Market Overview
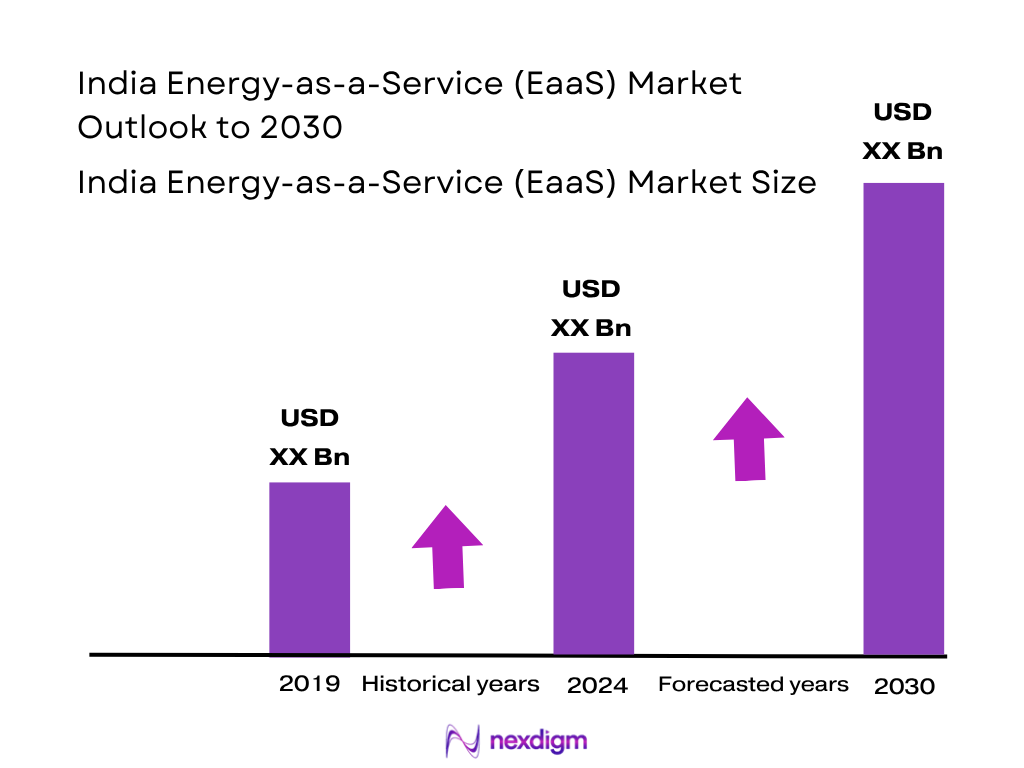
The India EaaS market is valued at USD 2,178.2 million in 2024, based on a five‑year historical analysis. It reflects rapid uptake of energy‑supply bundled services, optimization and demand response offerings across commercial and industrial sectors, fuelled by corporates’ decarbonization targets and efficiency mandates under national programs such as Smart Cities and rooftop solar initiatives.
Adoption in major metros such as Mumbai, Delhi NCR, Bengaluru, Chennai and Hyderabad drives dominance of the market due to their high density of commercial buildings, industrial parks, IT campuses and progressive state-level renewable energy regulations. These cities feature active ESCO pilots, smart grid roll‑outs, and strong CAPEX-to-OPEX transitions propelled by corporates and real estate players, ensuring concentrated growth in these hubs.
