Market Overview
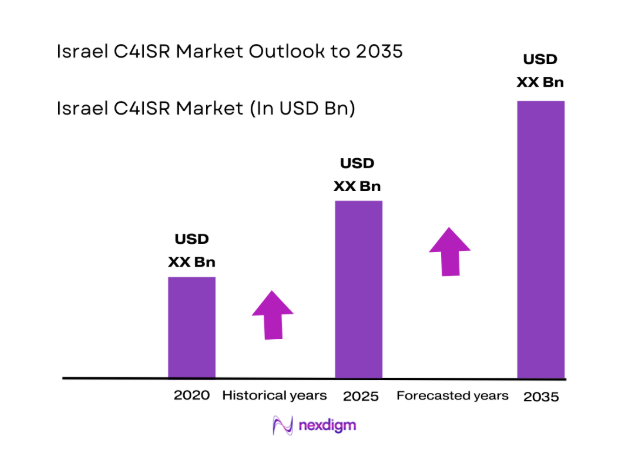
The Israel C4ISR market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense modernization, indigenous technology development, and operational network upgrades. System deployments increased across multiple domains, with platform upgrades supporting around ~ operational units and integrated across ~ command nodes. Demand intensity remained high due to persistent security requirements and accelerated digital battlefield transformation. Procurement activity focused on interoperability, artificial intelligence integration, and real-time data fusion, supporting resilient command structures and rapid decision-making cycles across active operational environments.
The market is primarily concentrated around Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Beersheba, driven by proximity to defense headquarters, technology clusters, and military command centers. These regions benefit from mature defense infrastructure, skilled workforce availability, and close coordination between military users and system developers. Strong policy support streamlined procurement pathways, and classified innovation ecosystems further reinforce regional dominance. Peripheral regions participate mainly through deployment and operational usage rather than system development or integration activities.
Market Segmentation
By Application
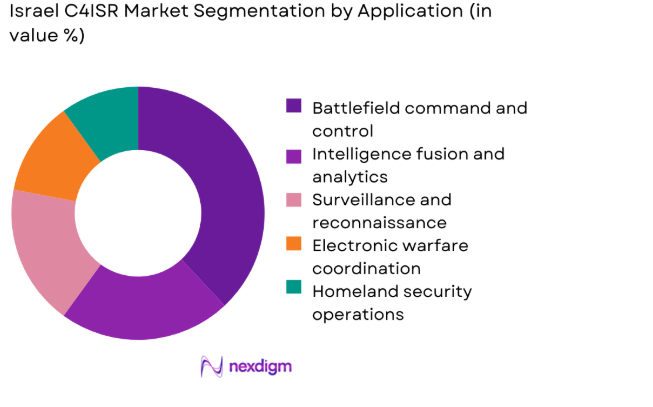
Battlefield command and control dominates the Israel C4ISR market due to its central role in multi-domain operations and rapid threat response requirements. High operational tempo and continuous border monitoring necessitate real-time situational awareness, secure communications, and integrated intelligence dissemination. Command applications benefit from sustained investment in software-defined systems, AI-enabled analytics, and joint-force interoperability. Surveillance, intelligence fusion, and electronic warfare coordination also contribute, but command-centric architectures remain foundational. The emphasis on speed, resilience, and data accuracy drives prioritization of command and control applications across land, air, naval, cyber, and space operational environments.
