Market Overview
The India genomic testing market is valued at USD 550 million, supported by recent industry reports that highlight its substantial traction in diagnostics. This growth is propelled by expanding physician adoption, falling test costs, rising awareness of personalized healthcare, and increasing penetration into non‑metro regions such as Tier II and III cities. The substantial increase in clinical usage and proactive, preventive healthcare practices is also a critical enabler.
Key metropolitan centers—primarily Delhi–NCR, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad—dominate the genomic testing landscape due to their well‑developed healthcare ecosystems, advanced laboratory infrastructure, and strong presence of diagnostics chains and biotech firms. These cities benefit from higher disposable incomes, greater clinician awareness of genomics, and the presence of leading research institutes facilitating rapid adoption and service availability.
Market Segmentation
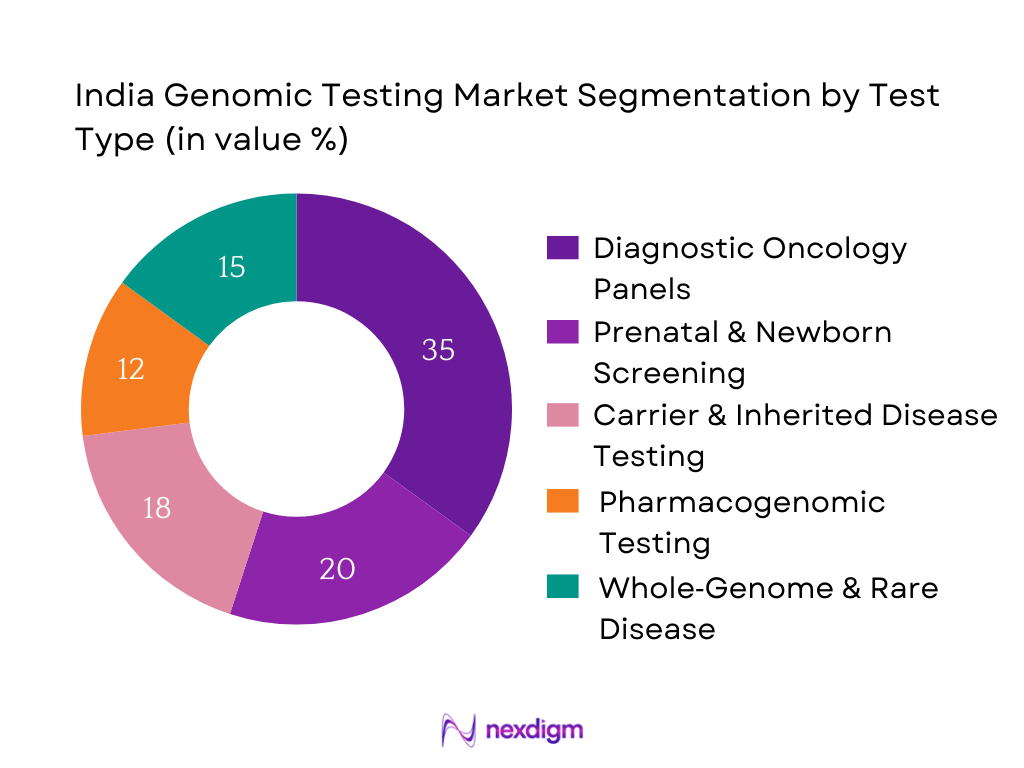
By Test Type
Within the India genomic testing market, Diagnostic Oncology Panels hold a dominant share. This prominence stems from rising cancer incidence and the urgent need for precision oncology to tailor treatment using genetic insights. Leading hospitals and diagnostic chains are increasingly integrating NGS‑based oncology panels as part of standard care pathways, driven by clinicians prioritizing targeted therapeutics and improved patient outcomes. Further, affordability gains and insurance pilots for cancer testing in clusters of metros have propelled demand. Oncology tests also command higher per‑test revenues, making them a financially attractive offering for laboratories. Thus, Oncology Panels continue to lead in terms of utilization and revenue within Test Type segmentation.
