Market Overview
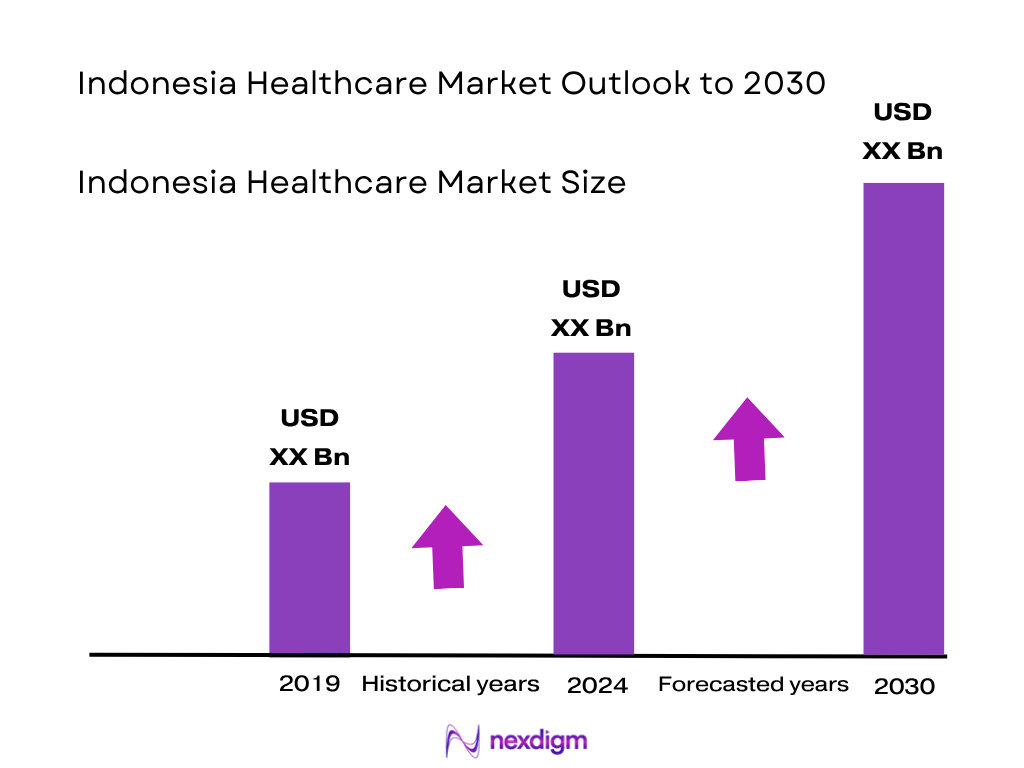
The Indonesia healthcare market is projected to reach USD 11.6 billion in value, based on historical data and projected trends. The market expanded significantly—from prior years into 2023 and then 2024—driven primarily by major national health insurance coverage (JKN/BPJS), rapid expansion of private hospital capacity, and rising per‑capita healthcare spend. Increasing demand for diagnostics, advanced medical devices, and telemedicine platforms are key growth engines supporting the market’s current valuation.
Urban centres such as Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bali dominate the market owing to high income levels, concentration of private tertiary hospitals, and strong penetration of insurance plans like BPJS. Java island leads due to superior healthcare infrastructure, high density of medical tourism facilities, and greater adoption of digital health platforms. Rural regions lag due to infrastructure gaps and limited specialist access.
