Market Overview
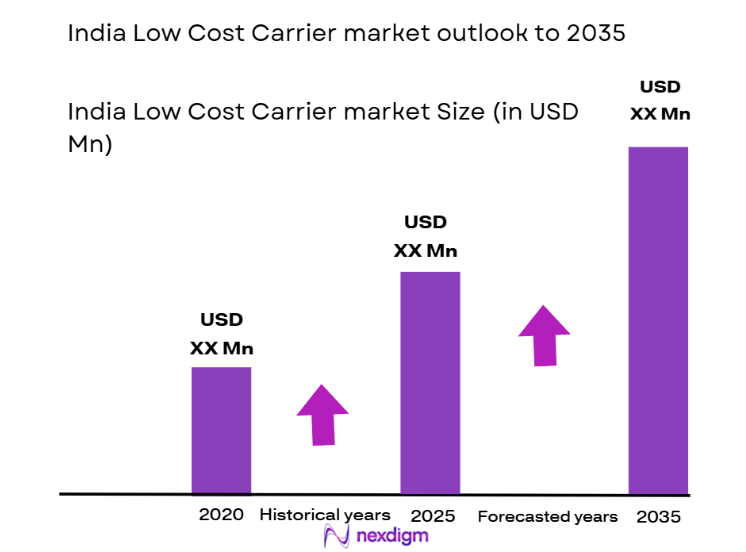
The India Low Cost Carrier market has witnessed significant growth due to a combination of factors such as an expanding middle-class population, increasing disposable incomes, and a government focus on improving domestic air connectivity. As per recent assessments, the market is expected to reach USD ~ million. This rise is propelled by the preference of Indian consumers for budget-friendly travel, making low-cost carriers an attractive choice for both business and leisure travel. Airlines operating under the low-cost model focus on reducing operational costs, primarily by minimizing the frills associated with traditional carriers, thus allowing them to offer affordable tickets. The implementation of government schemes such as UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik) has also improved air travel access to regional and underserved markets, driving further demand for low-cost air travel. Consequently, these market dynamics continue to fuel the expansion of low-cost carriers across the nation.
Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, and Kolkata remain central hubs for the low-cost carrier market in India, primarily due to their large populations, robust economic activities, and high connectivity. These metropolitan areas act as key focal points for business and leisure travelers. The airports in these cities have undergone extensive infrastructure upgrades, making them ideal for low-cost airlines looking to expand their operations. Additionally, government policies supporting infrastructure development and increasing competition have helped these cities maintain dominance in the aviation sector. As a result, the airline market in these regions continues to expand, with more people opting for air travel over other forms of transportation due to its cost-effectiveness and convenience.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
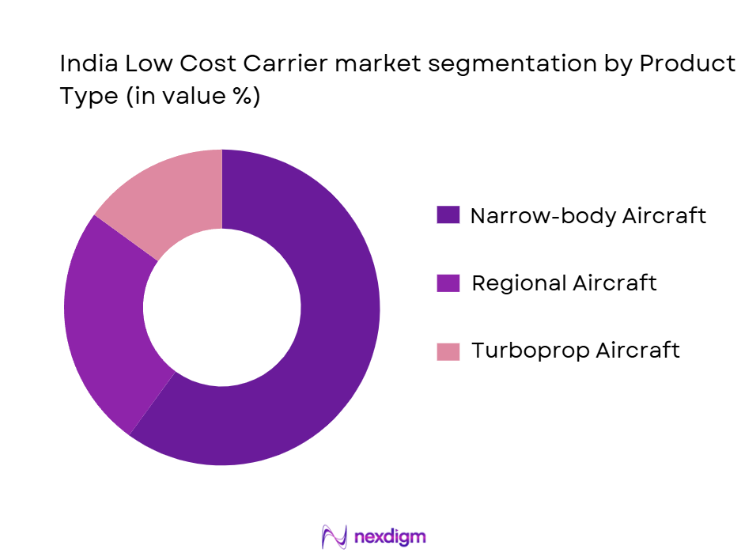
The India Low Cost Carrier market is segmented by product type into narrow-body aircraft, regional aircraft, and turboprop aircraft. Narrow-body aircraft dominate the market share due to their superior operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ability to service both short- and medium-haul routes. These aircraft are ideal for serving high-demand routes that form the backbone of low-cost carrier operations. They are also relatively cheaper to maintain and operate compared to wide-body aircraft, making them a preferred choice for budget airlines. Their versatility and ability to utilize regional airports with shorter runways have solidified their position as the dominant sub-segment in India’s low-cost carrier market.
