Market Overview
The India IVF market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting a rapidly formalizing assisted reproduction ecosystem shaped by urban clinic networks, standardized laboratory workflows, and increasing clinical specialization. Care delivery models emphasize end-to-end treatment pathways covering diagnostics, ovarian stimulation, embryology, cryopreservation, and follow-up, supported by equipment suppliers and pharmaceutical distribution. Pricing opacity, package-based offerings, and fragmented service standards persist, while regulatory compliance has improved governance of donor programs and laboratory accreditation.
Southern and western metropolitan clusters dominate service density due to mature hospital ecosystems, deeper specialist pools, and higher awareness among urban working populations. National referral corridors connect Tier I hubs with Tier II feeder cities through spoke clinics and teleconsult triage. Medical travel corridors reinforce concentration around aviation-linked metros. Public sector fertility centers remain limited, while private chains anchor ecosystem maturity through standardized labs, centralized procurement, and compliance frameworks aligned with evolving assisted reproduction policy enforcement.
Market Segmentation
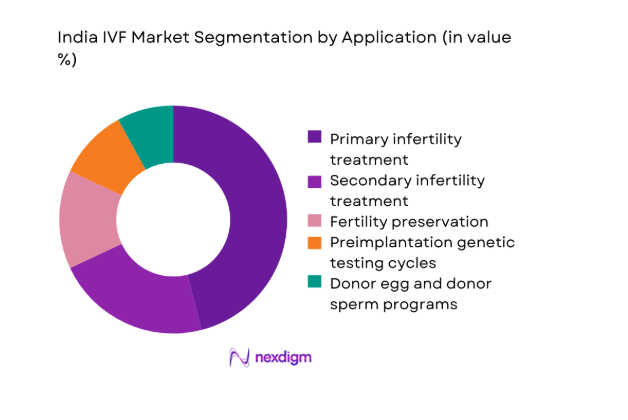
By Application
Primary infertility treatment dominates due to rising diagnosis rates, delayed family planning, and broader access to standardized stimulation and embryology protocols. Secondary infertility treatment follows as repeat cycles increase with improved patient counseling and cycle planning. Fertility preservation demand strengthens among urban professionals and oncology care pathways integrating cryopreservation. Preimplantation genetic testing grows where recurrent implantation failure and inherited condition screening are clinically indicated. Donor programs expand selectively under tighter compliance frameworks, with registry-based sourcing shaping availability and transparency. Application mix reflects clinic capabilities, referral sophistication, and counseling quality, with comprehensive centers capturing higher-value care pathways through bundled protocols and lab-enabled differentiation.
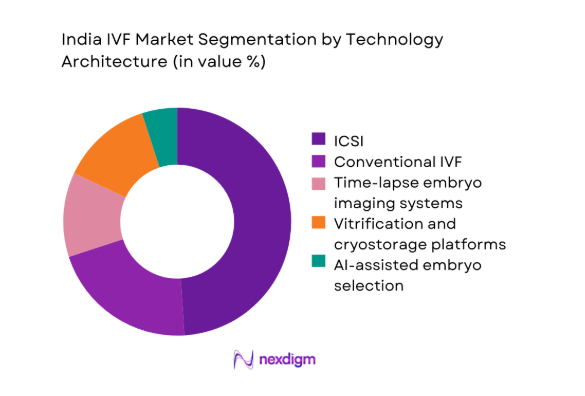
By Technology Architecture
ICSI remains dominant due to male-factor infertility prevalence and protocol standardization across high-throughput labs. Conventional IVF retains relevance for selected cohorts with favorable prognostics and lower intervention needs. Time-lapse imaging adoption increases in centralized labs seeking workflow efficiency and consistent embryo assessment. Vitrification and cryostorage platforms are foundational as freeze-all strategies gain acceptance to optimize endometrial receptivity and scheduling flexibility. AI-assisted embryo selection emerges in pilot deployments within chain clinics emphasizing outcome consistency and quality assurance. Architecture choices align with lab throughput, embryologist training depth, and capital deployment strategies, reinforcing differentiation among organized providers.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is characterized by organized clinic chains scaling standardized lab protocols alongside regional specialists emphasizing clinician-led differentiation. Competitive intensity centers on network density, clinical governance, and service integration across diagnostics, pharmacy coordination, and cryostorage continuity.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Nova IVF Fertility | 2011 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Indira IVF | 2011 | Udaipur | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Cloudnine Fertility | 2007 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Apollo Fertility | 2019 | Chennai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Birla Fertility & IVF | 2021 | Gurugram | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India IVF Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising infertility prevalence linked to delayed parenthood and lifestyle factors
Urbanization intensified between 2022 and 2025, with female median age at first birth rising from 23 to 24 in multiple metros, while obesity prevalence among reproductive-age adults increased from 24 to 27 across state health dashboards. Tobacco use among men declined from 28 to 26, yet semen parameter abnormalities recorded in tertiary hospitals rose from 31 to 36 cases per 100 screenings. Endocrine disorders diagnoses expanded from 41 to 52 per 10,000 clinic visits. Workplace stress indicators recorded 3.2 million outpatient mental health visits in 2024, affecting cycle adherence and outcomes. Public health registries documented 18 million reproductive-age women seeking infertility evaluation in 2025, sustaining demand.