Market Segmentation
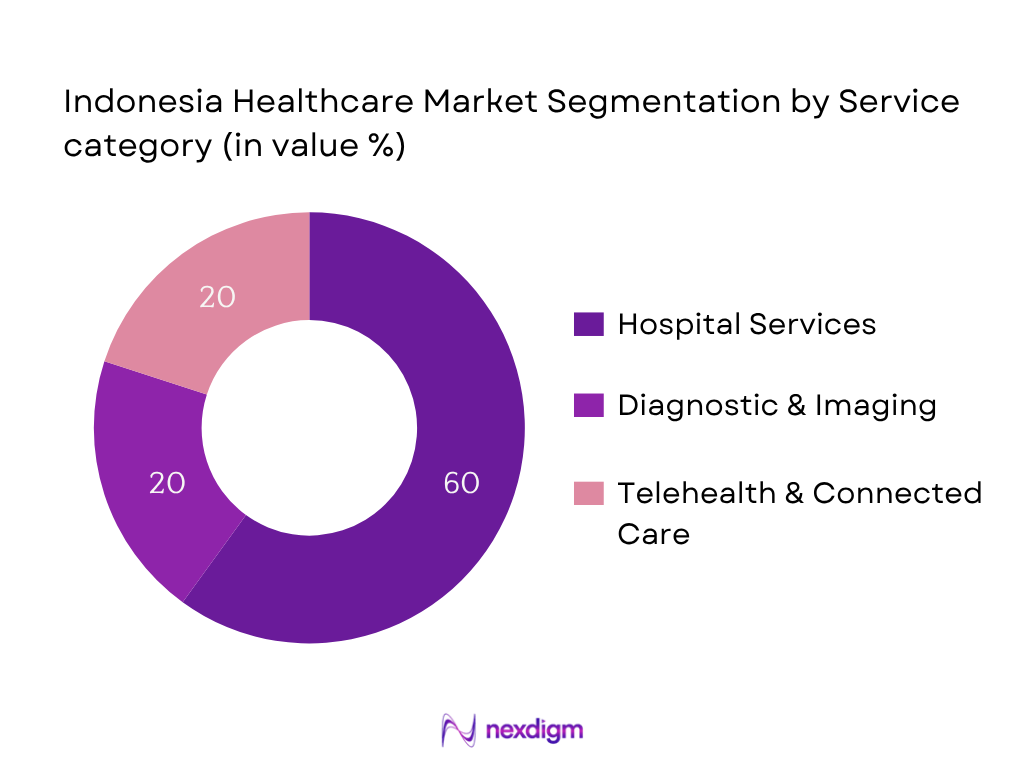
By Service Category
Hospital Services dominates in market share (~60 % in 2024) because Indonesia’s growing middle class relies predominantly on inpatient and outpatient hospital care, especially private institutions. Expansion investments by groups such as Mayapada and Mitra Keluarga boost service volume. Hospitals offer comprehensive diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical services under insurance coverage, making them the go‑to provider for complex healthcare needs.
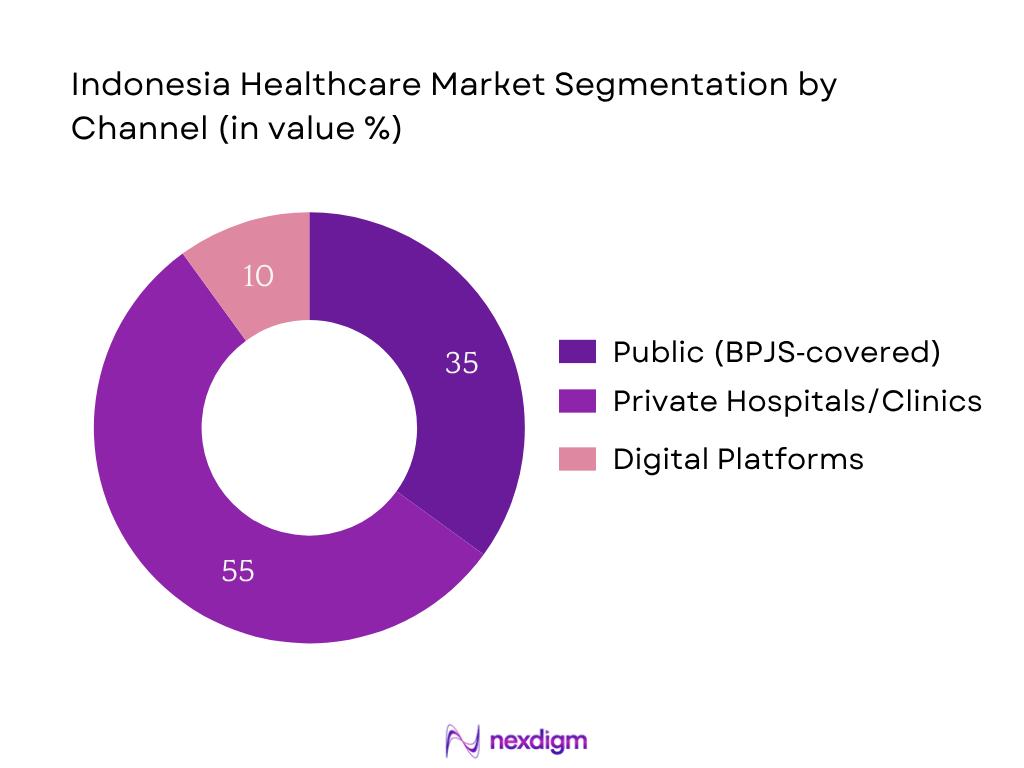
By Channel
Private hospitals and clinics lead with ~55 % market share in 2024 as they deliver higher service quality, faster turnaround, and advanced specialties compared to crowded public facilities. Rising consumer willingness to pay, growing trust in brands like Siloam, Mayapada, and Mitra Keluarga, and foreign investment in private hospital expansion reinforce dominance in this channel.
