Market Overview
The India Spacecraft market current size stands at around USD ~ million and reflects steady expansion driven by institutional missions and private participation. Activity levels increased during 2024 and 2025 as satellite launches, payload manufacturing, and platform integration accelerated nationwide. Government-backed programs continued to dominate deployment volumes, while commercial participation expanded through small satellite manufacturing and mission services. Demand remained concentrated in earth observation, communication, and navigation platforms supporting civil and defense needs.
Southern and western regions dominate operational activity due to established launch facilities, research centers, and manufacturing clusters. Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Sriharikota form the core ecosystem supported by component suppliers and testing infrastructure. Policy reforms encouraging private participation strengthened regional competitiveness. Growing startup density and improved access to launch services have further supported geographic concentration. Institutional demand continues to anchor long-term capacity development across these regions.
Market Segmentation
By Fleet Type
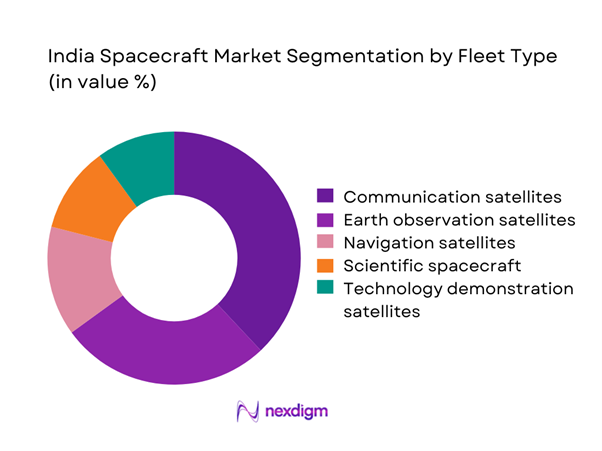
The market is primarily driven by communication and earth observation spacecraft, which account for the majority of deployments due to national connectivity and surveillance priorities. Small satellites have gained prominence owing to lower development cycles and modular architectures. Scientific and exploration missions remain strategically important but contribute smaller operational volumes. Technology demonstration satellites are increasingly used for propulsion, materials, and onboard processing validation. Fleet composition reflects a shift toward agile, mission-specific spacecraft optimized for cost and deployment efficiency.
By Application
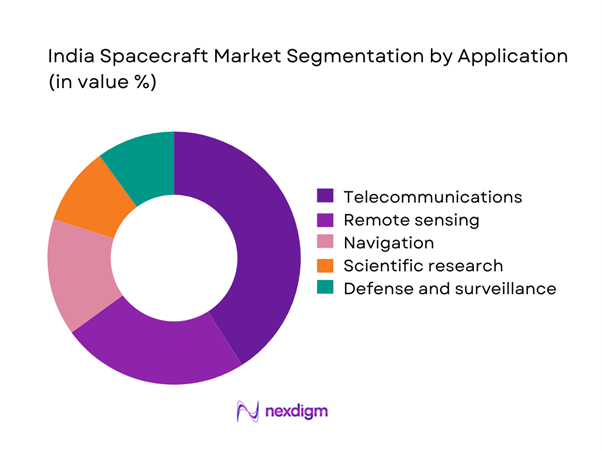
Telecommunications applications dominate usage due to expanding broadband and secure communication requirements. Remote sensing supports agriculture, disaster monitoring, and infrastructure planning. Navigation applications maintain steady demand from civilian and defense sectors. Scientific missions contribute to technology development and deep space exploration initiatives. Defense and surveillance applications continue to grow as strategic priorities emphasize space-based intelligence and monitoring capabilities.