Expansion of organized fertility clinic chains in Tier I and Tier II cities
Between 2022 and 2025, organized fertility networks expanded footprints from 110 to 165 operational centers across Tier I and Tier II corridors, improving standardized lab access and referral capture. Aviation-linked metros handled 62 million domestic passengers in 2024, supporting medical travel flows into hub clinics. State health licensing portals recorded 420 new ART facility applications in 2023 and 2024 combined, reflecting formalization momentum. Embryologist certification counts rose from 2,400 to 3,100 under professional councils, strengthening service capacity. Digital appointment platforms processed 9.8 million reproductive health bookings in 2024, accelerating funnel conversion for chain clinics.
Challenges
High out-of-pocket costs and limited insurance coverage
Insurance claim acceptance for assisted reproduction procedures increased from 6,400 cases in 2022 to 9,700 in 2024 across insurer disclosures, yet coverage exclusions remain prevalent. Household health expenditure surveys recorded 2.1 million families delaying specialist care in 2023 due to financing constraints. Consumer grievance portals logged 14,200 complaints in 2024 related to package clarity and ancillary charges. Microfinance penetration for healthcare rose from 1.6 to 2.3 million borrowers between 2022 and 2025, insufficient to offset access gaps. State social security schemes covered only 11 of 36 jurisdictions for limited infertility diagnostics in 2025, constraining equitable access.
Shortage of trained embryologists and reproductive endocrinologists
Professional council registers showed embryologist density rising from 1.8 to 2.3 per million population between 2022 and 2025, below tertiary care requirements in high-volume corridors. Fellowship intake in reproductive medicine expanded from 420 to 610 seats nationally, while annual attrition to overseas placements reached 180 clinicians in 2024. Laboratory accreditation audits recorded 27 percent nonconformity findings in 2023 related to documentation and quality control, straining throughput. Continuing education participation improved from 3,200 to 5,100 attendees in 2025, yet uneven distribution across regions perpetuates service variability and scheduling bottlenecks.
Opportunities
Penetration into Tier II and Tier III cities with hub-and-spoke models
District health infrastructure mapping in 2024 identified 112 Tier II and Tier III cities with diagnostic imaging and anesthesia coverage sufficient for day-care procedures, enabling spoke clinic deployment. Road connectivity upgrades added 18,000 kilometers between 2022 and 2025, reducing travel friction to hub labs. Teleconsult utilization in reproductive health rose from 1.1 million to 2.4 million sessions, supporting triage and protocol adherence. Nurse practitioner training enrollments increased from 6,800 to 9,200, enabling task-shifting at spokes. Cold-chain logistics for biologics expanded warehouse nodes from 74 to 103, supporting stimulation drug availability in non-metro corridors.
Integration of AI and automation in embryo selection and lab workflows
Between 2022 and 2025, certified medical AI deployments in imaging rose from 27 to 96 installations across private hospitals, establishing governance frameworks transferable to embryology workflows. Data centers accredited for health workloads expanded rack capacity from 8,000 to 14,500, enabling secure image processing pipelines. Laboratory automation procurement tenders increased from 190 to 340 nationally, reflecting workflow digitization appetite. Clinical audit committees reported documentation turnaround improvements from 72 to 38 hours post-automation pilots. Training programs certified 1,200 lab technologists in digital QA protocols by 2025, supporting scalable adoption under regulated quality systems.
Future Outlook
Over the coming decade, consolidation among organized providers will continue alongside disciplined expansion into underserved urban clusters. Regulatory enforcement is expected to standardize donor registries and laboratory quality systems. Digital triage, centralized labs, and outcomes governance will shape competitive advantage. Partnerships with employers and oncology care pathways will broaden access channels. Service models will increasingly emphasize continuity of care, transparency, and clinical governance across networks.