Market Segmentation
By Service Type
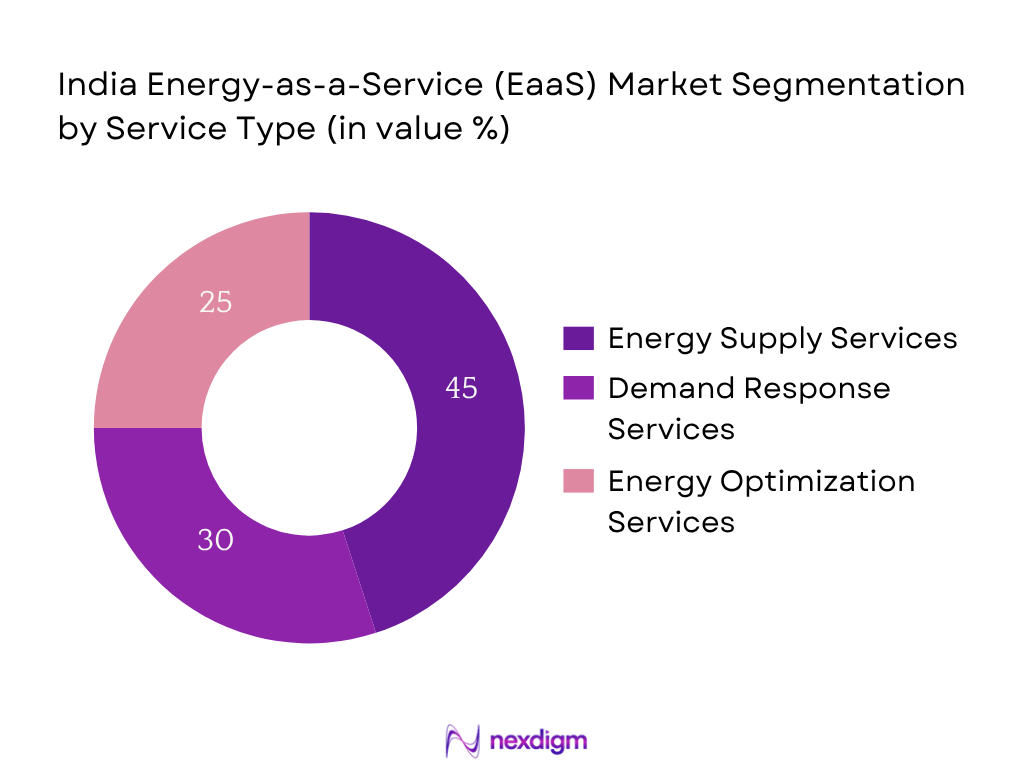
The India EaaS market is segmented by service type into Energy Supply Services, Demand Response Services, and Energy Optimization Services. Energy Supply Services held the largest share in 2024, due to the prevalence of captive solar PV installations and third‑party supply contracts that offer firms predictable energy costs and built‑in renewable sourcing. Corporates and industrial facilities prefer bundled supply solutions to manage price risk and meet sustainability commitments.
By End User
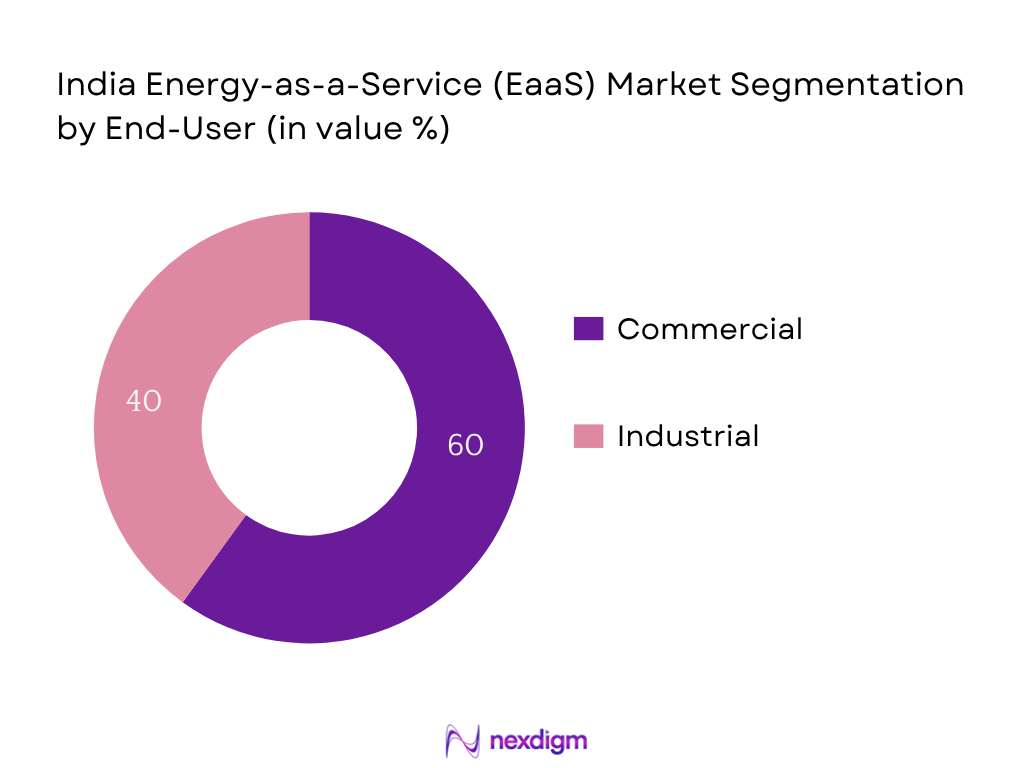
The India EaaS market is segmented into Commercial and Industrial end‑users. The Commercial segment dominates with the larger share in 2024, reflecting the concentration of EaaS adoption in office complexes, retail chains, hospitality, IT parks and educational campuses. These clients demand integrated energy supply, demand response and optimization under performance‑based contracting. Institutional focus on sustainability reporting and operational cost reduction drives preference for EaaS among commercial entities.
