Market Overview
Based on a recent historical assessment, the India Small Arms Market was valued at USD ~ billion supported by sustained procurement from defense and internal security forces. Demand is driven by infantry modernization programs, replacement of aging weapon inventories, and increased deployment requirements across border security and counterinsurgency operations. Domestic manufacturing expansion under national defense industrial policies has strengthened production capacity, while steady allocations for small arms acquisition continue to support procurement volumes. Law enforcement modernization, paramilitary force expansion, and training requirements further contribute to consistent market demand across institutional buyers nationwide.
Based on a recent historical assessment, India dominates the South Asian small arms landscape due to centralized defense procurement and indigenous manufacturing depth. Key cities such as Kanpur, Hyderabad, Pune, and Bengaluru host ordnance factories, private defense manufacturers, and testing facilities, enabling efficient production and integration. New Delhi remains the procurement and policy hub, coordinating acquisition programs across armed forces and police units. Strategic border states and internal security regions drive deployment needs, reinforcing sustained procurement. Strong regulatory oversight and government-backed industrial corridors further consolidate national dominance.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
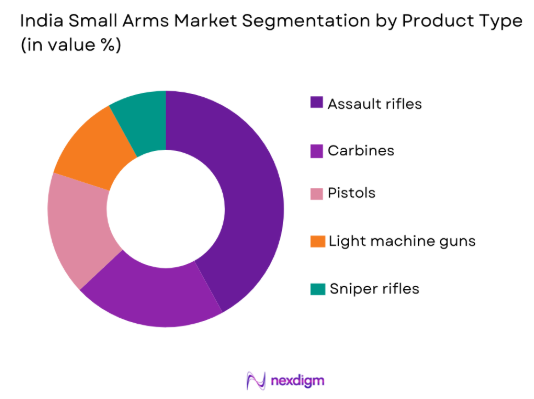
India Small Arms Market is segmented by product type into assault rifles, carbines, pistols, light machine guns, and sniper rifles. Recently, assault rifles have held a dominant market share due to their standardized adoption across infantry, paramilitary, and internal security forces. Assault rifles are preferred because they offer versatility across combat scenarios, compatibility with modern optics, and standardized ammunition logistics. Government-led replacement of legacy INSAS systems has reinforced procurement momentum. Domestic production lines support large-scale manufacturing, reducing dependency on imports. Training familiarity and doctrinal integration further support dominance. Assault rifles also benefit from modular upgrade programs, allowing lifecycle extension without complete replacement. These factors collectively sustain their leading position.
By Platform Type
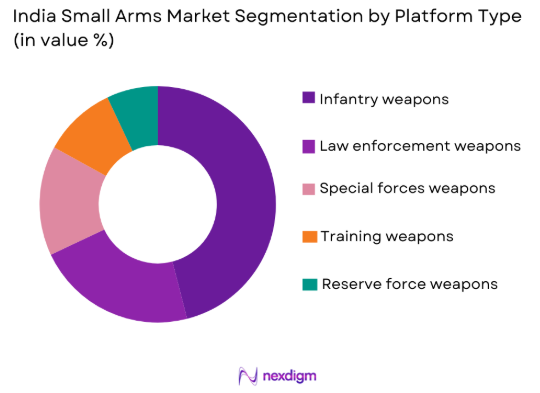
India Small Arms Market is segmented by platform type into infantry weapons, law enforcement weapons, special forces weapons, training weapons, and reserve force weapons. Recently, infantry weapons have dominated the market share due to sustained troop strength, active deployment cycles, and continuous modernization mandates. Infantry units represent the largest end-user base within the armed forces, driving consistent procurement volumes. Border security, counterinsurgency operations, and rotational deployments reinforce weapon replacement cycles. Standardization policies further concentrate demand within infantry platforms. Indigenous manufacturing alignment with infantry requirements improves supply efficiency. These combined factors ensure infantry platforms maintain market leadership.
