Market Overview
The India Space Based Solar Power market current size stands at around USD ~ million with measurable activity during 2024 and 2025. Deployment planning, prototype validation, and mission design investments expanded steadily across these two years without commercial scale generation. Government backed programs and early private participation supported subsystem development, orbital studies, and transmission experimentation. Technology readiness levels improved through ground simulations and low orbit demonstrations. The market remained pre-commercial, with value concentrated in research, testing, and systems integration. Funding activity focused on long term capability building rather than short term power generation returns.
The market is primarily concentrated around national space and defense corridors with strong infrastructure and research ecosystems. Southern and western regions dominate due to launch facilities, aerospace manufacturing clusters, and policy alignment. Urban technology hubs contribute through software, simulation, and power electronics expertise. Government laboratories anchor ecosystem development through long term missions and regulatory coordination. Supply chains remain specialized, with limited commercial vendors and high dependence on strategic partnerships.
Market Segmentation
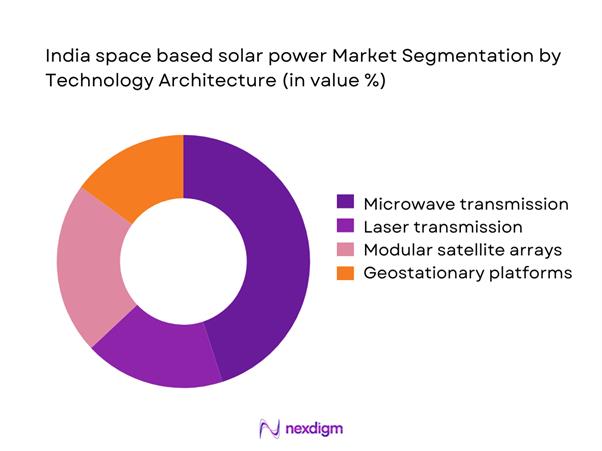
By Technology Architecture
The technology architecture segment is dominated by microwave-based power transmission systems due to higher efficiency stability and existing research maturity. Modular satellite arrays attract attention because of scalability and phased deployment benefits. Laser-based transmission remains in experimental stages, constrained by atmospheric attenuation and regulatory complexity. Geostationary systems dominate planning due to continuous solar exposure advantages. Research institutions prioritize architectures that align with current launch capabilities and orbital safety standards. Technology selection is heavily influenced by transmission reliability, conversion efficiency, and long-term maintenance feasibility. Development emphasis remains on architectures that can be validated through incremental demonstration missions.
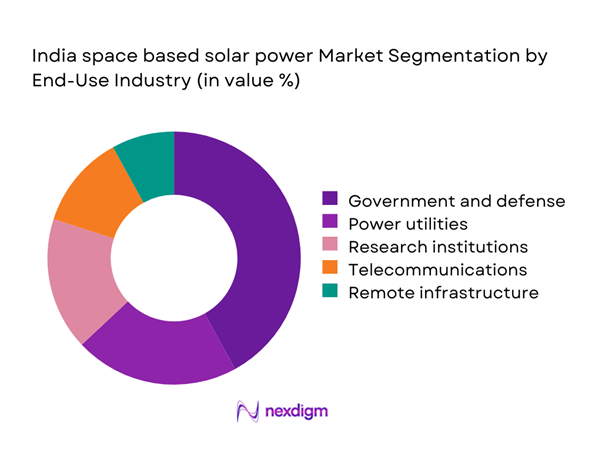
By End-Use Industry
The end-use industry segmentation is led by government and defense applications due to strategic energy security priorities. Civil power utilities participate mainly through feasibility collaborations rather than deployment ownership. Remote infrastructure operators show growing interest for disaster resilience and backup power capabilities. Research organizations account for a notable share through prototype testing and systems validation programs. Telecommunications and critical infrastructure segments contribute through feasibility studies and pilot integration projects. Overall demand concentration reflects national strategic objectives rather than commercial power market dynamics.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape remains highly concentrated with strong government influence and limited private participation. Market activity is driven by aerospace manufacturers, space agencies, and specialized subsystem developers. Entry barriers remain high due to technological complexity and regulatory requirements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ISRO | 1969 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NewSpace India Limited | 2019 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| L&T Aerospace | 2008 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2007 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ananth Technologies | 1992 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Space Based Solar Power Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising national energy security requirements
National energy security priorities continue to strengthen interest in space based solar power development programs. Dependence on terrestrial renewable sources faces intermittency and geographic constraints affecting long term reliability planning. Space based systems offer continuous energy availability independent of weather variability or seasonal fluctuations. Strategic policymakers increasingly view orbital solar platforms as sovereign infrastructure assets supporting national resilience. Energy diversification strategies during 2024 and 2025 highlighted vulnerability to supply disruptions. Defense planners emphasize uninterrupted power availability for critical installations and communication networks. Cross sector coordination has improved alignment between energy and space development agencies. Public sector funding mechanisms increasingly prioritize projects enhancing strategic energy autonomy. National roadmaps increasingly incorporate space based solar research objectives. These factors collectively accelerate policy and institutional backing for sustained program development.