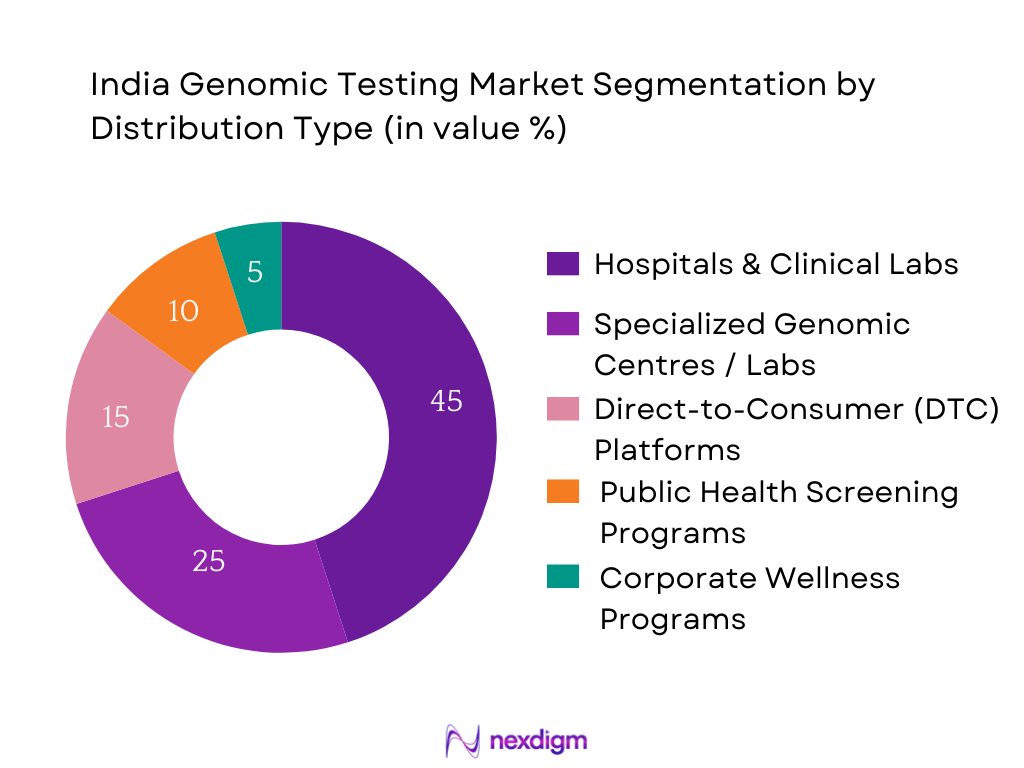
By Distribution Channel
The Hospitals & Clinical Labs channel dominates the India genomic testing market. These institutions serve as primary points of contact for physicians and patients, embedding genomic testing into broader diagnostic workflows. Hospitals benefit from established trust, integrated sample collection logistics, and bulk testing capabilities, enabling greater volumes. Additionally, clinical labs tied to hospital networks can offer bundled services—including imaging, pathology, and genomics—encouraging higher adoption. Insurance partnerships and institutional billing systems further facilitate utilization by reducing out‑of‑pocket burden for patients. Consequently, hospitals and clinical laboratories remain the preferred and most utilized channels for genomic diagnostics across private and public healthcare sectors in India.
Competitive Landscape
The India genomic testing market is led by several prominent players, including MedGenome, Strand Life Sciences, Mapmygenome, DNA Labs India, and Xcode Life. These companies have established leadership through expansive test portfolios, robust lab infrastructure, strong clinician networks, and strategic partnerships. This concentrated landscape underscores the influence of organizations with both clinical reach and technological capabilities, ensuring high visibility and trust in the genomic testing domain.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | NGS Capacity | Geographic Reach | TAT (Turn‑around Time) | Bioinformatics Capability | Pricing Tier | Regulatory Compliance |
| MedGenome | 2013 | Bengaluru | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Strand Life Sciences | 2006 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Mapmygenome | 2011 | Hyderabad | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| DNA Labs India | 2015 | Delhi–NCR | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Xcode Life | 2017 | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – | – |
India Genomic Testing Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The rapid enhancement in India’s healthcare funding is creating the necessary infrastructure to reduce genomic testing costs. In fiscal year 2022–23, central and state governments together allocated 2.1 % of GDP to health expenditure—up from 1.6 % in FY21—enabling expansion of diagnostic capabilities in secondary and tertiary hospitals. India’s nominal GDP per capita stood at USD 2,731 in 2024, translating into higher per capita fiscal capacity for infrastructure investment. This augmented budget flow is facilitating acquisition of Next‑Generation Sequencing platforms and subsidizing lab modernization, directly contributing to declining per‑test costs in genomic diagnostics by spreading fixed overheads over increased test volumes.