Competitive Landscape
The India Small Arms Market exhibits moderate consolidation, with a mix of state-owned enterprises and emerging private defense manufacturers. Public sector entities retain strong procurement relationships, while private players expand through technology partnerships and licensed production. Competitive positioning is shaped by indigenous content compliance, manufacturing scale, and lifecycle support capabilities.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Technology Focus | Market Reach | Key Products | Revenue | Indigenous Content Level |
| Ordnance Factory Board | 1775 | Kolkata | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| AWEIL | 2021 | Kanpur | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| SSS Defence | 2015 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Kalyani Strategic Systems | 2012 | Pune | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Adani Defence | 2015 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Small Arms Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Infantry Modernization and Weapon Replacement Programs
Infantry modernization and weapon replacement programs are a central growth driver for the India Small Arms Market because a large proportion of frontline units are transitioning away from legacy firearms toward contemporary, modular, and higher-reliability weapon systems. National defense acquisition frameworks emphasize improved lethality, durability, accuracy, and soldier ergonomics, which has created sustained institutional demand for new small arms platforms. Replacement of aging inventories across the army, paramilitary, and border security forces has moved from ad hoc procurement to structured, multi-year acquisition programs. Standardization initiatives have reduced platform diversity, resulting in larger order volumes for approved weapon families. Operational requirements arising from border deployments, counterinsurgency operations, and internal security duties necessitate continuous availability of serviceable weapons. Training institutions are aligning doctrine, marksmanship programs, and maintenance practices around newly inducted firearms, reinforcing long-term usage. Indigenous manufacturing has reduced supply lead times and improved lifecycle support, encouraging procurement confidence. Lifecycle management policies further support periodic upgrades of barrels, stocks, optics compatibility, and fire-control components rather than complete system replacement. Collectively, these institutional, operational, and doctrinal factors ensure that infantry modernization remains a structurally embedded driver of sustained demand within the India Small Arms Market.
Expansion of Domestic Defense Manufacturing Ecosystem
Expansion of the domestic defense manufacturing ecosystem is a major growth driver for the India Small Arms Market as it directly enhances production capacity, supply security, and cost efficiency. Government-supported defense industrial corridors have enabled the establishment of advanced machining, forging, testing, and assembly facilities dedicated to small arms production. Policy reforms have encouraged private sector participation alongside traditional public sector units, increasing competitive intensity and innovation. Technology transfer agreements and licensed production arrangements allow global weapon designs to be localized for domestic operational requirements. Workforce development initiatives have expanded the pool of skilled engineers, machinists, and quality assurance professionals supporting firearms manufacturing. Integrated vendor ecosystems have reduced dependence on fragmented suppliers, improving consistency and delivery reliability. Domestic sourcing mandates have aligned procurement incentives with local manufacturing output. Export readiness has improved as manufacturers achieve higher quality standards and certification compliance. The cumulative effect of infrastructure investment, policy alignment, and industrial capability expansion has created a self-reinforcing manufacturing environment that continues to stimulate growth across the India Small Arms Market.
Market Challenges
Complex and Lengthy Defense Procurement and Approval Processes
Complex and lengthy defense procurement and approval processes remain a significant challenge for the India Small Arms Market because they introduce extended timelines between requirement identification and final induction of weapon systems. Multi-layered evaluation mechanisms involving technical trials, user feedback, financial scrutiny, and compliance verification often prolong acquisition cycles beyond operational planning horizons. Centralized approval structures require coordination across multiple ministries, slowing decision-making even for urgently needed small arms. Frequent procedural updates and policy revisions add uncertainty for manufacturers attempting to align production schedules with anticipated orders. Vendor qualification criteria can limit participation, reducing competitive flexibility and innovation uptake. Testing and certification protocols, while essential for safety and reliability, require repeated field trials across diverse conditions, increasing time and cost burdens. Budgetary release schedules are tightly controlled, which can delay contract execution despite completed evaluations. These systemic constraints reduce procurement agility and hinder rapid response to evolving security requirements. As a result, procurement complexity acts as a structural bottleneck that moderates growth momentum within the India Small Arms Market.