Government focus on renewable and clean energy leadership
Government commitment to renewable leadership drives consistent support for advanced solar technologies including orbital systems. Long term clean energy targets require innovation beyond terrestrial generation capabilities. Space based solar aligns with decarbonization objectives without land use constraints. National missions emphasize technological leadership to enhance global positioning in clean energy innovation. Policy frameworks encourage collaboration between space agencies and energy ministries. Dedicated funding windows were introduced during 2024 and 2025 to support feasibility studies. Research grants prioritize power transmission efficiency and system reliability improvements. Interministerial coordination strengthens alignment between climate goals and aerospace development. Public sector leadership reduces early stage investment risks significantly. This focus continues to accelerate institutional momentum for space solar initiatives.
Challenges
High capital investment and long development cycles
Space based solar projects require substantial upfront capital across design, testing, and launch phases. Development timelines extend over multiple years before functional validation becomes possible. High technology risk increases financing complexity for both public and private stakeholders. Infrastructure requirements include launch systems, orbital platforms, and ground receiving stations. Cost recovery horizons remain uncertain due to absence of commercial scale precedents. Budget approvals often face scrutiny due to competing national priorities. Long gestation periods discourage short term private sector participation. Program continuity depends heavily on sustained government funding commitments. Cost overruns remain a key concern in early mission planning stages. These factors collectively slow commercialization momentum within the market.
Technological limitations in wireless power transmission
Wireless power transmission efficiency remains a core technical constraint for orbital solar systems. Energy losses during conversion and transmission reduce overall system viability significantly. Atmospheric interference affects signal stability and transmission accuracy. Safety regulations impose strict limits on permissible transmission intensities. Hardware reliability under prolonged space exposure remains under evaluation. Precision targeting challenges increase system complexity and operational risk. Technology readiness levels remain below commercial deployment thresholds. Continuous testing is required to validate long duration performance metrics. Integration of transmission and receiving systems adds engineering complexity. These limitations delay transition from experimental to operational deployments.
Opportunities
ISRO-led demonstration missions and public-private partnerships
Demonstration missions led by ISRO provide structured platforms for technology validation and risk reduction. Public-private partnerships enable shared investment and accelerated capability development. Collaborative missions allow private firms to access launch infrastructure and technical expertise. Demonstrations improve confidence among stakeholders and potential investors. Incremental mission success builds a roadmap toward scalable deployment. Knowledge transfer from government programs strengthens domestic industry capabilities. Partnerships reduce entry barriers for emerging aerospace firms. Demonstration data supports regulatory approvals and safety validations. Joint programs align national innovation goals with commercial viability. These initiatives create foundational momentum for long term market growth.
