Market Overview
The Qatar Fighter Aircraft market, valued at USD ~ billion , continues to expand driven by the country’s strategic investment in defense capabilities and its position as a key player in the Gulf region. The market is primarily propelled by defense procurement contracts such as the ongoing F‑15QA acquisition, as well as a growing need for advanced air superiority and strike capabilities amidst regional security challenges. The Qatari government’s strong defense budget allocations and long-term defense partnerships with the U.S. and European countries fuel this growth. Additionally, the market is influenced by the integration of cutting-edge technologies into defense platforms, such as stealth and advanced avionics, ensuring the sustained growth of this segment throughout the forecast period.
Qatar is the dominant player in the Gulf region’s fighter aircraft market, with its continuous investment in defense modernization, particularly in advanced fighter jets like the F‑15QA and potential future acquisitions like the F‑35. Qatar’s central role in regional security, along with its strong military alliances, drives its prominence. The nation’s investment in multi-role combat aircraft further strengthens its position. Additionally, countries like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and other Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states also play a significant role in the defense aerospace market, due to their similar defense modernization goals and shared security concerns.
Market Segmentation
By Aircraft Type
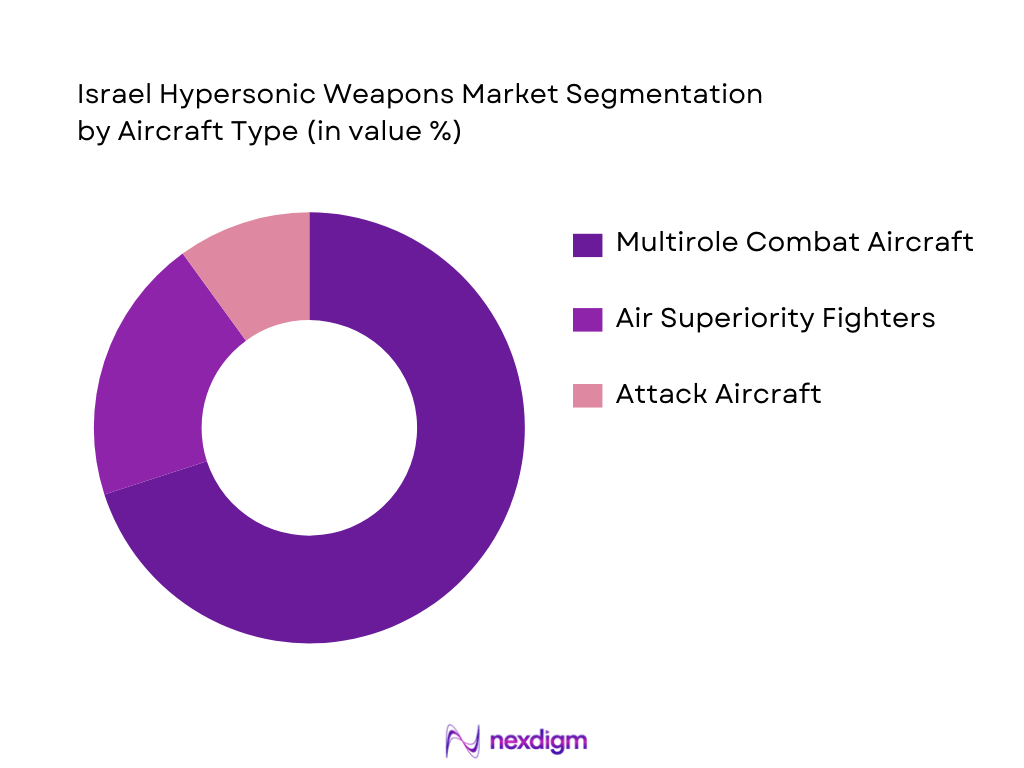
The Qatar Fighter Aircraft market is segmented by aircraft type into multirole combat aircraft, air superiority fighters, and attack aircraft. Multirole combat aircraft, particularly the F‑15QA, dominate the market due to their flexibility in both air-to-air and air-to-ground combat. These aircraft are seen as essential for maintaining superior defense capabilities, enabling Qatar to safeguard its airspace and project power across the region. The F‑15QA, with its advanced avionics and payload capacity, remains a cornerstone of Qatar’s defense strategy, providing unmatched versatility and enhancing its strategic deterrence capabilities.