Market Challenges
Regulatory clarity for genomic testing is constrained by sluggishly rising public health allocation—just 2.1 % of GDP in FY23 —which limits the government’s capacity to promulgate and enforce detailed genomic guidelines. Simultaneously, major urban‑rural disparities persist: over 1.72 million infant deaths per year indicate gaps in neonatal care, reflecting broader infrastructural limitations in diagnostics, logistics, and skilled personnel outside metro areas. These conditions make it difficult for regulators to standardize protocols or ensure consistent quality across India’s dispersed genomic testing network, hampering uniform adoption and reliability of testing services nationwide.
Opportunities
Tier‑II & Tier‑III expansion and oncologist partnerships enabled by growing health funding and rare disease data India is home to an estimated 70 million individuals affected by rare genetic disorders. With central health spending reaching 2.1 % of GDP in FY23, there’s a strengthening fiscal base for extending diagnostic infrastructure into smaller cities. As hospital chains and public health labs receive these funds, capacity to offer genomic testing in Tier‑II and Tier‑III cities grows. Simultaneously, leading cancer‑care institutions in metros are formalizing diagnostic collaborations—leveraging data on rare and inherited disorders—to expand oncology panels into regional referral networks. These developments indicate a strong foundation for future market growth: current capability and funding exists, enabling outreach beyond metros and deeper subspecialty integration, especially through oncologist alliances.
Future Outlook
As genomic testing gains traction, the India market is anticipated to exhibit strong growth, driven by expanding clinical adoption, rising demand in Tier II/III cities, integration in cancer and prenatal care, and planned public health genomics initiatives. Technological improvements and affordable testing models will further enhance penetration. The India genomic testing market was valued at USD 550 million, based on 2024 data. Industry projections estimate CAGR of 18 % through 2030, potentially elevating market size to approximately USD 2,066 million by then.
Major Players
- MedGenome
- Strand Life Sciences
- Mapmygenome
- DNA Labs India
- Xcode Life
- Clevergene Biocorp
- Centogene India
- Eurofins Genomics India
- LifeCell International
- Genes2Me
- GeneTech India
- Dr Lal PathLabs
- Metropolis Healthcare
- Avesthagen (Avestagenome)
- SciGenom Labs
Key Target Audience
- Chief Strategy Officers of hospital chains
- Heads of Diagnostics & Lab Services (large hospital groups)
- Venture Capital & Investment Firms (healthcare/biotech focus)
- Cancer Center Directors (e.g., Tata Memorial Centre, AIIMS Oncology Wing)
- Heads of Government Health Agencies (e.g., ICMR, DBT/Genome India Project)
- Clinical Genomics Unit Leads in public health programs
- Biotech Incubator Managers (e.g., BIRAC, DBT-supported incubators)
- Insurance Payer Product Heads focusing on diagnostics coverage
Research Methodology
Step 1: Data Collection & Ecosystem Mapping
We constructed a detailed ecosystem map of genomic testing—covering diagnostics labs, hospitals, biotech firms, DTC platforms—through comprehensive desk research drawing upon secondary data (published reports, industry databases) and proprietary primary inputs.
Step 2: Market Sizing & Segmentation Analysis
Using bottom‑up (lab test volumes, average pricing) alongside top‑down (healthcare spend trends, genomics penetration proxies), we segmented the market by test type and channel, ensuring consistency and validation with financial disclosures and industry benchmarks.
Step 3: Expert Validation & Interviews
Key hypotheses were validated via in-depth interviews with industry stakeholders—lab directors, hospital chiefs, biotech founders—using structured video and telephonic discussions to capture operational metrics such as turnaround times, pricing strategies, and capacity utilization.
