Market Overview
The Indonesia Education Market is valued at USD 50 billion, reflecting robust investments and growth in the education sector backed by governmental reforms and private sector engagement. The market has witnessed consistent growth, with factors such as increased disposable income and a growing demand for quality education being pivotal drivers. The significant focus on improving literacy rates and expanding educational access across urban and rural regions continues to shape the market landscape.
Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung are the dominant cities within the Indonesia Education Market. These cities are characterized by a dense population, high urbanization rates, and a concentration of educational institutions, driving demand for both public and private educational services. The presence of prestigious universities and educational programs within these cities further solidifies their standing as educational hubs in the country, attracting both domestic and international students.
The Indonesian government’s commitment to education reform is reflected in its initiatives, including the increased funding allocation to the education sector, which has risen steadily to about 20% of the national budget. The government aims to develop the quality of human capital through vocational education and training, investing IDR 38 trillion (roughly USD 2.5 billion) for technical and vocational education in 2023 alone. These initiatives are designed to enhance the employability of youth and address the skills gap in the labor market, ultimately contributing to the nation’s economic growth.
Market Segmentation
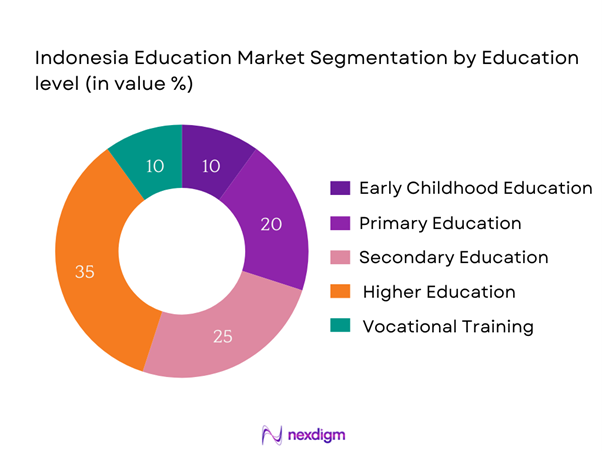
By Education Level
The Indonesia Education Market is segmented by education level into early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, higher education, and vocational training. Within this segmentation, higher education commands a significant market share due to the increasing emphasis on university-level education among the youth. This trend is fueled by aspirations for better job prospects and higher wages, reflecting a shift in societal values towards advanced learning. Institutions such as Universitas Indonesia and Universitas Gadjah Mada have established strong reputations, contributing to the popularity and preference for higher education.
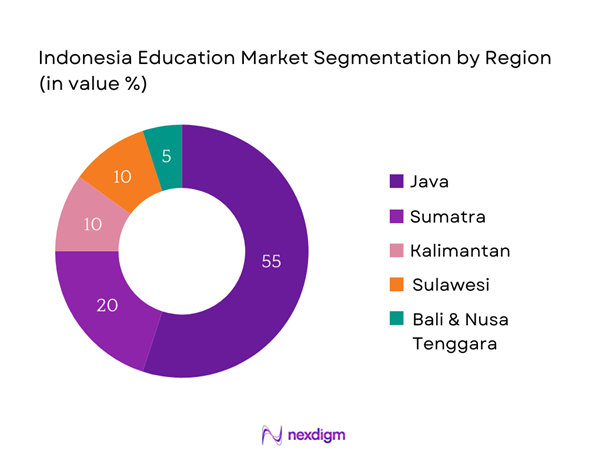
By Region
The Indonesia Education Market is further segmented by region, including Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and Bali & Nusa Tenggara. Java dominates this segmentation, holding the largest market share due to its high population density and industrial development. The concentration of educational institutions and government funding in this region leaves a significant impact on education access. The presence of major urban centers like Jakarta provides a competitive edge, attracting students and educational investment.
