Market Overview
The India Stealth Technologies market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense modernization and indigenous capability expansion. During 2024 and 2025, steady growth was supported by increased defense allocations, ongoing aircraft development programs, and rising deployment of low-observable platforms. Demand accelerated due to integration of advanced materials, signature management solutions, and platform-level stealth enhancements. The market remains driven by long-term strategic planning rather than short-cycle procurement behavior, supporting stable technology investments across multiple defense verticals.
The market is geographically concentrated around key defense manufacturing clusters and aerospace corridors. Southern and western regions dominate due to the presence of aircraft manufacturing units, naval shipyards, and defense electronics hubs. Strong research infrastructure, proximity to military testing facilities, and policy-driven industrial corridors support sustained development. Government-backed innovation programs and expanding private-sector participation further strengthen regional ecosystems, reinforcing India’s growing self-reliance in stealth technology development.
Market Segmentation
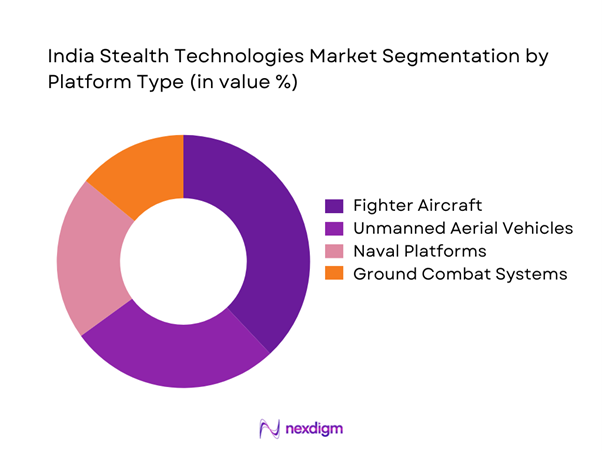
By Platform Type
The platform-based segmentation is led by airborne systems due to higher stealth integration intensity and continuous modernization programs. Fighter aircraft and unmanned aerial systems dominate demand, supported by sustained development activity and operational requirements. Naval platforms represent a growing segment driven by acoustic and radar signature suppression needs. Ground-based platforms show gradual adoption, primarily for surveillance and mobility protection. Platform dominance is influenced by lifecycle costs, integration complexity, and mission-critical performance requirements across services.
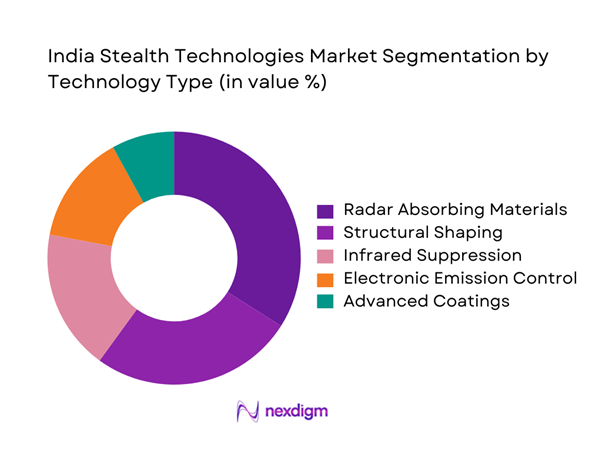
By Technology Type
Technology segmentation is led by radar-absorbing materials and structural shaping techniques, reflecting their widespread application across platforms. Infrared suppression technologies show increasing adoption driven by evolving threat environments. Electromagnetic emission control systems are gaining importance due to electronic warfare integration. Advanced composite materials and surface coatings support weight reduction and performance enhancement, while emerging metamaterial applications are gradually entering development and testing phases.
