Market Overview
The Israel command and control systems market current size stands at around USD ~ million, reflecting sustained defense digitization priorities and modernization of multi-domain operational frameworks. Investment flows into secure networking, decision-support software, and resilient communications are estimated at USD ~ million, while lifecycle service commitments and platform upgrades account for USD ~ million in ongoing programs. Capital allocation emphasizes hardened architectures and interoperability across land, air, maritime, and cyber domains, with procurement pathways shaped by long-term capability roadmaps and domestic industrial participation requirements.
Demand concentration is strongest around major operational hubs and technology clusters supporting defense integration, testing, and deployment. Urban defense ecosystems with mature secure connectivity infrastructure and proximity to operational commands concentrate implementation activity. Border-adjacent operational zones exhibit elevated deployment density driven by persistent security requirements. A mature supplier ecosystem, dense systems integration capabilities, and a policy environment prioritizing indigenous development and export controls shape regional adoption patterns and influence deployment sequencing across operational theaters.
Market Segmentation
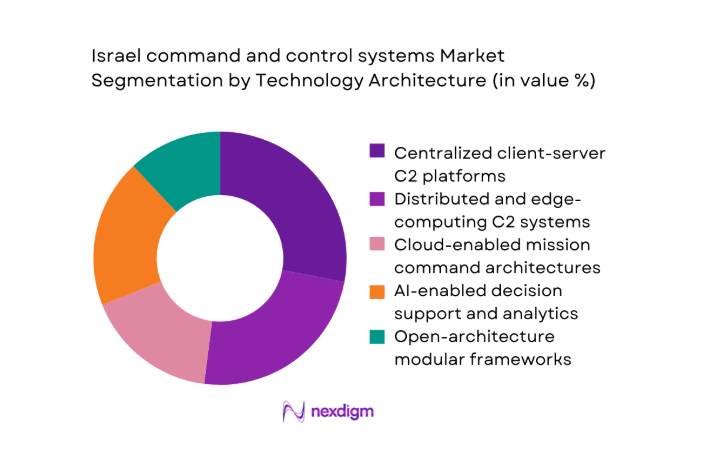
By Technology Architecture
Centralized client-server deployments continue to anchor legacy command posts, but distributed and edge-enabled architectures increasingly dominate new procurements due to resilience requirements in contested electromagnetic environments. AI-enabled decision support and sensor fusion layers are embedded within modular open frameworks, enabling rapid upgrades without full system replacement. Cloud-enabled mission command is selectively adopted within sovereign environments, supported by hardened private networks. Interoperability standards across ISR, cyber, and kinetic systems reinforce preference for modular architectures that integrate legacy platforms, accelerate deployment cycles, and reduce operational friction across joint and coalition operations.
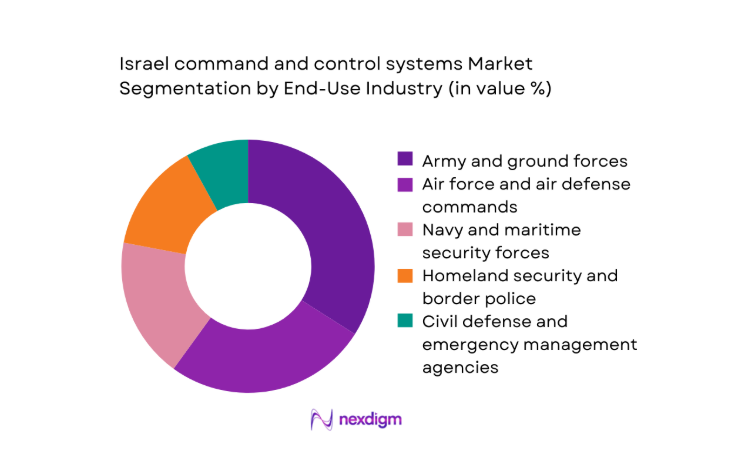
By End-Use Industry
Defense forces remain the dominant end users, driven by continuous operational readiness requirements across land, air, and maritime commands. Homeland security and border protection agencies account for expanding deployments as perimeter surveillance and emergency coordination mature into integrated command environments. Civil defense adoption grows through emergency management modernization and multi-agency coordination mandates. Interoperability with cyber defense operations increases uptake among specialized security units. Procurement cycles and doctrine-driven modernization prioritize platforms capable of multi-domain integration, rapid deployment, and lifecycle scalability across heterogeneous operational theaters.