Competitive Landscape
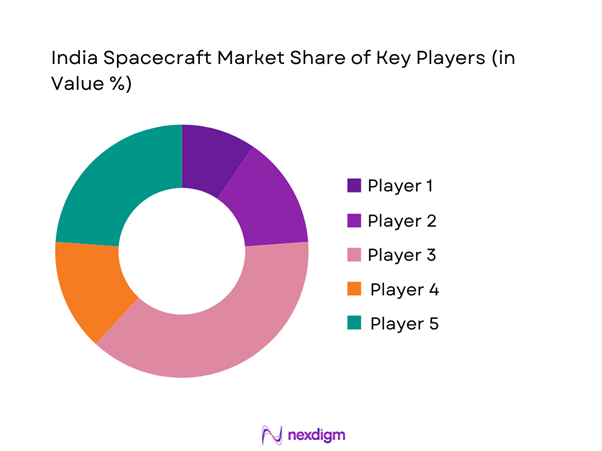
The competitive landscape is characterized by strong government presence alongside emerging private manufacturers and system integrators. Public sector entities dominate mission execution, while private firms increasingly contribute to subsystems, launch services, and data applications. Strategic partnerships, technology collaborations, and policy-driven procurement shape competitive positioning across the ecosystem.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Indian Space Research Organisation | 1969 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| NewSpace India Limited | 2019 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen & Toubro Defence | 2015 | Mumbai | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2007 | Hyderabad | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Ananth Technologies | 1992 | Bengaluru | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Spacecraft Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Government-led space missions expansion
Government investment in national space programs has consistently increased mission frequency and spacecraft development activity across multiple application areas. Institutional missions in 2024 and 2025 supported sustained demand for satellites, payloads, and integration services. Policy frameworks enabled faster approvals and expanded mission scopes across civil and strategic domains. Public funding ensured continuity of launch schedules and long-term program planning stability. Infrastructure upgrades improved testing, assembly, and mission control capabilities nationwide. Strategic autonomy goals further strengthened commitment toward indigenous spacecraft manufacturing capacity. Government procurement remained the primary revenue driver across system integrators and component suppliers. Mission diversification encouraged development of specialized platforms for communication, navigation, and observation purposes. Increased collaboration with private firms accelerated technology transfer and industrial participation. These factors collectively sustained steady market expansion throughout the assessment period.
Rising private sector participation
Private enterprises increasingly entered spacecraft manufacturing, payload development, and downstream service segments. Regulatory reforms simplified licensing and enabled commercial launch and satellite operations. Venture-backed startups introduced cost-efficient designs and faster development cycles. Collaboration with government agencies improved technical capabilities and market access. Growing investor confidence supported infrastructure expansion and talent acquisition. Private firms focused on small satellite constellations and data-driven services. Technology innovation improved component reliability and performance metrics. Demand from commercial communication and imaging services strengthened order pipelines. Competitive dynamics encouraged operational efficiency and specialization. The expanding private ecosystem significantly diversified the overall market structure.
Challenges
High development and deployment costs
Spacecraft development requires substantial capital allocation across design, testing, and launch phases. Advanced materials and precision engineering increase production complexity. Long development cycles delay revenue realization and elevate financial risk exposure. Limited economies of scale restrict cost optimization for specialized missions. Infrastructure dependencies further elevate operational expenditures. Risk mitigation requirements add additional engineering overheads. Funding constraints affect smaller players disproportionately within the ecosystem. Access to affordable launch opportunities remains limited. Insurance and compliance costs add to overall financial burden. These factors collectively constrain rapid market scalability.
Regulatory and procedural complexity
Multiple regulatory clearances are required across design, launch, and operations stages. Compliance requirements often extend project timelines and increase administrative burden. Evolving space policies create uncertainty for long-term investment planning. Coordination between civil and defense authorities can delay approvals. Export controls restrict technology collaboration with international partners. Licensing frameworks are still maturing for commercial operators. Policy interpretation varies across jurisdictions and agencies. Documentation and reporting obligations increase operational workload. Regulatory clarity remains critical for private sector confidence. These complexities continue to challenge market participants.