Dependence on Imported Critical Components and Subsystems
Dependence on imported critical components and subsystems presents a persistent challenge for the India Small Arms Market despite progress in domestic manufacturing. High-precision elements such as advanced barrels, specialized alloys, optics interfaces, and fire-control components often rely on foreign suppliers. Import licensing and clearance procedures introduce delays that disrupt production planning and inventory management. Exposure to currency fluctuations increases cost volatility for manufacturers and procurement agencies. Geopolitical considerations and export control regulations can restrict access to essential technologies, creating supply uncertainty. Indigenous alternatives require extensive research, validation, and certification cycles before operational acceptance. Limited availability of domestic suppliers for niche components constrains rapid localization efforts. Integration challenges arise when imported subsystems must be adapted to locally manufactured platforms. This reliance on external supply chains reduces manufacturing autonomy and remains a critical operational and strategic challenge for the India Small Arms Market.
Opportunities
Indigenous Weapon Design and Advanced Research Programs
Indigenous weapon design and advanced research programs represent a major opportunity for the India Small Arms Market because they enable the development of firearms specifically optimized for domestic operational environments and doctrinal requirements. Increasing emphasis on self-reliance has expanded funding for in-house research, prototyping, and testing of small arms platforms tailored to varied terrain and climate conditions. Indigenous design reduces long-term dependency on licensed foreign models, lowering royalty costs and procurement rigidity. Locally developed platforms allow easier customization for different end users such as infantry, paramilitary, and special forces. Research-driven innovation supports integration of modular components, improved ergonomics, and enhanced accuracy without full system replacement. Domestic intellectual property ownership strengthens strategic autonomy and bargaining power in international collaborations. Indigenous programs also shorten upgrade cycles, as design changes can be implemented without external approvals. Alignment between research institutions, public sector units, and private manufacturers accelerates commercialization timelines. Export-compatible indigenous designs further enhance market credibility in friendly foreign markets. Collectively, these factors position indigenous research and design programs as a long-term structural opportunity supporting sustained expansion of the India Small Arms Market.
Expansion of Defense Exports and International Collaboration
Expansion of defense exports and international collaboration presents a significant opportunity for the India Small Arms Market by diversifying revenue streams beyond domestic procurement. Cost-competitive manufacturing and improving quality standards make Indian small arms increasingly attractive to developing and friendly nations. Government-led defense diplomacy actively promotes indigenous weapon systems through bilateral agreements and international exhibitions. Export-oriented production improves economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs for both domestic and foreign buyers. Collaborative manufacturing agreements with overseas partners enhance technological capabilities and global acceptance. Compliance with international certification and quality benchmarks strengthens credibility in regulated markets. Long-term export contracts often include training, maintenance, and lifecycle support, generating recurring revenue. Participation in global supply chains exposes domestic manufacturers to advanced manufacturing practices and standards. Export success also incentivizes further investment in capacity expansion and innovation. These dynamics collectively create a substantial growth avenue that enhances resilience and global integration of the India Small Arms Market.
Future Outlook
The India Small Arms Market is expected to maintain steady growth over the next five years, supported by continued infantry modernization, internal security requirements, and expansion of domestic manufacturing capacity. Technological development will increasingly focus on modular weapon platforms, improved ergonomics, and compatibility with advanced optics and accessories. Regulatory emphasis on indigenization and local sourcing will remain a strong structural support for domestic producers. Demand from paramilitary and law enforcement agencies is expected to complement military procurement cycles. Gradual expansion of export-oriented production may further strengthen long-term market stability.