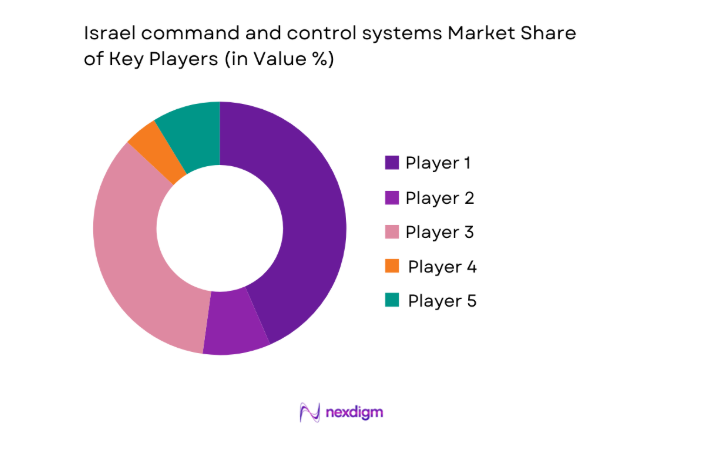
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment is shaped by vertically integrated primes and specialized subsystem providers offering secure communications, analytics, and integration services. Competitive differentiation centers on interoperability depth, cyber resilience, deployment velocity, and lifecycle support capabilities aligned with sovereign requirements and operational doctrine.
| Company Name | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Formulation Depth | Distribution Reach | Regulatory Readiness | Service Capability | Channel Strength | Pricing Flexibility |
| Elbit Systems | 1966 | Haifa | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Rafael Advanced Defense Systems | 1948 | Haifa | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Israel Aerospace Industries | 1953 | Lod | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Tadiran Communications | 1969 | Holon | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Elta Systems | 1967 | Ashdod | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
Israel command and control systems Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Modernization of IDF multi-domain operations doctrine
Operational doctrine integration across land, air, maritime, cyber, and space functions intensified during 2022–2025, with 2024 exercises involving 9 joint brigades and 4 multi-service task groups coordinating ISR, fires, and logistics. National digital transformation programs expanded secure data exchange nodes to 27 operational sites in 2023, increasing command responsiveness during cross-domain drills. Network hardening mandates introduced 14 new cyber resilience protocols in 2025, improving mission continuity. Defense readiness reviews documented 6 operational theaters requiring unified situational awareness platforms. Interoperability standards adoption aligned 11 legacy systems to common interfaces, reducing coordination latency and enabling synchronized operational planning across joint commands nationwide.
Heightened border security and missile defense requirements
Persistent border security pressures from 2022–2025 increased deployment tempo across 5 operational zones, with 2024 seeing 1,200 cross-domain coordination events integrating surveillance, air defense, and ground response units. Missile defense readiness mandates expanded command post coverage to 18 fixed and mobile nodes by 2025. Early warning integration consolidated 23 sensor feeds into unified dashboards, reducing response time across alert cycles. Civil defense coordination drills in 2023 involved 120 municipal control rooms interfacing with national command. Regulatory directives added 8 redundancy requirements for contested environments, strengthening continuity of command during multi-vector threat scenarios across northern and southern operational theaters.
Challenges
High dependency on classified programs limiting vendor participation
Program classification levels expanded during 2022–2025, with 2024 directives restricting vendor access across 19 secure development environments. Security clearance bottlenecks constrained onboarding of 340 specialized engineers, delaying integration timelines. Procurement cycles extended by 7 months due to compartmentalization protocols and segmented testing approvals. Export control reviews increased documentation requirements across 12 compliance stages, reducing cross-border collaboration for subsystem validation. Development sandboxes remained isolated from 9 allied interoperability labs, limiting real-world stress testing. Audit mandates introduced 5 additional certification checkpoints in 2025, increasing delivery complexity and elongating qualification pathways for new entrants.