By Technology
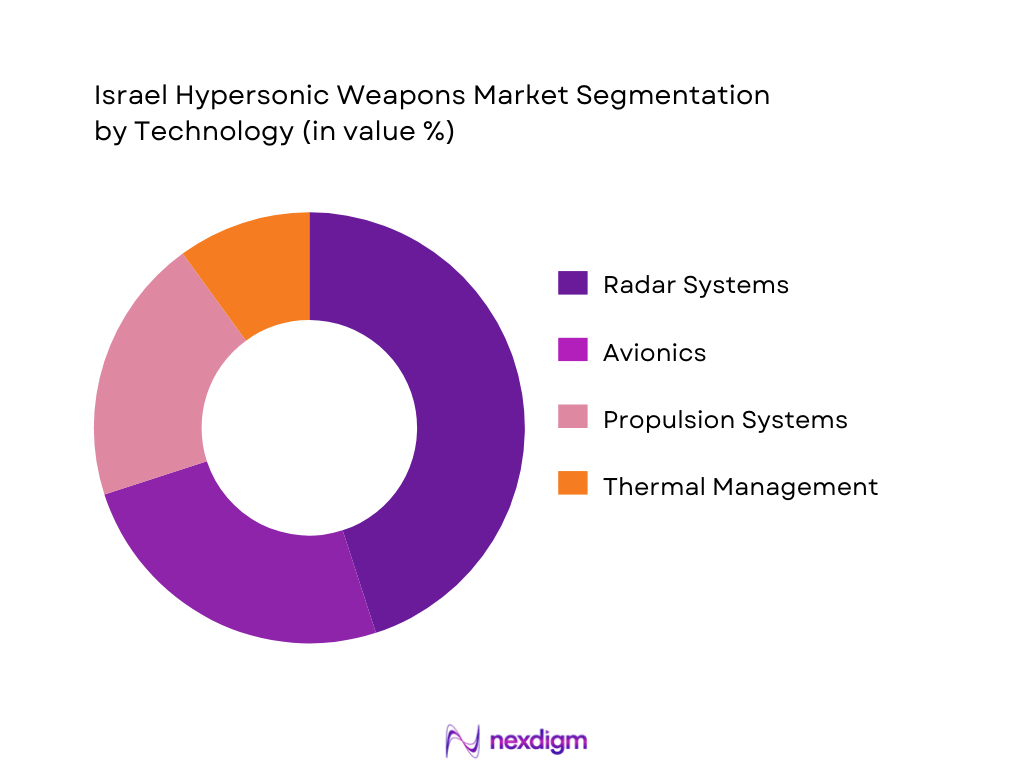
This segment includes radar systems, avionics, propulsion systems, and thermal management systems used in fighter aircraft. In Qatar, the radar systems segment holds the largest share, driven by the high demand for advanced detection and tracking systems in fighter jets like the F‑15QA. These advanced radar systems, including AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array) radars, enhance situational awareness and are critical for achieving operational superiority in complex and contested environments. The integration of such high-tech radar systems significantly improves Qatar’s defense capabilities, especially in regional security scenarios.
