Market Overview
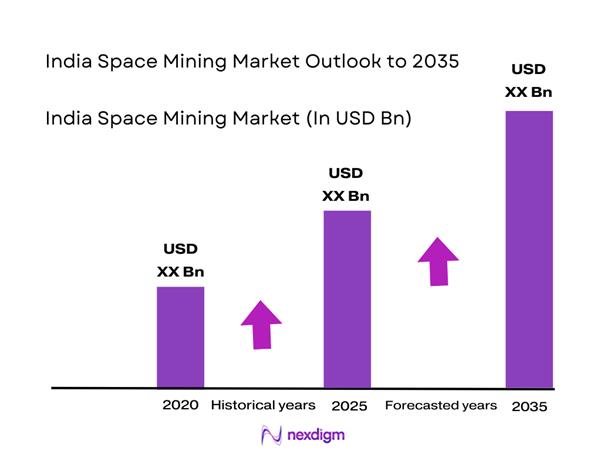
The India Space Mining Market current size stands at around USD ~ million driven by experimental missions and early technology investments. Activity levels during 2024 and 2025 reflected growing institutional participation, prototype testing, and increasing budgetary alignment toward extraterrestrial resource utilization. Government-backed programs and private ventures collectively supported exploration payloads, robotic systems, and feasibility assessments. Technology readiness improved through orbital demonstrations, while policy clarity encouraged exploratory capital allocation. The ecosystem remained developmental, with limited commercialization but strong forward momentum. Research collaborations and space infrastructure upgrades further strengthened foundational capabilities.
India’s space mining ecosystem is concentrated around established aerospace hubs with advanced launch and satellite integration infrastructure. Southern and western regions benefit from proximity to space research centers, manufacturing clusters, and mission control facilities. Demand is driven by government agencies, private launch service providers, and research institutions. Policy support and indigenous technology initiatives enhance ecosystem maturity. Strong academic linkages and skilled workforce availability further support innovation. Regional collaboration with global space programs also reinforces long-term market development.
Market Segmentation
By Mission Type
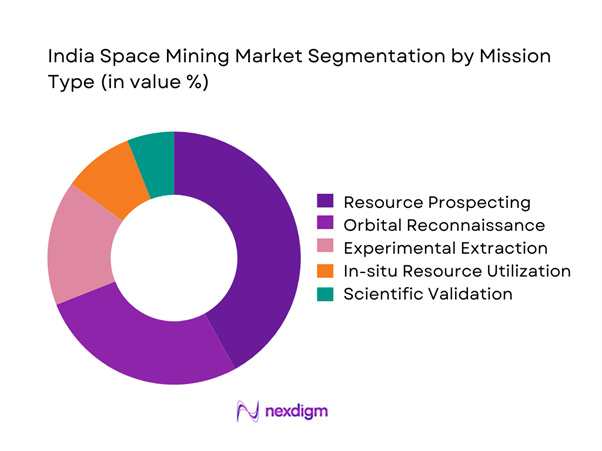
The market is primarily segmented by mission type, with resource prospecting and orbital reconnaissance dominating early deployments. These missions account for significant activity due to lower technical risk and strong alignment with national exploration priorities. Experimental extraction and in-situ utilization missions are emerging as secondary segments, supported by advancements in robotics and autonomous systems. Scientific validation missions also contribute meaningfully, especially in lunar and near-earth object exploration. Commercial extraction remains limited but is gaining attention as technology maturity improves. Overall segmentation reflects a gradual transition from exploration-focused initiatives to resource-oriented missions.
By Technology Platform
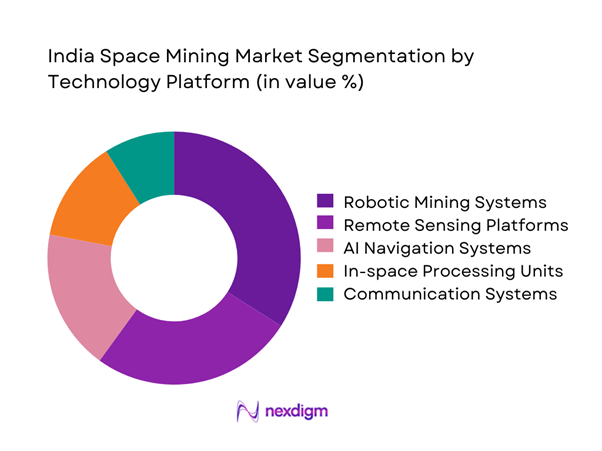
Technology-based segmentation shows dominance of robotic and autonomous systems due to operational feasibility and lower human risk. Remote sensing and AI-enabled navigation platforms are widely adopted for terrain analysis and mission planning. In-space processing technologies are still nascent but show strong development potential. Additive manufacturing and material handling systems are gradually entering testing phases. Communication and telemetry platforms remain critical enablers across all mission categories. The segment reflects a strong orientation toward automation and data-driven operations.
