Market Overview
The satellite attitude and orbit control system market is expected to experience significant growth, with a market size based on recent historical assessments reaching USD ~ billion. This market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for advanced satellite systems that provide efficient control over satellite orientation, as well as the rising number of satellites launches across various sectors. Technological advancements in propulsion systems, integration with new satellite constellations, and increasing commercial and government investments in space exploration contribute to this market’s expansion. Factors such as the continuous advancement of miniaturization technologies, high-performance demands from geostationary and low-earth orbit satellites, and government space programs will further drive the demand for these control systems.
Key regions contributing to the dominance of the satellite attitude and orbit control system market include North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, with countries such as the United States, Russia, China, and India leading the way in satellite production and launch activities. The United States is the largest contributor due to its robust space programs and government-backed space initiatives. China and India are also making significant strides, with increasing investments in satellite infrastructure and space missions. These countries are further bolstered by their commitment to space exploration, technological innovation, and long-term government strategies to become global leaders in space technologies.
Market Segmentation
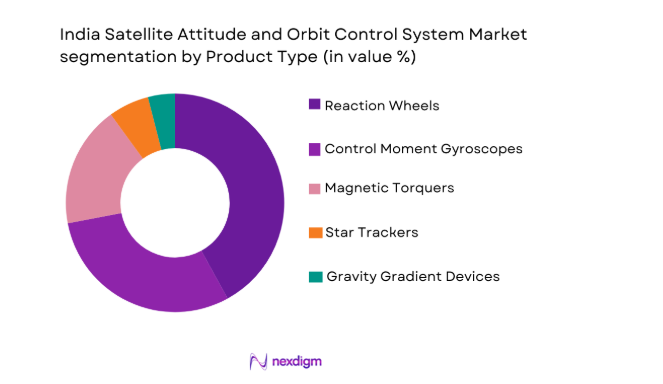
By Product Type
The satellite attitude and orbit control system market is segmented by product type into various sub-segments such as reaction wheels, control moment gyroscopes, and magnetic torquers. Currently, the reaction wheels segment dominates the market due to their widespread use in satellite control systems, offering a compact and precise method for controlling satellite orientation. Reaction wheels are favored for their high efficiency, precision, and reliability in maintaining satellite position and stability. As a result, reaction wheels are a critical component in geostationary satellites, low-earth orbit satellites, and scientific spacecraft, where precision and stability are paramount for communication, navigation, and observational tasks. The adoption of reaction wheels is anticipated to continue growing, driven by advancements in manufacturing techniques, cost reductions, and the increasing demand for reliable and efficient satellite systems.
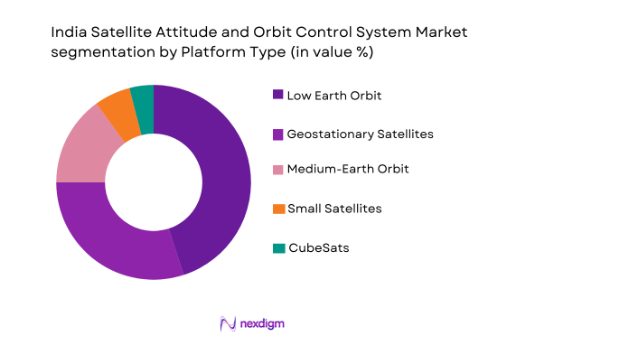
By Platform Type
The satellite attitude and orbit control system market is also segmented by platform type into geostationary satellites, low-earth orbit satellites, medium-earth orbit satellites, small satellites, and CubeSats. The low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite segment is leading the market due to the rapid expansion of satellite constellations for communication, earth observation, and internet access. LEO satellites are smaller, cost-effective, and have shorter orbital lifespans, making them ideal for deployment in large constellations. The increasing need for global internet coverage, broadband connectivity in remote areas, and advancements in satellite miniaturization technologies contribute to the dominance of the LEO segment. As countries and private companies aim to expand their satellite networks for various applications, the demand for attitude and orbit control systems for LEO satellites is expected to remain strong.