Integration with national renewable energy targets
National renewable energy targets create alignment opportunities for space based solar integration. Long term decarbonization strategies require continuous baseload alternatives. Space based systems complement terrestrial renewables by ensuring consistent generation. Policy alignment strengthens justification for sustained research funding. Energy planners increasingly evaluate hybrid grid architectures incorporating space inputs. Integration studies during 2024 and 2025 advanced system modeling accuracy. Strategic inclusion enhances future scalability and investment confidence. Alignment with climate commitments improves international collaboration potential. Space solar supports diversification within renewable portfolios. This integration pathway strengthens long term market relevance.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to remain in a developmental phase through the forecast period, driven by research intensity and policy support. Technological validation and demonstration missions will shape long term feasibility. Increasing collaboration between government and private players will define progress. Regulatory clarity and funding continuity will determine commercialization timelines. The outlook remains strategically positive with gradual transition toward operational deployment.
Major Players
- ISRO
- NewSpace India Limited
- L&T Aerospace
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Ananth Technologies
- Godrej Aerospace
- HAL
- Alpha Design Technologies
- Dhruva Space
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Data Patterns
- Paras Defence
Key Target Audience
- Government of India space and energy ministries
- Indian Space Research Organisation and affiliated agencies
- Defense procurement authorities
- Renewable energy policy bodies
- Infrastructure development agencies
- Strategic investors and sovereign funds
- Aerospace manufacturers and integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core technology parameters, deployment models, regulatory frameworks, and application areas were identified through structured domain mapping. Market boundaries were defined using operational scope and system architecture relevance.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative indicators were assessed across development stages, technology readiness, and ecosystem participation. Segment structures were built using usage patterns and institutional involvement levels.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were validated through consultations with industry professionals, aerospace engineers, and policy specialists. Feedback loops refined assumptions and ensured consistency with ongoing programs.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated through triangulation of technical, regulatory, and strategic inputs. Final outputs were structured to reflect market dynamics, risks, and growth pathways.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and orbital solar power scope delineation, Technology taxonomy and system architecture mapping, Capacity and revenue estimation using satellite deployment and power beaming models, Value chain revenue attribution across space and ground segments, Primary interviews with ISRO officials and aerospace energy experts)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and power transmission pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and program development flow
- Regulatory and policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising national energy security requirements
Government focus on renewable and clean energy leadership
Advancements in reusable launch vehicles and satellite miniaturization
Increasing defense demand for resilient power sources
Long-term cost advantages over terrestrial renewables - Challenges
High capital investment and long development cycles
Technological limitations in wireless power transmission
Regulatory and spectrum allocation constraints
Launch cost volatility
Limited commercial-scale operational precedents - Opportunities
ISRO-led demonstration missions and public-private partnerships
Integration with national renewable energy targets
Export potential for space power technologies
Advancements in high-efficiency photovoltaic materials
Strategic defense and space infrastructure investments - Trends
Growing focus on modular satellite architectures
Increased collaboration between space and energy sectors
R&D in microwave and laser power beaming
Policy alignment with space commercialization reforms
Integration of AI and autonomous satellite operations - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Demonstration satellites
Operational power satellites
Hybrid space-energy platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Grid-scale power generation
Defense and strategic power supply
Disaster management and emergency power
Remote and off-grid electrification - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Microwave power transmission
Laser-based power transmission
Modular satellite arrays
Geostationary orbital systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Power utilities
Defense and aerospace
Government and space agencies
Telecommunications and remote infrastructure - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Ground-to-space uplink
Space-to-ground downlink
Inter-satellite power transfer - By Region (in Value %)
North India
South India
East India
West India
Central India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology maturity, Launch capability, Power transmission efficiency, Cost structure, Strategic partnerships, R&D investment, Regulatory alignment, Domestic manufacturing capability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
NewSpace India Limited
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Ananth Technologies
Tata Advanced Systems
Larsen & Toubro Aerospace
Godrej Aerospace
Dhruva Space
Bellatrix Aerospace
Pixxel
Astra Microwave Products
Alpha Design Technologies
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Bharat Electronics Limited
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


