Market Overview
Based on a recent historical assessment, the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market was valued at USD ~ billion, supported by sustained public expenditure on space transportation programs and validated industry reporting from Global Market Insights. Market momentum is driven by national priorities focused on lowering launch costs, increasing mission frequency, and achieving strategic autonomy in orbital access. Continuous funding for reusable vehicle testing, propulsion recovery, and autonomous guidance systems, combined with growing commercial satellite deployment requirements, has reinforced long-term program continuity and infrastructure investment across the domestic launch ecosystem.
Based on a recent historical assessment, Bengaluru dominates the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market due to its role as the core center for launch vehicle design, propulsion development, and systems integration. Sriharikota remains critical because of its established launch complexes, mission control facilities, and recovery coordination capabilities. India maintains dominance due to centralized policy execution, integrated public sector manufacturing, and coordinated collaboration between government agencies and private launch startups, enabling faster technology validation, infrastructure utilization, and end-to-end mission readiness.
Market Segmentation
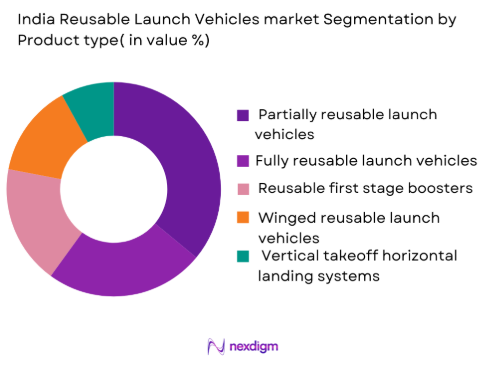
By Product Type
India Reusable Launch Vehicles market is segmented by product type into partially reusable launch vehicles, fully reusable launch vehicles, reusable first stage boosters, winged reusable launch vehicles, and vertical takeoff horizontal landing systems. Recently, partially reusable launch vehicles have a dominant market share due to lower engineering risk, faster qualification timelines, and compatibility with existing launch infrastructure. These systems enable recovery of high-value boosters while retaining proven upper-stage architectures, reducing refurbishment complexity. Government preference for incremental reusability, supported by completed flight demonstrations and validated recovery techniques, has accelerated adoption. Additionally, partially reusable systems align with near-term mission reliability requirements and budget discipline, reinforcing procurement continuity and sustained operational deployment across national launch programs.
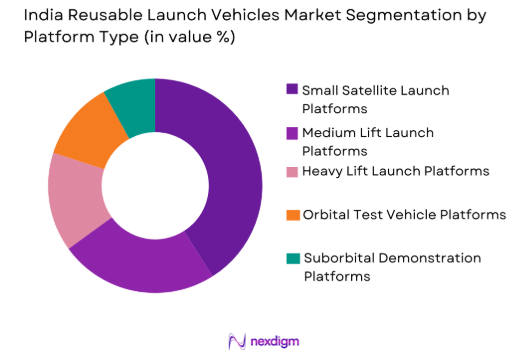
By Platform Type
India Reusable Launch Vehicles market is segmented by platform type into small satellite launch platforms, medium lift launch platforms, heavy lift launch platforms, orbital test vehicle platforms, and suborbital demonstration platforms. Recently, small satellite launch platforms have a dominant market share due to rising demand for Earth observation, communication, and experimental payload missions. These platforms benefit from shorter launch preparation cycles, lower payload integration complexity, and higher launch cadence requirements. Reusability significantly enhances cost efficiency for small satellite missions, making these platforms attractive for both government and commercial operators. Infrastructure compatibility and growing private participation further reinforce their dominance within the domestic launch ecosystem.