Competitive Landscape
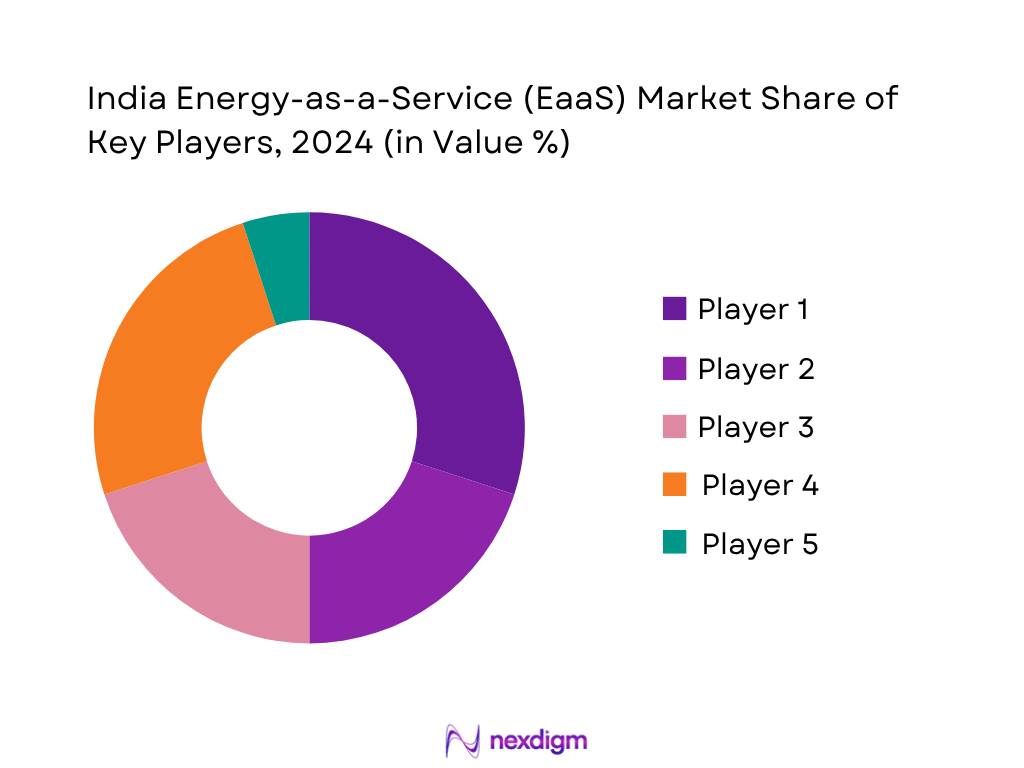
The India EaaS market is dominated by a handful of major firms, blending global energy service capabilities with domestic ESCO execution. Consolidation is driven by the scale needed to finance renewable installations, deliver optimization analytics, manage contracts and guarantee energy outcomes across commercial and industrial portfolios. These players wield significant influence through large deployments, strategic tie‑ups and multi‑city operations.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Service Offerings | Installed Capacity (MW)/Projects | Contract Models | Key End‑Users | Technology Partnerships |
| Tata Power EZ‑Home + Microgrid | 1915 | Mumbai, India | – | – | – | – | – |
| EESL | 2009 | New Delhi, India | – | – | – | – | – |
| ReNew Power (EnKing) | 2011 | Gurugram | – | – | – | – | – |
| Fourth Partner Energy | 2016 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – |
| Smart Joules | 2010 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – |
India Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Decentralization of Energy Systems
Decentralized energy generation is accelerating in India: solar rooftop and off‑grid installations reached 5.05 GW off‑grid and 18.84 GW rooftop as of June 2025, contributing to 116.25 GW total solar capacity. Utility‑scale solar additions in 2024–25 totaled 23.83 GW, up from 15.03 GW the prior year, hitting 105.65 GW cumulative. This surge in distributed solar deployment empowers facility owners and ESCOs to adopt Energy‑as‑a‑Service models with localized generation, avoiding central grid dependencies and reducing energy procurement risks.
