Market Overview
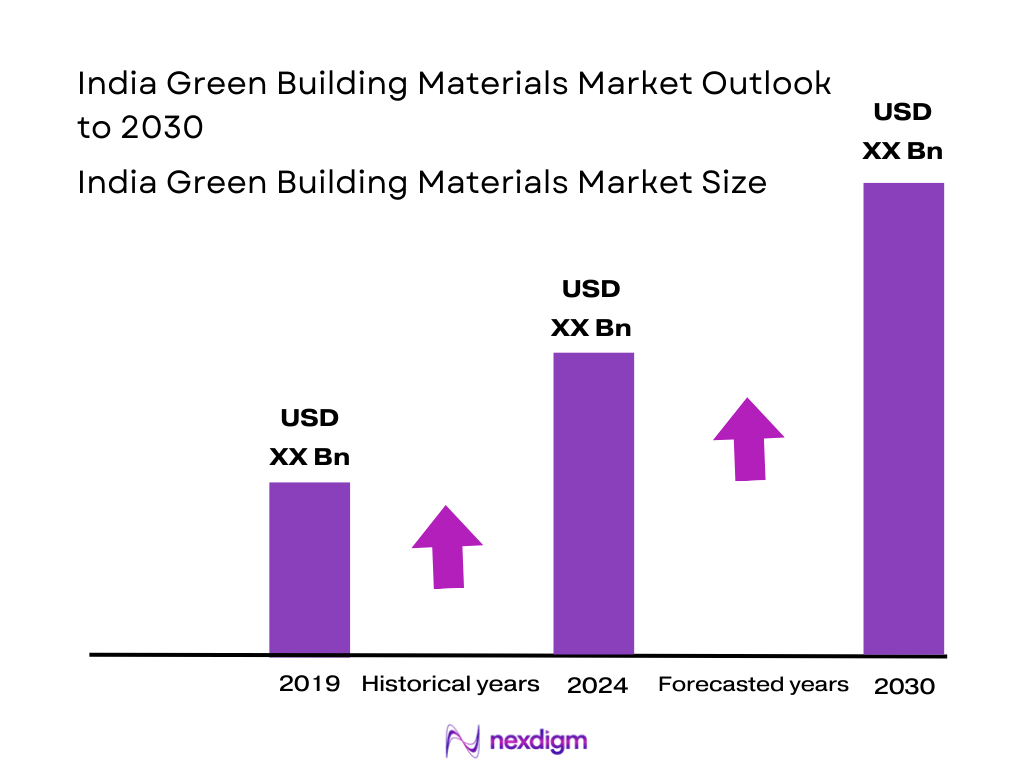
The India Green Building Materials market is valued at USD 14,173.0 million. This figure is based on recorded annual revenues and underscores the substantial demand for sustainable construction materials in India. The rise is driven by increasing construction of energy-efficient buildings, stringent building codes (like ECBC/GRIHA/IGBC), and investor focus on embodied‑carbon reduction in projects. The 2023 data aligns closely with this valuation, reflecting a robust uptick from previous years as developers pivot toward green-certified products.
The market is particularly concentrated in megacities such as Delhi‑NCR, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Pune, where urban growth and regulatory momentum coincide. These cities dominate because of their high rate of commercial and residential developments pursuing GRIHA, IGBC, or LEED certification, as well as state-level incentives for energy‑efficient buildings. Additionally, pilot net‑zero zones and green infrastructure corridors in these metros attract higher usage of green materials, propelling demand in their spheres.
The India Green Building Materials market registered revenues of USD 14,173.0 million in 2024. The market is projected to reach USD 26,637.8 million by 2030, implying a CAGR of 11.1% for the forecast period.