Competitive Landscape
The India Reusable Launch Vehicles market is characterized by a controlled level of consolidation, with government-led organizations retaining primary influence over system development, testing, and deployment while private aerospace startups expand competitive depth. Public sector entities continue to anchor long-term programs through assured funding, infrastructure ownership, and mission assurance mandates. At the same time, emerging private players are strengthening competition by focusing on small satellite missions, rapid development cycles, and selective reusability technologies. Competitive positioning is largely determined by propulsion capability, reusability maturity, integration with national launch infrastructure, and alignment with government procurement frameworks.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Reusability Capability |
| Indian Space Research Organisation | 1969 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hindustan Aeronautics Limited | 1940 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Skyroot Aerospace | 2018 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Agnikul Cosmos | 2017 | Chennai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen and Toubro Aerospace | 2008 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Reusable Launch Vehicles Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
National mandate for cost-efficient space transportation:
National mandate for cost-efficient space transportation is a primary growth driver for the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market as national space policy prioritizes lowering per-launch expenditure while preserving mission reliability and strategic autonomy. Government-backed programs emphasize reusability to recover high-value components such as boosters, avionics, and propulsion systems, which significantly reduces lifecycle costs compared to expendable launch architectures. Sustained public funding enables long-duration research, testing, and validation cycles necessary for reusable system maturation without exposing programs to commercial volatility. Reusable launch vehicles align with the objective of increasing launch frequency to support Earth observation, communication, and scientific missions. Infrastructure investments in landing systems, tracking networks, and refurbishment facilities further reinforce adoption momentum. Cost efficiency enables domestic launch solutions to remain competitive against international providers. This driver also supports long-term procurement stability, encouraging private supply chain participation. Reduced marginal launch costs enhance affordability for downstream satellite operators. Collectively, these factors structurally reinforce demand for reusable launch vehicle development and deployment.
Expansion of private sector participation in launch ecosystems
Expansion of private sector participation in launch ecosystems drives the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market by accelerating innovation, reducing development timelines, and diversifying technology approaches. Private launch startups introduce agile engineering practices, rapid prototyping, and iterative testing methodologies that complement government-led development models. Public–private collaboration frameworks grant access to testing facilities, regulatory clearances, and mission infrastructure, lowering entry barriers. Venture capital funding enables parallel propulsion, guidance, and materials research streams that improve system resilience. Commercial launch demand incentivizes higher cadence operations, making reusability economically attractive. Increased competition encourages efficiency in manufacturing and supply chains. Workforce mobility between public and private entities enhances technical depth. Private participation expands mission flexibility beyond government payloads. This ecosystem diversification significantly strengthens long-term market growth.
Market Challenges
High technological complexity and system validation requirements
High technological complexity and system validation requirements present a critical challenge for the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market due to the need for repeated safe operations under extreme thermal, mechanical, and aerodynamic stress. Reusable systems must maintain structural integrity and propulsion performance across multiple missions, increasing engineering difficulty. Extensive ground testing, flight trials, and post-flight inspections extend development timelines and raise costs. Certification frameworks demand exhaustive subsystem-level data validation before operational acceptance. Any in-flight anomaly risks delaying programs and eroding institutional confidence. Thermal protection systems, autonomous recovery software, and reusable propulsion cycles require continuous refinement. Limited historical flight data increases uncertainty during scaling phases. Engineering talent scarcity further constrains rapid progress. These cumulative factors slow commercialization and operational deployment.
Infrastructure limitations for recovery and refurbishment operations
Infrastructure limitations for recovery and refurbishment operations challenge the scalability of reusable launch vehicles within India’s existing spaceport framework. Legacy launch infrastructure was designed primarily for expendable vehicles, requiring substantial upgrades for reusable missions. Recovery operations demand dedicated landing zones, tracking systems, and maritime or terrestrial logistics support. Refurbishment facilities require advanced diagnostics, skilled technicians, and specialized tooling. Capital expenditure requirements create bottlenecks for rapid capacity expansion. Regulatory approvals further extend infrastructure development timelines. Limited refurbishment throughput restricts achievable launch cadence. Geographic constraints complicate recovery planning. These infrastructure gaps delay full economic realization of reusability benefits.
Opportunities
Commercial small satellite constellation deployment demand
Commercial small satellite constellation deployment demand creates a major opportunity for the India Reusable Launch Vehicles market by driving frequent, cost-sensitive launch requirements. Satellite constellations for Earth observation, navigation, and communication rely on rapid deployment and replenishment strategies. Reusable launch vehicles significantly lower per-mission costs, improving constellation economics. Domestic launch availability reduces dependence on foreign providers and scheduling constraints. Reusability enables higher launch cadence with faster turnaround times. Government and private operators increasingly prioritize responsive launch capabilities. Demand growth stimulates private investment in scalable launch platforms. Integration with small satellite manufacturing ecosystems enhances value capture. This opportunity supports sustained market expansion.
Defense-driven responsive space launch requirements
Defense-driven responsive space launch requirements present a strategic opportunity for reusable launch vehicles by enabling rapid deployment and replacement of critical assets. Military planners prioritize short notice launch readiness to address emerging threats. Reusable systems reduce turnaround time between missions compared to expendable vehicles. Secure domestic launch capability strengthens national resilience and deterrence posture. Defense funding provides long-term demand stability. Technology developed for defense missions often transfers to civilian applications. Integrated launch readiness improves operational flexibility. Reusability supports cost-effective sustainment of space-based defense infrastructure. This opportunity anchors long-term procurement pipelines.