Competitive Landscape
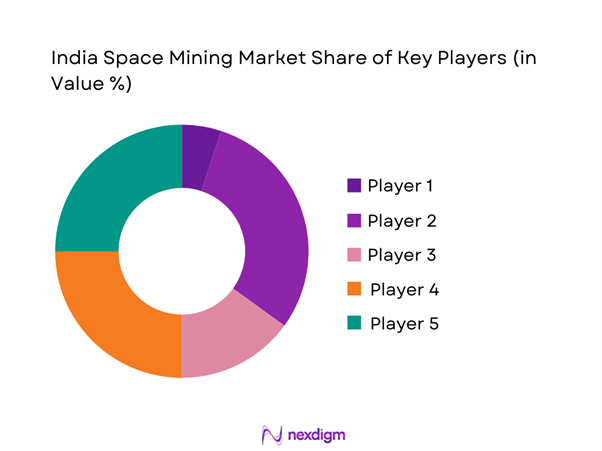
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of government-backed entities and emerging private technology developers. Market participation remains concentrated, with high entry barriers related to capital intensity and technical complexity. Collaboration between public institutions and startups defines competitive dynamics. Innovation depth and regulatory alignment significantly influence positioning. Long-term success depends on mission execution capability and technology reliability.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Indian Space Research Organisation | 1969 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Skyroot Aerospace | 2018 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Agnikul Cosmos | 2017 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bellatrix Aerospace | 2015 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dhruva Space | 2012 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Space Mining Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising national investment in space exploration
National investment expansion has strengthened research capabilities and enabled advanced experimentation across orbital and lunar exploration programs. Public funding allocations during 2024 and 2025 supported infrastructure upgrades, mission planning, and technology validation initiatives. Increased governmental commitment enhanced confidence among private participants and academic collaborators. Strategic alignment with long-term space objectives accelerated development of mining-relevant technologies. Budgetary support facilitated testing of autonomous systems and remote sensing platforms. Policy continuity ensured stability for long-term research investments. Inter-agency coordination improved efficiency across exploration programs. Enhanced funding also improved talent retention and technical skill development. National priorities emphasized resource security through extraterrestrial exploration. These combined factors significantly strengthened the operational foundation for space mining initiatives.
ISRO-led deep space mission expansion
ISRO-led missions played a central role in advancing space mining feasibility through deep space exploration activities. Mission planning during 2024 and 2025 incorporated resource mapping and surface analysis objectives. Successful technology demonstrations enhanced confidence in autonomous operations. Mission data improved understanding of extraterrestrial material composition and accessibility. Collaboration with private entities expanded technological experimentation scope. Deep space missions enabled testing of communication and navigation reliability. Operational learnings reduced technical uncertainties associated with extraction environments. Mission success improved investor sentiment toward space mining projects. Long-duration missions supported validation of robotic endurance capabilities. Overall mission expansion directly strengthened the market’s technical readiness.
Challenges
High capital and technology development costs
Space mining requires substantial upfront investment in specialized equipment and mission development. High costs associated with launch systems limit participation from smaller entities. Technology development cycles remain long and capital intensive. Advanced robotics and sensing systems require sustained funding commitments. Financial risks increase due to uncertain mission outcomes. Infrastructure development adds further cost burdens. Limited commercial returns during early phases constrain funding availability. Cost optimization remains difficult due to lack of economies of scale. Technological failures can significantly impact project timelines. These cost challenges slow overall market expansion.
Limited commercial viability in early stages
Commercial viability remains constrained due to unproven revenue models and long development timelines. Market participants face uncertainty regarding resource monetization mechanisms. Limited operational data restricts accurate return forecasting. Regulatory ambiguity further complicates commercial planning. Early-stage missions prioritize research over revenue generation. Infrastructure limitations reduce scalability of extraction operations. Risk perception remains high among potential investors. Supply chain immaturity affects operational efficiency. Market demand for extracted resources is still emerging. These factors collectively hinder near-term commercialization prospects.
Opportunities
Public-private partnership expansion
Public-private partnerships present strong opportunities for accelerating space mining development. Collaborative models reduce financial risks through shared investment structures. Government support enhances credibility for private ventures. Joint missions allow technology transfer and knowledge sharing. Partnerships improve access to testing infrastructure and launch capabilities. Regulatory facilitation encourages private sector participation. Cooperative frameworks enable faster innovation cycles. Shared resources reduce duplication of development efforts. Partnerships also attract international collaboration opportunities. This model significantly strengthens long-term market sustainability.
