Market Overview
The Israel coherent radar market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting steady procurement activity and ongoing modernization priorities. Demand remains anchored in defense readiness objectives, with sustained emphasis on system reliability and mission continuity. Procurement cycles favor long service lifecycles and upgradeability over frequent replacements. Acceptance and certification processes are aligned with operational readiness requirements, shaping deployment timelines. Interoperability standards influence system configuration decisions across platforms. Lifecycle planning continues to prioritize availability, resilience, and long-term sustainment.
Activity concentrates around major defense clusters and coastal infrastructure, where mature integration ecosystems reduce deployment friction and accelerate certification. Central and northern corridors host dense command networks, enabling efficient sensor fusion and training continuity. Naval bases and airfields sustain steady upgrade cycles, while border regions emphasize persistent coverage. Policy alignment and security clearances shape supplier participation, and local manufacturing depth supports rapid fielding. Collaboration among primes, integrators, and software houses anchors resilience across environments.
Market Segmentation
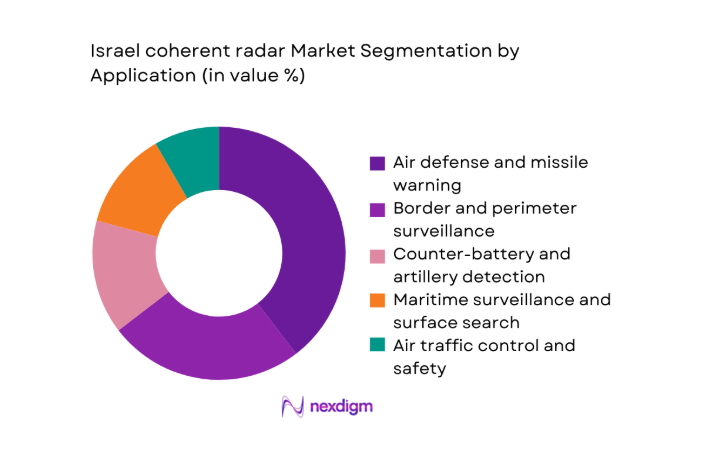
By Application
Air defense and missile warning dominates due to continuous readiness mandates, layered sensor doctrines, and persistent integration with command networks supporting rapid cueing and engagement. Border surveillance and counter battery roles follow, driven by terrain diversity, asymmetric threat profiles, and requirements for sustained uptime. Maritime surveillance and air traffic safety maintain steady adoption because port density and airspace management require dependable coherent processing. Weather and environmental monitoring remains niche but influential for calibration practices. The application mix reflects mission criticality, integration complexity, and upgrade cadence, which collectively prioritize defense centric deployments over purely civil uses while preserving cross domain interoperability.
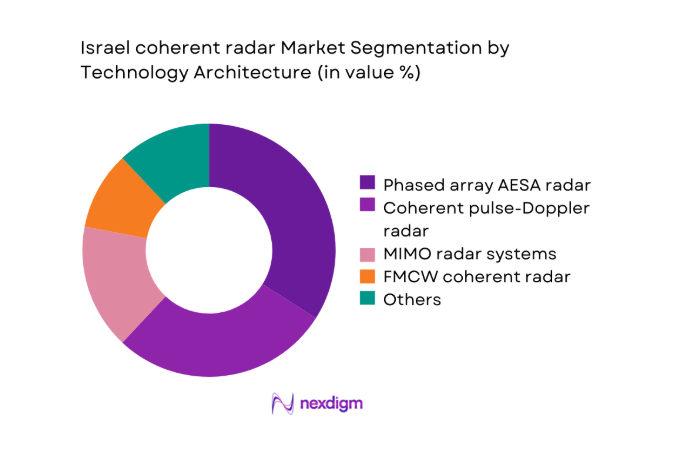
By Technology Architecture
AESA and phased array configurations lead because beam agility, reliability, and electronic protection align with multi domain requirements and dense spectrum environments. Coherent pulse Doppler systems remain prevalent for ground and naval missions, offering balanced performance and upgrade pathways. MIMO architectures are expanding where coverage continuity and interference mitigation matter, particularly across complex borders. FMCW coherent solutions support compact platforms, including unmanned deployments. Software defined radar underpins lifecycle flexibility, enabling incremental capability releases and faster certification cycles. Architecture choices therefore reflect mission density, upgrade economics, and integration readiness across platforms.