Competitive Landscape
The Indonesia Education Market is dominated by a few key players, including local and international institutions. This consolidation among major educational providers highlights the considerable influence of these companies in shaping educational trends within the region.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Market Specific Parameter 1 | Market Specific Parameter 2 | Market Specific Parameter 3 | Market Specific Parameter 4 | Market Specific Parameter 5 | Market Specific Parameter 6 |
| Universitas Indonesia | 1950 | Depok | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Universitas Gadjah Mada | 1949 | Yogyakarta | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Institut Teknologi Bandung | 1959 | Bandung | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Universitas Airlangga | 1954 | Surabaya | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Binus University | 2001 | Jakarta | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Indonesia Education Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing Emphasis on Quality Education
The Indonesian government has been significantly increasing its expenditure on education, which reached IDR 608 trillion (approx. USD 41.3 billion) in 2023. This investment has resulted in improved learning outcomes and educational quality across primary, secondary, and higher education sectors. According to the World Bank, over 80% of Indonesian children now complete primary school, demonstrating the government’s commitment to educational access and quality improvement. Furthermore, the implementation of the Indonesian National Education Standards has fostered a structured approach to enhance curriculum and instructional practices across schools.
Rising Middle-Class Population
The expansion of Indonesia’s middle class, projected to reach 141 million by 2024, is driving demand for quality education services. This demographic, primarily concentrated in urban areas, increasingly values educational attainment as a pathway to economic stability. According to the Asian Development Bank, a significant portion of this population is willing to invest in higher education and skill training, resulting in higher enrollment rates in private educational institutions. The growing middle class not only seeks improved academic options but is also contributing to the demand for specialized programs that cater to contemporary job markets.
Market Challenges
Infrastructure Limitations
Indonesia faces significant infrastructure challenges across its education system, particularly in rural areas where educational facilities can be substandard or lacking. As of late 2023, the Ministry of Education reported that approximately 25% of schools in remote areas lack adequate classrooms, sanitary facilities, and learning resources. This disparity not only limits access to quality education for many children but also affects student performance and retention rates. The government recognizes the need to improve school infrastructure but faces difficulties in efficiently allocating resources across the vast archipelago.
Teacher Training and Quality Issues
Challenges regarding teacher quality are a crucial issue within the Indonesia Education Market, with approximately 40% of teachers lacking formal qualifications as of 2023. To address this gap, the Indonesian government has initiated substantial reforms in teacher training programs, but many educators still do not receive adequate professional development. The World Bank indicated that improved training and continuous professional development are essential to enhance educational outcomes. The inconsistency in teacher quality across regions further complicates efforts to implement effective educational strategies nationwide.
Opportunities
Expansion of E-Learning Platforms
The demand for digital learning solutions has surged significantly, with around 40% of Indonesian students engaged in online learning as of early 2024. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend, and many institutions are now seeking partnerships with edtech companies to develop and integrate e-learning programs. Despite current limitations in internet penetration, which stands at about 78% in urban areas, governments and private players are investing heavily in technological infrastructure to make digital education more accessible, thereby solidifying the future growth potential of this sector.
Partnerships Between Public and Private Sectors
There is a growing recognition of the importance of collaboration between public and private sectors to improve education quality and enhance investment in the market. In 2023, the government launched a program that encourages private investment in public schools, allowing businesses to directly contribute resources and expertise. As a result, over 1,200 public-private partnership initiatives have been established, primarily focusing on technology-enhanced classrooms and vocational training programs. This trend promises to expand educational offerings and resources, catering to the evolving demands of students and the job market.
Future Outlook
Over the next several years, the Indonesia Education Market is expected to show significant growth driven by increased digital transformation in education, government policies focusing on enhancing educational quality, and rising consumer demand for diverse learning methodologies. The integration of technology in educational processes and a growing inclination toward vocational training are likely to propel the market forward. Additionally, the internationalization of education in Indonesia, with more foreign partnerships and exchange programs, will further stimulate growth.