Electrification Goals under Saubhagya & RDSS Schemes
Under the Saubhagya scheme, 2.86 crore households were electrified nationwide through grid and solar‑PV standalone systems, including 4.17 lakh households via off‑grid PV by late 2024. RDSS implementation in Maharashtra’s Vidarbha region includes 1,007 feeder separation projects, 727 substations, and thousands of kilometers of upgraded cabling to stabilize distribution networks and deliver daytime power to non‑agricultural users across 3,000 km of lines. These infrastructure upgrades underpin reliable delivery and integration for EaaS offerings in improved grids.
Market Challenges
Policy Uncertainty for Energy Services Business Models
Although Saubhagya and RDSS schemes enabled electrification infrastructure, there is limited national standardization of EaaS contract types. Regulatory frameworks that allowed 2.86 crore household connections via Saubhagya lack explicit operating guidelines for ESCO service models and revenue recovery, creating ambiguity for providers planning energy performance guarantees beyond mere supply access.
Integration Bottlenecks in Legacy Infrastructure
Despite total solar and wind capacity rising to 203 GW (accounting for 46.3% of total capacity) by October 2024, grid curtailment and uneven distribution infrastructure challenge integration. In regions like remote Bihar or Uttar Pradesh, electrification via Saubhagya reached millions of households, yet grid stability remains weak without upgraded feeder separation or smart meters, hampering reliable roll-out of demand‑response‑based EaaS services.
Market Opportunities
Public‑Private Partnerships in Urban Energy Projects
Urban areas like Chandigarh have grown renewable capacity from 5 MW in 2014‑15 to 90 MW by mid‑2025—an 18‑fold increase—through government‑sponsored rooftop and floating solar installations on public buildings, schools and municipalities. This creates openings for EaaS providers to partner via PPP models, offering performance-based solar, storage, and energy-as-a-service contracts in smart city initiatives across municipal portfolios, driving scalable deployment in urban clusters with guaranteed assets.
Capex‑to‑Opex Shift by MNCs and Data Centers
India added 28 GW of wind and solar capacity in 2024, plus 16.3 GW in the first five months of 2025, taking total non-hydro renewables to 184.6 GW by mid‑2025. Energy‑intensive data centers and multinational industrial firms are increasingly preferring OPEX‑based supply from third‑party solar installations or green energy contracts, avoiding capital expenditure and supply price risk. The rise in renewable capacity creates credible on‑taker models enabling EaaS providers to convert solar assets into service revenue streams for these clients.
Future Outlook
Over the next six years, the India Energy‑as‑a‑Service market is expected to register robust growth driven by rapidly expanding renewable capacities, continued corporate decarbonization, and the shift toward OPEX‑driven energy models. Smart city rollouts, energy credit trading platforms and demand response frameworks under new electricity reforms will open white‑space opportunities for EaaS providers. Enterprises and public sector bodies increasingly seek full‑stack performance contracting and outcome‑based energy services to meet ESG and energy cost targets.