Competitive Landscape
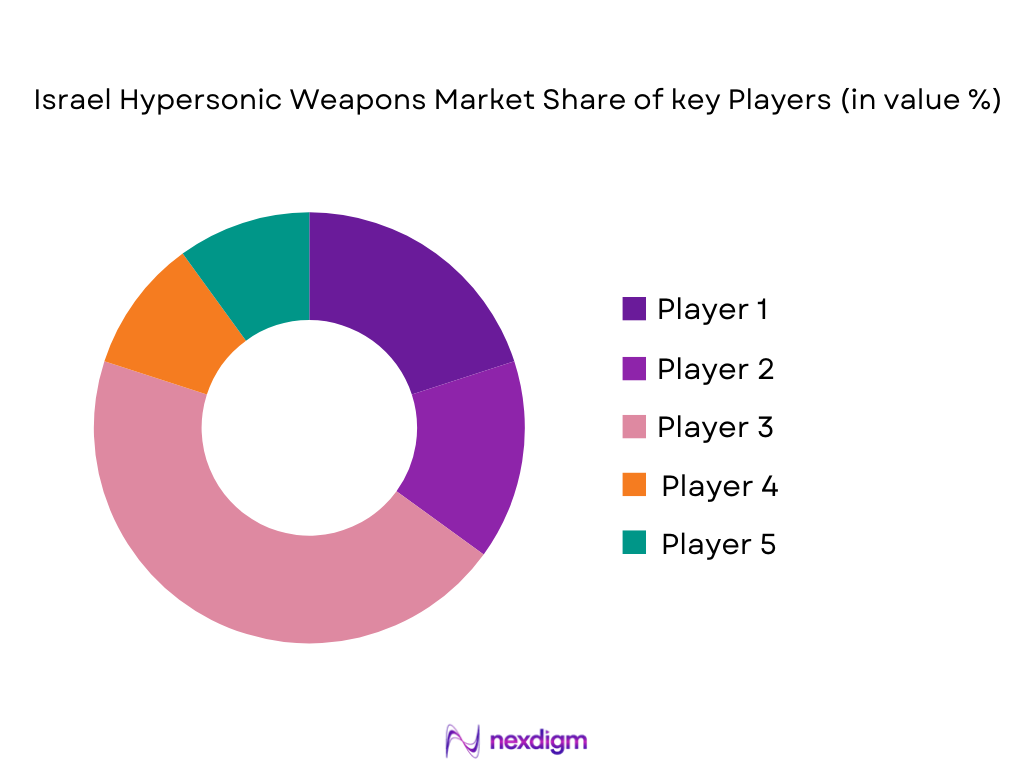
The Qatar Fighter Aircraft market is dominated by a select group of key players, including both local and global defense contractors. The presence of global defense giants like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Airbus, alongside local entities like Qatar’s Ministry of Defense, has solidified the competitive landscape. These companies are critical suppliers for Qatar’s advanced fighter aircraft programs, including the F‑15QA and Typhoon aircraft. The market is highly competitive, with global firms vying for multi-billion-dollar contracts to supply advanced fighter jets and related systems. The consolidation of industry leaders highlights the strategic importance of defense contracting in the region, where air superiority and technological advancements are pivotal.
| Company | Establishment Year | Headquarters | Aircraft Type | Technology Specialization | Regional Partnerships | Contract Volume | Recent Developments |
| Boeing | 1916 | Chicago, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Lockheed Martin | 1995 | Bethesda, USA | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Airbus | 1970 | Toulouse, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Dassault Aviation | 1929 | Paris, France | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
| Saab | 1937 | Linköping, Sweden | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ |
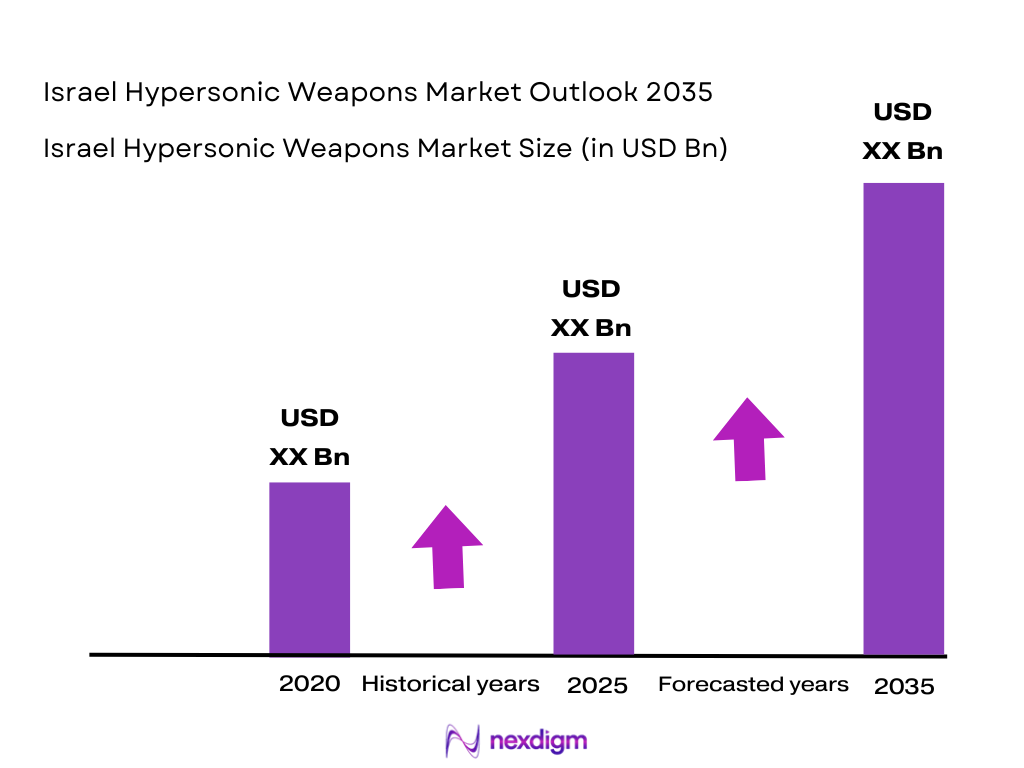
Israel Hypersonic Weapons Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
Evolving Regional Threat
One of the most significant growth drivers for the Israel Hypersonic Weapons Market is the evolving regional threat, particularly from Iran and other regional actors. The proliferation of speed‑threat missiles, including hypersonic technology, has raised alarm bells for Israel’s national security. Hypersonic missiles, capable of reaching speeds greater than Mach 5, pose a unique challenge as they are highly maneuverable and difficult to intercept. As Iran develops these capabilities, Israel is motivated to strengthen its own missile defense systems and develop counter-hypersonic weapons. Israel’s long-standing commitment to technological superiority, including the Iron Dome and Arrow defense systems, has extended to the hypersonic realm, accelerating investments in defense technology and hypersonic weapons to stay ahead of emerging threats in the region.
Defense Modernization & Procurement Policies
Israel’s defense modernization initiatives also act as a key growth driver in the hypersonic weapons market. The Israeli government has consistently prioritized military and technological advancements as part of its defense procurement policies. This is evident in Israel’s regular allocation of resources to high-tech defense systems, which includes hypersonic weapons. The procurement of advanced defense systems through both indigenous development and international partnerships ensures that Israel remains at the forefront of modern warfare technology, especially in countering threats from missile and air defense, which is integral to its national security.
