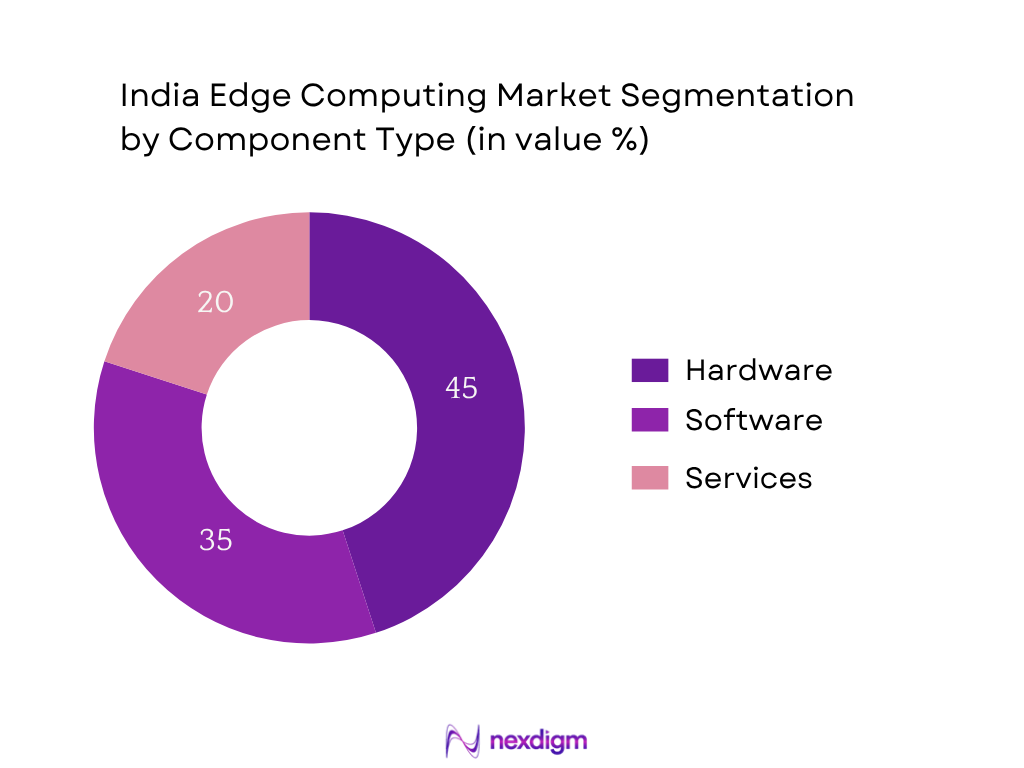
By Component
India’s edge computing market is segmented into Hardware, Software, and Services. In 2024, Hardware held the largest share, as enterprises invested heavily in edge servers, gateways, and processing devices due to increasing IoT endpoints and latency‑critical industrial use cases. Legacy infrastructure upgrades and edge data centre capacity expansion (especially media servers and micro‑data centres) further drove hardware dominance, while software and services grew rapidly but remain secondary in revenue share.
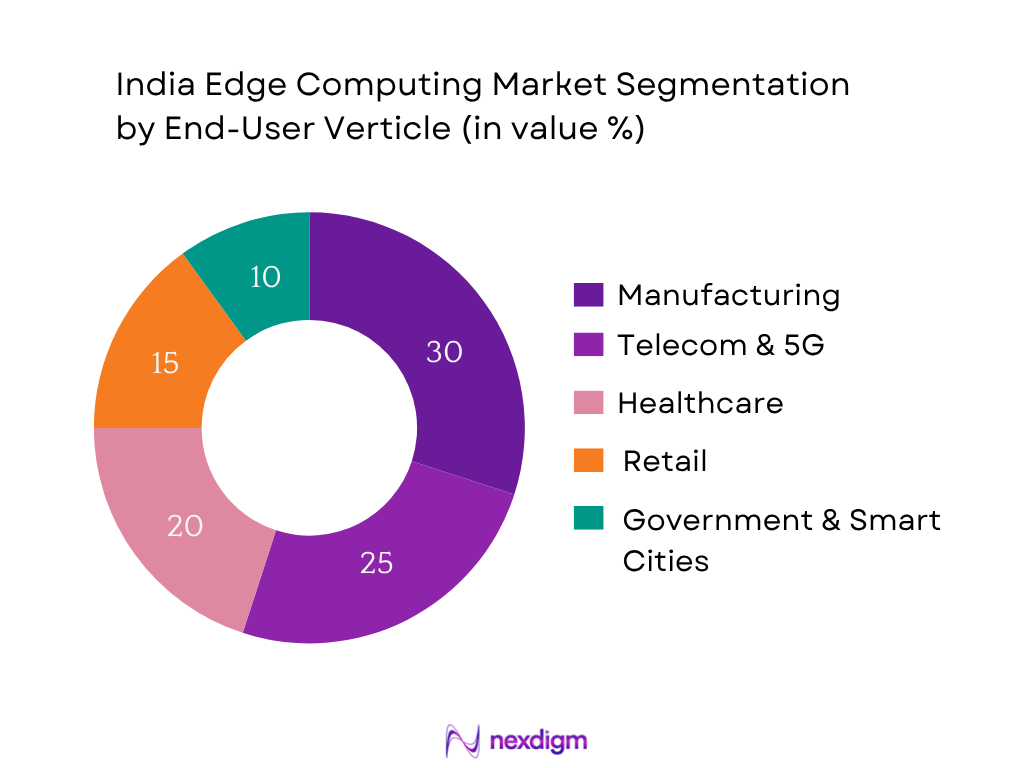
By End‑User Vertical
The market is also segmented by end‑user industry: Manufacturing, Telecom & 5G, Healthcare, Retail, and Government & Smart Cities. Manufacturing leads in 2024 share. Large industrial players in automotive, heavy engineering and heavy manufacturing accelerated rollout of IIoT and predictive‑maintenance systems, driving edge computing uptake. They require ultra‑low latency, onsite analytics, and integration with existing legacy machines—making manufacturing the dominant vertical for edge deployment in India.
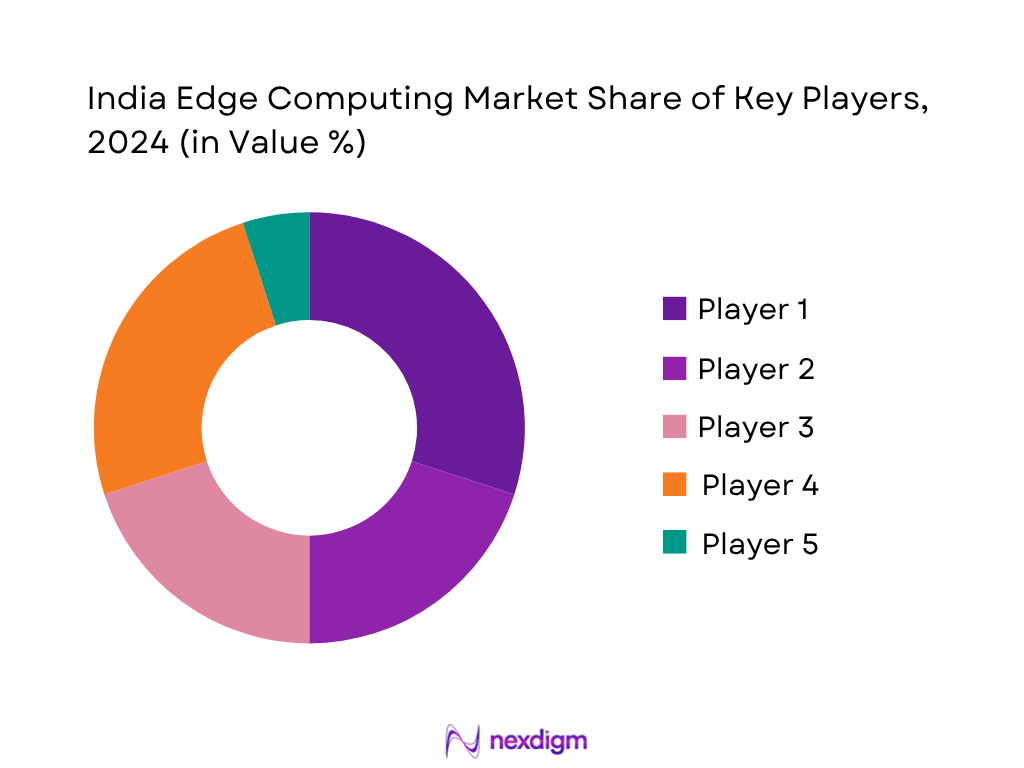
Competitive Landscape
The India edge computing space is concentrated, led by major IT and telecom players coupling infrastructure with computing capabilities. These companies hold strong influence across enterprise and telecom verticals, reflecting consolidation in both services and hardware-led edge deployments.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Edge‑focused Hardware Portfolio | Software/Platform Offerings | 5G/Telecom Edge Integration | Smart‑city/Industrial Use Cases | Edge Data Centre Footprint | Key Partnerships / Ecosystem |
| Tata Communications | 1986 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| HPE India | 1939 | Bangalore | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cisco Systems India | 1984 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| IBM India | 1911 | New Delhi | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Tech Mahindra | 1986 | Pune | – | – | – | – | – | – |
India Edge Computing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Surge in Industrial Automation and 5G Integration
Rapid growth in India’s industrial sector is reflected in gross fixed capital formation reaching approximately 33.5 % of GDP, indicating large infrastructure spending that includes automation and digitalization investments. India’s nominal GDP rose to around USD 3.91 trillion in 2024, offering expanded capacity for industry-led initiatives. Meanwhile, India has deployed over 200,000 km of optical fibre backbone and is rolling out about 2 lakh 5G base‑stations, enabling telcos to deliver mobile edge compute (MEC) services in manufacturing hubs and smart districts. This industrial modernization and 5G network densification drive demand for edge computing infrastructure close to factories and enterprise campuses.