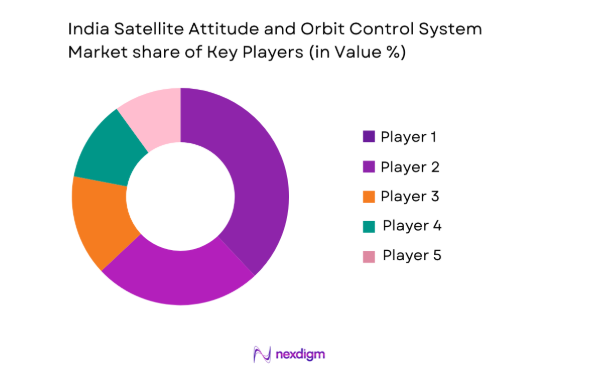
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the satellite attitude and orbit control system market is marked by both consolidation and intense competition among established players. Major global companies and emerging players continue to innovate, with a focus on enhancing system reliability, reducing size, and increasing functionality for next-generation satellite systems. Partnerships between government agencies, space organizations, and private sector entities are a key trend in market expansion, particularly in satellite manufacturing, launch services, and technology development. Players like Lockheed Martin, Airbus, and Thales Alenia Space maintain a dominant position, but emerging space startups are also gaining traction by focusing on cost-effective and small satellite systems. Innovation in propulsion systems and miniaturization technology remains a key competitive factor as players seek to meet the growing demand for more efficient satellite control systems.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue (USD) |
| Lockheed Martin | 1912 | Bethesda, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus | 1970 | Toulouse, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales Alenia Space | 2005 | Cannes, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Northrop Grumman | 1939 | Falls Church, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Boeing | 1916 | Chicago, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Government Investments in Space Programs
Government investments in space programs have significantly fueled the growth of the satellite attitude and orbit control system market. Many countries, including the United States, China, and India, have committed to expanding their space programs, which has resulted in increased demand for advanced satellite systems. These governments support their space programs through funding, grants, and strategic partnerships, creating a favorable environment for technological innovation and satellite infrastructure growth. Government-driven space initiatives, including satellite constellations for communications, earth observation, and military use, directly contribute to the demand for attitude and orbit control systems. These systems are essential for ensuring that satellites operate efficiently and maintain accurate positioning and orientation. Space programs require these technologies to meet the complex needs of modern satellite operations, which span communications, navigation, weather monitoring, defense, and scientific research. With the global focus on enhancing communication networks and exploring new frontiers in space, government investments are expected to continue boosting demand for satellite attitude and orbit control systems. These investments are not only helping established space agencies like NASA and ISRO expand their satellite programs, but they are also enabling private companies to participate in satellite technology development. By fostering innovation and encouraging the development of cost-effective systems, governments are playing a pivotal role in ensuring that the satellite industry remains competitive and scalable in the coming years. As satellite constellations become more prevalent and complex, the demand for reliable attitude and orbit control systems will continue to rise, driven by these government-backed initiatives and space-related projects. These investments will help accelerate the development of next-generation satellite systems and their control mechanisms, further advancing space exploration and satellite communications.
Technological Advancements in Satellite Systems
Technological advancements in satellite systems, including miniaturization, propulsion, and attitude control technologies, have been key drivers of market growth. With the rise of small satellites and CubeSats, there is a growing need for compact and efficient attitude and orbit control systems that can meet the performance requirements of modern space missions. These small satellites offer a more cost-effective solution for a variety of applications such as remote sensing, telecommunications, and environmental monitoring. They are being deployed in large numbers as part of satellite constellations, necessitating sophisticated control systems that ensure their accurate positioning, synchronization, and stability. Innovations in propulsion systems, such as electric propulsion, enable satellites to perform maneuvers with greater efficiency and longer operational lifespans, reducing the need for traditional fuel-based propulsion. These advances in propulsion technology directly influence the demand for advanced attitude and orbit control systems, as they require more efficient mechanisms for maintaining satellite orientation and orbit. Furthermore, the demand for enhanced performance in satellite applications, such as global communications, navigation, and scientific data collection, pushes for continued improvement in control system technologies. These advancements have made it possible for satellite manufacturers to offer smaller, more reliable, and affordable solutions for space operations, further expanding the market for attitude and orbit control systems. As space exploration and satellite applications continue to grow, the need for systems that provide greater accuracy, efficiency, and longevity will drive the continued evolution of satellite control technologies. Thus, technological innovation is expected to remain a major growth driver in this market, especially with the rise of satellite constellations and increasing demands for complex and sophisticated satellite operations in various industries.
Market Challenges
High Development and Operational Costs
One of the significant challenges faced by the satellite attitude and orbit control system market is the high development and operational costs. Developing and manufacturing advanced satellite control systems requires substantial investments in research, engineering, and testing to ensure these systems meet the high standards required for space missions. These systems often involve complex technologies, such as reaction wheels, control moment gyroscopes, and other specialized components that are costly to produce. Additionally, the testing and certification processes needed to ensure reliability in harsh space environments add another layer of expense. Operational costs are also a barrier, particularly for smaller players in the market or emerging space agencies in developing countries. While commercial satellite manufacturers and governments may have the necessary budgets to absorb these costs, smaller private companies may face significant financial challenges when trying to incorporate high-performance control systems into their satellite projects. The cost of launching satellites into orbit, the need for extensive ground support infrastructure, and the ongoing operational expenses for maintaining and controlling satellites in space further increase the financial burden on satellite operators. For the market to continue expanding, these cost barriers must be addressed. Advances in manufacturing technologies, economies of scale, and the development of more affordable control systems could help alleviate some of these financial challenges, but high upfront costs remain a significant obstacle for many players in the market. Despite technological advancements and the growing adoption of smaller satellites, these high costs present a major hindrance to widespread market participation, especially for emerging players and organizations with limited resources.
