Market Overview
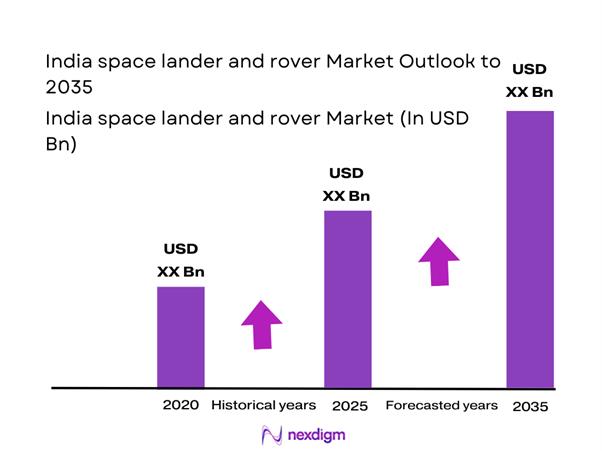
The India space lander and rover market current size stands at around USD ~ million, supported by increasing mission deployments and steady program funding momentum. Activity during 2024 and 2025 reflected heightened prototype development, system validation programs, and subsystem manufacturing scaling. Government-backed missions continued to anchor demand, while private participation increased through component supply and subsystem integration. Technology readiness improved across propulsion, navigation, and payload subsystems, strengthening domestic capabilities. The market structure remains project driven, with spending linked to mission cycles rather than continuous production.
The market is geographically concentrated around key space and aerospace hubs including Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Thiruvananthapuram, and Pune. These regions benefit from proximity to research centers, launch facilities, and established aerospace manufacturing ecosystems. Strong academic collaboration, policy support, and access to skilled engineering talent further reinforce regional dominance. Supply chains are closely linked to government agencies and emerging private integrators. Regulatory clarity and national space policies continue to shape development pace and commercial participation across these clusters.
Market Segmentation
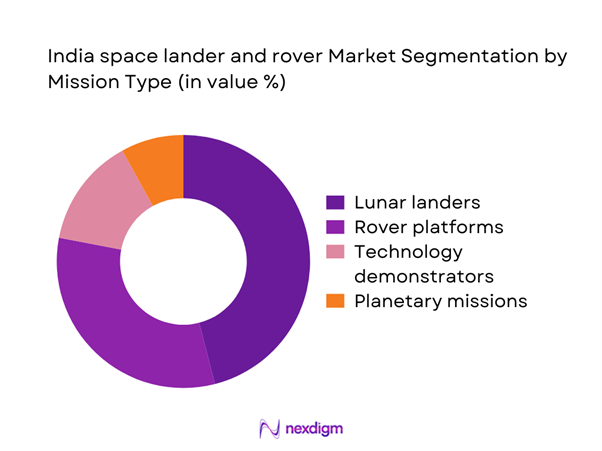
By Mission Type
The market is primarily driven by lunar lander missions, followed by rover-based exploration platforms supporting surface mobility and scientific analysis. Technology demonstration missions have gained momentum as testing grounds for propulsion, navigation, and communication subsystems. Planetary exploration beyond lunar missions remains limited but strategically important for long-term capability building. The dominance of mission-specific procurement creates variability in demand cycles, while increasing emphasis on reusable components improves program efficiency. Growing collaboration between public agencies and private developers supports diversification across mission categories, enabling gradual expansion into commercial and research-driven deployments.
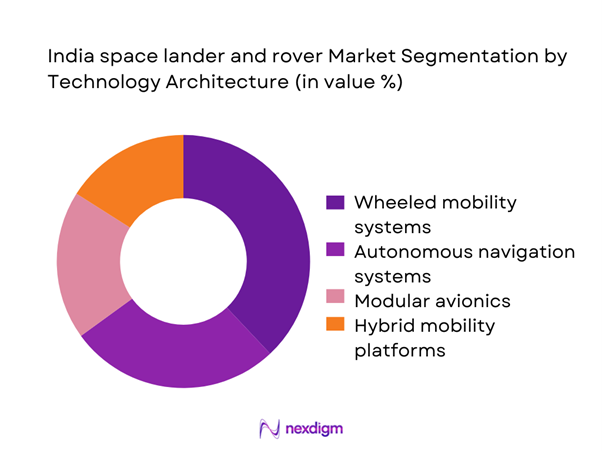
By Technology Architecture
Technology architecture segmentation is shaped by increasing adoption of autonomous navigation, modular avionics, and lightweight structural systems. Wheeled rover configurations dominate due to terrain adaptability and proven mission reliability. Hybrid mobility systems are gaining attention for future missions requiring enhanced maneuverability. Onboard artificial intelligence and sensor fusion technologies are being integrated to reduce ground dependency and enhance operational autonomy. Communication architecture evolution, including relay-based systems, supports extended mission durations. Continuous investment in indigenous component development strengthens long-term technological self-reliance.