Market Challenges
High R&D Cost and Technical Risk
One of the biggest challenges in the Israel Hypersonic Weapons Market is the high cost and technical risk associated with research and development (R&D). Developing hypersonic systems requires significant investment in cutting-edge propulsion technologies, such as scramjet engines, and advanced materials capable of withstanding the extreme heat generated at hypersonic speeds. The complexity of these technologies presents both financial and technical hurdles, as the risk of failure is substantial. Moreover, Israel’s focus on self-sufficiency in defense technology means that they are investing heavily in proprietary solutions, making R&D even more capital-intensive. This challenge is compounded by the long development cycles required for hypersonic weapons, meaning that only long-term investments will bear fruit.
Interoperability with Existing Defense Layers
Another key challenge for the Israel Hypersonic Weapons Market lies in ensuring interoperability with its existing missile defense systems. Israel already has a robust multi-layered defense architecture that includes systems like the Iron Dome for short-range missiles, David’s Sling, and the Arrow system for longer-range threats. However, integrating hypersonic weapons into this network presents technological and operational challenges, as hypersonic missiles require a different approach to tracking, interception, and defense compared to traditional ballistic and cruise missiles. Ensuring that these new weapons systems can seamlessly integrate with existing defense infrastructure while maintaining operational effectiveness will be critical for maximizing their value and minimizing vulnerabilities.
Market Opportunities
Co‑Development Partnerships
Co-development partnerships offer significant opportunities for Israel in advancing its hypersonic weapons program. Israel’s established defense alliances with countries like the United States, South Korea, and NATO members provide a fertile ground for collaboration. These partnerships allow for the sharing of research, testing, and resources, significantly reducing R&D costs and enhancing the technological capabilities of hypersonic weapons. For instance, Israel’s collaboration with South Korea in missile defense technologies could be expanded to include joint hypersonic weapons development. By partnering with other nations, Israel can leverage external expertise and potentially enter global markets with co-developed hypersonic systems, increasing both the technological and economic viability of such projects.