Technological Limitations of Existing Systems
While current satellite attitude and orbit control systems have achieved significant advancements, they still face technological limitations that present challenges for market growth. One of the key limitations is the size and power consumption of existing systems, particularly in the context of smaller satellite platforms such as CubeSats and small satellites. These satellites have limited space and power budgets, making it difficult to integrate traditional attitude control systems that are typically larger and more power-hungry. Reaction wheels, control moment gyroscopes, and other conventional systems may not be suitable for smaller satellites that require lightweight, energy-efficient solutions. Additionally, existing systems often struggle to meet the increasing demands of satellite constellations, where precise control is required to ensure synchronization and long-term operational success. For instance, ensuring that multiple satellites in a constellation remain aligned and operate in harmony can be a complex task for traditional control systems. The limitations in size, power, and efficiency hinder the full potential of small satellite constellations, especially as the industry moves towards even more compact and lightweight satellite designs. As satellite missions become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for more advanced, scalable, and adaptable attitude control technologies that can meet the unique needs of various satellite types and missions. Continued innovation and research into more efficient systems are necessary to overcome these technological constraints and enable the broader adoption of advanced attitude and orbit control systems across all satellite platforms. As the demand for more cost-effective and energy-efficient systems grows, there is a need for new solutions that can perform high-precision maneuvers while minimizing the size and weight of control components.
Opportunities
Growth in Small Satellite Constellations
The growth of small satellite constellations presents a significant opportunity for the satellite attitude and orbit control system market. Small satellite constellations, typically composed of low-cost, compact satellites that work together to provide global coverage for communication, earth observation, and other services, are rapidly gaining popularity. As the demand for low-cost satellite launches and services increases, these constellations are becoming a cost-effective solution for various commercial and government applications. The rise of companies like SpaceX and OneWeb, which are planning to deploy large satellite constellations, is fueling this trend. These satellites rely on efficient and reliable attitude and orbit control systems to ensure their proper alignment, synchronization, and long-term stability. As small satellite constellations become a dominant method of satellite deployment, the demand for advanced control systems will rise. The need for efficient satellite positioning, maneuvering, and inter-satellite communication within these constellations makes it essential to deploy cutting-edge attitude and orbit control technologies. Furthermore, the lower launch costs and shorter development cycles associated with small satellites open up new opportunities for smaller players and emerging space companies, further expanding the market for control systems. As the space industry continues to innovate and prioritize the development of satellite constellations, the demand for reliable and scalable attitude and orbit control systems will grow, creating significant opportunities for market players. Moreover, this trend is accelerating the development of cost-effective solutions for satellite operators who want to capitalize on the growing demand for satellite services, ranging from internet connectivity to climate monitoring. As satellite constellations become more complex, the need for sophisticated control systems that ensure operational continuity will increase, representing a significant opportunity for the market to thrive.
Technological Innovations in Propulsion and Power Systems
Another significant opportunity in the satellite attitude and orbit control system market lies in technological innovations in propulsion and power systems. The development of electric propulsion systems, such as ion thrusters and Hall-effect thrusters, offers an efficient and sustainable alternative to traditional chemical propulsion systems. These systems provide significant advantages in terms of fuel efficiency, longer operational lifespans, and the ability to perform complex orbital maneuvers with lower energy consumption. As electric propulsion technologies evolve, the demand for advanced attitude and orbit control systems that can work seamlessly with these new propulsion systems will increase. These innovations also open up new opportunities for satellite missions that require precise and long-duration maneuvers, such as deep space exploration, satellite servicing, and asteroid mining. Moreover, the integration of advanced power management systems, including solar power and energy storage solutions, will contribute to the development of more self-sufficient and efficient satellite systems. As sustainability becomes a key focus in space exploration, these innovations in propulsion and power systems will drive the demand for more advanced, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly attitude and orbit control systems. The continued evolution of propulsion technologies will create new market opportunities for companies specializing in attitude and orbit control solutions, positioning them to capitalize on the growing demand for high-performance satellite systems. As these technologies mature, the adoption of electric propulsion is expected to become widespread, driving innovation in the control systems that complement them, ensuring that satellites can operate at maximum efficiency for extended periods.