Government Push for Smart Infrastructure
India’s infrastructure capex plan includes major smart‑city projects and industrial corridor upgrades worth ₹100,000 crore in airport and transit investments in FY 2024, providing significant backbone for edge deployments in civic systems. The government’s Smart Cities Mission now covers over 100 cities, each deploying edge-enabled applications for traffic management, waste monitoring and utility optimization. Municipalities in Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Bangalore are using edge clusters for real‑time analytics in urban systems. Public sector investment is accelerating edge node installations at urban edge points, boosting uptake. Infrastructure investments in energy, transport and utilities consistently absorb over 10 % of GDP, creating fertile ground for distributed compute.
Market Challenges
Limited Edge Data Center Infrastructure
India’s current data centre ecosystem remains concentrated: the majority of large‑scale collocated data centres are within 6 metro regions, with only ~15 operational hyperlocal micro‑data facilities across tier‑II cities as of 2024. Though data centre capacity in metros grew by 10 % YoY, low infrastructure development outside metros limits edge expansion in smaller industrial hubs. The high land and power costs for deploying edge PoPs combined with distribution-network gaps slow growth in periphery regions that are critical for real‑time compute near use cases.
High Cost of Edge Device Integration
Edge compute appliances and gateways typically cost enterprise users USD 5,000 to USD 20,000 per node, placing strain on SMEs and decentralized sites with limited IT budgets. With nominal GDP per capita at USD 2,696.7 in 2024, many smaller firms and public agencies find upfront capital expense prohibitive. Moreover, installation and integration with legacy OT systems incur recurring investments. Financing or leasing models are still nascent, adding to adoption friction, particularly in industries like retail or healthcare with tight budgets and fragmented infrastructure.
Market Opportunities
AI‑Powered Edge Analytics
The rise in connected IoT sensor endpoints and industrial automation provides immense potential for deploying AI/ML inference at edge, reducing dependency on central cloud. India recorded 2,885.5 million USD revenue from IoT devices in 2024, and edge devices were the fastest growing sub‑segment. Coupling this hardware base with accelerating deployment of GPU‑enabled edge servers and AI accelerators enables real‑time analytics for quality control, anomaly detection, and predictive alerts. Major smart city projects in over 100 municipalities further offer pilots for AI‑based traffic and energy optimization at edge nodes, creating adjacent opportunity for analytics platforms and edge data orchestration.
Telecom Edge Expansion with 5G Rollout
India’s telecom capital expenditure soared, with operators rolling out roughly 200,000 5G base stations and expanding fibre-optic backbone to over 250,000 km by mid‑2025 to support enhanced mobile broadband and enterprise MEC services. The unemployment rate stood at 4.2 % in 2024, prompting telcos to invest in digital infrastructure expansion as a lever for growth. These infrastructure investments create openings for deploying edge compute infrastructure at telco PoPs and tower sites, enabling enterprise-grade applications close to user traffic. Edge services tied to telecom deployments are expected to form the backbone of widespread distributed computing across regional enterprise and industrial clients.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast period through 2033, the India edge computing market is expected to witness transformative growth, driven by integration of AI/ML inference at edge, massive industrial automation initiatives, and widespread 5G edge deployments by major telecom providers. Edge solutions will increasingly support tier‑II and tier‑III city infrastructure in smart utilities and healthcare. Government initiatives and public‑private partnerships in smart‑city frameworks and industrial corridor development are expected to further accelerate uptake across sectors.