Market Segmentation
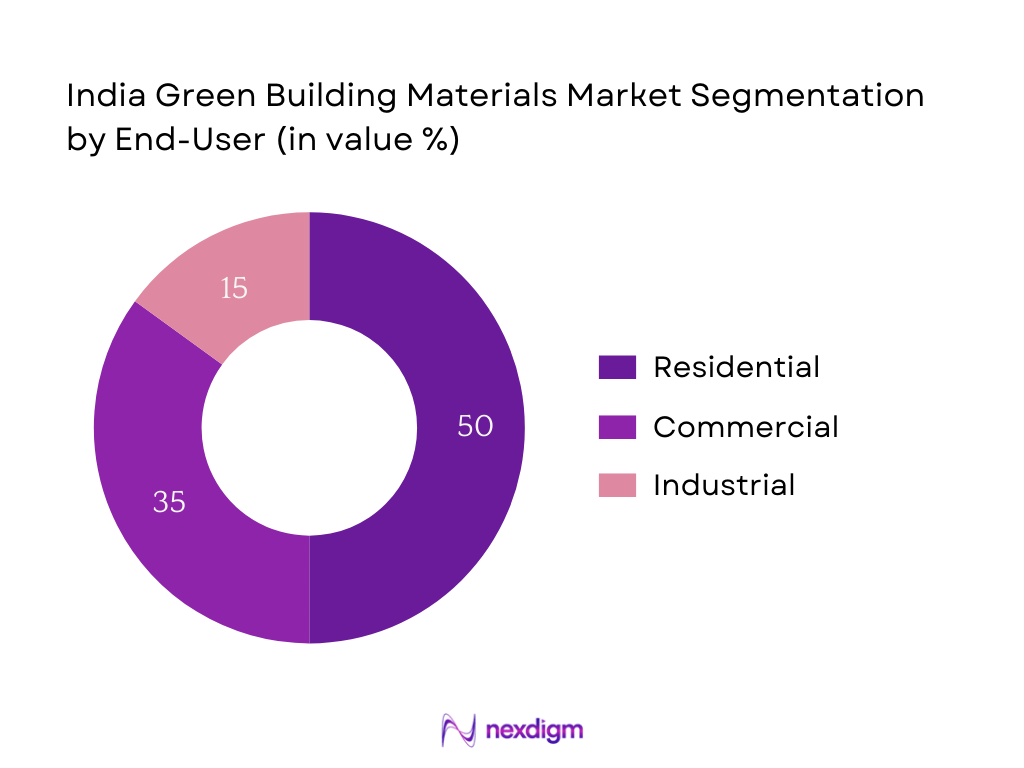
By End‑Use / Building Type
The India Green Building Materials market is segmented into Residential, Commercial, and Industrial categories. The Residential sub‑segment holds the largest share at 50%, owing to the strong advocacy for green-certified housing driven by both consumer preference and policy incentives (such as green BYPASS rebates and faster plan approvals). Rising income levels and awareness of healthy indoor environments further push residential developers to adopt eco‑friendly materials. The Commercial segment follows with a 35% share, fueled by corporate mandates for ESG compliance and the desire to reduce operational energy costs through sustainable building envelopes and systems. The Industrial segment trails at 15%, as green material uptake in warehousing and factory construction is emerging but still limited compared to other sectors.