Major Players
- Universitas Indonesia
- Universitas Gadjah Mada
- Institut Teknologi Bandung
- Universitas Airlangga
- Binus University
- Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana
- Universitas Negeri Jakarta
- LaSalle College Jakarta
- Jakarta Intercultural School
- Al-Azhar Islamic School
- Pelita Harapan International School
- Bali International School
- Santa Laurensia School
- Universitas Pelita Harapan
- Sekolah Bogor Raya
Key Target Audience
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (Ministry of Education and Culture, National Accreditation Board)
- Educational Investment Firms
- Non-Governmental Organizations
- Private Educational Institutions
- Corporations Involved in Educational Technology
- Vocational Training Centers
- Educational Publishers
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves constructing a comprehensive map encompassing all major stakeholders within the Indonesia Education Market. This is achieved through extensive desk research, leveraging a blend of secondary and proprietary databases to gather relevant data on various educational parameters, including enrollment rates, institutional types, and funding sources.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
During this phase, historical data pertaining to the Indonesia Education Market is compiled and analyzed. This process includes assessing enrollment figures, market penetration rates, and the revenue generation mechanisms used by educational institutions. Statistical evaluations ensure a solid foundation for predicting future market trends.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Market hypotheses are formulated and then validated through consultations with industry experts, educators, and institutional leaders. These sessions—often conducted through telephone interviews—yield valuable insights into current trends, market dynamics, and future projections.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
In the final stage, engagement with various educational institutions provides an in-depth understanding of product segments, student preferences, and institutional performance. This interaction serves to verify the data collected earlier and assure a cohesive, accurate analysis of the Indonesia Education Market, enhancing the overall quality of the report.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology
(Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Historical Development of Education System
- Timeline of Major Educational Reforms
- Business Cycle of Educational Institutions
- Supply Chain and Value Chain Analysis in Education
- Growth Drivers
Increasing Emphasis on Quality Education
Rising Middle-Class Population
Government Initiatives for Education Funding - Market Challenges
Infrastructure Limitations
Teacher Training and Quality Issues - Opportunities
Expansion of E-Learning Platforms
Partnerships Between Public and Private Sectors - Trends
Digital Transformation in Education
Shift Toward Inclusive Education - Government Regulation
Education Policy Framework
Accreditation and Quality Assurance - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Enrollment Numbers, 2019-2024
- By Investment in Education, 2019-2024
- By Education Level (In Value %)
Early Childhood Education
– Playgroups and Kindergartens (TK/PAUD)
– Montessori-Based Programs
– Islamic Early Childhood Schools (RA)
Primary Education
– SD (Sekolah Dasar) – National Curriculum
– SD with International Curriculum
– Religious-Based Primary Schools
Secondary Education
– SMP/SMA – General Academic Schools
– Madrasah Tsanawiyah / Aliyah
– International / Cambridge / IB Schools
Higher Education
– Public Universities (PTN)
– Private Universities (PTS)
– International Branch Campuses
Vocational Training
– SMK (Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan)
– Skill Development Centers
– Industry-Led Certification Programs - By Region (In Value %)
Java
Sumatra
Kalimantan
Sulawesi
Bali and Nusa Tenggara - By Ownership Type (In Value %)
Public Institutions
– Ministry-Run Schools (MOEC, MOHA)
– State-Owned Universities (e.g., UI, ITB)
Private Institutions
– Foundation-Run Schools (Yayasan)
– Foreign Curriculum Schools
– For-Profit Vocational and EdTech Providers - By Learning Method (In Value %)
Traditional Classroom Learning
E-Learning
Blended Learning - By Course Type (In Value %)
STEM Programs
– Science and Mathematics Olympiad Schools
– Engineering and IT-Focused Courses
– Robotics and Coding Bootcamps
Humanities and Social Sciences
– Economics, Law, Psychology Programs
– Language & Literature Courses
– Political Science and Public Administration
Arts and Sports
– Music and Performing Arts Academies
– Fine Arts & Design Institutes
– Physical Education and Sports Training Schools
- Market Share of Major Players by Value and Enrollment Numbers, 2024
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Business Strategies, Recent Developments, Strength, Weakness, Organizational Structure, Revenues, Number of Institutions, Number of Students Enrolled, Number of Graduates, Partnerships with Businesses, Technology Integration Status)
- SWOT Analysis of Major Players
- Pricing Analysis of Tuition Fees Across Different Education Segments
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Universitas Indonesia
Universitas Gadjah Mada
Institut Teknologi Bandung
Universitas Airlangga
Universitas Negeri Jakarta
Binus University
Universitas Pelita Harapan
Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana
LaSalle College Jakarta
Sekolah Bogor Raya
Bali International School
Jakarta Intercultural School
Al-Azhar Islamic School
Pelita Harapan International School
Santa Laurensia School
- Market Demand by User Type
- Purchasing Power and Budget Allocations
- Regulatory Requirements Impacting Users
- Needs, Desires, and Pain Point Analysis
- Decision-Making Process for Enrollment
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Enrollment Numbers, 2025-2030
- By Investment in Educational, 2025-2030