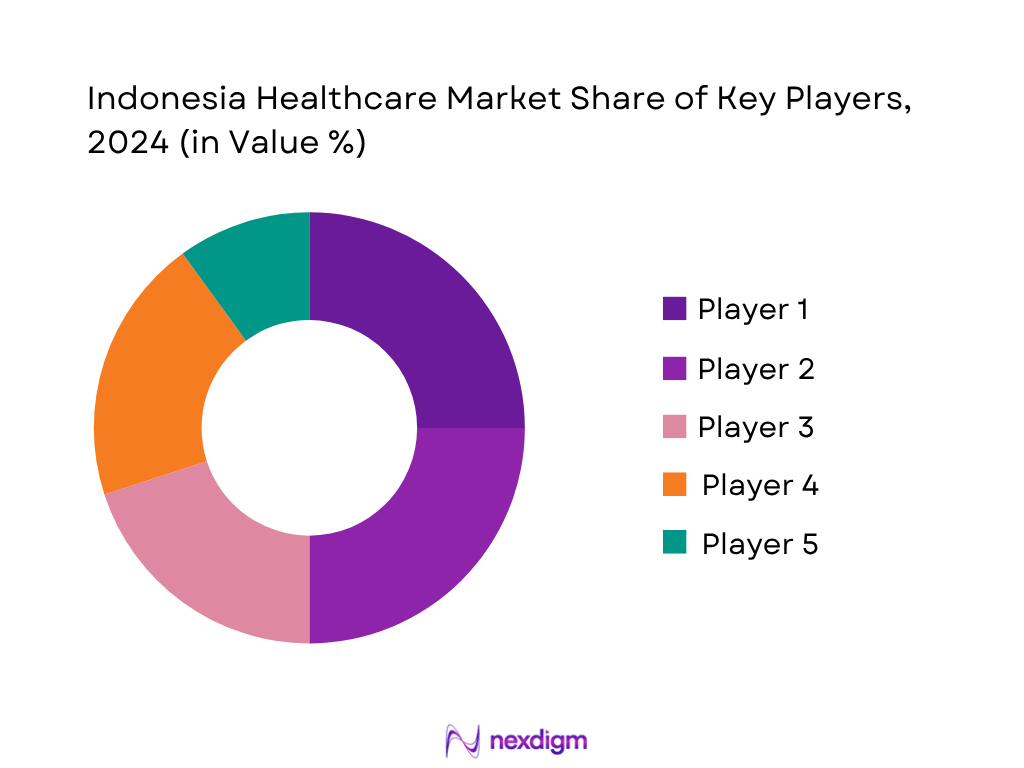
Competitive Landscape
The Indonesia healthcare market is dominated by major private groups such as Siloam Hospitals Group, Mitra Keluarga, Mayapada Healthcare, Hermina, and Omni Hospitals, alongside digital health platforms like Halodoc and Alodokter. This consolidation underscores their significant influence on service delivery, tech adoption, and nationwide expansion strategies.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Hospital Beds | Telehealth Platform | Diagnostic Labs | JCI Accreditation | Foreign Investment Partner | Digital Ecosystem |
| Siloam Hospitals Group | 2008 | Jakarta | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Mitra Keluarga | 1985 | Jakarta | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Mayapada Healthcare | 2008 | Jakarta | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hermina Hospital Group | 1994 | Bandung | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Omni Hospitals | 2012 | Tangerang (Greater Jakarta) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
Indonesia Healthcare Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Expansion of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) through BPJS
Indonesia’s National Health Insurance (JKN), administered by BPJS Kesehatan, covers approximately 277.5 million people, equivalent to 98% of the population as of 2024. In 2023, enrollment reached over 260 million (95%), up from 223 million in 2021. Public health expenditure rose to about 2.69% of GDP in 2022, increasing further into 2024. This vast coverage has notably expanded utilization: outpatient visits surged and hospital usage grew across Indonesia. As BPJS covers both public and participating private providers, it has facilitated a large shift in patient flow toward insured facilities, accelerating demand for hospital beds, diagnostics, and specialist services across both public and private sectors throughout 2023–2024.
