Market Overview
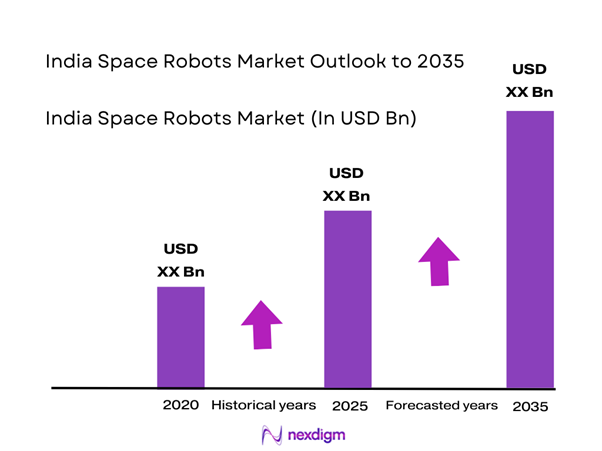
The India Space Robots Market market current size stands at around USD ~ million and reflects expanding deployment across orbital and planetary missions. Growing investments in autonomous systems, robotic manipulators, and surface mobility platforms are supporting operational efficiency. Demand has strengthened due to increased satellite servicing requirements and deep space exploration objectives. Government-backed programs continue to drive indigenous development of robotics hardware and control systems. The market shows steady integration of artificial intelligence and autonomous navigation technologies. Adoption is supported by long-term national space exploration roadmaps and institutional funding continuity.
The market is primarily concentrated around major space research and manufacturing hubs with established aerospace infrastructure. Southern and western regions dominate due to proximity to launch facilities, research centers, and defense manufacturing clusters. Strong policy backing and the presence of specialized engineering talent support ecosystem maturity. Public sector dominance shapes procurement and development priorities. Increasing private sector participation is gradually strengthening supply chain depth. Regional specialization continues to influence deployment and testing activities.
Market Segmentation
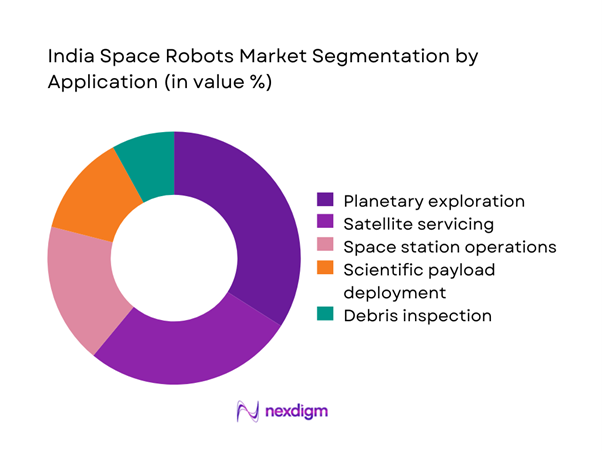
By Application
The application landscape is dominated by planetary exploration and satellite servicing activities, driven by expanding mission complexity. Robotic systems are increasingly used for surface mobility, payload deployment, and remote inspection functions. Growth in deep space missions has amplified demand for autonomous operations capable of functioning in extreme environments. Scientific exploration applications benefit from improved sensor integration and robotic dexterity. Orbital servicing applications continue to gain relevance due to satellite life extension needs. Overall application growth remains closely tied to national mission planning cycles.
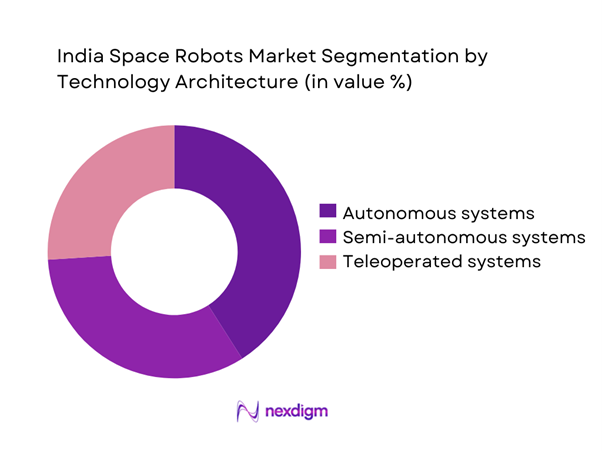
By Technology Architecture
Technology architecture segmentation reflects rising adoption of autonomous and semi-autonomous robotic systems. Fully autonomous systems are gaining prominence due to communication latency challenges in deep space missions. Semi-autonomous platforms remain essential for orbital servicing and controlled operations. Teleoperated systems continue supporting near-earth missions with real-time control requirements. Integration of artificial intelligence is enhancing navigation accuracy and task execution. Architecture selection largely depends on mission duration, distance, and operational risk levels.