Future Outlook
The satellite attitude and orbit control system market is poised for steady growth over the next five years, driven by increasing space exploration activities, advancements in satellite technologies, and growing demand for satellite constellations. With technological developments in propulsion systems, miniaturization, and system integration, the market is expected to see innovations in control system efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Regulatory support for satellite launches and space exploration will further bolster market expansion, particularly with the rise of private space ventures and governmental space programs. As more industries depend on satellite technologies for communication, earth observation, and navigation, the need for sophisticated attitude and orbit control systems will continue to grow.
Major Players
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus
- Thales Alenia Space
- Northrop Grumman
- Boeing
- Arianespace
- SpaceX
- MDA Corporation
- SSL (Space Systems Loral)
- Orbital Sciences Corporation
- Rocket Lab
- OneWeb
- Planet Labs
- SES S.A.
- Blue Origin
Key Target Audience
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
- Satellite operators
- Aerospace manufacturers
- Space agencies
- Research organizations
- Commercial satellite service providers
- Telecommunications companies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
This step involves identifying the critical factors that influence the India Satellite Bus market, such as technological advancements, market trends, regulatory frameworks, and economic conditions. These variables include government policies, technological innovations, and industry demand, which are essential in shaping the market landscape. By defining these variables, the research aims to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the market’s drivers and constraints. The identification of these key variables helps establish a strong foundation for subsequent analysis and forecasting.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
In this step, extensive data is collected through primary and secondary research sources, including industry reports, government publications, and expert interviews. This data is then analyzed to build a comprehensive market model, covering market size, growth trends, competitive landscape, and key drivers. By analyzing the market from different angles, this step ensures a complete understanding of current dynamics and future market potential. Data is also segmented by product type, platform, procurement channels, and other key factors to provide detailed insights.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
In this phase, initial hypotheses and market forecasts are validated through consultations with industry experts, including manufacturers, satellite operators, and policymakers. These consultations help ensure the accuracy and relevance of the research findings by incorporating insights from experienced professionals in the field. Expert validation also provides clarity on market assumptions and helps refine the methodology to reflect real-world industry conditions. The process ensures that the conclusions drawn are credible and aligned with actual industry trends.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final step involves synthesizing the collected data, insights, and expert feedback to produce a detailed and actionable market report. This synthesis includes compiling growth forecasts, market segmentation, competitive analysis, and trends that will guide stakeholders in making informed decisions. The output is rigorously reviewed for accuracy, and all assumptions are clearly documented. This step ensures that the final research output is comprehensive, reliable, and ready for presentation to key stakeholders in the industry.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Commercial Space Operations
Government Space Program Investments
Technological Advancements in Miniaturization
Demand for Improved Satellite Longevity - Market Challenges
High Development and Operational Costs
Limited Availability of Skilled Workforce
Strict Regulatory & Environmental Compliance
Dependence on Government Funding
Complexity of Spacecraft Integration - Market Opportunities
Growing Private Sector Participation
Adoption of CubeSat Technology
International Collaborations for R&D - Trends
Increased Use of Autonomous Satellite Systems
Focus on Sustainable Space Operations
Integration of AI for Satellite Management
Growth in Small Satellite Networks
Emergence of Low-Cost Propulsion Systems - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
National Space Policy Initiatives
Spacecraft Safety Standards
Launch Licensing and Compliance - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Reaction Wheels
Control Moment Gyroscopes
Magnetic Torquers
Star Trackers
Gravity Gradient Devices - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Low Earth Orbit
Geostationary Satellites
Medium Earth Orbit
Small Satellites
CubeSats - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Spacecraft Integration
Launch Vehicle Integration
Modular System Fitment
Standalone Attitude Systems
Hybrid System Fitment - By EndUser Segment (In Value%)
Commercial Sector
Government Space Agencies
Military & Defense
Private Satellite Operators
Research Institutions - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Direct Procurement
OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers)
System Integrators
Third-Party Distributors
Government Bidding - By Material / Technology (in Value%)
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Electronic Propulsion Systems
High-Precision Gyroscopes
Adaptive Optics
Microgravity Materials
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product Portfolio, Technological Expertise, Market Penetration, Regional Presence, Pricing Strategy)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Key Players
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
ArianeGroup
Lockheed Martin
Thales Alenia Space
Boeing
Airbus Defence and Space
Mitsubishi Electric
Northrop Grumman
Ball Aerospace
Sitael
Maxar Technologies
COM DEV
Honeywell
L3 Technologies
SpaceX
- Commercial Operators Seeking Cost Efficiency
- Space Agencies Focusing on Strategic Satellites
- Private Satellite Companies Expanding Data Networks
- Defense Organizations Enhancing Satellite Capabilities
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035