By Platform Type
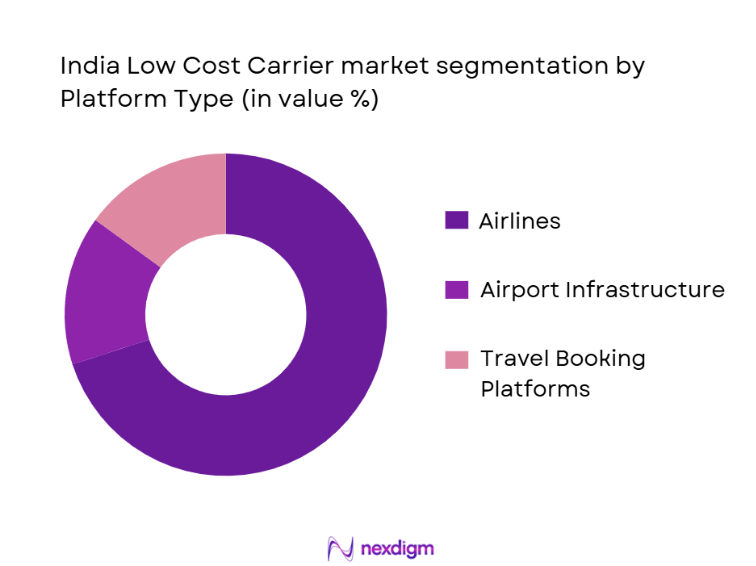
The India Low Cost Carrier market is segmented by platform type into airlines, airport infrastructure, and travel booking platforms. Airlines dominate this segment due to the substantial volume of passengers opting for budget-friendly travel. Low-cost carriers have tapped into the growing demand for affordable travel by focusing on no-frills service, which has made flying accessible to a larger portion of the population. These airlines operate with cost-cutting measures, such as high aircraft utilization rates and minimal services, allowing them to provide competitive ticket prices that cater to both business and leisure travelers. Consequently, airlines hold a significant market share within the platform type segment.
Competitive Landscape
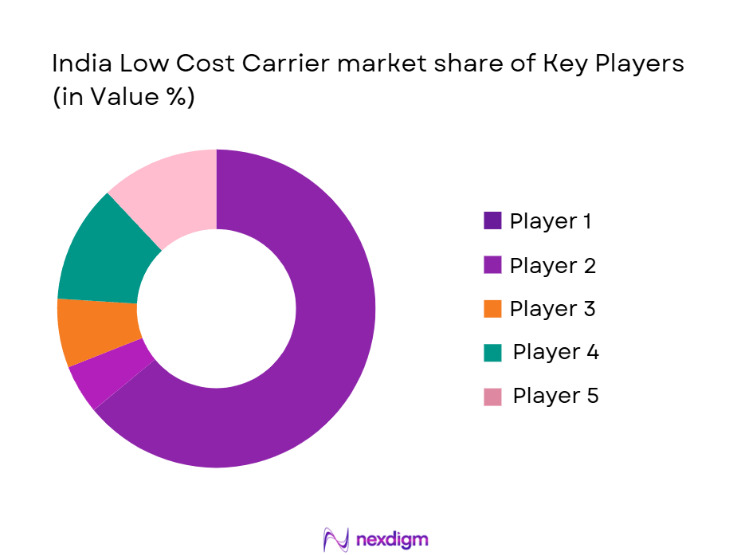
The competitive landscape of the India Low Cost Carrier market is characterized by a combination of well-established players and newer entrants, all competing for market share. The market has witnessed consolidation with a few players dominating the industry. IndiGo, SpiceJet, and GoAir lead the market, benefiting from strong brand recognition, extensive route networks, and cost-effective operational models. These players focus on aggressive pricing strategies, fleet expansion, and partnerships to maintain their competitive edge. Additionally, the market is seeing increasing competition from new entrants, which are expanding their footprint in underserved regions, driving further competition and potentially impacting profitability.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Additional Parameter |
| IndiGo | 2006 | Gurugram | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SpiceJet | 2005 | Gurgaon | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| GoAir | 2005 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Air India Express | 2004 | Kochi | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AirAsia India | 2014 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Low Cost Carrier Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increase in Disposable Income
The increase in disposable income among India’s growing middle class is one of the primary drivers for the demand for low-cost carriers. As more people find themselves with extra disposable income, they are increasingly opting for air travel, which was once seen as a luxury. The low-cost carrier model provides an affordable option, offering competitive prices that appeal to the cost-conscious consumer. This increase in disposable income has also contributed to the growth in business travel, as more small and medium enterprises (SMEs) require affordable travel solutions for their employees. The growing availability of budget-friendly flight options has made air travel more accessible to a broader section of the population, contributing significantly to the overall market growth.
Government Initiatives & Infrastructure Development
The Indian government’s focus on improving aviation infrastructure through schemes like UDAN (Ude Desh ka AamNaagrik) has played a crucial role in the growth of low-cost carriers. The scheme focuses on enhancing air connectivity to regional cities that were traditionally underserved. With improvements in infrastructure, including the development of smaller regional airports, low-cost carriers can tap into new, profitable markets. Additionally, the government’s relaxed aviation policies, lower taxes, and subsidies for regional connectivity have reduced operational barriers for low-cost airlines. This combination of infrastructure upgrades and policy support provides low-cost carriers with the necessary environment to expand their operations.
Market Challenges
Fuel Price Fluctuations
Fuel price volatility is a persistent challenge in the aviation industry, particularly for low-cost carriers that operate on narrow margins. Any significant increase in fuel prices directly impacts the operating costs of airlines. For low-cost carriers, which rely heavily on cost-cutting measures to offer affordable ticket prices, fuel price hikes may lead to fare increases or reduced profitability. This challenge forces airlines to either absorb the increased costs or pass them on to passengers, potentially reducing demand. Given that fuel makes up a significant portion of operating costs, managing fluctuations in global oil prices remains a critical issue for low-cost carriers.