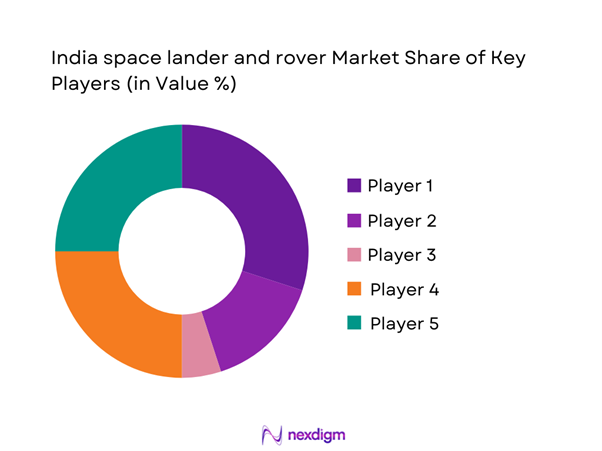
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by strong government dominance complemented by a growing ecosystem of private aerospace manufacturers and system integrators. Competition is driven by technological capability, mission reliability, and alignment with national space objectives. Long-term contracts, program continuity, and regulatory compliance remain key differentiators.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Indian Space Research Organisation | 1969 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Hindustan Aeronautics Limited | 1940 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen and Toubro | 1938 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2007 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ananth Technologies | 1992 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India space lander and rover Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing national focus on lunar and planetary missions
The national emphasis on planetary exploration has significantly expanded mission planning and technological ambition across the space sector. Government programs during 2024 and 2025 prioritized lunar surface access and scientific experimentation. This focus created sustained demand for lander and rover development activities. Strategic alignment with long-term exploration goals strengthened funding continuity. Mission visibility improved public and institutional confidence in space investments. Research organizations increased collaboration with engineering partners. Technological benchmarks advanced through iterative mission planning. Policy clarity supported accelerated approval cycles for exploration initiatives. Indigenous capability development gained stronger political backing. Overall momentum reinforced consistent program expansion across multiple mission stages.
Rising government investment in indigenous space technologies
Public funding allocation toward domestic space technology development increased steadily during 2024 and 2025 cycles. Budget prioritization supported infrastructure expansion and subsystem manufacturing capabilities. Investments emphasized propulsion, navigation, and surface mobility technologies. This funding encouraged reduced dependency on imported components. Enhanced grant availability supported private sector participation. Research institutions benefited from expanded testing facilities and simulation infrastructure. Technology transfer initiatives improved knowledge sharing across stakeholders. Long-term funding visibility improved supplier confidence and planning. Government-backed programs reduced commercialization risks. Overall investment flows strengthened the domestic innovation ecosystem.
Challenges
High development and mission execution costs
Space lander and rover programs require substantial capital for design, testing, and validation activities. Cost escalation arises from stringent reliability and safety requirements. Extended development timelines increase financial exposure for participating organizations. Specialized materials and components further elevate procurement expenses. Limited economies of scale restrict cost optimization opportunities. Infrastructure maintenance adds recurring expenditure pressures. Budget overruns remain a persistent concern for complex missions. Financial risk management becomes critical for long-duration projects. Dependence on government funding limits flexibility. These cost pressures constrain rapid market expansion.
Technological complexity and long development cycles
Designing lander and rover systems involves complex integration of mechanical, electronic, and software subsystems. Extensive testing is required to meet mission reliability standards. Development cycles often extend across multiple years before deployment. Iterative design revisions increase project timelines. Limited flight heritage for advanced systems raises validation challenges. Integration of autonomous features adds further complexity. Environmental simulation requirements increase engineering workload. Delays impact mission scheduling and funding allocation. Technology readiness gaps hinder rapid commercialization. Overall complexity slows market scalability.