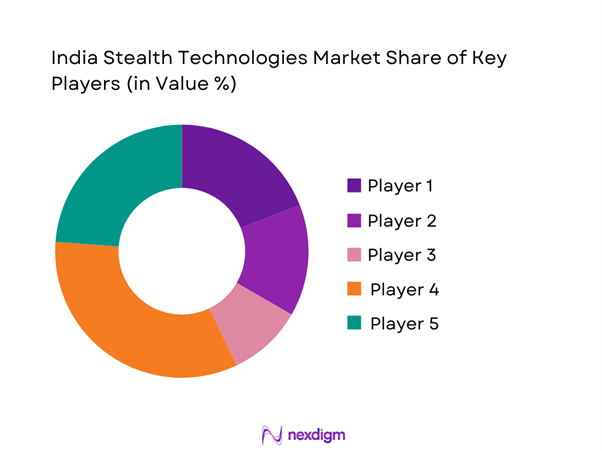
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of government-backed defense organizations and private-sector manufacturers supporting platform development and subsystem integration. Competition is driven by technological depth, indigenous capability development, and long-term defense contracts. Players focus on strengthening R&D, manufacturing scale, and compliance with defense procurement standards.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Hindustan Aeronautics Limited | 1940 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bharat Electronics Limited | 1954 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Bharat Dynamics Limited | 1970 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Larsen & Toubro Defence | 2010 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tata Advanced Systems | 2010 | India | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
India Stealth Technologies Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising indigenous fighter and UAV programs
Indigenous aircraft development programs expanded significantly during 2024 and 2025, increasing demand for stealth enabling technologies. Advanced fighter and unmanned systems required deeper integration of low observable materials across multiple structural components. Indigenous manufacturing mandates encouraged domestic suppliers to enhance stealth-related capabilities. Research programs focused on survivability improvements through reduced detection signatures. Government-backed projects created stable long-term demand visibility for suppliers. Collaboration between public laboratories and private manufacturers strengthened technology absorption. Increased testing frequency improved material performance validation cycles. Platform lifecycle upgrades further accelerated stealth adoption across fleets. Indigenous programs reduced dependence on imports and encouraged local innovation ecosystems. Overall momentum strengthened market confidence and investment continuity.
Increasing threat perception and regional tensions
Regional security dynamics intensified focus on survivability and detection avoidance during 2024 and 2025. Modern threat environments demanded improved radar and infrared signature reduction capabilities. Defense planners prioritized stealth as a force multiplier for air and naval operations. Increased border surveillance requirements drove adoption of low observable technologies. Strategic deterrence planning emphasized survivability against advanced sensor networks. Procurement decisions increasingly favored stealth-enabled platforms. Operational readiness assessments highlighted vulnerability of legacy systems. Modernization programs accelerated integration of advanced materials. Long-term defense doctrines reinforced stealth as a critical capability. Heightened threat perception sustained consistent demand across multiple services.
Challenges
High development and testing costs
Stealth technology development requires extensive prototyping and validation infrastructure investments. Advanced material testing facilities involve high capital and operational expenditures. Limited testing infrastructure increases development timelines and associated costs. Iterative design cycles add complexity to certification processes. Budget constraints restrict parallel development of multiple technology streams. Cost overruns remain a risk due to material experimentation failures. Specialized testing environments limit rapid scalability. Long validation cycles delay operational deployment schedules. Resource-intensive development restricts entry of smaller firms. Cost pressures influence procurement prioritization decisions.
Complexity of materials and manufacturing processes
Stealth materials require precision manufacturing under controlled environmental conditions. Variability in material properties impacts performance consistency. Manufacturing defects can significantly reduce stealth effectiveness. Skilled workforce availability remains limited for advanced composite handling. Integration of stealth materials with structural components increases design complexity. Quality assurance requirements raise production lead times. Supply chain dependency on specialized inputs creates vulnerability. Process standardization remains challenging across suppliers. High rejection rates increase operational inefficiencies. Manufacturing complexity slows rapid scaling efforts.
Opportunities
Next-generation AMCA and UCAV programs
Next-generation aircraft programs offer significant opportunities for advanced stealth integration. Indigenous design mandates encourage development of proprietary technologies. Long-term program timelines enable sustained R&D investments. Modular architecture allows incremental stealth upgrades. Increased automation supports improved material application accuracy. Program scale supports supplier ecosystem expansion. Collaboration opportunities enhance knowledge transfer. Advanced sensor fusion drives demand for reduced observability. Export potential increases commercial viability. These programs anchor long-term market growth.
Stealth upgrades for naval platforms
Naval modernization programs emphasize reduced acoustic and radar signatures. Fleet upgrades create demand for retrofit stealth solutions. Indigenous shipbuilding capabilities support technology absorption. Surface and subsurface vessels increasingly adopt stealth geometries. Sensor evasion requirements grow with maritime surveillance intensity. Maintenance cycles provide recurring upgrade opportunities. Coastal security needs drive adoption of advanced materials. Integration with electronic warfare systems enhances effectiveness. Lifecycle upgrades support steady revenue streams. Naval focus diversifies overall market demand.