Sensor & Detection Innovation
Innovations in sensor and detection technologies present promising opportunities for Israel to enhance its hypersonic weapons market. Hypersonic missiles travel at extreme speeds and altitudes, making them difficult to track using traditional radar and sensors. However, advancements in space-based sensors and over-the-horizon detection systems can help overcome this challenge. Israel, with its expertise in advanced radar and satellite technology, has the potential to lead in the development of tracking systems capable of detecting and engaging hypersonic threats. Developing such innovative systems would not only improve the nation’s missile defense capabilities but could also position Israel as a global leader in hypersonic defense technologies, opening opportunities for international sales and further R&D collaborations.
Future Outlook
Over the next five years, the Qatar Fighter Aircraft market is expected to see steady growth, driven by ongoing and potential future acquisitions, including the finalization of the F‑35 procurement deal. Continued defense budget allocation toward air defense modernization and the integration of next-generation technologies such as advanced radar systems, stealth capabilities, and propulsion systems will fuel this expansion. The country’s strategic defense needs and regional security concerns, alongside strengthening defense relationships with the U.S. and Europe, will remain key drivers for growth, ensuring Qatar’s dominance in the Gulf’s airspace and beyond.
Major Players in the Qatar Fighter Aircraft Market
- Boeing
- Lockheed Martin
- Airbus
- Dassault Aviation
- Saab
- Qatar Ministry of Defense
- Northrop Grumman
- Raytheon Technologies
- General Dynamics
- Leonardo
- Thales Group
- L3 Harris Technologies
- BAE Systems
- Rolls-Royce
- Pratt & Whitney
Key Target Audience
- Defense Procurement Agencies (e.g., Qatar Ministry of Defense)
- Government and Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Ministry of Defense, Qatar National Security Council)
- Investments and Venture Capitalist Firms
- Prime Defense Contractors (e.g., Boeing, Lockheed Martin)
- Aerospace Manufacturers
- Military Analysts and Strategists
- Regional Defense Alliances (e.g., Gulf Cooperation Council)
- Government Defense Agencies
Research Methodology
Step 1: Identification of Key Variables
The initial phase involves identifying all critical variables that influence the Qatar Fighter Aircraft market, including regional security dynamics, government defense spending, and aircraft procurement strategies. Secondary and primary research data sources will be analyzed to form a comprehensive ecosystem map of the key stakeholders.
Step 2: Market Analysis and Construction
Historical data related to Qatar’s fighter aircraft procurement and regional defense policies will be examined to assess market trends. Market penetration, the number of aircraft in service, and operational data will provide insights into future demand and growth forecasts.
Step 3: Hypothesis Validation and Expert Consultation
Industry consultations with experts in the defense sector will be carried out to validate market hypotheses. These experts, from both military and commercial backgrounds, will provide insights into strategic procurement decisions, technological requirements, and defense capabilities.
Step 4: Research Synthesis and Final Output
The final research phase involves synthesizing all data collected to produce actionable insights and projections for the Qatar Fighter Aircraft market. Direct interactions with defense contractors and government agencies will finalize the report’s findings, ensuring comprehensive and accurate conclusions.
- Executive Summary
- Research Methodology (Market Definitions and Defense Technology Taxonomy, Hypersonic System Classification, Assumptions and Defense Budget Mapping, Primary Research Approach – Military & Industry Experts, Data Triangulation from Procurement & Production, Limitations and Future Research Direction)
- Definition and Scope of Hypersonic Weapons (Flight Regime ≥ Mach 5,
- Maneuverability, Skip‑Glide vs Boost‑Glide, Interceptor vs Offensive)
- Genesis of Israel Hypersonic Capability (Strategic Imperative and Regional Threats)
- Defense Policy Drivers (National Security Doctrine, Missile Defense Architecture)
- Strategic Competitive Context (Iranian & Regional Hypersonic Threats and Global Hypersonic Arms Race)
- Israel R&D and Testbeds (Propulsion, Guidance, Sensors, Simulation)