Opportunities
Commercial lunar exploration missions
Emerging interest in commercial lunar activities presents new growth pathways for lander and rover platforms. Private entities increasingly seek access to lunar data and surface operations. Commercial payload delivery services create new revenue streams. Collaboration between public agencies and private developers accelerates mission planning. Technological advancements reduce entry barriers for non-government participants. Data commercialization potential enhances business viability. Standardized platforms enable cost sharing across missions. Growing international interest supports partnership opportunities. Policy frameworks increasingly accommodate private mission participation. These developments expand the addressable market scope.
Public-private partnerships in space robotics
Public-private collaboration models are gaining traction for space robotics development and deployment. Government agencies leverage private innovation to accelerate technology readiness. Private firms benefit from institutional support and mission access. Joint development reduces financial and technical risks. Shared infrastructure improves resource utilization efficiency. Collaborative programs encourage rapid prototyping and testing. Knowledge exchange strengthens domestic engineering capabilities. Contract-based partnerships enhance accountability and performance benchmarks. Long-term cooperation fosters ecosystem maturity. These partnerships drive sustainable industry growth.
Future Outlook
The India space lander and rover market is expected to witness steady advancement through 2035 driven by mission diversification and technological maturity. Increased private participation, enhanced policy support, and expanding international collaborations will shape market evolution. Focus on autonomy, modularity, and cost efficiency will define future development priorities. Long-term exploration goals will continue to anchor sustained investment momentum.
Major Players
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- Larsen and Toubro
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Ananth Technologies
- Godrej Aerospace
- Alpha Design Technologies
- MTAR Technologies
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Dhruva Space
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Walchandnagar Industries
- Data Patterns India
- Paras Defence and Space Technologies
Key Target Audience
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Department of Space, Government of India
- Defense Research and Development Organisation
- Private space technology manufacturers
- Aerospace component suppliers
- Satellite and mission integrators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- National regulatory and space policy bodies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market boundaries were defined through mission classifications, technology scope, and application relevance. Key performance indicators and system categories were mapped based on operational usage.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured using mission-level assessment, technology segmentation, and program-level evaluation to ensure accurate representation of market dynamics.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry experts, engineers, and policy specialists provided validation through structured interviews and technical assessments.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated using triangulation methods, ensuring consistency across qualitative insights and quantitative indicators.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for Indian planetary lander and rover systems, Mission taxonomy and platform classification for lunar and interplanetary programs, Bottom-up mission-based market sizing using spacecraft procurement and program budgets, Data triangulation using government tenders, mission disclosures, and satellite program databases, Assumptions and limitations related to mission cadence, technology readiness levels, and geopolitical constraints)
- Definition and scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission deployment landscape
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and vendor network
- Regulatory and policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Increasing national focus on lunar and planetary missions
Rising government investment in indigenous space technologies
Growing participation of private space startups
Strategic importance of planetary exploration
Advancement in autonomous navigation and robotics
Expansion of ISRO’s interplanetary mission roadmap - Challenges
High development and mission execution costs
Technological complexity and long development cycles
Dependence on government funding approvals
Limited private sector manufacturing scale
Mission failure risks and reliability constraints - Opportunities
Commercial lunar exploration missions
Public-private partnerships in space robotics
Export potential of rover subsystems and components
Integration of AI and advanced sensors
International collaboration programs - Trends
Shift toward modular lander and rover designs
Increased use of AI-based navigation systems
Miniaturization of payloads
Adoption of reusable and scalable platforms
Growth of private launch and mission services - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Lunar landers
Planetary landers
Rover platforms
Technology demonstration missions - By Application (in Value %)
Lunar exploration
Planetary science missions
Technology validation missions
Resource prospecting and ISRU testing - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Wheeled rover systems
Hybrid mobility platforms
Autonomous navigation systems
AI-enabled surface operations - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government space agencies
Defense and strategic research bodies
Commercial space enterprises
Academic and research institutions - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Direct-to-Earth communication
Relay satellite-based communication
Hybrid communication architecture - By Region (in Value %)
South India
North India
West India
East India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Mission capability, Technology readiness level, Payload capacity, Indigenous content ratio, Cost efficiency, Program experience, Integration capability, Government collaboration depth)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL)
Larsen & Toubro Aerospace
Tata Advanced Systems
Ananth Technologies
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Dhruva Space
Bellatrix Aerospace
Paras Defence and Space Technologies
Godrej Aerospace
Alpha Design Technologies
MTAR Technologies
Walchandnagar Industries
Data Patterns (India)
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