Complex system integration across legacy and new platforms
Legacy platforms fielded before 2010 remained operational across 41 command posts in 2024, requiring middleware adaptation to interface with modern C2 stacks. Integration programs in 2023 connected 16 disparate data schemas, increasing engineering hours by 2,800 across validation cycles. Field upgrades required 52 interoperability test scenarios per release to ensure continuity across ISR and communications layers. Network modernization across 2025 added 13 encryption profiles, complicating backward compatibility. Training pipelines supported 4,600 operators transitioning to new interfaces, extending deployment stabilization periods. Configuration drift across 21 software baselines elevated maintenance complexity and slowed synchronized rollouts nationwide.
Opportunities
AI-enabled decision support for faster operational tempo
Operational pilots during 2022–2025 embedded AI fusion engines across 7 command centers, correlating 48 sensor streams into unified operational pictures. In 2024, automated prioritization reduced cognitive load for 1,500 operators during high-tempo drills. Pattern recognition models trained on 3 years of operational logs enhanced alert triage across 12 threat categories. Institutional adoption guidelines issued in 2025 mandated explainability audits across 9 algorithm classes, enabling scaled deployment. Secure model update pipelines synchronized across 5 sovereign data environments. Expanded training curricula certified 620 analysts in human-machine teaming, improving mission tempo without expanding staffing levels.
Cloud and edge-enabled C2 for distributed forces
Edge compute nodes deployed across 22 forward locations during 2023–2025 enabled local processing for ISR feeds when connectivity degraded. In 2024, 31 mobile command vehicles adopted hardened micro-clouds to sustain operations across contested networks. Latency-sensitive workloads migrated to edge clusters supporting 14 mission profiles, improving continuity during network disruptions. Sovereign private cloud environments expanded across 6 secure data centers to support scalable mission applications. Policy updates in 2025 standardized 10 reference architectures for cloud-edge orchestration. Operator training accredited 980 personnel on hybrid deployment workflows, enabling resilient distributed command across multi-domain operations.
Future Outlook
The market is expected to deepen multi-domain integration through open architectures and resilient cloud-edge orchestration across operational theaters. AI-enabled decision support will expand under stricter governance frameworks. Interoperability mandates will accelerate modernization of legacy platforms. Export control compliance will shape deployment models and partnership structures through 2035.
Major Players
- Elbit Systems
- Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
- Israel Aerospace Industries
- Tadiran Communications
- Elta Systems
- Orbit Communication Systems
- Aeronautics Group
- Commtact
- RT LTA Systems
- BIRD Aerosystems
- Nice Systems
- Verint Systems
- Motorola Solutions Israel
- Radwin
- Gilat Satellite Networks
Key Target Audience
- Defense ministries and procurement directorates
- Armed forces operational commands
- Homeland security and border police agencies
- National cyber defense authorities
- Civil defense and emergency management agencies
- Defense systems integrators and OEMs
- Secure communications network operators
- Investments and venture capital firms
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The study defined operational scope across land, air, maritime, and cyber command environments, identifying architecture types, connectivity modes, and lifecycle service layers. Programmatic variables included doctrine alignment, interoperability standards, and resilience requirements. Regulatory constraints and export control considerations framed the analytical boundaries. Data variables emphasized deployment density, upgrade cycles, and integration pathways.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Market structure was constructed through bottom-up mapping of operational deployments, platform categories, and technology stacks. Segmentation reflected architecture and end-use adoption patterns. Value attribution followed lifecycle stages without disclosing scale. Scenario frameworks incorporated modernization roadmaps, interoperability mandates, and policy-driven procurement cycles shaping demand patterns.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Hypotheses were validated through structured consultations with program managers, systems architects, and operations planners. Cross-functional reviews tested assumptions on interoperability, cyber resilience, and deployment velocity. Iterative feedback loops refined drivers, constraints, and opportunity pathways under sovereign security requirements. Divergent views were reconciled through evidence-based workshops.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