Major Players
- Nova IVF Fertility
- Indira IVF
- Cloudnine Fertility
- Apollo Fertility
- Birla Fertility & IVF
- Manipal Fertility
- ART Fertility Clinics India
- Medicover Fertility India
- CK Birla Fertility
- Gaudium IVF
- BACC Healthcare
- Bloom IVF
- Dunya Healthcare India
- Oasis Fertility
- Motherhood Fertility
Key Target Audience
- Private fertility clinic chains
- Corporate hospital networks
- Medical device and lab automation vendors
- Pharmaceutical distributors for reproductive therapies
- Health insurers and third-party administrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names including Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and National Health Authority
- Medical tourism facilitators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Clinical pathway mapping, protocol variants, and lab workflow components were defined to frame scope and comparability. Regulatory requirements, donor registry norms, and accreditation criteria were incorporated to bound operational realities. Demand-side drivers across urban clusters and referral corridors were enumerated.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Care pathways were decomposed into diagnostics, stimulation, lab procedures, cryostorage, and follow-up. Capacity mapping across clinic networks and spoke-hub flows informed utilization constructs. Technology architectures were aligned with throughput, training depth, and compliance readiness.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Clinical leaders, embryology heads, and compliance officers validated pathway assumptions and workflow constraints. Procurement and operations managers reviewed technology adoption barriers and scaling levers. Policy practitioners reviewed regulatory interpretations affecting donor programs and lab audits.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were reconciled across care delivery, infrastructure readiness, and governance constraints. Findings were stress-tested for internal consistency and scenario robustness. Outputs were structured to support strategic planning, expansion prioritization, and operating model design.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and clinical pathway boundaries for assisted reproductive technologies in India, Treatment modality taxonomy and patient cohort stratification across IVF ICSI IUI donor and surrogacy cycles, Bottom-up cycle volume modeling from clinic throughput and success rates with revenue attribution per cycle type)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Care pathways and patient journey in assisted reproduction
- Ecosystem structure of clinics labs pharma and device suppliers
- Supply chain and referral channel structure
- Regulatory environment under ART Act and Surrogacy Act
- Growth Drivers
Rising infertility prevalence linked to delayed parenthood and lifestyle factors
Expansion of organized fertility clinic chains in Tier I and Tier II cities
Growing awareness and social acceptance of assisted reproduction
Medical tourism inflows for cost-competitive IVF treatment
Improving clinical outcomes through advanced lab technologies
Increasing disposable income and availability of EMI-based financing - Challenges
High out-of-pocket costs and limited insurance coverage
Variability in clinical outcomes and lack of standardized success reporting
Shortage of trained embryologists and reproductive endocrinologists
Regulatory compliance burden under ART Act and donor registry norms
Ethical concerns and stigma in conservative demographics
Supply chain dependence on imported lab equipment and consumables - Opportunities
Penetration into Tier II and Tier III cities with hub-and-spoke models
Bundled care packages and outcome-linked pricing models
Integration of AI and automation in embryo selection and lab workflows
Partnerships with corporate employers for fertility benefits
Expansion of fertility preservation services for oncology patients
Localization of consumables and equipment manufacturing - Trends
Consolidation of independent clinics into national chains
Rising adoption of vitrification and freeze-all protocols
Growth of egg freezing among urban working women
Digitization of patient management and lab information systems
Outcome transparency and marketing based on success rates
Increasing demand for donor programs and genetic screening - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Cycle, 2020–2025
- By Facility Type (in Value %)
Single-specialty fertility clinic chains
Multi-specialty hospital fertility departments
Standalone IVF laboratories
Public sector and academic fertility centers - By Treatment Application (in Value %)
Primary infertility treatment
Secondary infertility treatment
Fertility preservation
Preimplantation genetic testing cycles
Donor egg and donor sperm programs - By Technology Platform (in Value %)
Conventional IVF
ICSI
Time-lapse embryo imaging systems
Vitrification and cryostorage platforms
AI-assisted embryo selection - By Care Delivery Setting (in Value %)
Private fertility clinics
Corporate hospital networks
Public hospitals and teaching institutions
Medical tourism service providers - By Digital Integration Level (in Value %)
Standalone lab systems
Clinic-lab integrated platforms
Cloud-enabled embryology information systems
Remote monitoring and teleconsult platforms - By Region (in Value %)
North India
West India
South India
East and Northeast India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Clinic network scale, Success rate disclosures, Treatment portfolio breadth, Geographic footprint, Pricing and financing models, Lab technology sophistication, Doctor and embryologist depth, Brand and referral strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Nova IVF Fertility
Indira IVF
Cloudnine Fertility
Apollo Fertility
Birla Fertility & IVF
Manipal Fertility
ART Fertility Clinics India
Medicover Fertility India
CK Birla Fertility
Gaudium IVF
BACC Healthcare
Bloom IVF
Dunya Healthcare India
Oasis Fertility
Motherhood Fertility
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Cycle, 2026–2035