By Technology Architecture
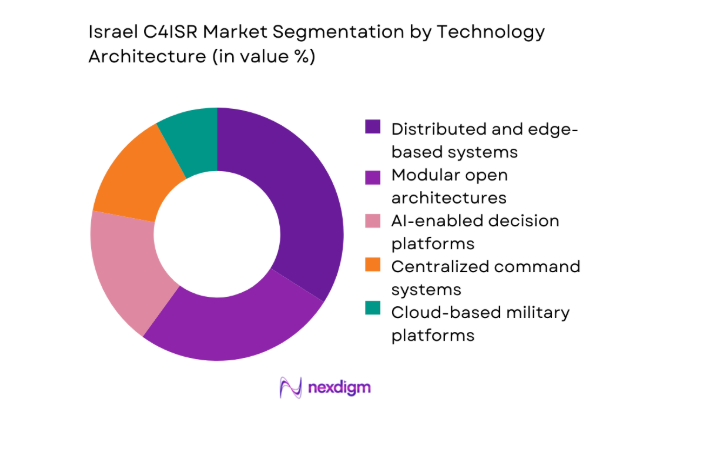
Distributed and edge-based architectures lead adoption due to their resilience against network disruptions and electronic warfare threats. These architectures enable decentralized decision-making, faster data processing, and mission continuity under contested conditions. Modular open systems further enhance flexibility, allowing rapid upgrades and integration of new sensors or analytics tools. Centralized systems remain relevant for strategic oversight, but operational emphasis increasingly favors hybrid architectures. Cloud-enabled and AI-supported frameworks strengthen scalability, predictive capabilities, and cross-domain integration, aligning technology architecture choices with Israel’s dynamic operational doctrine.
Competitive Landscape
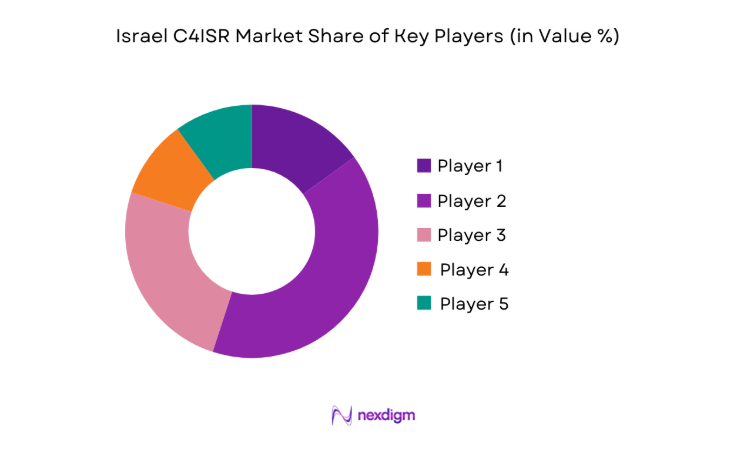
The Israel C4ISR market is characterized by a concentrated structure with strong domestic players supporting national security priorities. Companies compete on technological depth, system integration capability, and long-term service reliability, while maintaining compliance with stringent security and regulatory requirements.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Haifa | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Lod | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Haifa | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elta Systems | 1967 | Ashdod | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tadiran Communications | 1962 | Holon | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel C4ISR Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Increasing emphasis on multi-domain operations
Operational doctrines increasingly emphasize synchronized land, air, naval, cyber, and space actions requiring unified command visibility. During 2024 deployments, integrated data flows improved coordination between dispersed units across contested environments significantly. Advanced C4ISR platforms support rapid cross-domain tasking, shortening decision loops during high-tempo operational scenarios. Network-centric warfare priorities drive continuous upgrades to command software, sensors, and secure communications layers. Multi-domain exercises conducted in 2025 reinforced requirements for interoperable and resilient command infrastructures. These doctrines increase reliance on distributed architectures capable of sustaining operations under electronic and cyber pressure. Real-time intelligence fusion enables commanders to manage simultaneous engagements effectively across geographically separated theaters. Operational success increasingly depends on seamless integration between manned, unmanned, and autonomous systems. This strategic shift structurally elevates demand for advanced C4ISR capabilities across force levels. Consequently, procurement planning increasingly aligns with long-term multi-domain operational readiness objectives.