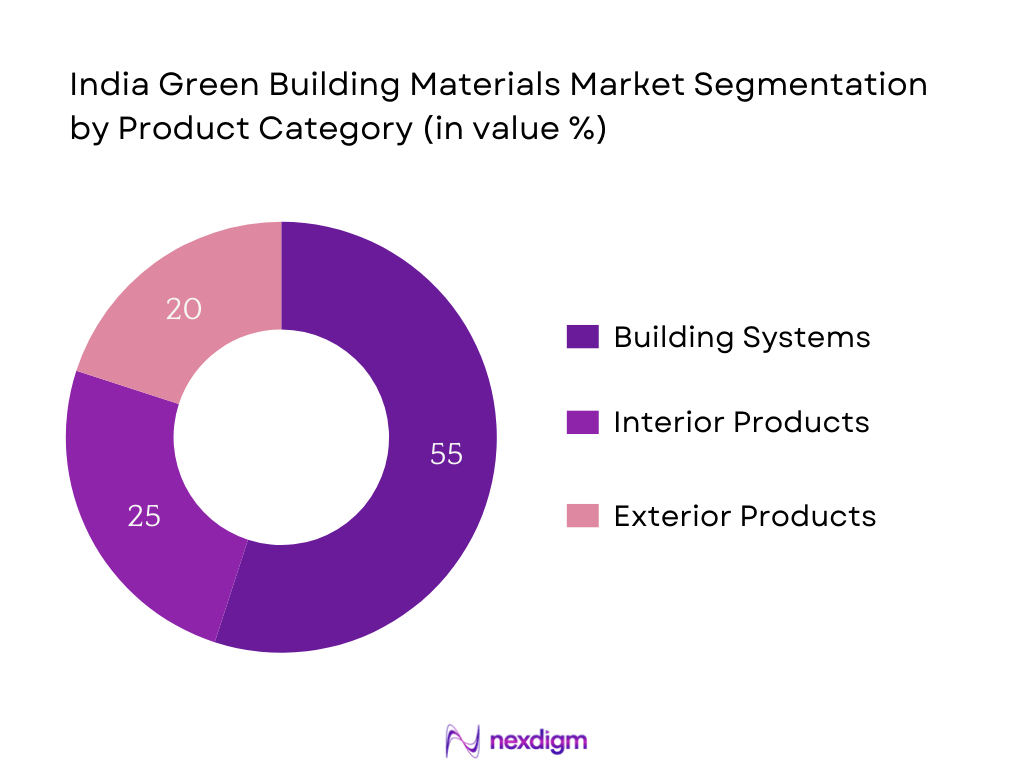
By Product Category
The market is divided into Building Systems, Interior Products, and Exterior Products. Building Systems dominate with 55% share—this segment includes critical systems such as insulation, high‑performance glazing, AAC blocks, and structural elements that contribute directly to energy performance and certification credits, making them high‑priority investments. Interior Products account for 25%, driven by increasing awareness of indoor air quality and low‑VOC requirements in paints, adhesives, and panels. Exterior Products hold 20%, supported by growing adoption of cool‑roof coatings and reflective façade finishes, especially in urban heat‑island mitigation efforts.
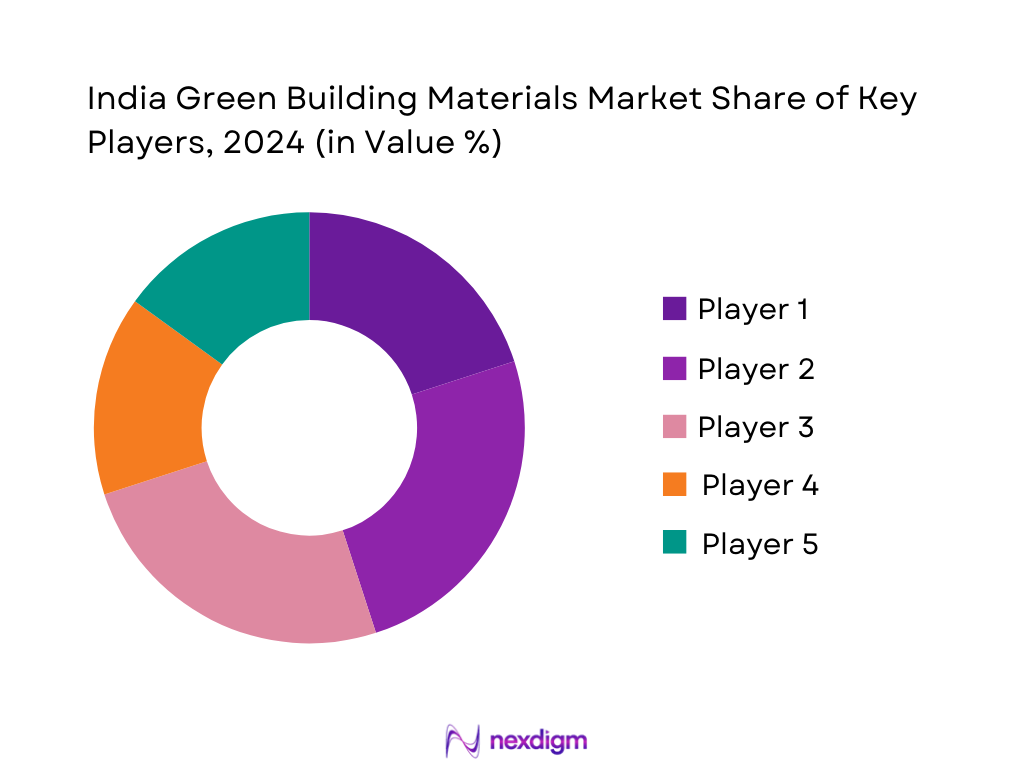
Competitive Landscape
The India Green Building Materials market features a compact set of prominent players across cement, glass, insulation, and boards—highlighting intense competition in performance, certifications, and distribution. The India Green Building Materials competitive landscape is shaped by major players such as UltraTech Cement, Saint‑Gobain India, JSW Cement, Owens Corning India, and ROCKWOOL India. These companies lead due to their certification portfolios (GreenPro, EPD), strong regional manufacturing footprints, and established relationships with large developers.