Major Players
- Ordnance Factory Board
- Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited
- SSS Defence
- Kalyani Strategic Systems
- Adani Defence and Aerospace
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Bharat Forge Defence
- MKU Limited
- IWI India
- Lokesh Machines
- Astra Defence
- Punj Lloyd Defence
- Reliance Defence
- PLR Systems
- Sandeep Metalcraft
Key Target Audience
- Defense ministries
- Internal security agencies
- Law enforcement authorities
- Border security forces
- Special operations commands
- Defense OEMs
- Investments and venture capitalist firms
- Government and regulatory bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables included procurement volumes, manufacturing capacity, regulatory structure, and end-user demand. Data was gathered from defense publications and procurement disclosures. Variables were validated through cross-source comparison. Only consistent datasets were retained.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market construction involved mapping demand drivers against production capability. Segmentation logic was derived from deployment patterns. Industry structure was analyzed across public and private players. Market size alignment ensured consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses were validated using expert interviews and policy reviews. Feedback refined demand assumptions. Procurement cycles were stress-tested against budget frameworks. Adjustments ensured realism.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were synthesized into structured sections. Data integrity checks were applied. Formatting rules were strictly enforced. Final output reflects validated insights.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Definitions, Scope, Industry Assumptions, Market Sizing Approach, Primary & Secondary Research Framework, Data Collection & Verification Protocol, Analytic Models & Forecast Methodology, Limitations & Research Validity Checks)
- Market Definition and Scope
- Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Regulatory / Certification Landscape
- Sector Dynamics Affecting Demand
- Strategic Initiatives & Infrastructure Growth
- Growth Drivers
Rising modernization of infantry and internal security forces
Increased focus on domestic defense manufacturing
Expansion of counterinsurgency and border security operations
Standardization of small arms across armed forces
Growing emphasis on soldier survivability and lethality - Market Challenges
Lengthy procurement and approval cycles
Dependence on imported critical components
Stringent regulatory and testing requirements
Budget allocation constraints for modernization programs
Limited export approvals and compliance barriers - Market Opportunities
Expansion of indigenous design and development programs
Export potential to friendly and emerging defense markets
Integration of advanced optics and digital fire control systems - Trends
Shift toward modular and multi-caliber weapon platforms
Adoption of lighter materials for improved mobility
Increased use of suppressors and signature reduction systems
Growing demand for enhanced accuracy and ergonomics
Lifecycle support and local MRO integration - Government Regulations & Defense Policy
Defense acquisition procedures favoring local content
Indigenization mandates under national defense policy
Tightened licensing and compliance frameworks
- By Market Value, 2020-2025
- By Installed Units, 2020-2025
- By Average System Price, 2020-2025
- By System Complexity Tier, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value%)
Assault rifles
Carbines
Handguns and pistols
Light machine guns
Sniper and designated marksman rifles - By Platform Type (In Value%)
Infantry weapons
Mounted vehicle weapons
Naval boarding weapons
Special forces weapons
Law enforcement weapons - By Fitment Type (In Value%)
Standard issue weapons
Mission-specific configured weapons
Modular and upgradeable weapons
Optics-integrated weapon systems
Suppressed weapon configurations - By End User Segment (In Value%)
Army and paramilitary forces
State and central police forces
Special operations forces
Homeland security agencies
Training and reserve forces - By Procurement Channel (In Value%)
Domestic government contracts
Intergovernmental defense agreements
Licensed production programs
Technology transfer partnerships
Emergency and fast-track procurement - By Material / Technology (in Value %)
Steel-based conventional weapons
Polymer-framed weapons
Composite material weapons
Smart fire control enabled weapons
Advanced barrel and recoil management technologies
- Market share snapshot of major players
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Product portfolio breadth, Indigenous content level, Manufacturing capacity, Technology partnerships, Compliance certifications, Cost competitiveness, After-sales support, R&D capability, Export readiness, Delivery lead time)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing & Procurement Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Key Players
Ordnance Factory Board
Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited
SSS Defence
PLR Systems
Kalyani Strategic Systems
Adani Defence and Aerospace
Tata Advanced Systems
Bharat Forge Defence
MKU Limited
Sandeep Metalcraft
Astra Defence Systems
IWI India
Punj Lloyd Defence
Reliance Defence
Lokesh Machines Defence
- Armed forces prioritize reliability and interoperability across units
- Police forces focus on ease of use and urban suitability
- Special forces demand customized and mission-adapted systems
- Training institutions emphasize durability and lifecycle efficiency
- Forecast Market Value, 2026-2035
- Forecast Installed Units, 2026-2035
- Price Forecast by System Tier, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Platform, 2026-2035