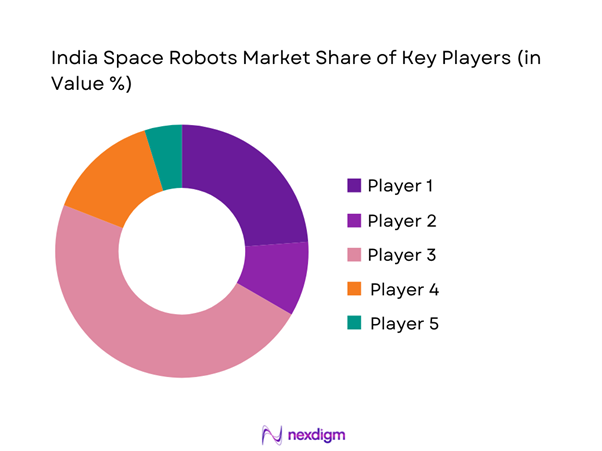
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by strong public sector leadership and increasing private sector participation. Market structure remains moderately consolidated with high entry barriers due to technical complexity and regulatory oversight.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| ISRO | 1969 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen & Toubro | 1938 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2001 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Godrej Aerospace | 1989 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ananth Technologies | 1992 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Space Robots Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising ISRO investments in planetary and lunar missions
Rising ISRO investments in planetary and lunar missions continue driving advanced robotic system development across national space programs. During 2024 and 2025, multiple mission approvals accelerated demand for autonomous manipulators and surface mobility platforms across missions. Robotic technologies increasingly support payload deployment, surface sampling, and remote operations under extreme environmental conditions in space missions. Government-backed exploration roadmaps emphasize robotics to enhance mission reliability, safety, and long-duration operational capability across complex space missions. Public sector funding allocations prioritize robotic systems supporting lunar surface mobility and autonomous sample handling for future missions. These investments stimulate domestic engineering participation and strengthen upstream component development for robotic subsystems within the space sector. Mission complexity growth requires advanced control algorithms, sensing modules, and fault-tolerant robotic architectures for deep space operations reliability. ISRO collaboration with domestic suppliers increases technology readiness and accelerates iterative robotic design cycles across mission development programs. Enhanced mission cadence elevates demand for standardized robotic platforms adaptable across multiple exploration objectives and payload configurations internationally. Sustained governmental commitment positions robotics as a foundational capability within national space exploration strategies over long-term programmatic horizons.
Increasing focus on indigenous space technology development
The strategic emphasis on indigenous technology development is strengthening domestic robotic system design capabilities across multiple mission profiles. Policy frameworks encourage local manufacturing of robotic subsystems, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers for critical components. Indigenous development initiatives enhance customization flexibility for mission-specific robotic applications and operating environments. Technology self-reliance supports faster prototyping cycles and localized testing infrastructure expansion. Domestic research institutions increasingly collaborate with industrial partners to advance robotic control algorithms. Indigenous innovation programs accelerate technology transfer from laboratories to operational missions. Local manufacturing capabilities improve supply chain resilience and reduce long-term procurement risks. Standardization efforts enable interoperability across different mission platforms and robotic subsystems. Increased domestic intellectual property creation strengthens long-term competitiveness in space robotics. Overall focus on self-reliance aligns with national strategic autonomy objectives.
Challenges
High development and qualification costs
High development and qualification costs significantly impact the pace of space robotics deployment across mission programs. Robotic systems require extensive testing under simulated space conditions, increasing engineering timelines and expenses. Qualification standards demand rigorous validation for radiation tolerance, thermal stability, and mechanical reliability. Specialized materials and components further elevate production complexity and cost structures. Limited production volumes restrict economies of scale for robotic subsystem manufacturing. Extended development cycles delay commercial scalability and technology maturation. Cost overruns can affect project prioritization within constrained government budgets. High capital requirements limit participation of smaller private enterprises. Certification procedures remain lengthy due to mission-critical safety requirements. Overall cost intensity remains a major barrier to rapid market expansion.
Limited domestic component ecosystem
The domestic component ecosystem for space robotics remains underdeveloped, affecting supply chain reliability and scalability. Dependence on imported sensors, actuators, and electronics increases procurement lead times. Limited local suppliers restrict component customization for mission-specific requirements. Qualification of new domestic vendors involves lengthy validation and certification processes. Supply chain fragmentation impacts integration timelines for complex robotic assemblies. Technology gaps persist in precision manufacturing and radiation-hardened electronics. Domestic capacity constraints increase vulnerability to geopolitical and trade disruptions. Scaling production remains challenging without established tier-two and tier-three suppliers. Limited component availability impacts cost optimization and delivery schedules. Ecosystem immaturity slows overall industry expansion and innovation pace.