Intense Competition
The India Low Cost Carrier market is highly competitive, with both established players and new entrants vying for market share. With airlines offering similar pricing models and services, differentiation becomes challenging, leading to aggressive price competition. This price competition puts pressure on margins, especially for low-cost carriers that operate with thin profit margins. Additionally, the increasing number of entrants in the market has intensified competition, with some carriers aggressively expanding their route networks, making it difficult for established players to maintain dominance in the market. The struggle to maintain profitability amid intense competition remains a significant challenge for low-cost carriers.
Opportunities
Expansion into Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities
There is a significant opportunity for low-cost carriers to expand into tier-2 and tier-3 cities in India. These cities have seen rapid economic growth, and their residents are increasingly seeking affordable travel options. As air travel becomes more accessible, low-cost carriers have the potential to capture new customer bases in these regions. Additionally, the Indian government’s focus on regional connectivity has provided low-cost carriers with favorable conditions to establish routes that cater to previously underserved areas. Expanding into these regions will not only boost the market share of low-cost carriers but also drive overall market growth
Technological Innovations
The continued adoption of technological innovations, such as AI, machine learning, and data analytics, presents a significant opportunity for low-cost carriers to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience. ByleveragingAI for predictive maintenance, scheduling, and route optimization, airlines can reduce costs and improve service delivery. Additionally, technology can help streamline ticketing, enhance online booking experiences, and provide personalized customer interactions. As the Indian consumer becomes more tech-savvy, airlines that leverage technology to offer efficient, personalized, and cost-effective services are well-positioned to maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the India Low Cost Carrier market is expected to experience substantial growth. This will be fueled by an expanding consumer base, government support for regional connectivity, and technological advancements that improve efficiency. Increased competition will encourage innovation, while evolving customer expectations will drive carriers to enhance service offerings. Low-cost carriers will continue to expand their routes, tapping into new markets and offering affordable air travel options for the Indian population. Technological developments in AI, fleet management, and sustainable aviation practices will further contribute to the market’s growth trajectory.
Major Players
- IndiGo
- SpiceJet
- GoAir
- Air India Express
- AirAsia India
- Vistara
- Jet Airways
- Zoom Air
- Akasa Air
- Trujet
- FlyBig
- Akasa Airways
- Deccan Air
- Star Air
- Alliance Air
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Airline operators and executives
- Airport authorities and aviation infrastructure providers
- Travel agencies and booking platforms
- Aircraft leasing companies
- Tourism boards and agencies
- Logistics and cargo services providers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial step involves identifying key variables such as market size, growth drivers, challenges, and segmentation to guide the analysis process.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
A comprehensive analysis of the market is conducted, including segmentation and regional trends, using both primary and secondary data sources.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Expert consultations and validation of initial hypotheses are carried out to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the findings.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The synthesized research findings are compiled into the final report, providing actionable insights for stakeholders and market participants.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Middle-Class Population
Government Initiatives & Infrastructure Investments
Expansion of Tourist and Business Travel - Market Challenges
Fuel Price Volatility
Regulatory Challenges
Intense Competition Among LCCs - Market Opportunities
Expansion into Tier 2 & 3 Cities
Strategic Alliances and Codeshare Agreements
Innovative Service Offerings - Trends
Rise of Ultra-Low-Cost Carriers (ULCCs)
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Aircraft Initiatives
Adoption of AI and Big Data for Operational Efficiency - Government Regulations
Liberalization of Air Travel Policies
Environmental Regulations for Emissions
Safety and Security Standards for Low-Cost Airlines
- By Market Value 2020-2025
- By Installed Units 2020-2025
- By Average System Price 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Narrow-body Aircraft
Single-aisle Aircraft
Turboprop Aircraft
Regional Aircraft
Long-Haul Aircraft - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Airlines
Airport Infrastructure
Ground Handling Equipment
In-flight Services Platforms
Travel Booking Platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
New Fleet Aircraft
Upgraded Fleet Aircraft
Retrofitted Fleet Aircraft
Fleet Expansion Initiatives
Aircraft Maintenance - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Domestic Travelers
International Travelers
Tourists
Corporate Travelers
Frequent Flyers - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct Purchases
Leasing Services
Second-hand Aircraft
Government Contracts
Partnerships with Travel Agencies
- Market Share Analysis
- CrossComparison Parameters (Market Value, Installed Units, System Price, Platform Demand, Fitment Type)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Key Players
IndiGo
SpiceJet
GoAir
Air India Express
AirAsia India
Vistara
Jet Airways
Zoom Air
Akasa Air
Trujet
FlyBig
Akasa Airways
Deccan Air
Star Air
Alliance Air
- Domestic Travel Preferences
- Corporate Travel Patterns
- Growth of Budget Tourism
- Influence of Online Booking Channels
- Forecast Market Value 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform 2026-2035