Opportunities
Expansion of small satellite deployments
Demand for small satellites increased due to lower costs and faster deployment cycles. Commercial imaging, communication, and IoT applications drive sustained interest. Modular architectures allow rapid customization for mission-specific needs. Launch aggregation services improve deployment efficiency. Technology miniaturization enhances payload capabilities within limited mass constraints. Private operators increasingly adopt small satellite platforms. Government programs also support constellation-based missions. Manufacturing scalability improves with standardized designs. Export opportunities emerge for cost-competitive platforms. This segment offers strong long-term growth potential.
Growth in space-based data applications
Satellite-derived data supports agriculture, urban planning, and disaster management applications. Analytics-driven services increase value extraction from space assets. Integration with artificial intelligence enhances data usability. Demand from enterprises and government agencies continues to rise. Improved data accessibility expands commercial adoption. Downstream service models generate recurring revenue opportunities. Partnerships between data providers and software firms are increasing. Regulatory support encourages wider data utilization. Market maturity enables diversified service offerings. This trend strengthens the overall spacecraft ecosystem.
Future Outlook
The India Spacecraft market is expected to maintain strong momentum through 2035, supported by sustained government programs and expanding private participation. Continued policy support and infrastructure development will enhance domestic manufacturing capabilities. Technological advancements will enable more efficient spacecraft platforms. Increasing commercial demand and international collaboration will further strengthen long-term industry growth prospects.
Major Players
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- NewSpace India Limited
- Larsen & Toubro Defence
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Ananth Technologies
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Skyroot Aerospace
- Agnikul Cosmos
- Pixxel
- Dhruva Space
- Bellatrix Aerospace
- Alpha Design Technologies
- Godrej Aerospace
- Data Patterns
Key Target Audience
- Satellite manufacturers and system integrators
- Launch service providers
- Space technology startups
- Defense procurement agencies
- Indian Space Research Organisation
- Department of Space
- Private satellite operators
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Market boundaries were defined using spacecraft classifications, mission types, and operational applications. Data parameters were aligned with national space programs and private sector participation levels.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Demand drivers, technology adoption patterns, and deployment trends were evaluated using structured industry mapping. Segmentation frameworks were developed based on fleet types and applications.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Insights were validated through expert interactions across manufacturing, launch services, and policy domains. Assumptions were refined using operational and regulatory perspectives.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
All findings were consolidated through triangulation and consistency checks. The final output reflects balanced qualitative and quantitative assessments aligned with market realities.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope alignment for Indian spacecraft ecosystem, Spacecraft classification and mission-type segmentation logic, Bottom-up market sizing using satellite manufacturing and launch data, Revenue attribution across civil, defense and commercial programs, Primary interviews with ISRO officials, private OEMs and launch service providers, Data triangulation using government budgets, launch manifests and satellite registries)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and mission profiles
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and manufacturing flow
- Regulatory and policy environment
- Growth Drivers
- Challenges
- Opportunities
- Trends
- Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Communication satellites
Earth observation satellites
Navigation satellites
Scientific and exploration spacecraft
Technology demonstration satellites - By Application (in Value %)
Telecommunications
Remote sensing and imaging
Navigation and positioning
Scientific research
Defense and surveillance - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Small satellites
Medium satellites
Large satellites
CubeSats and nano satellites - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Government and defense
Commercial satellite operators
Research and academic institutions
NewSpace startups - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
LEO-based systems
MEO-based systems
GEO-based systems
Interplanetary and deep space systems - By Region (in Value %)
North India
South India
West India
East India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Revenue share, Spacecraft portfolio breadth, Mission success rate, Manufacturing capacity, Technology readiness level, Government contract exposure, Export capability, Strategic partnerships)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)
Ananth Technologies
Larsen & Toubro Defence
Tata Advanced Systems
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Bharat Electronics Limited
Skyroot Aerospace
Agnikul Cosmos
Pixxel
Dhruva Space
Bellatrix Aerospace
Alpha Design Technologies
Godrej Aerospace
Data Patterns
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