- Supply Chain Overview
- Growth Drivers
Evolving Regional Threat (Iran & Proliferation of Speed‑Threat Missiles)
Defense Modernization & Procurement Policies
Allied Technology Collaborations & Foreign Co‑Development Programs
Domestic Industrial Capacity & Sovereign Capability Imperatives
- Market Challenges
High R&D Cost and Technical Risk (Propulsion, Materials)
Interoperability with Existing Defense Layers
Export Controls & Regulatory Barriers (ITAR / Local Regimes)
Sensor and Tracking Limitations for Hypersonic Engagement
- Market Opportunities
Co‑Development Partnerships (e.g., South Korea, NATO Partners)
Sensor & Detection Innovation (Space/Over‑the‑Horizon Tracking)
Dual‑Use Commercialization (Space Launch, Fast Logistics)
Export to Differentiated Defense Market
- Technology Trends
Scramjet Evolution and Combined‑Cycle Engines
AI‑Enabled Navigation and Autonomous Interception
Materials & High‑Thermal Tolerance Structures
Directed Energy Integration for Hypersonic Defense
- Regulatory & Policy Landscape
Defense Budget Allocation Framework
Export Licensing and Strategic Trade Controls
Allied Security Cooperation Policies
- SWOT Analysis
- Hypersonic Weapons Value Chain & Stakeholder Ecosystem
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Market Value, 2020-2025
- Volume Consumption Across Subsegments, 2020-2025
- Composite Adoption Intensity, 2020-2025
- By System Type (In Value %)
Hypersonic Interceptors (Sky Sonic, Arrow‑X derived interceptors)
Hypersonic Offensive Missiles (Domestic Indigenous Programs)
Hypersonic Boost‑Glide Test Platforms
Hypersonic Subscale Prototypes (Research & Qualification)
Directed Energy Counter‑Hypersonic Sub‑Systems
- By Technology Component (In Value %)
Propulsion (Scramjet, Combined Cycle, Rocket Boosters)
Avionics & Guidance (Inertial, GPS/INS, AI‑Assisted Navigation)
Thermal Protection Systems
Seeker & Sensor Suites (Radar, IR, EO)
Materials & Structures (High Temp Alloys, Composites)
- By Application (In Value %)
Strategic Deterrence (Long‑Range Strike Capability)
Missile Defense (Exo‑Atmospheric Interceptors)
Tactical Precision Strike
Defense Export Potential
Space Launch Boost Components
- By End User / Procurer (In Value %)
Israel Ministry of Defense / IDF
Export Customers (Allies / Defense Partners)
Prime Defense OEMs / Tier‑1 Integrators
Domestic Technology Providers
R&D Institutions & Universities
- By Procurement Mode (In Value %)
Government‑Funded R&D Programs
Foreign Military Sales / Co‑Development Agreements
Public‑Private Partnerships
Export & Offset Agreements
Defense Export Contracts
- Market Share – Key Participants in Israel Hypersonic Domain
- Cross‑Comparison Parameters (Company Strategic Focus (Interceptor vs Offense), Technology Footprint (Propulsion, Seekers, Materials), R&D Investment / Defense Contract Wins, Hypersonic Test Capabilities & Validation Facilities, Production Facilities & Scalability (Domestic vs Co‑Production), Integration Capabilities (Networked Defense Suites), Export Licenses / Foreign Military Sales Footprint, Partner Ecosystem & Defense Alliances)
- SWOT – Major Competitors in Israel Hypersonic Context
- Pricing & Contracting Terms Analysis (Defense Tender Basis)
- Detailed Profiles of Major Companies
Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) – Prime Integrator
Rafael Advanced Defense Systems – Hypersonic Defense Systems
Elbit Systems – Sensor & Integration Provider
ELTA Systems – Radar & Tracking Subsystems
Lockheed Martin Corporation – Allied Tech Partner
Raytheon Technologies Corporation – Interceptor Tech Partner
Northrop Grumman Corporation – Guidance & Avionics
Boeing – Missile Integration Systems
BAE Systems plc – Subsystem Developer
L3Harris Technologies Inc. – Communication & Defense Systems
General Dynamics Corporation – Aerospace Systems
Thales Group – Sensors & Defense Electronics
Aerojet Rocketdyne Holdings Inc. – Propulsion Systems
Tactical Missiles Corporation – Specialist Hypersonic Developer
BrahMos Aerospace Pvt. Ltd. – Regional Hypersonic Partner
- Operational Requirements & Mission Profiles
- Procurement Specifications & Defense Authorization Metrics
- Budget Cycles and Allocation Forecasts
- Decision Drivers (Cost‑Per‑Interceptor, Kill Probability, Integration Demands)
- Performance Expectations & Pain Points
- Forecast by Value & Growth Scenarios, 2026-2035
- Forecast by Volume & Composite Penetration, 2026-2035
- Future Demand by Aircraft Segment, 2026-2035