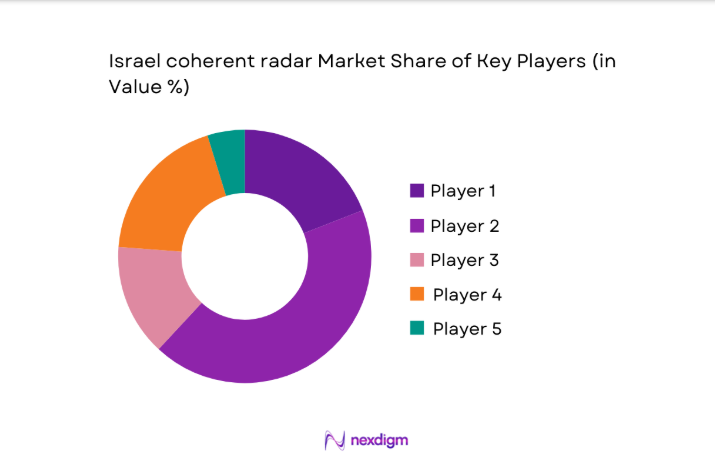
Competitive Landscape
Competition centers on domestic integration depth, export compliance readiness, and long term service commitments, with partnerships shaping delivery capacity and upgrade roadmaps.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elta Systems | 1969 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Israel | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Thales | 1893 | France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Leonardo | 1948 | Italy | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel coherent radar Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Rising air and missile defense requirements
Rising air and missile defense requirements continue reshaping acquisition priorities, as 24 operational platforms and 25 upgrade tracks remain synchronized. Integrated command networks demand coherent processing reliability, which encourages sustained investment in sensor resilience and cross domain interoperability standards. Recent readiness exercises highlighted detection continuity, prompting agencies to streamline maintenance cycles and certification sequences across platforms. Training pipelines expanded during 25 intake cycles, reinforcing operator proficiency and accelerating fielding confidence across diverse mission environments. Border proximity increases alert density, which necessitates rapid beam steering and dependable clutter suppression during complex operational scenarios. System architects therefore prioritize scalable arrays, modular software baselines, and consistent spares planning to preserve availability metrics. The ecosystem benefits from standardized interfaces, enabling faster integration with legacy command posts and contemporary decision support tools. Procurement frameworks emphasize lifecycle support, aligning sustainment milestones with operational tempo across air, land, and maritime theaters. Testing regimes incorporate 24 scenario sets, improving validation depth without extending acceptance timelines or overburdening certification authorities. These dynamics collectively sustain demand momentum while reinforcing performance expectations across deployments and modernization programs.
Border security and persistent surveillance needs
Border security and persistent surveillance needs remain prominent, with 24 coverage sectors and 25 coordination nodes requiring uninterrupted situational awareness. Terrain variability drives demand for adaptive waveforms, ensuring consistent detection across urban clutter, desert expanses, and maritime approaches. Operators prioritize uptime metrics, which reinforces investments in redundancy, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics across distributed sites. Data fusion workflows benefit from coherent returns, enabling improved track continuity and reduced operator workload during extended monitoring periods. Interagency coordination frameworks expanded during 25 planning cycles, improving tasking efficiency and cross border information exchange. Training schedules incorporate 24 simulation modules, strengthening response consistency during escalation or routine patrol activities. Integration with unmanned platforms extends dwell time, while network links preserve command visibility across dispersed checkpoints. Policy alignment supports sustained procurement, as compliance processes streamline certification for incremental capability releases. Supply chains adapt to spares forecasting, reducing downtime risks and supporting mission assurance objectives. Persistent surveillance therefore anchors long term planning, balancing coverage density with manageable operational complexity.