| Company | Est. Year | Headquarters | Green Certifications (e.g., GreenPro, EPD) | Main Product Focus | Manufacturing Footprint | Technical Support Network | Recent Innovation |
| UltraTech Cement | 2000s | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – |
| Saint‑Gobain India | 1950s | Gurgaon | – | – | – | – | – |
| JSW Cement | 1980s | Mumbai | – | – | – | – | – |
| Owens Corning India | 1990s | Pune | – | – | – | – | – |
| ROCKWOOL India | 2000s | Pune | – | – | – | – | – |
India Green Building Materials Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Urbanisation Rate
India’s urban population reached 522,939,628 in 2023, up from 511,327,815 in 2022—reflecting an increase of over 11 million people in one year; this is sourced from national urban population records. In 2024, total urban population climbed further to 534,916,498, an addition of approximately 12 million individuals moving into city areas. This sizeable influx into urban centers intensifies demand for housing and commercial infrastructure under more stringent energy-efficiency norms. As new construction rises, the corresponding requirement for green building materials—such as low‑U‑value glazing, high‑performance blocks, and thermal insulation—escalates sharply. The sheer volume of urban dwellers in key metros leads to bulk adoption of sustainable construction inputs, directly feeding into the green building materials market growth.
Energy Security Mandates
In fiscal year 2023–24, India produced 1,949 TWh of electricity, with 1,734 TWh generated by utilities—reflecting the scale of energy consumption that green building materials help mitigate. Installed power generation capacity reached 467,885 MW in March 2025, of which 190,573 MW came from renewables such as solar and wind. Total electricity generation increased from 1,414,281 GWh in 2022–23 to 1,734,375 GWh in 2023–24—an absolute rise of over 320,000 GWh. With such rapidly growing electricity demand, policies are intensifying to manage load through energy-efficient infrastructure. Green materials that lower building energy consumption, including high‑performance insulation and reflective surfaces, become instrumental in reducing peak load and enhancing energy security. The absolute increases in both capacity and generation—measured in terawatt-hours and megawatts—underscore the pressing need for materials that alleviate pressure on India’s expanding power infrastructure.
Market Challenges
High First Cost
While explicit data on green material prices isn’t available from macro sources, adopting energy-efficient items often translates to higher initial investment in project budgets. These early cost barriers are magnified against India’s per capita electricity consumption of 1,395 kWh (FY 2023–24) and total generation of 1,949 TWh. Developers, facing rising power demand delivered by electricity generation increasing from 1,414,281 GWh to 1,734,375 GWh, weigh upfront premiums against longer-term energy savings that are not immediately quantifiable in absolute macro terms. The challenge is especially critical in lower‑margin residential and affordable segments, where implicit first-cost concerns deter adoption of thermal insulation, low‑E glazing, and other green materials that could reduce reliance on this escalating electricity supply pressure. Without quantifiable macro-level cost offsets, high initial costs continue to limit broader adoption.