Step 4: Forecast Modeling & Synthesis
We synthesized insights into a forecasting model projecting market size and CAGR, complemented by trends analysis, competitor benchmarking, and validation loops with expert panels to ensure the highest accuracy and relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions & Assumptions; Abbreviations; Market Sizing & Forecasting Approach, Combining Bottom‑Up (labs, test volumes) & Top‑Down (macro health spend, genomics penetration); Data Sources — Primary (clinicians, diagnostic chain heads, patients), Secondary; Limitations & Validation)
- Definition and Scope
- Genesis & Development of Genomic Testing in India
- Evolving Regulatory & Reimbursement Framework (e.g., ICMR guidelines, genome sequencing initiatives)
- Supply‑Value Chain Architecture (labs, sequencing platforms, bioinformatics players, DTC channels)
- Ecosystem Stakeholders (diagnostic chains, hospitals, research institutes, bio‑informatics vendors)
- Growth Drivers (declining per‑test cost, rising hereditary disease awareness, government genome initiatives)
- Market Challenges (regulatory ambiguity, infrastructure disparities, data privacy concerns, reimbursement gaps)
- Opportunities (tier‑2 & tier‑3 city penetration, partnerships with oncologists, wellness segment expansion)
- Emerging Trends (NGS adoption, AI interpretation tools, home sample collection, DTC growth)
- Enabling Regulations & Government Support (ICMR sequencing policies, regional genome projects)
- Porter’s Five Forces (e.g., threat of new entrants—tech‑based startups; buyer power of hospitals/labs)
- SWOT Analysis (India-specific genomic testing context)
- By Value (USD million), 2019-2024
- By Test Volume (number of tests processed), 2019-2024
- By ASP (average selling price per test), 2019-2024
- By Test Type (In Value %)
Predictive/Presymptomatic Testing
Carrier Testing
Prenatal & Newborn Screening
Diagnostic Oncology Panels
Pharmacogenomic Testing
Rare Diseases/Whole Genome Sequencing - By Application (In Value %)
Cancer Diagnostics
Inherited Disease Diagnosis
Cardiovascular Risk Profile
Wellness & Health Risk Profiling (DTC)
Ancestry & Ethnicity - By Technology (In Value %)
PCR‑based panels
Next‑Generation Sequencing (targeted, WES, WGS)
Microarrays / SNP‑based chips
Bioinformatics & AI‑based interpretation (ML accuracy metrics) - By End‑User Channel (In value %)
Hospital & Clinical Labs
Specialized Genomic Centres & NGS Labs
Direct‑to‑Consumer (DTC) Platforms
Public Health Screening Programs - By Geography / Region (In Value %)
North India
South India
West & Central India
East & Northeast India
- Market Share by Value & Volume (India-wide; by segment)
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Lab Accreditation & Sequencing Capacity (e.g. CAP, NABL; # NGS platforms), Test Portfolio Breadth (onsite panels, rare disease tests, WGS), Bioinformatics & Interpretation Tools (AI adoption, proprietary algorithms), Turnaround Time (TAT), Sample Collection Reach (DTC + coverage in tier‑2/3 cities), Pricing & Affordability (ASP vs competitors), Partnerships (hospitals, research bodies, pharma), Regulatory Approvals / Compliance (ICMR, other accreditations))
- SWOT for Each Major Player
- Pricing Structure Analysis by SKU & Channel
- Detailed Company Profiles:
MedGenome
Strand Life Sciences
Mapmygenome
DNA Labs India
Xcode Life
Clevergene Biocorp
Centogene India
Eurofins Genomics India
LifeCell International
Genes2Me
GeneTech India
Dr Lal PathLabs
Metropolis Healthcare
Avesthagen (Avestagenome)
SciGenom Labs
- Utilization Patterns (urban vs rural, hospital vs wellness segments)
- Customer Pricing Sensitivity & Budget Constraints
- Physician & Lab Advocacy, Stakeholder Trust
- Pain Points (turnaround time, affordability, interpretation expertise)
- Purchase & Decision‑Making Funnels
- By Value (USD million), 2025-2030
- By Test Volume (number of tests processed), 2025-2030
- By ASP (average selling price per test), 2025-2030