Challenges
High development and lifecycle costs
High development and lifecycle costs challenge planning, even as 24 platform variants and 25 configuration baselines increase engineering workload. Certification cycles demand extensive testing, which extends schedules and strains integration teams across multiple concurrent upgrade efforts. Sustainment budgets prioritize availability, but component obsolescence introduces recurring redesign and qualification activities for critical subsystems. Software maintenance burdens grow as capabilities expand, requiring disciplined configuration management and rigorous regression testing practices. Training pipelines must accommodate new features, adding time and resource pressures across operational units and support organizations. Infrastructure upgrades for cooling and power impose additional constraints, particularly at remote sites with limited capacity. Procurement frameworks attempt to smooth expenditures, yet long lead components complicate scheduling and inventory optimization strategies. Risk management offices increasingly require parallel prototypes, which elevates upfront commitments before field validation occurs. Vendor coordination across tiers introduces contractual complexity, slowing decision cycles and sometimes deferring capability insertion opportunities. These factors collectively constrain pace, even while operational demand remains consistently high.
Export control and regulatory constraints
Export control and regulatory constraints shape program timelines, with 24 documentation packages and 25 review gates embedded within approval pathways. Compliance teams must reconcile technical disclosures with security policies, which lengthens coordination cycles across agencies and partners. International collaborations require careful interface definition, limiting architecture openness and constraining component sourcing flexibility. Testing artifacts and cryptographic modules undergo repeated audits, extending acceptance schedules and increasing administrative overhead for integrators. Training for compliance officers expanded during 25 sessions, reflecting the growing complexity of cross border program governance. Contract negotiations incorporate contingency clauses, which can slow milestone commitments and complicate supplier alignment. Configuration changes trigger revalidation steps, affecting rollout sequencing across operational units and maintenance depots. Data handling rules restrict cloud analytics usage, prompting investment in secured on premise processing alternatives. Documentation harmonization efforts reduce duplication, yet approval calendars still dictate delivery rhythms and upgrade windows. Regulatory discipline therefore ensures security objectives, but it continues influencing speed and architectural choices.
Opportunities
Upgrades of legacy radar fleets to AESA and MIMO
Upgrades of legacy radar fleets to AESA and MIMO create momentum, with 24 retrofit candidates and 25 modernization work packages identified. Phased implementation allows continuity, minimizing downtime while introducing beam agility and improved interference resilience across coverage sectors. Modular backends simplify integration, enabling incremental capability releases without disrupting established command interfaces and training regimes. Operators report efficiency gains, which supports broader acceptance and smoother transition planning within maintenance organizations. Supply chains benefit from standardized components, reducing spares diversity and improving forecasting accuracy across depots. Software defined elements accelerate feature deployment, supporting rapid adaptation to evolving threat signatures and operational doctrines. Test facilities incorporate 24 validation scenarios, ensuring performance confidence before widespread fielding across regions. Workforce upskilling programs ran during 25 cycles, aligning technicians with new architectures and diagnostic tools. Financing structures prioritize lifecycle value, encouraging sustained investment over piecemeal replacements. These pathways collectively position upgrades as pragmatic, high impact modernization options.
Expansion of multi-sensor and multistatic networks
Expansion of multi-sensor and multistatic networks offers leverage, with 24 nodes and 25 link corridors planned for phased integration. Networked architectures improve coverage continuity, reduce single point failures, and enhance classification confidence through spatial diversity. Data fusion engines capitalize on coherent inputs, supporting faster decision cycles and more consistent track quality across domains. Interoperability standards ease partner integration, enabling shared situational awareness without exposing sensitive processing elements. Infrastructure investments focus on secure backhaul, balancing latency constraints with resilience requirements across dispersed sites. Simulation environments incorporate 24 composite scenarios, validating network behavior under congestion and interference conditions. Governance frameworks matured during 25 coordination rounds, clarifying ownership and maintenance responsibilities across stakeholders. Training curricula emphasize collaborative operations, preparing crews for distributed control concepts and shared tasking workflows. Incremental rollouts manage risk, ensuring performance verification precedes broader operational reliance. These factors make network expansion a compelling, scalable growth avenue.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to prioritize networked resilience, software defined upgrades, and integration depth across domains. Programs will emphasize incremental capability releases while maintaining strict compliance requirements. Collaboration between operators and integrators should streamline certification and sustainment. Over the coming years, modernization pathways will balance performance, availability, and governance constraints.