Future Outlook
The India Stealth Technologies market is expected to witness sustained expansion driven by indigenous platform development and modernization initiatives. Continued policy support and defense self-reliance programs will strengthen domestic capabilities. Advancements in materials science and digital design tools will enhance system effectiveness. Growing private sector participation is likely to accelerate innovation and capacity building. Long-term defense planning will continue to anchor market growth through 2035.
Major Players
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- Bharat Electronics Limited
- Bharat Dynamics Limited
- Larsen & Toubro Defence
- Tata Advanced Systems
- Mahindra Defence Systems
- Alpha Design Technologies
- Astra Microwave Products
- MTAR Technologies
- Godrej Aerospace
- Data Patterns India
- Dynamatic Technologies
- Walchandnagar Industries
- Paras Defence and Space
- Centum Electronics
Key Target Audience
- Ministry of Defence
- Defence Research and Development Organisation
- Indian Air Force procurement divisions
- Indian Navy acquisition teams
- Public sector defense manufacturers
- Private defense manufacturing firms
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Defence procurement and regulatory agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Key variables were identified based on platform types, technology layers, and application areas relevant to stealth systems. Data points were mapped across defense programs, procurement cycles, and technology maturity levels. Industry structure and value chain relationships were also defined.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was developed through analysis of ongoing defense programs and technology deployment trends. Segmentation was established based on application and platform relevance. Qualitative and quantitative indicators were aligned for consistency.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through consultations with industry professionals, defense analysts, and technology specialists. Inputs were refined based on program-level insights and operational considerations. Cross-verification ensured alignment with sector realities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into a structured analytical framework. Insights were validated through triangulation of multiple data points. Final outputs were aligned with industry standards and decision-making requirements.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope for stealth and low-observable defense technologies, Platform-wise and technology-layer segmentation framework, Bottom-up defense procurement and program-based market sizing approach, Revenue attribution by platform lifecycle and subsystem integration value, Primary interviews with defense OEMs, DRDO scientists and procurement officials, Validation through tender analysis and program-level triangulation)
- Definition and scope
- Evolution of stealth capabilities
- Role of stealth in survivability, mission success, and deterrence
- Defense industrial ecosystem and domestic manufacturing structure
- Supply chain structure including
- Regulatory and policy environment governing defense stealth development
- Growth Drivers
Rising indigenous fighter and UAV programs
Increasing threat perception and regional tensions
Government push for Atmanirbhar Bharat in defense
Modernization of legacy defense platforms
Rising defense R&D expenditure - Challenges
High development and testing costs
Complexity of materials and manufacturing processes
Limited domestic supplier base for advanced composites
Long defense procurement cycles
Technology transfer and export restrictions - Opportunities
Next-generation AMCA and UCAV programs
Stealth upgrades for naval platforms
Growth in private defense manufacturing
Export opportunities to friendly nations
Advancements in materials science and AI-enabled stealth - Trends
Shift toward multi-spectral stealth solutions
Integration of AI in signature management
Use of advanced composites and metamaterials
Increasing indigenization of critical subsystems
Growing collaboration between DRDO and private players - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Fixed-wing combat aircraft
Unmanned aerial vehicles
Naval surface combatants
Submarines
Ground combat vehicles - By Application (in Value %)
Radar cross-section reduction
Infrared signature management
Acoustic signature suppression
Electromagnetic emission control
Multispectral camouflage - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Radar absorbing materials
Shaping and structural design
Infrared suppression systems
Electronic emission control systems
Metamaterials and advanced coatings - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Air Force
Navy
Army
Homeland security and border forces
Defense R&D organizations - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Platform-integrated systems
Network-enabled stealth systems
Sensor-fused stealth architectures - By Region (in Value %)
North India
South India
West India
East India
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Technology capability, Indigenous content level, Program participation, R&D intensity, Manufacturing scale, Government partnerships, Export presence, Financial strength)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Defence Research and Development Organisation
Bharat Electronics Limited
Bharat Dynamics Limited
Tata Advanced Systems
Larsen & Toubro Defence
Mahindra Defence Systems
Alpha Design Technologies
Astra Microwave Products
MTAR Technologies
Israel Aerospace Industries
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems
Saab AB
- Demand drivers from armed forces modernization plans
- Procurement and tendering process under MoD frameworks
- Vendor qualification and indigenization requirements
- Budget allocation and long-term capital acquisition planning
- Operational risk considerations and deployment constraints
- After-sales support, upgrades, and lifecycle management expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