Persistent regional security threats
Ongoing regional instability sustains continuous demand for intelligence, surveillance, and command coordination capabilities. Border monitoring, missile defense integration, and counter-terror operations require persistent situational awareness across domains. During 2024 operational cycles, threat monitoring intensity remained consistently high across multiple fronts. C4ISR systems enable early warning, rapid response coordination, and escalation management under uncertain conditions. Persistent threats justify accelerated modernization programs rather than episodic procurement approaches. Intelligence-driven operations increasingly rely on fused sensor data processed through centralized and edge nodes. Command systems support simultaneous defensive and offensive missions without degrading responsiveness. Security pressures also encourage redundancy, resilience, and hardened communication architectures. These conditions maintain stable utilization rates across deployed C4ISR platforms. As threats persist, sustained investment focus remains strategically unavoidable.
Challenges
Budget prioritization across competing defense programs
Defense budgeting requires balancing C4ISR investments against air, naval, missile defense, and manpower priorities. Despite operational importance, command systems compete with visible kinetic platforms for funding allocation. During 2025 planning cycles, prioritization tradeoffs intensified across modernization portfolios. Multi-year programs must align with fiscal ceilings and shifting threat perceptions. Incremental upgrades sometimes delay comprehensive architecture overhauls due to resource constraints. Budget pressures can fragment procurement into phased deployments rather than unified solutions. This complicates integration timelines and increases lifecycle management complexity. Financial oversight processes also extend approval cycles for advanced software-intensive programs. As a result, capability deployment pacing may lag operational requirements. Effective prioritization remains a persistent structural challenge.
Integration complexity across legacy and new systems
Israel operates diverse legacy platforms requiring interoperability with modern digital architectures. Integrating older sensors and communications with AI-enabled systems introduces technical complexity. During 2024 upgrades, interface mismatches and data standardization challenges persisted. Proprietary legacy protocols often limit seamless information exchange across domains. Integration testing extends deployment timelines and increases program management overhead. Cybersecurity certification further complicates integration across heterogeneous systems. Operational units require continuity, limiting tolerance for prolonged system downtime. These factors elevate technical risk during modernization initiatives. System-of-systems integration demands specialized engineering expertise and coordination. Consequently, integration complexity remains a major operational constraint.
Opportunities
Next-generation AI-driven decision systems
Artificial intelligence enables automated data correlation, predictive analytics, and decision support under information overload conditions. During 2024 trials, AI-assisted tools improved threat classification and response prioritization. Machine learning models enhance pattern recognition across multi-sensor data streams. These capabilities reduce cognitive burden on commanders during high-tempo operations. Indigenous software expertise supports rapid customization for operational doctrines. AI integration also enables adaptive learning from operational feedback loops. Decision systems increasingly evolve through software updates rather than hardware replacements. This creates scalable upgrade pathways across deployed platforms. Adoption accelerates as trust in algorithmic support improves. Overall, AI-driven systems represent a high-impact growth avenue.
Space-based ISR and small satellite integration
Space assets increasingly support persistent surveillance, communications, and navigation resilience. Small satellite constellations enhance redundancy and revisit rates over sensitive regions. During 2025 deployments, integration with terrestrial C4ISR systems improved data continuity. Space-based ISR supports strategic depth beyond line-of-sight limitations. Indigenous launch and satellite capabilities enable rapid constellation adjustments. Integration with ground command networks enhances multi-domain situational awareness. Space assets also strengthen resilience against terrestrial infrastructure disruption. Demand grows for seamless space-to-ground data fusion architectures. This expands system scope beyond traditional battlefield boundaries. Consequently, space integration presents substantial long-term opportunity.
Future Outlook
The Israel C4ISR market is expected to evolve through deeper AI integration, expanded space-based capabilities, and greater emphasis on resilience. From 2026 onward, modernization programs are likely to prioritize interoperability and autonomy. Long-term outlook remains stable, supported by security imperatives and sustained technological innovation.
