Market Overview
The Israel close in weapon systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained procurement cycles and accelerated modernization across naval and ground defense programs. Current deployment levels indicate steady absorption across frontline platforms, supported by ongoing system upgrades and lifecycle sustainment programs. Operational readiness remains high due to continuous integration of sensors, fire control, and interceptor components within standardized architectures. Program execution benefits from coordinated procurement planning, stable funding pathways, and aligned industrial participation.
Demand concentrates around coastal naval bases and forward-deployed ground formations, where layered defense infrastructure and persistent threat exposure drive acquisition prioritization. Urban-adjacent defense nodes benefit from mature command networks, hardened logistics corridors, and rapid maintenance turnaround capabilities. Concentrated industrial clusters support system integration, software updates, and sustainment services. Policy emphasis on indigenous development, interoperability mandates, and export controls further shapes deployment density and ecosystem maturity across priority operational theaters.
Market Segmentation
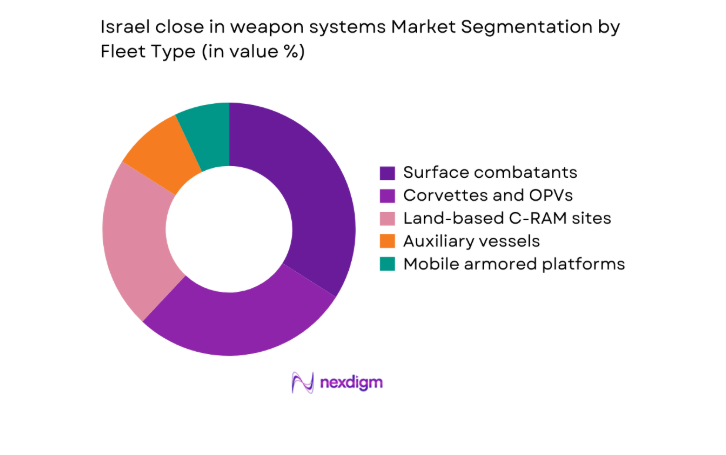
By Fleet Type
Naval surface combatants and littoral patrol fleets dominate deployments due to persistent maritime threat exposure and high-value asset protection requirements. Corvettes and offshore patrol vessels host integrated close-in weapon systems within layered defense architectures, enabling rapid cueing from shipborne sensors and cooperative engagement networks. Land-based counter-rocket and mortar configurations support forward operating areas, protecting critical infrastructure nodes and maneuver formations. Auxiliary vessels adopt modular mounts for point defense during high-risk transits. Platform modernization programs emphasize open architectures, enabling software-defined upgrades and sensor fusion across mixed fleets, reinforcing operational continuity across maritime and ground environments.
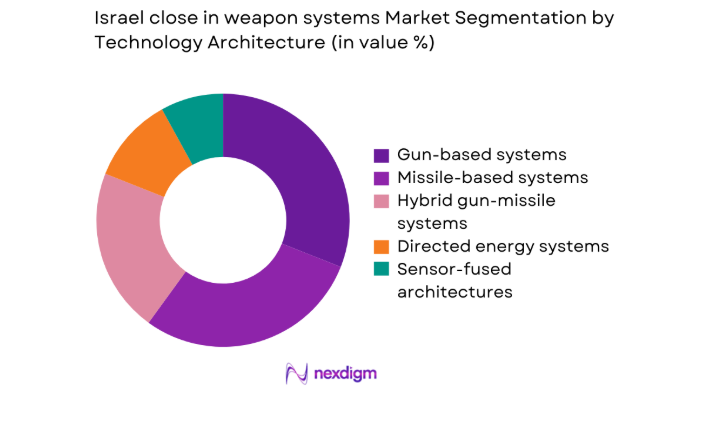
By Technology Architecture
Gun-based architectures retain operational relevance for high-rate terminal defense against saturation threats, benefiting from mature logistics and proven reliability. Missile-based systems extend engagement envelopes and enable layered interception against complex profiles, particularly low-altitude and maneuvering targets. Hybrid architectures integrate guns and interceptors with unified fire control, improving kill probability under constrained timelines. Directed energy systems progress through operational trials, prioritizing reduced cost per engagement and deep magazines. Sensor-fused architectures enhance discrimination accuracy through multi-sensor correlation, supporting cooperative engagement and minimizing fratricide risks across congested operational spaces.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment reflects concentrated system integration capabilities, with differentiation driven by fire control software maturity, interceptor performance, and platform integration depth. Long-cycle procurement favors suppliers with proven sustainment footprints, certification readiness, and operational validation across diverse threat profiles.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Raytheon | 1922 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | United States | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel close in weapon systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising missile and rocket threat environment
Persistent regional tensions elevate threat densities, increasing operational demand for resilient point defense across critical assets. Threat vectors diversify annually, requiring adaptive fire control and faster reaction timelines across deployed platforms. Exercise data from 2024 indicates increased simulated engagements during multi-axis attack scenarios across littoral approaches. Operational planners prioritize layered defenses integrating sensors, shooters, and networks under compressed decision timelines. Rapid cueing requirements intensify investment in sensor fusion and automated threat classification algorithms. Interoperability mandates encourage integration across naval and ground-based command networks during combined operations. Readiness assessments demonstrate increased operational tempo sustained across multiple deployment cycles without performance degradation. Training pipelines expand to accommodate higher system utilization and maintenance proficiency across frontline units. Maintenance planning adapts to higher firing rates and sensor duty cycles under elevated threat conditions. Policy emphasis on force protection reinforces procurement prioritization for point defense capabilities across platforms.