Rising Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
Indonesia faces a growing burden of NCDs; neurological and mental health conditions accounted for 10.7% of total disease burden, with over 19 million Indonesians aged 15+ suffering mental disorders as of 2022. At the same time, prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions has increased among adults in recent national health surveys (2023/2024). Government statistics show increasing hospital admissions for chronic conditions: inpatient claims for chronic NCD management under BPJS have risen by double-digit volume in 2023–2024 compared to earlier years, pressuring hospitals and diagnostic centres. This epidemiological shift is driving sustained service demand, especially in cardiology, oncology, and chronic disease management, and boosting the need for outpatient follow‑up, imaging, lab work, and pharmaceuticals across regions.
Market Challenges
Regional Disparities in Access to Quality Care
Despite near‑universal insurance coverage, access disparities persist. Indonesia has only 0.4 doctors per 1,000 population, lower than regional peers (Thailand ~0.9, Philippines ~0.8). Physicians and specialists remain concentrated in Java, Jakarta and Bali. Meanwhile, rural provinces in Kalimantan and Papua have significantly fewer healthcare facilities per capita. Utilization data from national household surveys (2024) shows lower hospital and outpatient visits among lower‑wealth quintiles and in remote areas, citing travel time and limited provider availability. These inequities challenge uniform market reach and distort demand toward urban centres. Infrastructure gaps in diagnostics and limited clinical specialists further contribute to quality variation, making rural expansion difficult without targeted public investment.
High Out‑of‑Pocket (OOP) Expenditure Despite BPJS Coverage
Although BPJS reduced OOP as share of total health expenditure from 45.3% in 2014 to 25.1% by 2021, OOP still accounts for a substantial part of spending, especially for services not fully covered such as advanced diagnostics or private clinic fees. In 2023–2024, national surveys revealed significant OOP spending for lab testing, imaging, dental care and supplementary services—even among BPJS beneficiaries who opted for upgraded facilities. Government budget brief confirms healthcare budget share remained at around 5.6% of state budget in 2024, with households still bearing direct costs for specialized care not fully reimbursed by JKN. High OOP hampers affordability for insured population and limits consumption of elective, chronic care and private services.
Opportunities
Rise of Telehealth and Digital Therapeutics
Indonesia’s digital infrastructure push saw integration of 9,718 Puskesmas and 2,813 hospitals into JKN’s digital roadmap during 2023–2024, supported by a USD 47 million allocation for information systems integration. As clinical coding and electronic referrals scaled to training of 1,800 FKRTLs, teleconsultation and e‑prescription usage surged. Private platforms such as Halodoc and Alodokter reported increasing monthly user numbers (2024). Public‑private collaboration, underpinned by substantial state investment and rising smartphone penetration, suggest strong opportunity for expansion of remote diagnostics, e‑pharmacy and digital therapeutics throughout the country, including tier‑2 cities, to reach insured populations with decentralized care.
Investment in Tier‑2 and Rural Health Infrastructure
Government health budget allocation of 5.6% of state expenditure in 2024 continues programmatic investment into rural facility expansion, as reflected in World Bank‑backed JKN reforms and MoH infrastructure grants. New Puskesmas and upgraded hospital facilities are underway in Sumatra, Kalimantan and Sulawesi. JKN’s equitable utilization data (2024 national household survey) identified gaps in service utilization linked to wealth and insurance status. To address this, district health budgets have increased facility count and staff deployment. These improvements pave the way for increased diagnostic centre density and private clinic investments in tier‑2 cities. Investors and healthcare operators have opportunity to partner with local governments to build capacity and capture rising demand from underserved regions.
Future Outlook
Over the forecast horizon, the Indonesia healthcare market is expected to deliver solid growth driven by continued expansion of universal health coverage, private hospital bed capacity increases, and rapid digital health adoption. Government initiatives digitizing health records (Satusehat), combined with private sector investments into telemedicine, imaging, and device infrastructure, will support rising service utilisation across both public and private channels.
