Market Overview
The India space batteries market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by increasing satellite launches and mission deployments across national programs. During the recent period, demand expanded steadily due to higher launch frequencies, growing satellite constellations, and broader adoption of advanced energy storage systems. The market observed rising adoption of lithium-based chemistries in 2024 and 2025, supported by indigenous development efforts. Growth momentum remained stable as mission durations increased and reliability requirements intensified across orbital and deep-space programs.
India’s market activity is primarily concentrated around Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Thiruvananthapuram due to strong space research infrastructure. These regions benefit from proximity to launch centers, satellite integration facilities, and battery testing laboratories. Policy-driven ecosystem development and private sector participation further strengthen demand concentration. Manufacturing clusters supporting electronics, materials engineering, and aerospace subsystems also reinforce supply-side maturity. The presence of skilled workforce and space-grade qualification facilities continues to attract long-term investments.
Market Segmentation
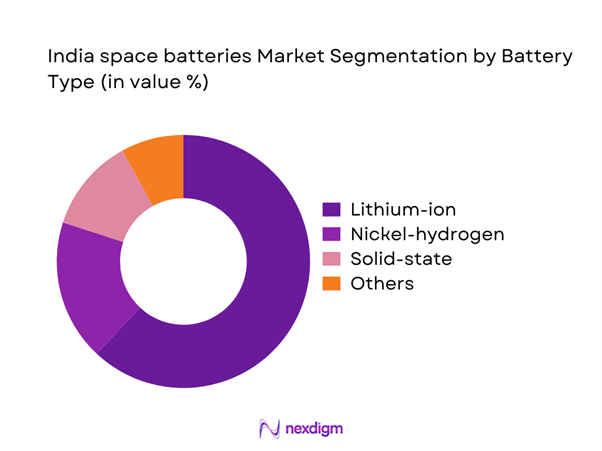
By Battery Type
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the India space batteries market due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and established flight heritage. In 2024 and 2025, lithium-ion systems accounted for the majority of deployed space power units owing to compatibility with satellite and launch vehicle platforms. Nickel-hydrogen batteries maintain relevance for specific orbital missions requiring high reliability. Emerging solid-state batteries are gaining attention for future missions because of safety advantages. Custom radiation-hardened chemistries are increasingly adopted for deep-space and defense missions.
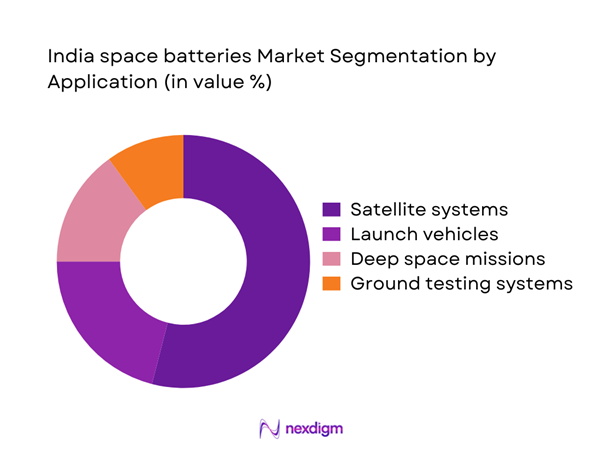
By Application
Satellite power systems represent the dominant application segment, driven by expanding communication, earth observation, and navigation missions. Launch vehicle applications follow due to growing mission frequency and enhanced onboard power requirements. Deep space missions are gaining momentum as India increases planetary exploration efforts. Ground testing and mission simulation systems contribute steadily to demand. The increasing complexity of spacecraft electronics is reinforcing the need for reliable onboard energy storage solutions.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of government-linked manufacturers and private technology providers specializing in space-grade energy systems. Companies compete on reliability, qualification experience, and long-term supply capabilities. Strategic collaborations with space agencies and system integrators are common. Technological depth and compliance with space-grade standards define competitive positioning. Entry barriers remain high due to certification complexity and mission-critical performance requirements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ISRO Satellite Centre | 1972 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre | 1963 | Thiruvananthapuram | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ananth Technologies | 1992 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Godrej Aerospace | 1989 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bharat Electronics Limited | 1954 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
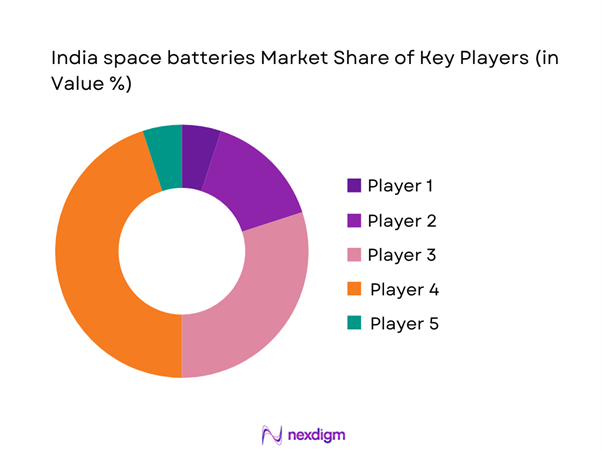
India space batteries Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising satellite launch frequency in India