Findings were synthesized into coherent narratives linking doctrine, technology evolution, and procurement dynamics. Insights were stress-tested against regulatory frameworks and operational constraints. Final outputs prioritized decision relevance, implementation feasibility, and policy alignment. The synthesis emphasized actionable pathways for modernization while maintaining compliance with security and governance requirements.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and operational scope of C2 systems across land, air, naval, cyber domains, Platform and mission-based taxonomy for ISR-integrated C2 architectures, Bottom-up contract and program-based market sizing across IDF procurements, Revenue attribution by prime contractor, subsystem vendors, and lifecycle services, Primary interviews with IDF program managers, defense primes, and systems integrators, Triangulation using SIPRI transfers)
- Definition and Scope
- Market evolution
- Operational doctrine and usage pathways
- Ecosystem structure
- Defense supply chain and integration pathways
- Regulatory and export control environment
- Growth Drivers
Modernization of IDF multi-domain operations doctrine
Heightened border security and missile defense requirements
Integration of ISR, cyber, and kinetic operations in real time
Government investments in digital battlefield transformation
Demand for resilient C2 in contested electromagnetic environments
Interoperability requirements with allied forces and NATO standards - Challenges
High dependency on classified programs limiting vendor participation
Complex system integration across legacy and new platforms
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities in networked C2 architectures
Budget cyclicality tied to security events and fiscal priorities
Export control and compliance constraints on technology deployment
Talent shortages in secure software and systems engineering - Opportunities
AI-enabled decision support for faster operational tempo
Cloud and edge-enabled C2 for distributed forces
Interoperable open architectures for rapid capability upgrades
Dual-use C2 platforms for civil defense and emergency response
Export of Israeli C2 solutions to allied defense markets
Integration of autonomous systems and swarm control nodes - Trends
Shift toward multi-domain command and control frameworks
Adoption of open standards and modular architectures
Increased use of AI/ML for sensor fusion and targeting support
Expansion of cyber-resilient and zero-trust C2 networks
Growing role of unmanned and autonomous platform control
Convergence of military and homeland security C2 platforms - Government Regulations
- SWOT Analysis
- Stakeholder and Ecosystem Analysis
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- Competition Intensity and Ecosystem Mapping
- By Value, 2020–2025
- By Shipment Volume, 2020–2025
- By Active Systems, 2020–2025
- By Revenue per Unit Economics, 2020–2025
- By Fleet Type (in Value %)
Land-based tactical command posts
Airborne command and control platforms
Naval combat management and C2 suites
Joint operations and strategic command centers
Unmanned systems control nodes - By Application (in Value %)
Battlefield management and situational awareness
Air defense and missile interception coordination
Border security and perimeter surveillance command
Cyber defense and multi-domain operations coordination
Intelligence fusion and ISR tasking
Homeland security and emergency response coordination - By Technology Architecture (in Value %)
Centralized client-server C2 platforms
Distributed and edge-computing C2 systems
Cloud-enabled mission command architectures
AI-enabled decision support and analytics
Open-architecture and modular C2 frameworks - By End-Use Industry (in Value %)
Army and ground forces
Air force and air defense commands
Navy and maritime security forces
Homeland security and border police
Civil defense and emergency management agencies - By Connectivity Type (in Value %)
Tactical radio networks
Secure IP and fiber networks
Satellite communications links
5G and private LTE mission networks
Mesh networking for contested environments - By Region (in Value %)
Northern command region
Southern command region
Central command region
Naval coastal command zones
Joint and national strategic command centers
- Market structure and competitive positioning
Market share snapshot of major players - Cross Comparison Parameters (platform coverage, interoperability standards, cybersecurity certification, AI-enabled analytics capability, lifecycle support depth, export readiness and compliance, integration with ISR and sensors, total cost of ownership)
- SWOT Analysis of Key Players
- Pricing and Commercial Model Benchmarking
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Elbit Systems
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems
Israel Aerospace Industries
Tadiran Communications
Orbit Communication Systems
Elta Systems
Aeronautics Group
Commtact
RT LTA Systems
BIRD Aerosystems
NSO Group Technologies
Nice Systems
Verint Systems
Motorola Solutions Israel
Radwin
- Demand and utilization drivers
- Procurement and tender dynamics
- Buying criteria and vendor selection
- Budget allocation and financing preferences
- Implementation barriers and risk factors
- Post-purchase service expectations
- By Value, 2026–2035
- By Shipment Volume, 2026–2035
- By Active Systems, 2026–2035
- By Revenue per Unit Economics, 2026–2035