Major Players
- Siloam Hospitals Group
- Mitra Keluarga
- Mayapada Healthcare Group
- Hermina Hospital Group
- Omni Hospitals
- Eka Hospital
- Awal Bros Hospital Group
- Primaya Hospital Group
- BPJS Kesehatan
- Prodia Diagnostic Laboratories
- Kimia Farma
- Halodocter (Halodoc)
- Alodokter
- Lifepack
- Bio Farma
Key Target Audience
- Hospital chains and healthcare service operators
- Investments and venture capitalist firms (e.g. Bain Capital, regional PE firms)
- Government and regulatory bodies (Ministry of Health, BPJS Kesehatan, Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board)
- Private insurance companies
- Healthcare device and diagnostics equipment providers
- Telehealth and digital health platform developers
- Pharmaceutical distributors active in Indonesia
- Public healthcare financing agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
We map Indonesia’s healthcare ecosystem—including BPJS coverage, private hospital capacity, diagnostic labs, telehealth adoption—via secondary and proprietary data sources to define critical variables influencing market size and dynamics.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data (2023, 2024) on revenue by service type, facility channel, telehealth uptake and device import/investment flows are compiled to model bottom‑up market size and segmentation metrics.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Prepared market assumptions are validated through expert interviews with hospital administrators, regulatory officials (e.g. BPJS, MOH), and industry executives from major private healthcare firms.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Engagement with multiple healthcare operators and digital health platforms ensures triangulation of bottom‑up estimates, supporting validated, comprehensive market figures and forecast outputs.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Assumptions, Abbreviations, Market Sizing Approach, Consolidated Research Approach, Understanding Market Potential Through In-Depth Industry Interviews, Primary Research Approach, Limitations and Future Conclusions)
- Definition and Scope
- Healthcare Ecosystem Overview
- Timeline of Healthcare Policy Evolution
- Patient Journey and Care Continuum Analysis
- Health System Financing and Public-Private Expenditure
- Value Chain and Stakeholder Mapping
- Growth Drivers
Expansion of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) through BPJS
Rising Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)
Government Investment in Healthcare Infrastructure
Growing Medical Tourism in Jakarta and Bali
Adoption of Digital Health and EHR Systems - Market Challenges
Regional Disparities in Access to Quality Care
High OOP Expenditure Despite BPJS Coverage
Limited Availability of Skilled Healthcare Workforce
Regulatory Delays in Drug and Device Approvals
Dependence on Imported Medical Equipment - Opportunities
Rise of Telehealth and Digital Therapeutics
Investment in Tier-2 and Rural Health Infrastructure
Growing Demand for Elderly and Chronic Care Services
Entry of Global Players in Diagnostics & Lab Chains - Trends
Integration of AI and Big Data in Clinical Decision Support
Rise of Preventive Health and Personalized Medicine
Retail Pharmacy Chain Consolidation
Mobile Healthcare Units for Remote Access - Government Regulations
BPJS Policies & Reimbursement Guidelines
MOH Licensing and Hospital Accreditation
Regulations for Telemedicine and e-Pharmacy - SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- By Value, 2019-2024
- By Volume, 2019-2024
- By Healthcare Access Points (Hospitals, Clinics, Telemedicine, Pharmacies), 2019-2024
- By Service Type (In Value %)
Inpatient Care
Outpatient Care
Preventive & Wellness Services
Diagnostic Imaging & Pathology
Emergency & Trauma Services - By Healthcare Facility Ownership (In Value %)
Public Hospitals
Private Hospitals
Primary Healthcare Clinics (Puskesmas)
Private Specialty Clinics
Telehealth Platforms - By Therapeutic Area (In Value %)
Cardiology
Oncology
Orthopedics
General Surgery
Maternity & Childcare - By Payer Type (In Value %)
BPJS (National Health Insurance)
Private Insurance
Out-of-Pocket (OOP)
Employer-Funded Health Plans
NGO/Government Aid - By Region (In Value %)
Java
Sumatra
Kalimantan
Sulawesi
Papua
- Market Share of Leading Players by Value and Volume
- Cross Comparison Parameters (Company Overview, Key Business Segments, Number of Hospital Beds, Number of Outlets (Clinics/Pharmacies), Digital Health Offerings, Service Specialization (e.g., Oncology, Cardiology), Accreditation Status (e.g., JCI, MOH), Partnerships and International Collaborations)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Competitors
- Pricing Analysis by Procedure Category (Surgery, Diagnostics, Consultation)
- Detailed Company Profiles
Siloam Hospitals Group
Mitra Keluarga Hospitals
Mayapada Hospital Group
RSUPN Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo
Eka Hospital Group
Hermina Hospital Group
Awal Bros Hospital Group
Omni Hospitals
Primaya Hospital
Halodoc
Alodokter
Kimia Farma
Prodia Diagnostic Laboratories
BPJS Kesehatan
Bio Farma
- Consumer Preferences and Patient Behavior
- Insurance Coverage and Utilization Patterns
- Healthcare Spending Patterns and Budget Allocations
- Accessibility and Trust in Healthcare Services
- Unmet Needs and Service Gaps
- By Value, 2025-2030
- By Volume, 2025-2030
- By Healthcare Access Points, 2025-2030