The increasing number of satellite launches has significantly expanded demand for reliable space-grade battery systems across platforms. Government-backed missions and commercial satellite deployments accelerated in 2024, driving sustained battery procurement cycles. Higher mission cadence requires consistent supply of qualified power storage units across satellite classes. Enhanced launch infrastructure has further reduced deployment intervals, strengthening battery demand stability. Increased payload diversity has expanded energy storage requirements across varying mission profiles. The growing number of low earth orbit missions increased cumulative battery deployment volumes significantly. Reusable launch systems also contributed to higher battery utilization rates across missions. Mission reliability standards have driven higher adoption of proven battery technologies. Increased satellite lifespans have amplified long-term battery performance requirements. This sustained launch activity continues reinforcing demand stability across the India space batteries market.
Expansion of ISRO and private space missions
ISRO’s expanded mission roadmap has significantly influenced battery demand growth across multiple mission categories. Private sector participation increased notably during 2024 and 2025, supporting parallel mission development. Collaboration between public and private entities accelerated technology deployment timelines. Commercial launch service providers required dependable battery systems for repeated missions. Expanded space exploration initiatives increased energy storage requirements for longer mission durations. Rising payload complexity demanded higher-capacity and radiation-resistant battery architectures. Private satellite constellations strengthened recurring demand patterns for space-grade batteries. Mission diversification increased adoption of customized battery configurations. Testing and validation cycles expanded alongside mission volume growth. This combined expansion continues strengthening long-term market momentum.
Challenges
High qualification and certification costs
Space battery certification involves extensive testing under extreme environmental conditions, increasing development complexity. Qualification processes require long-duration thermal, vibration, and radiation testing cycles. High certification costs restrict participation of smaller manufacturers in the market. Multiple validation stages extend development timelines and delay commercialization. Specialized testing facilities remain limited within the domestic ecosystem. Compliance with mission-specific standards further elevates engineering effort. Requalification is often required for design modifications or material changes. These processes increase financial risk for manufacturers. Certification costs directly impact pricing competitiveness across suppliers. This challenge remains a significant barrier to rapid market expansion.
Radiation and thermal performance constraints
Space batteries must withstand extreme radiation exposure without performance degradation. Thermal cycling in orbit imposes additional material and design challenges. Battery chemistries must maintain stability across wide temperature fluctuations. Radiation shielding requirements increase system weight and complexity. Long-duration missions intensify performance degradation risks. Ensuring consistent power delivery under harsh conditions remains technically demanding. Design margins are limited due to spacecraft mass constraints. Failure risks necessitate extensive redundancy planning. These constraints slow innovation cycles and increase development costs. Performance reliability remains a core challenge for manufacturers.
Opportunities
Indigenous battery manufacturing initiatives
Government initiatives promoting domestic manufacturing have created favorable conditions for battery localization. Policy support has encouraged investment in advanced battery research facilities. Indigenous production reduces dependency on imported components and technologies. Local manufacturing improves supply chain resilience for space missions. Collaborative programs between research institutions and manufacturers are expanding. Technology transfer initiatives support capability development across the value chain. Indigenous development aligns with national self-reliance objectives. Increased funding has accelerated prototype development and testing. Local manufacturing also shortens lead times for mission integration. These initiatives offer strong long-term growth potential.