Major Players
- Tata Communications
- HPE India
- Cisco Systems India
- IBM India
- Tech Mahindra
- Wipro
- Infosys
- Dell Technologies India
- Microsoft Azure India
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) India
- Intel India
- Huawei India
- Siemens India
- Nokia India
- EdgeConneX (India operations)
Key Target Audience
- Organizations likely to purchase this India Edge Computing Market Report include:
- CTOs / CIOs of large manufacturing and industrial enterprises
- Heads of Infrastructure & IT in telecom operators (e.g. Airtel, Jio, Vi)
- Investment & venture capital firms specializing in deep tech startups (investments and venture capitalist firms)
- Government and regulatory bodies (e.g. Ministry of Electronics & IT, Department of Telecommunications)
- Heads of Digital Transformation in BFSI & healthcare verticals
- Heads of Smart Cities missions and municipal IT departments
- Edge infrastructure service providers/operators
- Procurement leaders in retail and logistics firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Mapping ecosystem stakeholders—including hardware OEMs, software providers, telco operators, edge data‑centre operators. Desk research via secondary and proprietary databases (e.g. government, industry reports) helps define variables such as installed edge capacity, operator roll‑out, vertical usage.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Analyse historical data (2021‑2024) on revenue by component and vertical, adoption rates by industry, penetration of edge infrastructure. Use a bottom‑up revenue model based on installed edge nodes, device counts, average pricing.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market assumptions and preliminary forecasts validated via structured interviews (CATI/CATI+ digital) with telecom operators, industrial digitalisation leads, smart‑city project managers, and edge platform vendors for revenue and deployment confirmation.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Direct engagement with top edge infrastructure providers, telecom MEC teams, enterprise adopters for cross‑validation. Data synthesized to ensure coherence and accuracy, supplemented by triangulation between bottom‑up and top‑down approaches.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Edge Computing in India
- Edge Computing Integration Across Sectors
- Technology Lifecycle and Adoption Stage
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Mapping
- Edge-to-Cloud Architecture Overview
- Growth Drivers
Surge in Industrial Automation and 5G Integration
Government Push for Smart Infrastructure
Data Explosion and Low-Latency Demands
Cloud-to-Edge Shift in BFSI and Healthcare
IoT Device Proliferation in Manufacturing - Market Challenges
Limited Edge Data Center Infrastructure
High Cost of Edge Device Integration
Interoperability and Standardization Gaps - Market Opportunities
AI-Powered Edge Analytics
Telecom Edge Expansion with 5G Rollout
Rising Investments in Hyperlocal Data Centers - Trends
Edge-Native Application Development
Cybersecurity Innovations at the Edge
AI at the Edge – ML Inference Deployments - Government Regulations
Data Residency and Sovereignty Rules
Cloud and Edge Infrastructure Guidelines - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Installed Node Capacity, 2019-2024
- By Component (In Value %)
Hardware
Software
Services - By Deployment Type (In Value %)
On-Premise
Cloud
Hybrid - By Application (In Value %)
Smart Cities
Industrial IoT
Connected Healthcare
Autonomous Vehicles
Video Surveillance & Content Delivery - By End-User Industry (In Value %)
Manufacturing
BFSI
Energy & Utilities
Telecommunications
Transportation & Logistics - By Region (In Value %)
North India
South India
West India
East India
- Market Share of Major Players (Value-Based)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Technological Focus, Key Clients by Industry, Deployment Models, Number of Edge Data Centers, Edge-Centric Product Portfolio, Partnerships and Alliances, Revenue Share from Edge Solutions)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Models – Per Node vs. Subscription vs. Licensing
- Detailed Profiles of Major Players
Tata Communications
Wipro
Infosys
NTT India
HCLTech
Dell Technologies India
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) India
Cisco Systems India
IBM India
Google Cloud India
Microsoft Azure India
Amazon Web Services (AWS) India
Tech Mahindra
Larsen & Toubro Infotech
EdgeConneX (India Operations)
- Enterprise Technology Adoption Roadmap
- Investment Trends by Vertical
- Digital Transformation Maturity Mapping
- Decision Making Criteria (Latency, Security, ROI)
- Regional and Sector-Specific Demands
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Installed Node Capacity, 2025-2030