Major Players
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elta Systems
- Tadiran Communications
- Orbit Communication Systems
- Aeronautics Group
- Controp Precision Technologies
- RT LTA Systems
- UVision Air
- Cellebrite
- NSO Group
- Elbit Systems C4I and Cyber
- IAI Malat
- Elta North America
Key Target Audience
- Israel Defense Forces procurement directorates
- Ministry of Defense acquisition departments
- Homeland security and border protection agencies
- Intelligence and cyber command units
- Defense system integrators
- Secure communications operators
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational scope, system taxonomy, and platform classifications were defined. Mission-critical functions and deployment environments were identified. Technology architectures and application domains were mapped.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Program-level demand drivers and deployment patterns were analyzed. Segmentation frameworks were constructed based on operational usage. Adoption dynamics were evaluated across domains.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through domain expert interactions. Operational feedback informed capability relevance assessments. Integration challenges and future requirements were refined.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were consolidated into a structured analytical narrative. Cross-validation ensured internal consistency. Final insights were aligned with strategic defense context.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope of C4ISR within Israeli defense doctrine, platform- and domain-based segmentation aligned to IDF force structure, bottom-up program-level market sizing using procurement and upgrade cycles, revenue attribution by system lifecycle stage and contract type, primary validation through Israeli defense OEMs and former IDF C4I officials, triangulation of SIPRI data with national budget disclosures and export records, assumptions linked to classified program opacity and export control constraints)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution in Israel’s network-centric warfare doctrine
- Operational usage across multi-domain operations
- Defense-industrial and innovation ecosystem structure
- Supply chain, integrators, and subsystem sourcing
- Regulatory and security clearance environment
- Growth Drivers
Increasing emphasis on multi-domain operations
Persistent regional security threats
High adoption of AI and data fusion technologies
Strong domestic defense R&D ecosystem
Continuous modernization of IDF command networks
Expansion of C4ISR exports - Challenges
Budget prioritization across competing defense programs
Integration complexity across legacy and new systems
Cybersecurity risks and electronic warfare threats
Dependence on classified and restricted technologies
Export control and geopolitical constraints
Talent shortages in advanced software and AI - Opportunities
Next-generation AI-driven decision systems
Space-based ISR and small satellite integration
Interoperability solutions for allied operations
C4ISR upgrades for unmanned and autonomous platforms
Cyber-resilient and quantum-secure communications
Dual-use technologies for civilian security markets - Trends
Shift toward software-defined C4ISR
Increased use of real-time data analytics
Edge computing at tactical levels
Modular open systems architecture adoption
Integration of cyber and electronic warfare data
Greater emphasis on resilience and redundancy - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land-based tactical C4ISR systems
Airborne and UAV-integrated C4ISR systems
Naval and coastal surveillance C4ISR systems
Space-enabled and satellite-linked C4ISR assets
Joint and multi-domain command platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Battlefield command and control
Intelligence fusion and data analytics
Surveillance and target acquisition
Electronic warfare coordination
Homeland security and border monitoring - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Centralized command architectures
Distributed and edge-based architectures
AI-enabled decision support systems
Cloud-based military data platforms
Open-architecture and modular C4ISR - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Israel Defense Forces
Homeland security and border agencies
Defense intelligence organizations
Export-oriented defense programs
Critical infrastructure security operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Satellite communications
Line-of-sight tactical networks
Beyond-line-of-sight data links
Secure IP-based military networks
Hybrid and multi-layer connectivity - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Command region
Southern Command region
Central Command region
Naval operational zones
Space and cyber operational domains
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (technology breadth, system interoperability, AI and analytics capability, cybersecurity resilience, export footprint, integration capability, lifecycle support, pricing flexibility)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elta Systems
Elbit Systems C4I and Cyber
Aeronautics Group
Orbit Communication Systems
Tadiran Communications
Controp Precision Technologies
RT LTA Systems
UVision Air
Cellebrite
NSO Group
Elta North America
IAI Malat
- Operational demand and mission-critical requirements
- Procurement and classified tender dynamics
- Vendor selection and technology sovereignty criteria
- Defense budget allocation and multi-year planning
- Implementation risks and interoperability barriers
- Lifecycle support and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