Modernization of naval and coastal defense assets
Fleet recapitalization programs prioritize survivability upgrades across aging platforms operating in contested littoral environments. Modern combat systems architectures enable modular upgrades without extended dry dock availability disruptions. Integration milestones achieved in 2024 demonstrate reduced installation timelines across standardized combat system interfaces. Platform modernization emphasizes cooperative engagement compatibility with shore-based command and sensor networks. Software-defined fire control supports rapid threat library updates across distributed fleets. Sustainment contracts expand availability-based logistics to ensure high operational readiness across deployments. Training modernization aligns crew proficiency with advanced automation and human-machine teaming interfaces. Digital twins support predictive maintenance planning and accelerated certification cycles for upgrades. Interoperability testing validates compatibility with coalition systems during combined maritime security exercises. Modernization pathways reduce lifecycle risks while extending platform relevance across evolving threat landscapes.
Challenges
High unit costs and lifecycle sustainment expenses
Sustainment intensity increases with higher operational tempo, amplifying component wear across sensors and effectors. Spare parts provisioning faces variability due to specialized components and long qualification cycles. Depot-level maintenance requires skilled technicians, creating workforce bottlenecks across sustainment facilities. Configuration management complexity grows as platforms adopt modular software-defined components across fleets. Inventory optimization remains challenging under fluctuating readiness requirements across multiple theaters. Training burdens increase as crews transition between legacy and upgraded system configurations. Validation and safety certification cycles extend timelines for fielding incremental capability upgrades. Integration testing demands specialized ranges and instrumentation with constrained scheduling availability. Sustainment planning must balance readiness targets against maintenance windows and operational commitments. Lifecycle management complexity elevates total ownership burdens across long-duration platform programs.
Integration complexity with existing C2 and sensors
Legacy command systems exhibit interface limitations when integrating advanced fire control software modules. Data latency across heterogeneous sensor networks constrains real-time cueing effectiveness during saturation attacks. Certification requirements necessitate extensive interoperability testing across multiple software baselines. Cybersecurity hardening adds integration overhead across networked engagement architectures. Electromagnetic compatibility challenges arise from dense sensor suites on compact platforms. Configuration drift across fleets complicates standardized deployment of updates and patches. Operator training must address human-machine interface changes across successive software revisions. Coalition interoperability requires alignment with varying data standards and messaging protocols. Validation environments struggle to replicate congested electromagnetic conditions encountered operationally. Integration roadmaps demand coordinated scheduling across shipyards, depots, and operational units.
Opportunities
Adoption of directed energy for cost-per-shot reduction
Directed energy systems offer scalable engagement options for high-volume, low-cost defensive firing sequences. Power and thermal management improvements enable sustained firing profiles across compact platforms. Operational trials in 2024 demonstrate improved beam stability against small aerial threats. Integration with sensor fusion enhances target tracking precision and engagement reliability. Hybrid architectures combine lasers with kinetic interceptors for layered engagement flexibility. Training curricula evolve to incorporate safety protocols and engagement doctrine for energy weapons. Sustainment models shift toward component health monitoring and optical maintenance regimes. Software-defined beam control supports rapid adaptation to changing atmospheric conditions. Logistics footprints reduce reliance on kinetic interceptor resupply during extended operations. Directed energy adoption supports resilience under prolonged saturation attack conditions.
Upgrades and mid-life modernization programs
Mid-life upgrades extend platform relevance while incorporating advances in sensors and fire control software. Open architectures facilitate incremental capability insertion without major structural modifications. Fleet-wide retrofit campaigns standardize interfaces to reduce integration risk across diverse platforms. Digital certification accelerates validation cycles for software enhancements across operational units. Modernized systems improve cooperative engagement effectiveness across networked defense architectures. Sustainment efficiencies emerge from standardized components and shared maintenance tooling. Training modernization aligns operator proficiency with updated automation and decision support tools. Upgrade pathways preserve platform availability during phased installation schedules. Interoperability improvements enhance coalition operations during combined exercises and deployments. Modernization programs create sustained demand across integration and sustainment ecosystems.