Future Outlook
The India Reusable Launch Vehicles market is expected to witness sustained and structurally strong growth over the next five years, driven by continued government commitment to lowering launch costs and enhancing sovereign access to space. Advancements in reusable propulsion systems, autonomous guidance and landing technologies, and high-temperature thermal protection materials are likely to improve operational reliability and turnaround efficiency. Regulatory support for private launch service providers, including simplified licensing and shared infrastructure access, is expected to deepen private sector participation. Demand-side momentum will be reinforced by expanding small satellite constellations, increased defense requirements for responsive launch capability, and greater integration of reusable systems into routine national space missions.
Major Players
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Larsen and Toubro Aerospace
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Godrej Aerospace
- Ananth Technologies
- MTAR Technologies
- Walchandnagar Industries
- Alpha Design Technologies
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Dhruva Space
- Paras Defence and Space Technologies
- Apex Space
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Defense organizations
- Commercial satellite operators
- Launch service providers
- Aerospace manufacturers
- Space infrastructure developers
- Technology integrators
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables including launch vehicle types, reusability levels, and end-user demand were identified. Technical and regulatory parameters were mapped. Economic indicators were defined. Data relevance was validated.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Supply and demand data were integrated to construct market structure. Historical benchmarks supported validation. Assumptions were documented. Data triangulation ensured consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts reviewed assumptions and findings. Feedback refined segmentation logic. Technical accuracy was validated. Insights improved robustness.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Validated data was synthesized into structured analysis. Findings were cross-checked. Narrative coherence was ensured. Final outputs aligned with scope.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Increasing national focus on cost efficient space access
Rising demand for frequent small satellite launches
Government support for indigenous launch technologies
Expansion of private participation in the space sector
Need for rapid launch and responsive space capabilities - Market Challenges
High development and testing costs for reusable systems
Technological complexity in reusability and recovery
Limited operational flight heritage
Stringent safety and reliability requirements
Infrastructure constraints for recovery and refurbishment - Market Opportunities
Commercialization of reusable launch services
Export of reusable launch technologies and subsystems
Integration with future space transportation architectures - Trends
Shift toward fully reusable launch architectures
Increased use of autonomous landing and recovery systems
Growing reliance on advanced composites and additive manufacturing
Collaboration between government and private launch startups
Emphasis on rapid turnaround and launch cadence
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Partially Reusable Launch Vehicles
Fully Reusable Launch Vehicles
Reusable First Stage Boosters
Winged Reusable Launch Vehicles
Vertical Takeoff Horizontal Landing Systems - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Small Satellite Launch Platforms
Medium Lift Launch Platforms
Heavy Lift Launch Platforms
Orbital Test Vehicle Platforms
Suborbital Demonstration Platforms - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
New Build Launch Vehicle Programs
Retrofit and Upgrade Programs
Technology Demonstrator Vehicles
Experimental Flight Test Vehicles
Operational Reusable Fleets - By End User Segment (In Value%)
Government Space Agencies
Defense and Strategic Programs
Commercial Satellite Operators
Private Launch Service Providers
Research and Academic Institutions - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct Government Contracts
Public Private Partnership Programs
In House Development Programs
Technology Transfer Agreements
International Collaboration Contracts - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Advanced Composite Structures
High Temperature Thermal Protection Systems
Reusable Cryogenic Propulsion Systems
Autonomous Guidance and Control Software
Additive Manufactured Structural Components
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Reusability Level, Payload Capacity, Launch Frequency, Recovery Method, Cost Efficiency, Technology Maturity, Government Backing, Commercial Orientation, Integration Capability, Manufacturing Approach)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porte’s Five Forces
- Key Players
Indian Space Research Organisation
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Ananth Technologies
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Larsen and Toubro Aerospace
Tata Advanced Systems
Godrej Aerospace
Alpha Design Technologies
MTAR Technologies
Walchandnagar Industries
Paras Defence and Space Technologies
Bellatrix Aerospace
Dhruva Space
Apex Space
- Government agencies prioritizing strategic autonomy in launch capabilities
- Commercial operators seeking reduced launch costs and faster schedules
- Defense users focusing on rapid deployment and replacement missions
- Research institutions leveraging reusable platforms for experimental missions
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035