Growth of private launch and satellite startups
The emergence of private space startups has expanded demand for flexible battery solutions. New entrants require scalable and cost-effective energy storage systems. Startup-led innovation accelerates adoption of advanced battery chemistries. Increased launch frequency creates recurring procurement opportunities. Commercial missions emphasize performance optimization and weight reduction. Private companies drive faster design iterations compared to traditional programs. Collaboration between startups and suppliers enhances technology adaptation. Market entry of new players diversifies application requirements. Increased competition stimulates innovation across battery technologies. This ecosystem expansion supports sustained market growth.
Future Outlook
The India space batteries market is expected to witness steady expansion through the forecast period driven by sustained mission activity. Growing private sector participation and technological advancements will enhance product diversity. Continued government support for space exploration will reinforce demand stability. Advancements in battery efficiency and reliability will further shape future adoption patterns.
Major Players
- ISRO Satellite Centre
- Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
- Ananth Technologies
- Godrej Aerospace
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Larsen & Toubro Aerospace
- Data Patterns India
- Amara Raja Advanced Cell Technologies
- Exide Industries
- Saft Groupe
- GS Yuasa Corporation
- EaglePicher Technologies
- EAS Batteries
- Saft India
Key Target Audience
- Satellite manufacturers
- Launch service providers
- Space system integrators
- Defense and aerospace agencies
- Government and regulatory bodies including ISRO and IN-SPACe
- Private space startups
- Battery technology developers
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key parameters including battery chemistries, application scope, and mission profiles were identified. Technology adoption trends and regulatory constraints were mapped. Market boundaries were defined based on space-grade qualification criteria.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was analyzed across applications, technology types, and end-user segments. Demand patterns were assessed using deployment and mission activity indicators. Market structure was built using validated industry inputs.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through interactions with industry professionals and technical experts. Insights were cross-verified against operational trends and deployment activity. Refinements were incorporated based on expert feedback.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated to develop a structured market view. Data consistency checks were performed. Final insights were aligned with industry dynamics and future outlook considerations.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and satellite-grade battery scope mapping, spacecraft and launch vehicle segmentation framework, bottom-up capacity and mission-based market sizing, revenue attribution by platform and program lifecycle, primary interviews with ISRO suppliers and battery integrators, data triangulation across mission manifests and supplier disclosures, technology readiness and lifecycle assumption validation)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission-critical application landscape
- Space battery ecosystem structure
- Domestic and international supply chain dynamics
- Regulatory and space qualification environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising satellite launch frequency in India
Expansion of ISRO and private space missions
Demand for high energy density and long-life batteries
Growth of small satellite and constellation programs
Increased defense and surveillance space spending - Challenges
High qualification and certification costs
Radiation and thermal performance constraints
Limited domestic raw material supply
Long development and validation cycles
Dependence on imported cell technologies - Opportunities
Indigenous battery manufacturing initiatives
Growth of private launch and satellite startups
Advancements in solid-state battery research
Export opportunities for space-grade components
Government incentives under space reforms - Trends
Shift toward lightweight and high-cycle batteries
Increased use of modular battery architectures
Adoption of AI-enabled battery management systems
Rising collaboration between ISRO and private firms
Focus on long-duration deep space missions - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Satellites
Launch vehicles
Deep space probes
Crewed space missions
Ground support and test platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Power storage
Backup and redundancy systems
Payload operation support
Thermal management support
Emergency power systems - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Lithium-ion
Lithium-polymer
Nickel-hydrogen
Solid-state batteries
Custom radiation-hardened chemistries - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government space agencies
Defense and strategic programs
Commercial satellite operators
Private launch service providers
Space research institutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone power systems
Integrated spacecraft power units
Smart battery management systems
Telemetry-enabled battery modules - By Region (in Value %)
South India
West India
North India
East India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology capability, space qualification level, manufacturing scale, cost competitiveness, mission heritage, R&D intensity, government partnerships, export readiness)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
ISRO Satellite Centre
Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre
Ananth Technologies
Data Patterns India
Tata Advanced Systems
Larsen & Toubro Aerospace
Godrej Aerospace
Amara Raja Advanced Cell Technologies
Exide Industries
Bharat Electronics Limited
Saft Groupe
GS Yuasa Corporation
EaglePicher Technologies
Saab Space
EAS Batteries
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035