Future Outlook
The market outlook anticipates continued prioritization of layered point defense across maritime and ground domains, with increasing emphasis on networked engagement and automation. Directed energy integration will mature alongside hybrid architectures, while software-defined upgrades accelerate capability refresh cycles. Interoperability mandates and indigenous development priorities will shape procurement pathways. Export controls and certification regimes will continue influencing deployment patterns. Sustainment models will evolve toward availability-based frameworks.
Major Players
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Raytheon
- Lockheed Martin
- BAE Systems
- Thales Group
- Rheinmetall
- Leonardo
- Saab
- Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
- MBDA
- Northrop Grumman
- ASELSAN
- Hanwha Defense
Key Target Audience
- Defense ministries and procurement directorates
- Naval acquisition commands
- Army air defense and force protection units
- Homeland security agencies responsible for critical infrastructure protection
- System integrators and prime contractors
- Platform OEMs and shipyards
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Government and regulatory bodies with agency names
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Operational roles, platform classes, threat profiles, integration architectures, and sustainment pathways were defined through structured scoping workshops. Capability boundaries, performance attributes, and deployment contexts were mapped to establish a consistent analytical framework across maritime and ground domains.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Segmentation structures were constructed across fleet types and technology architectures. Deployment densities, integration milestones, and readiness indicators from recent operational cycles were synthesized to model adoption dynamics and capability pathways.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Assumptions were validated through structured consultations with operators, maintainers, and systems engineers. Feedback loops refined integration feasibility, sustainment constraints, and modernization timelines across representative platform categories.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were reconciled across operational, technical, and policy dimensions. Insights were consolidated into coherent narratives, ensuring internal consistency across segmentation, analysis, and forward-looking assessments.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and System Scope Boundaries for CIWS in Israel, Platform and Fleet Taxonomy Mapping across Naval and Land C-RAM Deployments, Bottom-up Unit Shipment and Installed Base Estimation by Platform Class, Contract Value Attribution and Multi-year Program Revenue Phasing, Primary Interviews with IDF, Navy Procurement, and Integrators, Supplier Financials, Tender Archives, and Export Control Data Mining, Triangulation with Test Ranges, Deployment Announcements, and Assumption Reconciliation)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Usage and operational concepts
- Ecosystem structure
- Supply chain and integration pathways
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising missile and rocket threat environment
Modernization of naval and coastal defense assets
Shift toward multi-layer air and missile defense architectures
Operational lessons from recent conflicts and tests
Advances in sensors, fire control, and interceptors
Government focus on indigenous defense production - Challenges
High unit costs and lifecycle sustainment expenses
Integration complexity with existing C2 and sensors
Spectrum congestion and electronic warfare threats
Stringent testing, certification, and safety requirements
Export controls and technology transfer ограничения
Supply chain dependencies for critical components - Opportunities
Adoption of directed energy for cost-per-shot reduction
Upgrades and mid-life modernization programs
Export-driven scale for Israeli-developed systems
Joint development with allied navies and forces
Retrofit opportunities for legacy platforms
AI-enabled fire control and threat discrimination - Trends
Convergence of C-RAM and naval CIWS roles
Increased emphasis on networked and cooperative engagement
Growth of laser and hybrid intercept solutions
Modular open systems architectures adoption
Emphasis on software-defined upgrades
Higher automation and reduced crew workload - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Surface combatants
Corvettes and offshore patrol vessels
Auxiliary and support ships
Land-based C-RAM sites
Armored and mobile platforms - By Application (in Value %)
Anti-ship missile defense
Rocket, artillery, and mortar interception
Unmanned aerial vehicle defense
Manned aircraft terminal defense
Surface and asymmetric threat defense - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Gun-based CIWS
Missile-based CIWS
Hybrid gun-missile systems
Directed energy and laser-based systems
Sensor-fused multi-layer architectures - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Navy
Army and ground forces
Air force and air defense command
Homeland security and border protection
Critical infrastructure protection - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
C2-integrated systems
Network-centric cooperative engagement
Multi-sensor fusion networks
Battle management integrated nodes - By Region (in Value %)
Northern Command area
Central Command area
Southern Command area
Coastal and littoral waters
Offshore economic zone
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (System performance envelope, Interceptor or gun rate of fire, Sensor and fire control integration depth, Platform compatibility, Upgrade and scalability roadmap, Local content and offset capability, Lifecycle support footprint, Cost per engagement)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Raytheon
Lockheed Martin
BAE Systems
Thales Group
Rheinmetall
Leonardo
Saab
Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace
MBDA
Northrop Grumman
ASELSAN
Hanwha Defense
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