Opportunities
Commercial in-orbit servicing and refueling missions
Commercial in-orbit servicing creates significant opportunities for advanced robotic system deployment across satellite fleets. Increasing satellite congestion drives demand for inspection, repair, and refueling capabilities. Robotic arms and autonomous docking technologies enable life extension of existing orbital assets. Service-based mission models improve asset utilization efficiency for operators. Growth in small satellite constellations increases demand for maintenance solutions. Robotics enable non-invasive servicing without mission interruption. Commercial participation diversifies revenue streams beyond government-led programs. Technology maturation supports scalable servicing architectures for multiple platforms. In-orbit servicing reduces space debris risks and enhances orbital sustainability. These applications open new long-term growth pathways for space robotics.
Participation in international space exploration programs
International collaboration presents opportunities for technology exchange and joint robotic mission development. Participation in multinational programs enhances exposure to advanced engineering standards. Collaborative missions enable shared development costs and reduced financial risk. Indian robotics capabilities can integrate into global exploration initiatives. Joint research accelerates innovation in autonomy and navigation systems. International programs increase visibility of domestic robotic technologies. Cross-border partnerships improve access to advanced testing infrastructure. Participation strengthens global credibility of national space capabilities. Knowledge sharing accelerates technology maturation cycles. These collaborations support long-term growth and technological leadership.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the India Space Robots Market remains positive, driven by expanding mission complexity and sustained public investment. Increasing private sector participation will strengthen innovation and commercialization pathways. Advancements in autonomous technologies will enhance mission efficiency and safety. International collaborations are expected to deepen technological capabilities. Long-term growth will be supported by strategic national space objectives.
Major Players
- ISRO
- Larsen & Toubro
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Godrej Aerospace
- Ananth Technologies
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Dhruva Space
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Pixxel
- Maxar Technologies
- Northrop Grumman
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Thales Alenia Space
- Astrobotic Technology
Key Target Audience
- Space exploration agencies
- Defense and strategic organizations
- Satellite operators
- Space system integrators
- Robotics technology developers
- Launch service providers
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies including ISRO and IN-SPACe
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were identified based on mission types, robotic system categories, and deployment environments. Technology maturity, application scope, and operational complexity were mapped. Market boundaries were defined to ensure relevance and consistency.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Data was structured through segmentation analysis and trend mapping. Demand drivers and constraints were assessed across applications. Market behavior was analyzed using deployment and adoption patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through expert discussions with industry stakeholders and technical specialists. Feedback loops ensured alignment with real-world operational dynamics.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Insights were consolidated through triangulation of qualitative and quantitative inputs. Final outputs were structured to ensure accuracy, coherence, and strategic relevance.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for space robotics, Space robotics taxonomy and platform classification logic, Bottom-up market sizing using mission-level and program-level spend analysis, Revenue attribution across hardware, software, and services in space robotics, Primary interviews with ISRO officials, OEMs, and space system integrators)
- Definition and scope of space robotics in the Indian space ecosystem
- Evolution of robotic systems in Indian space missions
- Role of robotics across orbital, lunar, and interplanetary programs
- Space robotics value chain and ecosystem structure
- Domestic manufacturing and supply chain dynamics
- Regulatory and institutional framework governing space robotics
- Growth Drivers
Rising ISRO investments in planetary and lunar missions
Increasing focus on indigenous space technology development
Expansion of private space startups under IN-SPACe framework
Growing need for satellite servicing and life-extension missions
Advancements in AI and robotics for space applications - Challenges
High development and qualification costs
Limited domestic component ecosystem
Long mission development and approval cycles
Technological complexity and reliability requirements
Dependency on government funding and programs - Opportunities
Commercial in-orbit servicing and refueling missions
Participation in international space exploration programs
Development of dual-use space robotics technologies
Growth of private launch and satellite service providers
Rising demand for autonomous deep-space systems - Trends
Shift toward autonomous robotic operations
Increased use of AI-based navigation and control
Miniaturization of robotic subsystems
Collaboration between ISRO and private players
Growing emphasis on reusable and serviceable space assets - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Orbital robotic arms
Planetary rovers
Autonomous landers
In-orbit servicing robots
Inspection and maintenance robots - By Application (in Value %)
Satellite servicing and repair
Planetary exploration
Space station operations
Debris removal and inspection
Scientific payload deployment - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Teleoperated robotic systems
Semi-autonomous robotic systems
Fully autonomous robotic systems
AI-enabled adaptive robotics - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government space agencies
Defense and strategic programs
Commercial satellite operators
Space research institutions
Private space startups - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Ground-controlled robotics
Satellite relay-controlled robotics
AI-enabled autonomous systems - By Region (in Value %)
South India
West India
North India
East India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology capability, Mission heritage, Product portfolio breadth, Manufacturing scale, R&D intensity, Strategic partnerships, Pricing strategy, After-sales and support capability)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Larsen & Toubro Defence
Tata Advanced Systems
Godrej Aerospace
Ananth Technologies
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Dhruva Space
Bellatrix Aerospace
Pixxel
Maxar Technologies
Northrop Grumman
Astrobotic Technology
Airbus Defence and Space
Thales Alenia Space
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