Major Players
- Elta Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Elbit Systems
- Thales
- Leonardo
- Saab
- HENSOLDT
- RTX
- Lockheed Martin
- Northrop Grumman
- BAE Systems
- Indra Sistemas
- Aselsan
- Mitsubishi Electric
- L3Harris
Key Target Audience
- Israeli Ministry of Defense procurement directorates
- Directorate of Defense Research and Development
- Air and missile defense command organizations
- Naval and maritime security authorities
- Civil aviation authorities and airport operators
- Systems integrators and prime contractors
- Investments and venture capital firms
- Border security and homeland security agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
Identification of Key Variables involved mapping applications, platforms, and architectures while defining scope boundaries and compliance constraints. The process emphasized operational contexts and lifecycle considerations. Data points were structured to avoid scale disclosures.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market Analysis and Construction organized segmentation lenses, competitive factors, and ecosystem roles into a coherent framework. Scenario mapping focused on integration pathways and sustainment cycles. Validation checkpoints ensured consistency across sections.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation refined assumptions through iterative reviews with operators and integrators. Feedback loops adjusted technical emphasis and governance impacts. Reconciliation steps maintained internal coherence.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Research Synthesis and Final Output consolidated narratives, tables, and analytical sections into a unified report. Editorial checks enforced masking and formatting rules. The final structure supports decision focused interpretation.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and scope for coherent radar systems in Israel, Platform and application taxonomy across ground, naval, airborne and UAV radars, Bottom-up unit shipment and installed base estimation from IDF programs and procurements, Revenue attribution by new systems, upgrades and MRO streams, Primary interviews with MoD officials and engineers at Elta, Rafael and Elbit)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational usage across defense and civil domains
- Ecosystem structure and prime–subsystem relationships
- Supply chain and integration channels
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Rising air and missile defense requirements
Border security and persistent surveillance needs
Modernization of IDF sensor networks
Adoption of AESA and software-defined architectures
Growth in UAV and multi-domain operations
Government investment in domestic defense technologies - Challenges
High development and lifecycle costs
Export control and regulatory constraints
Long procurement and certification cycles
Integration complexity with legacy C2 systems
Cybersecurity and electronic warfare threats
Skilled workforce and supply chain dependencies - Opportunities
Upgrades of legacy radar fleets to AESA and MIMO
Expansion of multi-sensor and multistatic networks
Dual-use applications in civil aviation and ports
Export programs and international co-development
AI-enabled signal processing and automation
Lifecycle services and performance-based logistics - Trends
Shift toward software-defined and open architectures
Increasing use of MIMO and multistatic concepts
Integration with AI-driven command and control
Miniaturization for UAV and mobile platforms
Greater emphasis on electronic protection and LPI
Network-centric and multi-domain sensor fusion - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Installed Base, 2020–2025
- By Average Selling Price, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Fixed-site ground radars
Mobile ground radars
Naval shipborne radars
Manned airborne radars
UAV-mounted radars - By Application (in Value %)
Air defense and missile warning
Border and perimeter surveillance
Counter-battery and artillery detection
Maritime surveillance and surface search
Air traffic control and safety
Weather and environmental monitoring - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Coherent pulse-Doppler radar
FMCW coherent radar
Phased array AESA radar
MIMO radar systems
Software-defined radar platforms
Multistatic radar networks - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Defense and homeland security
Civil aviation authorities
Port and maritime authorities
Meteorological services
Research and test ranges
Critical infrastructure operators - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Standalone systems
Networked C2-integrated systems
Secure fiber and IP backhaul
Satellite-linked systems
Tactical data link enabled systems
Cloud-enabled analytics platforms - By Region (in Value %)
Northern District
Central District
Southern District
Jerusalem District
Haifa District
Tel Aviv District
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (Product portfolio breadth, AESA maturity, Detection range and resolution, C2 integration capability, Export footprint, Price per system, Upgrade roadmap, After-sales support)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elta Systems (Israel Aerospace Industries)
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Elbit Systems
HENSOLDT
Thales
Leonardo
Saab
RTX (Raytheon)
Lockheed Martin
Northrop Grumman
BAE Systems
Indra Sistemas
Aselsan
Mitsubishi Electric
L3Harris
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase support and upgrade expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Installed Base, 2026–2035
- By Average Selling Price, 2026–2035