Awareness Gaps
Absolute indicators show that electricity demand rose by more than 320,000 GWh year-on-year (from 1,414,281 GWh to 1,734,375 GWh), and total installed capacity reached 467,885 MW by March 2025. Despite these massive energy figures, many stakeholders—including small developers and local builders—lack awareness of how specific green building materials (e.g., cool roof coatings, AAC blocks, high‑performance glazing) can mitigate such demand. This knowledge gap prevents wider usage of materials that could contribute to lowering load on the grid by mitigating heating/cooling needs. Without accessible macro-context making the link between generation figures and material performance, uptake remains concentrated among informed large-scale projects, undercutting more distributed green adoption across India’s building sector.
Emerging Opportunities
Retrofitting Market
India’s electricity generation surged from 1,414,281 GWh to 1,734,375 GWh from FY 2022–23 to FY 2023–24—an incremental usage of over 320,000 GWh. With a grid under such expanding stress, retrofitting existing buildings with green materials like efficient insulation, thermal glass, and reflective roofing offers a tangible means to curb energy demand. Given the large base of older stock built before stricter energy norms, retrofitting represents a substantial untapped opportunity. The absolute increase in generation signals urgency—creating demand for retro‑insulation, façade upgrades, and other retrofit solutions that enhance energy efficiency. This is reinforced by vast generation load baselines but no newer macro figures on retrofit coverage, making this segment a prime growth avenue.
Net‑Zero Building Mandates
India’s installed renewable capacity accounted for 190,573 MW out of 467,885 MW total by March 2025, with predicted doubling by 2035. The rising share of renewables amid such expanding infrastructure encourages building codes and rating systems to lean toward net‑zero-ready standards. Developers in high-demand regions recognize this, and project launches increasingly model net-zero operational performance. While net‑zero-focused new builds remain underrepresented in macro data, the absolute presence of substantial renewable generation capacity provides a firm operational backbone—enabling buildings to pursue net‑zero status via onsite or grid‑offset strategies. In parallel, demand for green building materials capable of achieving net‑zero-ready performance (e.g., ultra‑insulation, solar‑reflective surfaces, airtight systems) is poised to expand as infrastructure and policy converge on deeper sustainability.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast period, the India Green Building Materials market is expected to witness continued robust expansion, supported by multiple converging forces. The rollout of stricter building codes, rising commercial and residential green building adoption, net‑zero commitments by developers, and availability of financing for sustainable construction will catalyze further demand. Upcoming tier‑II city growth and retrofit opportunities in aging building stock further broaden the market scope. Market players are likely to diversify into innovative low‑carbon, circular‑economy materials and enhance service capabilities to compete effectively.
Major Players
- UltraTech Cement
- JSW Cement
- Ambuja Cements
- Dalmia Bharat Cement
- Saint‑Gobain India
- Asahi India Glass Ltd (AIS)
- Owens Corning India
- ROCKWOOL India
- HIL Limited (Birla Aerocon)
- Everest Industries
- Greenply Industries
- Nuvoco Vistas
- Fenesta Building Systems
- Magicrete Building Solutions
- Greenpanel Industries
Key Target Audience
- Private real estate developers
- EPC companies / major contractors
- Industrial facility operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Architects / green rating consultants
- Sustainability‑focused institutional investors
- Public sector undertaking housing authorities
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase comprises constructing an ecosystem map of all relevant stakeholders—manufacturers, developers, rating bodies, and policy enablers. This is anchored in secondary desk research with access to proprietary databases, codes, and rating frameworks to isolate the critical variables influencing market direction.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
This stage entails analysis of historical revenue data for the India green building materials market, mapping demand by product and end‑use. Energy performance metrics, certification volumes, and cost‑per‑m² inputs are assessed to validate revenue estimates and segment trends.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses, such as growth drivers and confidence in retrofit adoption rates, are validated via interviews with sector experts—developers, rating body officials, and materials heads—providing operational and financial insights via structured CATI (computer-assisted telephone interviews).