Major Market Players
- Tata Power EZ‑Home / TP Renewable Microgrid
- Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL)
- ReNew Power / EnKing International
- Fourth Partner Energy
- Smart Joules
- Cleantech Solar
- EcoEnergy Insights (Carrier)
- Amplus Solar (PETRONAS)
- Mahindra Teqo
- BLP Energy (Bharat Light & Power)
- CleanMax Solar
- Hero Future Energies
- OMC Power
- Husk Power Systems
- SunSource Energy
Key Target Audience
- CFOs and energy procurement heads at large commercial and industrial enterprises
- Chief Sustainability Officers at real estate and IT park operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms (focused on energy transition and ESG)
- Ministry of Power and Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)
- State Regulatory Commissions and DISCOM leadership
- Urban local bodies executing smart‑city energy contracts
- Facility management firms sourcing EaaS contracts for clients
- Industrial associations such as CII, FICCI negotiating sector energy services
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves mapping stakeholders in the India EaaS market, including ESCOs, DISCOMs, corporate buyers, technology vendors and financing institutions. Secondary databases, policy documents and industry reports are used to define critical variables such as service types, contract models, incentive schemes and capacity metrics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data on contract volumes, installed renewable capacity under EaaS models and revenue flows are collected from industry disclosures and financial filings. Market sizing is triangulated using bottom‑up estimates of deployed projects and average contract values, cross‑validated against national renewable installation data.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses about growth drivers, pricing norms and adoption barriers are validated via CATI interviews with executives at key ESCOs, facility managers and corporate energy buyers. These consultations yield qualitative insights on contract structuring, customer decision criteria and project economics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final synthesis involves detailed engagement with major providers to verify service mix, contract terms, installed base, and pricing for energy supply and optimization contracts. Bottom‑up estimates are reconciled with top‑down macro indicators including commercial energy consumption growth and smart meter deployments.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Data Triangulation, Market Sizing Methodology, Consolidated Research Approach, Primary Research Breakdown, Industry Expert Validation, Limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Energy Sector Value Chain Mapping
- Evolution of EaaS in India
- Key Stakeholder Mapping (ESCOs, DISCOMs, OEMs, Facility Owners)
- India Energy Services Timeline – Policy, Tech & Adoption Milestones
- Demand Lifecycle: Commercial, Industrial, Residential
- Energy Infrastructure Snapshot and Electrification Penetration
- Load Patterns and Consumption Trends (Urban, Rural, Tier-2)
- Growth Drivers
Decentralization of Energy Systems
Electrification Goals under Saubhagya & RDSS Schemes
Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Demand for Decarbonization
Investment in Smart Infrastructure
Government Push for ESCO Adoption and UJALA Extension - Market Challenges
Policy Uncertainty for Energy Services Business Models
Integration Bottlenecks in Legacy Infrastructure
Financing Constraints and Long Payback Periods
Lack of Standardization in EaaS Contracts
DISCOM Financial Health and Billing Inefficiencies - Market Opportunities
Public-Private Partnerships in Urban Energy Projects
Capex-to-Opex Shift by MNCs and Data Centers
Rise in Green Building Certifications
National Hydrogen and Storage Missions - Market Trends
AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance and Load Management
Subscription-Based and Outcome-Linked Models
IoT Deployment in Energy Systems
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading Pilots - Regulatory & Policy Landscape
Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Mandates
Energy Conservation Act Amendments
Renewable Energy Open Access Rules
Smart City Mission Integration - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- By Value (INR), 2019-2024
- By Volume (in MW), 2019-2024
- By Installed Base (Connected Buildings / Projects), 2019-2024
- By Average Revenue per Unit of Service, 2019-2024
- By Service Type (In Value %)
Energy Supply Services
Operational & Maintenance Services
Energy Optimization & Efficiency Services
Energy Asset Financing
Demand Response Services - By Technology Integration (In Value %)
Smart Metering
Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS)
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Renewable Energy Systems (Solar, Wind)
Storage and Battery Systems - By End User (In Value %)
Industrial (Textile, Cement, Chemical, Automotive, etc.)
Commercial (IT Parks, Malls, Educational Institutions, Hospitality)
Residential Gated Communities and Housing Societies
Government Buildings & Utilities
Healthcare & Pharma Facilities - By Energy Source (In Value %)
Solar Power
Wind Power
Hybrid Systems
Natural Gas-Based Generation
Grid-Connected vs. Off-Grid - By Region (In Value %)
North India
South India
West India
East India
Central India
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Service Offerings, Renewable Energy Asset Ownership, Contract Structures, Key Clients and Projects, Deployment Scale, Geographic Footprint in India, Technology Partnerships and OEM Tie-Ups, Revenue Breakdown by End-User Vertical, Sustainability & ESG Initiatives)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Structure and Contract Comparison
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Tata Power EZ Home / TP Renewable Microgrid
Amplus Solar (A member of PETRONAS)
EcoEnergy Insights (Carrier)
Smart Joules
Cleantech Solar
Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL)
ReNew Power
Hero Future Energies
Fourth Partner Energy
EnKing International (EKI Energy Services)
Mahindra Teqo
BLP Energy (Bharat Light & Power)
OMC Power
Husk Power Systems
SunSource Energy
- Adoption Readiness by Sector
- Budget Allocation and Procurement Patterns
- Barriers to Entry for EaaS Providers
- Decision Criteria – Cost, Reliability, Compliance
- Energy Consumption Patterns & Shift Toward Efficiency
- By Value (INR), 2025-2030
- By Volume (in MW), 2025-2030
- By Installed Base (Connected Buildings / Projects), 2025-2030
- By Average Revenue per Unit of Service, 2025-2030