Development of lunar and asteroid mining missions
Lunar and asteroid missions offer substantial opportunities for resource exploration and extraction. Advancements in propulsion and navigation enhance mission feasibility. Scientific interest supports continuous mission planning. Resource mapping initiatives improve targeting accuracy. Technology readiness improvements enable extended surface operations. Mission scalability allows phased investment approaches. Data from these missions enhances commercial confidence. Strategic importance of extraterrestrial resources drives policy backing. Long-term mission pipelines encourage ecosystem growth. These missions represent the most promising expansion pathway.
Future Outlook
The India Space Mining Market is expected to progress steadily through 2035, supported by technological maturation and sustained government involvement. Increasing private participation will enhance innovation depth and operational efficiency. Policy clarity and international collaboration are likely to accelerate mission deployment. Advancements in automation and in-space processing will define future competitiveness. The market is positioned for gradual transition from exploration to early-stage commercialization.
Major Players
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Dhruva Space
- Pixxel
- Astrome Technologies
- Team Indus
- Ananth Technologies
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Larsen and Toubro Defence
- Godrej Aerospace
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Alpha Design Technologies
- SatSure
Key Target Audience
- Space exploration agencies
- Private aerospace manufacturers
- Satellite and launch service providers
- Robotics and automation companies
- Defense and strategic research bodies
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Ministry of Space and ISRO regulatory divisions
- Advanced materials and propulsion developers
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Core variables related to mission type, technology platform, and regulatory environment were identified. Market boundaries were defined based on operational scope and application relevance. Data points were filtered to align with space mining activities.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Qualitative and quantitative inputs were analyzed to construct market structure. Technology maturity and deployment trends were mapped across segments. Assumptions were validated using industry-level indicators.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Findings were cross-verified through expert discussions and industry consultations. Technical feasibility and adoption drivers were assessed through multiple validation layers.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated to ensure consistency across sections. Data triangulation ensured logical coherence. Final outputs were refined to reflect realistic market dynamics.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Scope Alignment for Space Resource Extraction, Space Mining Value Chain and Segmentation Framework Development, Bottom-Up Market Sizing Using Mission and Payload Economics, Revenue Attribution Across Exploration and Extraction Phases, Primary Interviews with ISRO Scientists and Private Space Startups, Data Triangulation Using Launch Databases and Policy Sources, Assumptions on Regulatory Readiness and Technology Maturity)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission application pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and value chain structure
- Regulatory and policy environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising national investment in space exploration
ISRO-led deep space mission expansion
Growing demand for in-space resource utilization
Strategic importance of space-based minerals
Increasing private sector participation
Advancements in robotics and AI - Challenges
High capital and technology development costs
Limited commercial viability in early stages
Regulatory uncertainty around space mining rights
Technological risks and mission failure rates
Limited deep-space infrastructure
Long return on investment cycles - Opportunities
Public-private partnership expansion
Development of lunar and asteroid mining missions
Export potential for space resource technologies
Advancement of in-space manufacturing
Strategic alignment with global space economies
Technology spillover into terrestrial mining - Trends
Shift toward autonomous mining systems
Integration of AI and machine learning
Growing focus on lunar resource utilization
Increased funding for private space startups
Collaboration with international space agencies
Development of reusable space mining platforms - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Revenue per Mission, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Orbital prospecting satellites
Robotic landers
Autonomous mining rovers
In-orbit processing platforms
Earth return vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Resource prospecting and mapping
In-situ resource utilization
Rare earth element extraction
Water and fuel production
Scientific and experimental mining - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Robotic excavation systems
AI-based autonomous navigation
In-space material processing systems
Additive manufacturing systems
Remote sensing and telemetry systems - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Space exploration agencies
Defense and strategic research bodies
Commercial space companies
Energy and propulsion developers
Advanced materials manufacturers - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Deep space communication networks
Satellite relay systems
Ground station integrated links
Inter-satellite communication systems - By Region (in Value %)
Southern India
Western India
Northern India
Eastern India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology readiness, Mission success rate, Cost efficiency, R&D intensity, Strategic partnerships, Regulatory compliance, Launch capability, Service portfolio)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Indian Space Research Organisation
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Pixxel
Dhruva Space
Bellatrix Aerospace
Astrome Technologies
Team Indus
SatSure
Ananth Technologies
Larsen & Toubro Defence
Tata Advanced Systems
Godrej Aerospace
Bharat Electronics Limited
Alpha Design Technologies
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Revenue per Mission, 2026–2035