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Final phase includes targeted outreach to manufacturers and developers to verify and enrich bottom‑up data. Discussions focus on product mix shifts, project uptake, technical support investment, and expectations for forthcoming code changes, ensuring a robust, validated analysis.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions, Standards and Certifications, Rating Frameworks (IGBC, GRIHA, ECBC), LCI/LCA Methodologies, Primary and Secondary Data Sources, Market Sizing Techniques, Product Benchmarks, Validation and Triangulation, Data Assumptions and Limitations)
- Definition and Scope
- Evolution of Green Building Codes and Mandates
- Rating Systems Mapping (IGBC, GRIHA, LEED India, ECBC/ECSBC)
- Material Usage Across Certification Credits
- Market Ecosystem and Stakeholder Value Chain
- Green Floor Area Stock by Rating System and Typology
- Policy Timeline and Investment Landscape
- EPD, GreenPro, BIS, and IS Code Adoption Trends
- Key Growth Drivers (Urbanisation Rate, Energy Security Mandates, Corporate ESG Targets, Circular Economy Push)
- Market Challenges (High First Cost, Awareness Gaps, Fragmented Supply Chains, Technical Manpower Shortages)
- Emerging Opportunities (Retrofitting Market, Net-Zero Building Mandates, Tier 2/3 City Penetration, Product Innovation)
- Trends and Innovations (Bio-based Materials, Circularity, Prefabrication, Carbon Credits Monetisation)
- Government Regulation and Subsidies (State-Level Incentives, GST Benefits, MNRE/CPWD Norms)
- Construction Tender & Policy Tracker (Project Pipeline, Key Upcoming Mandates)
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Value Chain and Logistics Benchmarking (Lead Time, Supplier-to-Site Costs, Storage)
- Stakeholder Mapping (Influence Matrix, Procurement Behaviour)
- SWOT Analysis of Sector
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Average Price Index (Cost per m², Tonnes, Cubic Meters), 2019-2024
- By Material Type (In Value %)
Green Cement & Blended Cement (PPC, PSC, LC3)
Fly Ash and GGBS
AAC Blocks, Hollow Bricks, Fly Ash Bricks
Insulation Materials (Mineral Wool, Glass Wool, EPS/XPS, Cellulose)
Energy-Efficient Glass (Low-E, Solar Control, DGU)
Engineered Wood and Recycled Panels
Sustainable Roofing (Cool Roof Coatings, SRI Tiles, Green Roof Layers)
Gypsum Boards, Recycled Plasters - By Building Type (In Value %)
Residential (Affordable, Mid-Income, Luxury)
Commercial (Retail, Office, Hospitality)
Institutional (Education, Healthcare)
Industrial and Warehousing
Government and Public Infrastructure - By Application System (In Value %)
Roofing and Façade
Insulation and Moisture Barriers
Interior Panels and Partitions
Structural Blocks and Concrete
Flooring and Finishings
Glass and Fenestration Systems - By Project Stage (In Value %)
New Construction
Green Retrofit
Adaptive Reuse Projects
Deep Energy Retrofit - By Certification/Compliance (In Value %)
IGBC
GRIHA
LEED India
ECBC / Eco-Niwas Samhita (ENS)
BEE Star Rating System for Buildings
- Market Share Analysis (By Volume and Value, By Region, By Product Category)
- Competitive Mapping (Product Portfolio, Certification & EPD Adoption, Regional Penetration, R&D and Innovation)
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Embodied Carbon (kgCO₂e/unit), Thermal Performance (λ, U-Value), Acoustic Rating (STC/Rw), Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC), Fire Safety Classifications (IS 3808, BS 476), VOC Content (g/L), Green Certifications (GreenPro, EPD, LEED credits), Service & Distribution Reach (Regions, Warehousing, Technical Assistance))
- Pricing & Product Benchmarking (Pack Size, Coverage Area, Application Rates)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Company Profiles
UltraTech Cement
JSW Cement
Ambuja Cements
Dalmia Bharat Cement
Saint-Gobain India
Asahi India Glass Ltd (AIS)
Greenply Industries
Everest Industries
HIL Limited (Birla Aerocon)
Owens Corning India
ROCKWOOL India
Nuvoco Vistas
Fenesta Building Systems
Magicrete Building Solutions
Greenpanel Industries
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Average Price Index (Cost per m², Tonnes, Cubic Meters), 2025-2030


